One of the problems facing automotive engineers is steering lightness. For a long time this problem was solved in one way; The diameter of the steering wheel increased and the drive ratio increased. This method made it possible to operate even heavy trucks with ease. At the same time, the engineers did not impose any requirements for comfort. Therefore, the driver had to make 5-6 turns with the huge steering wheel, which was extremely inconvenient. However, modern experts have found a more elegant solution to the problem - electric power steering.
Purpose and advantage
In technical documents, the electric power steering wheel is designated as ESP. The translation of this abbreviation from English means “electric power steering”. It is an alternative to hydraulic booster. The main purpose of the electric amplifier is to reduce the effort exerted by the motorist on the steering wheel while driving the car.
The electric amplifier itself is a high-tech unit that operates on the basis of electronics. This means that hydraulics are completely excluded from the process. This device is rapidly gaining popularity among car enthusiasts and car manufacturers. Unlike the hydraulic booster, it has a lower production cost. In addition, such an element is easier to maintain and breaks less often. The electric amplifier is controlled using various sensors. They analyze the received data and transmit them in the form of signals to the mechanisms that are responsible for turning the wheels. Electric amplifiers are improved every year. Manufacturers make improvements to them, reducing the number of possible malfunctions. The main advantages of the electric booster over the hydraulic mechanism:
- reliability;
- environmental friendliness and technical safety;
- the ability to drive a vehicle in automatic mode;
- silent operation;
- simple maintenance;
- easy and smooth control of the machine;
- the ability to drive a car if the ESD fails;
- ensuring consistency between rotation angles and proportionality between resistance forces.
Mechanism design
According to its structural principle, the EUR is radically different from the classical mechanism. The design of the electric amplifier directly depends on the manufacturer. The most common option consists of an electric motor on the steering column, a mechanical transmission and a control system based on an electrical unit. Each detail has its own important role.
Electrical engine
The electric motor is usually an asynchronous electric motor. This is what sets the EUR in motion. There are several electric motor layouts:
- the electric motor transmits force to the steering shaft;
- the electric unit acts on the steering rack.
In the first case, the electric amplifier is built directly into the steering column. The electric motor transmits torque to the steering shaft using a mechanical transmission. However, the second option is the most popular and in demand. It is also called EMUR or electromechanical power steering. Structurally, it can consist of two gears or an amplifier with a parallel drive. The first mechanism transmits torque using one of the gears. On the second, the torque is transmitted via an electric motor. The parallel drive amplifier transmits power through a belt drive or ball screw nut.
Gearbox
A gearbox is a mechanical transmission that consists of a gear and a worm element. The shape of the device may vary depending on the specific car model, as well as the engineering capabilities of the manufacturer. The gearbox is necessary to convert the force of turning the steering wheel to the steering rack or from the steering wheel to the electric motor. The connection of parts, as a rule, occurs at an angle of ninety degrees.
Description of design
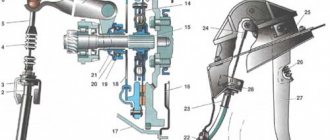
Steering elements : 1 — right steering rod assembly; 2 — right steering gear support; 3 — steering gear support bracket; 4 — intermediate cardan shaft; 5 — electric amplifier; 6 — steering wheel; 7 — steering column pipe; 8 — left steering gear support; 9 — steering mechanism; 10 — left steering rod assembly
The steering is safety-resistant, with electric power steering and a height (tilt) adjustable steering column. Steering mechanism is rack and pinion type with variable gear ratio. The mechanism is secured in the engine compartment on the front panel of the body with two brackets through rubber supports. The left support secures the steering gear housing from turning. The fastening bolts are welded, two on each side of the front panel.
Steering mechanism with rod assembly : 1 - outer tie rod end; 2 — adjusting rod; 3 — inner tie rod end; 4 — right protective cap; 5 — steering gear housing pipe; 6 — cover; 7 — locking plate of the tie rod mounting bolts; 8 — gear shaft; 9 — steering gear housing; 10 - left protective cap
The steering gear housing is cast from an aluminum alloy. On the right side, a pipe with a longitudinal window is inserted into the crankcase, secured with a nut. A helical drive gear (pinion shaft) is installed in the crankcase, which meshes with the rack.
