The flywheel is part of the crank mechanism, clutch system and engine starting system, in the form of a large mass disk with a ring gear. Some modifications of flywheels have their own abbreviations - read about them in the “types of flywheels” section.
photo gallery:
Flywheel purpose
An engine flywheel is needed to gain rotational inertia of the crankshaft, which allows the pistons to overcome dead spots. In addition, this part of the internal combustion engine transmits torque to the starter and gearbox. The uneven rotation of the crank mechanism is reduced.
In other words, the flywheel is conventionally a pendulum rotating in one direction. Without it, it is impossible to start the internal combustion engine, and the service life of almost all engine systems will be reduced.
What systems does it apply to?
Despite the fact that the part is attached to the crankshaft of the internal combustion engine, the flywheel belongs to several engine systems at once:
- gearbox of the starting system - rotation is transmitted to it;
- starter - the operation of the flywheel ensures the initial rotation of the internal combustion engine shaft;
- gearbox - torque is transmitted to it from the clutch disc;
- crank mechanism – impulses of uneven rotation are smoothed out.
Rice. 2 Engagement of the flywheel ring with the starter bendix
Rice. 3 Rigid connection of flywheel 1 with clutch disc 2
The large dimensions of the flywheel allow this part to gain inertia during the initial rotation. Since it is rigidly connected to the crankshaft, the pistons do not linger at the bottom/top point, but are drawn further along the rotation for a new cycle of fuel compression/ignition.
Rice. 4 Overcoming dead spots by the pistons due to the inertia of the flywheel
Due to the presence of dead spots, the shaft rotates unevenly, first gaining angular speed, then losing it. Therefore, the diameter of the flywheel is selected individually for each motor in order to smooth out the values of these angular velocities at different periods of time. The main problems are:
- the location of the rotating flywheel at one end of the crankshaft means a sharp increase in the load on the bearing on this side;
- increasing the overall weight of the crankshaft - the load increases on both bearings, cranks and connecting rods.
Rice. 5 Location of the flywheel on the internal combustion engine shaft
Therefore, the bearings are strengthened to rotate under extreme operating conditions for the entire declared life.
Location inside the internal combustion engine
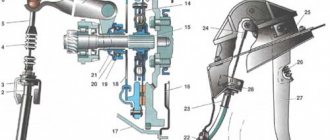
This part is always located at the main bearing of the crankshaft, which is the most powerful in the engine. The assembly drawing of the flywheel allows you to see the location inside the internal combustion engine in more detail. It is attached to the crankshaft flange by a hub, the reverse side engages with the main clutch disc. The ring gear on the outer diameter of the flywheel is designed to engage with the starter bendix when the internal combustion engine starts.
Rice. 6 Engine drawing with flywheel location
Since all of these drives use gears, a mark on the flywheel indicates its normal position relative to the clutch shaft and drive plate. To ensure that the part, in turn, does not create vibrations on the crankshaft of the internal combustion engine, the flywheel is balanced on a stand.
Usage[edit | edit code]
Used in machines that have an uneven supply or use of energy, storing energy when the energy supply is higher than the consumption, and releasing it when the consumption exceeds the energy supply. Also used in hybrid engines as energy storage and for regenerative braking, gyrobuses.
Often the function of a flywheel is performed by a massive rotating element of the mechanism. Such as a potter's wheel, massive watermill wheels or massive gear wheels.
In addition to energy, a rotating flywheel (like any rotating body) also has angular momentum, which is associated with the observation of the gyroscopic effect, which consists in the precession of the rotation axis around its original direction when an external force appears that does not coincide with the direction of the rotation axis.
The first example of the use of the gyroscopic effect can be considered the invention of the spinning top (yo-yo).
One of the first applications of the gyroscopic effect was the transition in the 19th century from firing round cannonballs to oblong projectiles, the rotation of which made it possible to maintain their orientation in space, and the oblong shape significantly increased their mass (blank) or explosive charge with equal aerodynamic resistance.
The flywheel is also the rotor of the gyroscope, used in gyrocompasses and in general in gyroscopic devices for orientation in space, in particular torpedoes (Aubrey device), rockets and spacecraft. The most common examples of a flywheel are a bicycle wheel or the rotating disk of an electric vinyl record player.
