A driveshaft is a device for transmitting torque from a gearbox or transfer case to the rear wheels.
Widely used on rear-wheel drive and all-wheel drive vehicles from the beginning of the twentieth century to the present. The cardan transmission device was first described in the 16th century, but the creation of the device in practice occurred much later.
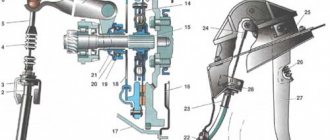
Cardan shaft device
The cardan transmission diagram includes the following elements:
- One or more sections of thin-walled hollow pipe;
- Splined sliding connection;
- Forks;
- Crosspiece;
- Suspension bearing;
- Fastening elements;
- Rear movable flange.
The unit itself can be single-shaft or double-shaft.
In the second case, the mechanism includes an intermediate cardan shaft, to the rear section of which a shank with external splines is welded, and a sliding sleeve is fixed to the front section through a hinge. Single-shaft systems do not have an intermediate section. At the front of the car, the unit is fixed in the gearbox using a movable spline connection (a movable coupling of the front part of the propeller shaft). To do this, there is a hole with internal slots at the end of the mechanism. The driveshaft design implies the possibility of longitudinal displacement of the splines when the vehicle is moving.
Next, the driveshaft suspension bearing is installed, which is attached to the body through a bracket. This serves as an additional fastening of the unit, preventing its excessive displacement when driving.
Next comes the driveshaft fork, which is located between the front and middle parts. A cross is installed here, on which there are needle bearings. The presence of forks and a cross makes it possible to transmit torque at different bending angles of the “cardan”.
At the rear, the transmission is attached to the rear axle gearbox via a flange. In this case, the shank, equipped with external splines, fits into the flange of the main gear drive.
Car design for dummies
The gearbox is connected to the engine through the clutch housing and occupies a certain fixed position in relation to the car body. The rear axle, in which the main gear is mounted, is suspended from the frame or body of the car using leaf springs or springs. When the springs deflect, the rear axle changes its position, so the gearbox and rear axle cannot be rigidly connected to each other. To transmit torque from the driven shaft of the gearbox to the drive shaft of the main gear at a changing angle, a cardan drive is used.
The cardan transmission in most passenger cars consists of one thin-walled steel pipe and two universal joints.
Operating principle of HF
The principle of operation of the cardan transmission is the ability to transport torque when the position of the “cardan” in space changes. This principle is implemented through two mechanisms:
- Sliding fork of the cardan shaft;
- Cross joint.
A sliding fork is necessary to slightly increase the length of the mechanism when driving on uneven roads. Due to the long spline connection, the supply of torque does not stop when the suspension, together with the rear axle, moves up or down.
The hinge, in turn, ensures rotation of the wheels when the bending angle of the CV changes. It is believed that the mechanism is capable of working productively at angles of no more than 20°. Then its active wear begins.
A few words about repairing the cardan mechanism
The repair procedure for the cardan mechanism consists of the following steps:
- Firstly, we determine the exact cause of the breakdown through a detailed inspection of the unit in an inspection hole or on a lift;
- After this, already knowing what needs to be changed, you need to prepare the tools and parts for replacement. The most commonly performed procedures are:
- replacement of consumables.
When selecting new parts, it is important to consider the overall dimensions of your mechanism, especially the length of the torque forks, since it changes the most when the shafts operate. You can find out the dimensions from special technical literature.
For example, let's pay attention to the dimensions of the “cardan” of some UAZ models:
Having prepared the necessary tools, all that remains is to fix the breakdown. Fortunately for many motorists, the design of the driveshaft is quite primitive, as a result of which assembly and disassembly of this mechanism is very simple.
In general, there are no particular difficulties in understanding the general essence of cardan shafts. Despite the simplicity of the device and acceptable reliability, such mechanisms have large dimensions and considerable weight, which affects their limited serial use. In any case, “cardans” were used previously and are still in use, so it would be useful for every motorist to know about their structure and operating principles. We hope the material presented above helped you figure this out. Good luck on the roads and in car maintenance!
Types of cardan drives
In the modern automotive industry, the following types of cardan transmissions can be used:
- Equipped with a unequal velocity joint (classic car driveline);
- Equipped with CV joints (constant velocity joints);
- Equipped with semi-cardan elastic joints;
- Equipped with rigid semi-cardan joints.
The system with the NUS hinge is considered classic. There are forks, crosspieces, and needle bearings. Suitable for most rear wheel drive vehicles.
Modern SUVs often use a system equipped with CV joints. Such devices provide more comfortable driving conditions, almost completely eliminating vibrations.