The rack has helical teeth with variable pitch : zone 1 - with fine pitch, zone 2 - with coarse pitch
Steering column with electric power steering : 1 - input shaft; 2 - column pipe; 3 — column bracket; 4 — electric amplifier; 5 — electric amplifier control unit; 6 — steering column tilt adjustment lever; 7 — tie rod; 8 — rear bracket for electric amplifier; 9 - spring; 10 — output shaft; 11 — bolt-axle; 12 — front bracket for electric power steering; 13 — power connector of the control unit; 14 — control connector of the control unit; 15 - nut
To reduce the load on the gear shaft and its bearings under extreme operating conditions, a plastic gear bushing with a metal support plate is inserted into the crankcase. The gear shaft rotates on two bearings: the front (at the end of the shaft) is a needle bearing, the rear (closer to the steering column shaft) is a ball bearing. Since axial loads can be high in helical gearing, a thrust roller bearing is additionally installed on the drive gear shaft, consisting of a plastic cage with rollers, lower (inner) and upper (outer) rings. The lower bearing ring is pressed onto the drive gear shaft until it touches the inner ring of the ball bearing, and the upper ring is installed in the crankcase cover. In addition, the crankcase cover presses the outer race of the ball bearing against the end of the bearing seat. The drive gear seal is installed in the cover, and there is an O-ring between the cover and the steering gear housing. The entry of dirt into the connection between the shaft and the cover is prevented by a protective cover (boot) placed on the drive gear shaft. The rack is pressed against the gear teeth by a spring through a stop sealed in the crankcase with a rubber ring. To reduce friction, a plastic insert is installed between the stop and the rack. The spring, in turn, is tightened by an adjusting nut (internal octagon “24”). At the manufacturer's factory, when assembling the steering mechanism, the required clearance in the engagement of the rack and gear is set, after which the crankcase threads are cored (pressed) at two points (without damaging the nut). The right end of the rail rests on a plastic bushing, which is inserted into the pipe behind the longitudinal window. Adjustment of the gap between the gear and rack is carried out after disassembling the steering mechanism or if a knock occurs during operation. The gap can only be adjusted with the steering gear removed. The crankcase pipe of the mechanism is covered with a rubber corrugated cover. The inner tie rod ends are attached to the rack with bolts passing through the connecting plates, the spacer bushings of the rubber-to-metal joints and the tie rod support mounted on the rack. The spontaneous loosening of the bolts is prevented by a locking plate placed on the bolt heads. To lubricate the gear, rack and bearings, FIOL-1 grease is used (approximately 20–30 g for the entire mechanism).
Steering wheel angle adjustment lever with tie rod
The steering output shaft is connected to the gear shaft through an intermediate shaft, which has cardan joints at the ends. The steering column bracket, attached with four nuts to the body bracket, is pivotally connected to the steering column itself, which allows you to change the angle of the steering column. At the front, a front bracket is attached to the electric power steering housing with screws and is connected by two axle bolts to the steering column bracket. At the rear, a rear bracket is attached to the electric power steering housing, to which the steering column pipe is welded, and two guide plates with slots are welded to the steering column bracket. A tie rod passes through the slots of the guide plates of the steering column bracket and the spacer sleeve of the rear bracket of the electric booster, at one end of which a lever is screwed (special left-hand thread), and at the other there is a self-locking nut (right-hand thread). When the lever is turned down, it unscrews from the stud. In this case, the tightening force in the connection between the guide plates of the steering column bracket and the rear bracket of the electric power steering is weakened, which allows you to manually change the position of the steering column. Thus, the column can rotate in a vertical plane relative to its bracket, allowing you to adjust the position of the steering wheel. The movement of the steering column is limited by the length of the slots in the guide plates. After installing the steering column in the required position, the lever is turned up and the connection is tightened, fixing the column. Two springs are installed between the rear bracket of the electric power steering and the steering column bracket, which pull the column to the upper position when the tightening force in the connection is loosened.
Control system
The electronic amplifier control system includes:
- input sensors;
- electronic control unit;
- executive device.
Input sensors, in turn, are divided into:
- steering wheel torque sensor;
- steering angle sensor.
In addition, the amplifier control system uses information that is transmitted from the ABS control unit (wheel speed sensors) and from the powertrain control unit (crankshaft speed sensor). The device processes the received data and gives commands to the head mechanism.
Repair of the electric booster on a Priora, replacement of the EUR
So, you need to replace the electric booster on the Priora or simply check the condition of its contacts. In any case, repair involves complete removal of the unit. Prepare the necessary tools:
- Chisel and hammer.
- Deep head for 8 and 13.
- Extension and ratchet, alternatively you can use a wrench.