The ability of the flywheel to maintain the direction of the axis of rotation is used in ship stabilizers.
In everyday life, the flywheel is most often used in cars: any piston engine is equipped with a flywheel, often combining functions as part of the clutch and starting system (flywheels are equipped with a ring gear to transmit torque from the starter). In addition to bringing the crank mechanism out of its dead center, the flywheel in the engine reduces the unevenness of rotation to an acceptable level, which increases the service life of the transmission (the remaining unevenness is damped by the torsional vibration damper springs or the automatic transmission clutch, then by torus rubber and viscous couplings).
Flywheel design
Initially, the parts were made of solid cast iron; nowadays, in addition to the classic modifications, there are additional types of flywheels: damper and lightweight. The car is equipped with this unit at the factory, but in some cases the owner can tune the internal combustion engine by replacing it with another modification.
Classic solid
The traditional solid flywheel is cast as a disc from gray cast iron. This structural material is not suitable for the manufacture of gears, but it sharply reduces the cost of the part and increases the service life.
Then a flywheel rim with teeth is pressed onto the outer diameter of the workpiece for periodic engagement with the starter bendix at the moment of starting the internal combustion engine. The diameter of the finished product is usually 40 cm, the number of teeth depends on the specific transmission scheme of the car.
Rice. 7 All metal flywheel
On one side, the surface of the flywheel has the form of a flange for connection to similar mounting holes of the main clutch disc. To protect against mechanical damage, a flywheel casing is used, bolted to the cylinder block.
If you regularly connect/disconnect the starter, the teeth may break. Therefore, the rim (crown) is considered a consumable part and is sold separately. The housing (body) is usually not subject to repair; it is replaced entirely after the service life has been exhausted.
Rice. 8 Flywheel crown
In modern cars, ignition in the combustion chambers is controlled by the DPKV or TDC sensor. It counts the teeth of the outer ring of the flywheel passing by, determining the position of the crankshaft at each moment in time. The signal is sent to the on-board computer; based on the position of the shaft, it is calculated which cylinder is compressing the fuel mixture at that time, and a spark is supplied for ignition.
Lightweight
When solving the main problem when equipping the crankshaft with a flywheel - removing the internal combustion engine pistons from the dead points, another problem automatically arises:
- a heavy part puts more stress on the crankshaft and increases the acceleration time of the car;
- The angular speed of the flywheel cannot decrease instantly; there is a delay when braking.
Rice. 9 Lightweight flywheel
Therefore, to improve the specified characteristics of the motor, the weight of the part is reduced by several kilograms by making slots closer to the center. The dynamics improve by a maximum of 5 - 7%, however, at low speeds the following disadvantages arise:
- difficult movement on slippery and dirty roads;
- reduction in torque;
- when switching to a higher gear, the speed is insufficient, the clutch disc wears out;
- slight increase in fuel consumption;
- rapid loss of torque, despite almost instantaneous acceleration.
For lightweight aluminum alloy parts or those with slots in the body, use the standard flywheel housing that is equipped with the machine at the factory.
Dual mass
The problem of compensating for rotational vibrations is solved by a damper flywheel, the design of which is similar to the overrunning clutch of a generator. Unlike a gasoline engine, a diesel engine is low-speed by default. The dynamics of the car are achieved through the transmission ratio. The kinematic drive diagram here is more complex, the parts are stronger, and the components are stronger.
Rice. 10 Dual mass flywheel
The dual-mass flywheel of an internal combustion engine has a complex design:
- one disk (housing) is mounted on the crankshaft and has an outer ring for engagement with the starter;
- the second is fixed on the clutch disc;
- the disks rotate relative to each other on radial and thrust bearings;
- damping springs are also located between the discs in a polymer separator that prevents blocking.
Rice. 11 Design of damper flywheel
At the moment of starting the internal combustion engine, a package with a soft spring operates; during normal engine operation, a hard spring is activated. To lubricate friction parts, a paste with molybdenum sulfide is used, which is placed in the flywheel for the entire service life of the vehicle, which is about 150,000 km. Moreover, the lubricant should not get on the clutch parts; it is removed from the ends of the flywheel discs during maintenance and inspection.