Elastic hinges are a rubber coupling capable of transmitting torque at bends of no more than 8°. The rubber is quite soft, so a shaft with a similar structure ensures a smooth start of movement and the absence of sudden dynamic loads. In addition, flexible connections require no maintenance. The rigid semi-cardan joint has a complex technical device and transmits torque due to gaps in the spline connection. Due to the complexity of manufacturing, technical shortcomings and rapid wear, it is not used in the automotive industry.
ADVANTAGES
The advantages of cardan transmission include:
- Work with significant torques.
- Possibility of connecting transmission units installed at large distances from each other.
- Implementation of all-wheel drive on a car.
- Simplicity of design.
- Resistance to loads.
But at the same time, the cardan increases the metal consumption of the transmission and requires significant space for installation, which affects the usable volume of the cabin.
Cardans with unequal velocity joints do not require maintenance and at the same time have a significant service life. Despite the use of bearings in the design, there is no need to lubricate them during operation, since the joint itself is maintenance-free, and the lubricant supplied by the manufacturer is enough for the entire service life.
The cardan is a non-repairable unit. When bent, the cardan requires complete replacement. This is due to the fact that the unit is balanced during manufacturing. Bends lead to imbalance, which increases vibrations and loads in the gearbox and final drive and accelerates wear of the joints.
The hinges are also not repairable, therefore, if increased vibration appears from the cardan side, or third-party sounds (crunches, clicks), the components of the hinge are replaced. Usually the crosspiece and its bearings are subject to replacement, but if the lugs are very worn out, the assembly assembly is replaced.
[custom_ads_shortcode3]
Frequent malfunctions and their elimination
All malfunctions can be divided according to emerging signs of failure:
- Vibration when moving - the bearings of the cross or the sliding sleeve are worn out, the balancing of the shaft is disrupted;
- Knocks when starting - the sliding joint splines are worn out, the fastening bolts are loose;
- Oil leakage from the bearings means wear of the seals.
To eliminate the problems described above, the “cardans” are dismantled and defective, and faulty parts are replaced. If there is an imbalance, the shaft must be balanced under dynamic conditions.
Design and principle of operation
A cardan shaft consists of several elements: a shaft, two crosspieces, a sliding fork, seals, fastening parts and a number of other elements, depending on the design. The driveshaft can consist of one, two, three or more sections. The length, thickness and weight of the shaft depend on the dimensions of the vehicle.
Cardan cross.
A single-section propeller shaft consists of a central part and tips with crosses attached to it. The central part is made of steel pipe. The use of a pipe is due to the need to reduce the weight of the shaft and save metal. Only very short shafts are made solid.
Single-section shafts are mainly used in sports cars. For example, a single-section cardan is used in the design of the Nissan GT-R.
The driveshaft is one of the most repairable parts. It is easy to remove from the car, and the repair consists of replacing the crosspieces and the suspension bearing
Cardan joint.
The operation of the cardan transmission is ensured by hinge mechanisms based on crosses. Crosses allow two mating shafts to rotate at varying angles to each other. The highest efficiency is achieved when the rotation angle is between 0° and 20°. When this figure is exceeded, the crosspiece is subjected to heavy load. In addition, the shaft loses balance and begins to vibrate.
Another important element is the sliding spline joint of the cardan. Its use is due to the fact that the car’s suspension, especially when overcoming obstacles, significantly stretches in height. The gearbox or transfer case, to which one end of the shaft is attached, is rigidly fixed inside the body, and the axle gearbox (the second point of attachment of the cardan) is connected to the suspension. As a result, when moving over an obstacle, the distance between the gearbox and the axle gearbox increases. In this case, the driveshaft must “stretch”, and the sliding spline joint helps it do this.
Another important component of the driveline is the suspension bearing. It provides additional support for the composite shaft, holding it in place and not preventing it from rotating. The bearing bracket is attached to the body. The number of bearings depends on the number of sections that make up the shaft.
Prospects for the development of a cardan transmission system
The classic ShNUS has some technological disadvantages. The rotation speed of its shafts changes during movement. In this case, the driven shaft can accelerate and decelerate at a stable speed of the drive shaft. This leads to accelerated wear of the mechanism and also creates excess load on the rear axle. Also, the operation of the hinge is accompanied by vibration. The purpose of the cardan drive can be performed by a shaft equipped with CV joints (front and rear). Similar systems are already used on some SUVs today. Also, the cardan transmission of the VAZ-2107 and other “classics” can be equipped with a CV joint. Repair kits are available for sale.
The use of a constant velocity joint eliminates the disadvantages inherent in the classic cross. The shaft rotation speed is leveled out, vibration disappears, the HF does not require balancing after repair, and the torque transmission angle increases to 17°.