It’s quite easy to remove the amplifier itself with your own hands, but in order to get to its mounts and the control unit, you will need to remove many parts of the dashboard: the steering wheel along with the airbag, the casing and the ignition switch. Once these components are removed, repairs to the amplifier can begin.
Principle of operation
In terms of its operating principle, the electronic amplifier is somewhat reminiscent of the classic version, but with the addition of electronics. At the beginning of the process, the driver needs to turn the steering wheel left or right. At this time, the torsion shaft is twisted, and on the reverse side it moves. The sensors present in the mechanism read all the information and transmit it to the computer. The electronic unit analyzes this data and compares it with the performance of other sensors. As a result, the ECU calculates the force for the electric motor that must be applied to make the steering wheel turn easier.
The electric motor, in turn, after receiving a command from the ECU, begins to influence the steering rack or shaft (depending on the type of ESP). The processing speed directly depends on the current strength. The larger the latter, the more the mechanism rotates, and vice versa. In addition to the standard operating situation of the EUR, other modes can be tested, namely:
- the car takes a turn at high speed;
- turning is carried out at low speeds;
- maintaining the wheels in the main position (centered);
- return of wheels from extreme to middle position;
- other variations at medium speed.
What to choose
If just a few years ago electronic power steering was installed only on small cars, now the range of their applications has grown significantly.
Where maximum driving quality is required, they demonstrate the highest performance in terms of handling. Besides. they are more economical and reliable, so over time, ESD will be able to replace power steering.
At the same time, it is necessary to understand that the amplifier is different from the amplifier. Here it is also worth taking into account the characteristics of the manufacturer.
In any case, cars from famous brands will demonstrate higher performance characteristics than their cheap Chinese counterparts.
You should also definitely do a short test drive before making your final choice of car. As a result, you will understand which amplifier is best suited for you.
Below is a video about the operation of electric power steering:
Advantages and disadvantages
An electronic amplifier, like any mechanism, is not without flaws. However, it has much more advantages. Among them are:
- fuel efficiency (due to the lack of load on the power unit, no additional fuel is wasted);
- reliability (no hydraulics, no leaks or leakage of oil);
- ease of maintenance;
- compact overall dimensions;
- vibration from the tires is not transmitted to the steering wheel;
- good interaction between the driver and the device;
- it is possible to adjust the characteristics independently;
- implementation of other driving assistants.
As for the disadvantages of the mechanism, they are as follows:
- there is no possibility to use ESD on trucks (Volvo is currently actively working on creating a similar mechanism, but it has not yet entered production);
- it is equipped only with expensive cars or flagship modifications of vehicles due to their high cost;
- poor protection against moisture.
It is worth noting that the main difference between the EUR and classical hydraulics and at the same time its main advantage is the possibility of implementing additional safety systems. For example, the car can be additionally equipped with an autopilot, auto parking and lane keeping systems, a steering mechanism and other services.
Major breakdowns
The electric power steering wheel cannot be called an ideal mechanism. Sooner or later, like other devices, it will require repair. The surest sign that the mechanism needs attention is the appearance of a corresponding icon on the dashboard. The indicator shows a steering wheel and an exclamation mark. In some models, the ESP inscription simply lights up, but this does not change the essence. According to statistics, sensors are the first to be replaced. Most often, the steering wheel rotation and torque sensors fail. The electric motor, through which the main control of the mechanism is carried out, may also break down. Another possible malfunction is failure of the electronic disk. It is usually installed in more modern vehicles. Due to the electronic disk, the angle of rotation of the steering wheel is read, as well as the sharpness and force applied by the driver.
The most reliable element is the ECU. The fact is that another backup unit is installed in the electrical unit, which will begin to function if the first one fails. We can conclude that moving mechanisms are most susceptible to breakdowns. However, ESDs are constantly being improved by manufacturers who try to reduce the possibility of breakdowns to a minimum. So, in many modern cars, the electric booster can work on sensors of other security systems and read information from their control units.
Application area
It is worth noting that with all the advantages of the electric power steering, it has a clear disadvantage - the small torque that the electric motor can create. As a result, its power is not enough for trucks, SUVs, and large limousines.
For such vehicles, hydraulic boosters are better suited, which are limited only by pump performance.
At the same time, most likely, compact electric motors with a powerful resource will not be invented in the near future.
Some automakers have tried to make a powerful electric power steering located separately from the steering shaft, but such a solution is extremely expensive, so it has no advantages over power steering. As a result, the scope of use of electric power steering is still very limited.