Kinds
Today there are three types of flywheels:
- Solid . It is a simple cast iron disk with teeth on the end. Such models are common on both domestic cars and foreign cars, especially economy class ones.
- Lightweight . As a rule, a lightweight version of the drive disc is installed either on cars with an automatic transmission or on tuned models. The main feature of such a disk is its reduced mass, as a result of which a decrease in inertia is achieved and an increase in engine efficiency of up to 5%. A lightweight flywheel is a structurally simplified version of the solid type. Its main purpose is to act as a gear that rotates when the starter starts.
- Dual mass or damper . Currently, it has become widespread due to its advantages - damping vibration, eliminating torsional vibrations of the crankshaft, increasing the wear resistance of synchronizers, protecting the transmission from overloads and reducing noise. A structurally more complicated flywheel model compared to previous types.
Operating principle
At the moment the internal combustion engine starts, rotation of the flywheel is ensured by the starter, the part receives an initial speed and gains inertia. Then the engine piston “hangs” at top dead center, and the shaft cannot rotate. However, due to the inertia of the flywheel, the crankshaft rotates slightly, which allows it to carry out the next compression cycle, ignite the fuel mixture, and obtain energy for the next rotation.
Rice. 12 The principle of operation of the flywheel with clutch
At the same time, the sensor monitors the position of the shaft and the pistons on it, respectively. The information transmitted by this device is analyzed by a computer, alternately supplying ignition to the corresponding combustion chambers.
With a dual-mass flywheel the situation is slightly different:
- at the moment of start, one half of this assembly receives a high angular velocity, the second remains motionless;
- at the same time, the first half of the flywheel begins to compress the spring, which ensures smooth rotation of the transmission disk rigidly connected to it;
- then the speeds of both halves are aligned relative to each other and operate in a single mode;
- at the moment the driver slows down the gas pedal, the second half begins to overtake the first;
- however, a hard impact on the motor parts does not occur again, since another spring begins to compress in the opposite direction;
- the speeds of the halves are equalized again, the cycle repeats again.
Rice. 13 Operating principle of a dual-mass flywheel
The DPKV sensor is still responsible for ignition, and the flywheel casing protects the unit from external influences. A similar damper is built into the clutch assembly, which becomes unnecessary when using a dual-mass flywheel.
Video on the topic
Related publications
- How does air conditioning work in a car?
- VVT-i: what is this system on Toyota
- What is a start-stop system on a car?
- How to determine the polarity of a car battery
Leave a review Cancel reply
Flywheel repair
The main malfunctions of the flywheel logically follow from its design:
- the teeth of the crown wear out and break;
- springs burst, lubricant leaks and gets onto the clutch disc (only for damper modifications).
Rice. 14 Development of teeth
Rice. 15 Damper spring failure
Attention: A failed DPVC sensor is not a flywheel failure. But the car will definitely not start, since the ignition sequence to the combustion chambers will be disrupted.
But during the destruction of the springs or bearings of the damper flywheel, parts of the parts can damage the starter and clutch parts, which will sharply increase the cost of repairing the machine.
Causes of malfunction
In addition to an aggressive driving style (fast acceleration/sharp braking), the causes of flywheel malfunction are:
- non-compliance with the requirements of the operating manual - speeds are switched at the “wrong” speed;
- poor contact – the starter and battery terminals must be firmly attached;
- wear of gearbox and crankshaft bearings - vibrations occur;
- wear of the internal combustion engine cushions - vibrations are transmitted to all engine elements;
- the adjustment of the fuel equipment is disrupted - the engine runs unevenly, intermittently;
- the quality of diesel fuel affects the combustion process, detonation is possible.
These reasons can greatly increase the amplitude of non-systemic oscillations in a diesel engine. System vibrations are taken into account by the manufacturer; to compensate for them, technical solutions are used in the design of the internal combustion engine itself.
Diagnostics
Since the flywheel rotates on the internal combustion engine shaft, it is very difficult to diagnose its malfunctions. For example, even for a visual inspection you will have to remove the cover and partially disassemble the clutch assembly. Extraneous sounds (crackling) are very similar to starter malfunctions, since the Bendix teeth engage with the flywheel crown.