Advantages and disadvantages
The main advantage of the cardan is its ability to withstand extreme loads and transmit torque. Its design allows you to eliminate almost all vibrations of a car moving over uneven surfaces, not to mention a good road.
Of course, HF also has a number of disadvantages. The main disadvantages include:
- Large mass adds extra pounds to the car, reducing its speed characteristics.
- Bulky – the driveshaft is a large mechanical structure, for which it is necessary to create a separate space under the bottom of the vehicle, which affects the ground clearance.
It is worth noting that the first modifications of the cardan transmission had another distinctive disadvantage - noise and vibration. But today, modern soundproofing materials make it possible to get rid of extraneous noise and slight vibrations during normal transmission operation.
Where else are cardan-type shafts used?
What is a driveshaft used for, other than connecting the gearbox to the axle and wheels? In reality, the scope of application of NUS hinges is quite large. They are used to create adjustable steering columns, where it is necessary to transmit torque from the steering wheel to the wheels. Cross joints are also used in tool sets. They allow you to work on bolts that are not in a straight line with the wrench extension.
Today, universal joints, despite their widespread use in many areas of industry, are considered obsolete. CV joints are becoming more and more developed, and crosspieces and forks are slowly becoming a thing of the past.
What else is worth reading
Car muffler device
Four-speed gearbox
Purpose of the lubrication system
How does a manual transmission work?
Hypoid transmission
general description
The program received its name from Gerolamo Cardano, who described it in the 16th century. (but did not invent).
The cardan transmission has a significant drawback - non-synchronism of shaft rotation (if one shaft rotates evenly, the other does not), which increases with increasing angle between the shafts. This eliminates the possibility of using a cardan drive in many applications, for example, in the transmission of front-wheel drive cars (where the main problem is transmitting torque to the steering wheels). In part, this disadvantage can be compensated by the use of paired hinges on one shaft, in which the intermediate shaft forks are in the same plane. However, where synchronization is required, as a rule, it is not a cardan drive that is used, but a constant velocity joint (CV joint) - a more advanced, but also more complex design for the same purpose.
Useful tips
Remember that you should never ignore any signs of a cardan malfunction. If you do not heed this advice, you may experience the following consequences:
- If the cardan breaks, the vehicle body itself is damaged. Additionally, the cardan can damage the pipeline that runs along the bottom of the car.
- If constant vibrations are observed, this will negatively affect the rigidity of the suspension and body mounts. All threaded connections and fastenings of interior panels will also begin to loosen. The car will literally begin to fall apart while driving.
- All parts directly connected to the driveshaft will wear out faster and more intensely. This will significantly shorten their service life and require early replacement and expensive repairs.
It is unlikely that any car owner will consciously want to face such troubles.
But in many ways they can be avoided if you follow a few simple rules. All these recommendations are aimed at increasing the service life of the driveshaft.
If you are interested in preserving the HF resource, then you need to:
- try to minimize vehicle operation in rough terrain;
- do not accelerate sharply;
- move away smoothly;
- do not skid the car for a long time;
- do not skimp on quality spare parts;
- carry out diagnostic measures;
- If complex faults occur, contact qualified technicians.
The driveshaft is in many ways an important element of a vehicle, which, although considered an intermediate link, plays a key role in the operation of rear-wheel drive and all-wheel drive vehicles.
The unit does not have an extremely complex structure, and its operating principle is clear to many. This allows you to independently solve problems that arise, detect faults in a timely manner and maintain the HF in working order for a long period of time, simply by following a few simple rules.
The process of removing and replacing the product
The sequence of actions when replacing the front axle drive on UAZ Patriot vehicles is described below.
- Place the car on an overpass or lift, first placing wheel chocks under the wheels.
- Mark the position of the driveshaft and flanges of the transfer gearbox and front axle with chalk or a chisel. The tags will allow you to continue operating the car with the old drive.
- Clean the bolts securing the drive to the flanges. To make product removal easier, apply WD40 to the connections.
- Unscrew the mounting points. If you cannot remove the bolts, cut the metal elements with a circular saw. To fasten the cardan at the front and rear, 4 bolts with nuts are used; the elements are unscrewed using 2 wrenches of 14 and 17 mm.
- Remove the worn drive and install a new part in its original place. During installation, it is recommended to use new bolts with a special sealant applied to the threads, which prevents the elements from being loosened during operation.
- A new drive requires balancing, which is performed at a service station. It is prohibited to operate a vehicle with parts that have not been balanced, because vibration increases and there is a risk of destruction of transmission elements.