Thus, during an external inspection after disassembly, it is possible to identify gear defects and burrs on the clutch disc side (when grinding, a maximum of 0.3 mm can be removed).
Replacing the crown
Since the rim teeth are made by milling on high-precision machines, it is impossible in principle to weld and grind them to ensure the factory configuration. Therefore, the crown is replaced by cutting off the angle grinder with abrasive equipment, pressing a new consumable element instead onto the cast iron body.
Rice. 16 Replacing the crown according to the mark
The main nuances of the repair are:
- flywheel mass - must correspond to the characteristics of the internal combustion engine;
- gear ratio - the number of teeth must remain the same for the DPKV sensor to operate correctly;
- mark - the relative position of the housing and the crown is marked with a line for correct balancing of the internal combustion engine assembly.
Rice. 17 Crankshaft position sensor
Service station specialists have a drawing of the motor, do not make mistakes, and work on professional equipment. At home, it is difficult to dismantle the rim without damaging the body and put a new crown on it.
Damper flywheel repair
Without exception, all manufacturers of dual-mass flywheels recommend replacing this complex design unit entirely after a car with a manual transmission has driven 150 thousand kilometers. However, some service shops have the equipment and highly qualified personnel to repair this unit.
The main problems are:
- complete absence of consumable parts on the market, even bearings have rare markings;
- selection of synthetic lubricant containing molybdenum sulfide;
- complex disassembly of permanent connections (rivets);
- no less complex assembly using rivets or welding with subsequent processing of the joints;
- preservation of the ring, without which the DPKV sensor does not work correctly, and balancing weights;
- complex processing of seats.
Rice. 18 Repair of dual-mass flywheel
The repair is cheaper than replacing the flywheel with a new damper part, but not by much.
Interchangeability of conventional, dual-mass and lightweight flywheels
Since a new dual-mass flywheel is very expensive, for most owners of cars equipped with these modifications, the issue of interchangeability of this clutch unit and the internal combustion engine is relevant. The main nuances are:
- after installing an all-metal flywheel instead of a damper one, both the comfort of operation and the service life of CV joints, gearbox, gearbox, and clutch as a whole will decrease;
- when replacing a traditional flywheel with a lightweight one, the discomfort is much less, but ideally the entire engine needs to be rebuilt for the new operating mode.
Rice. 19 Replacing a conventional flywheel with a lightweight one
If the owner replaces a regular flywheel with a damper one, it is necessary to install a new clutch kit and adjust it without fail. Otherwise, most often the reverse and 2nd gears are poorly engaged.
Thus, the classic all-metal flywheel is more suitable for gasoline cars, has a simple design, and has a long service life. A lightweight flywheel is used for tuning internal combustion engines by a limited number of drivers; dual-mass modifications are installed by default on diesel cars at the factory.
If you have any questions, leave them in the comments below the article. We or our visitors will be happy to answer them
Possible faults
Below are the most common part malfunctions.
- Wear of the crown. Over time, the teeth on the ring can wear out, causing the starter to slip on them when starting the engine. Starting the car will be problematic - it will not work the first time.
- Misalignment. The flywheel must be installed coaxially with the cardan and clutch disc. Otherwise, when moving on a vehicle, the so-called “beating” will be heard.
- Disc wear. The part of the part that performs the functions of the clutch disc is subject to the most severe loads. As a result of this, it can wear out, and burrs and depressions may appear on its surface. The result of all this is a reduction in the size of the contact area of the transmission discs and, as a result, poor clutch. Another sign of a breakdown is noise when the car moves.
- Wear of crankshaft fasteners. The place where the crankshaft is attached also wears out over time. As a result, backlash appears. It causes noise while the vehicle is moving.
All of the above breakdowns occur in single-mass or lightweight devices. In dual-mass models, dampers may also malfunction. It is most often expressed in their wear. As a result, the part of the structure connected to the crankshaft does not transfer all the energy to the part that is the clutch disc. You can tell that problems have arisen by looking at the following “symptoms”:
- noise, knocking;
- the appearance of so-called floating revolutions;
- spontaneous “twitching” that occurs at idle;
- increased vibration level when driving;
- jerking when changing gears.