The vacuum booster of the VAZ 2107 brake system is considered a reliable unit, since it rarely fails. The first problems with the element occur after 150–200 thousand kilometers. If a malfunction is detected, the problem can be solved in two ways - complete replacement or repair of the unit. Having studied the design and principle of operation of the amplifier, the skilled owner of the “seven” can implement both options independently.
- Design and principle of operation of VUT
Video: how a vacuum brake booster works
- Video: how to check the vacuum brake booster on the “seven”
- Video: replacing the VAZ 2107 vacuum booster with your own hands
- Video: how to change the VUT diaphragm on a “classic”
Symptoms of a problem
- Stiff brake pedal when the engine is running.
- When you press the pedal, the engine starts to rev, and when you slow down sharply, it stalls completely. The described symptom of malfunction is typical for cars in which the vacuum for VUT operation is taken from the intake manifold. If the membrane or vacuum tubes are not sealed, when you press the brakes, unaccounted air will be sucked in, so the engine stalls and begins to stall. The described symptom of VUT malfunction does not apply to cars in which the vacuum is created by a vacuum pump.
How to check?
A torn diaphragm is the main cause of vacuum brake booster failure. The operating principle of the amplifier is based on the difference in pressure in the vacuum and atmospheric chambers, which provides additional retracting force on the pedals. If the vacuum chamber, for example, due to a rupture of the membrane, is connected to a medium with atmospheric pressure, the vacuum created will not be enough for the normal operation of the amplifier.
How to check VUT:
- Start the engine and press the brake pedal all the way. The appearance of hissing indicates that the VUT is not sealed, so air is leaking through it;
- Press the brake pedal vigorously 3-4 times. Keep it pressed and start the engine. If the vacuum seal is working properly, after starting the engine, the force on the pedal will change and it will go down a little.
Repair or replacement?
During production, parts of the amplifier housing are connected by rolling. At home, it is impossible to replicate the factory quality of rolling. Gaps in the contact areas of the housing parts will lead to leaks in the system. Therefore, in the event of a malfunction, a complete replacement is recommended.
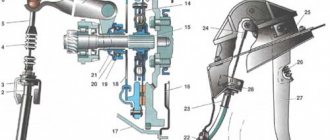
System design
You can learn the operating principle and design of the VUT from the article “How a vacuum brake booster works.” But for proper replacement with your own hands, it is much more important to understand the general structure of the brake system with a vacuum booster. The VUT is attached to the engine shield and is connected only to the main brake cylinder and the pedal lever.
Device
VAZ 2107 injector The VAZ 2107 injector consists of the following elements:
- Computer;
- Sensors;
- Fuel pipes and hoses;
- Fuel and air filter;
- Actuators;
- Gas tank;
- Wiring.
The injector power system contains the main element - a computer or ECU. Its permanent memory contains a program (algorithm) in accordance with which the control of actuators is implemented, these include:
- Fuel pump;
- Injectors;
- Idle air control;
- Canister valve.
Each of the above elements performs its own function.
Gasoline pump
Turned on by the ECU output signal through a relay. Has a strainer and fuel level sensor. The gasoline from it passes through the fuel filter. The pump is located in the tank and to remove it, you need to remove the back seat, remove the hatch and unscrew the fastener.
Nozzle
It is a sprayer equipped with a solenoid valve. Triggered by an ECU impulse. Accordingly, the duration of valve opening (the amount of gasoline supplied) depends on the time the pulse is applied. It is installed on a ramp common to all injectors, a constant pressure in which is maintained by a valve. If it is exceeded, the valve opens and gasoline returns back to the tank. The injector enters the intake manifold. The air flow, passing through the intake manifold, carries away a portion of gasoline ejected by the nozzle.
The structure of the VAZ 2107 fuel system
Idle speed control
The fuel system maintains engine idle speed using a regulator. It is a stepper motor connected to a conical shaped control body. Its approach reduces the air flow entering the intake manifold; its removal, on the contrary, increases it.
Canister valve
It is needed to turn on the ventilation of the adsorber, which accumulates gasoline vapors and releases them into the intake manifold at the right moment.
The following sensors are installed on the VAZ 2107:
- Crankshaft position;
- Mass air flow;
- Throttle position;
- Coolant temperature;
- Speed;
- Oxygen content in exhaust gases.
Crankshaft position
This parameter is needed by the ECU to open the injectors in a timely manner. If this sensor malfunctions, the VAZ 2107 will not drive.
Air flow
Allows you to supply fuel in the right quantity. The signal from this sensor is sometimes incorrect. The reason for this may be its malfunction caused by high humidity or low temperature. An air filter with condensation inside or dirty will adversely affect this sensor.
Coolant temperature
The parameter is needed so that the ECU understands whether the engine is warmed up. This is necessary for the correct operation of a cold motor. The mixture is enriched due to temperature correction.
Oxygen concentration
The oxygen content in the exhaust gases must be measured to adjust the composition of the fuel mixture. It doesn't work when it warms up. This is advisable because the mixture is enriched.
Symptoms and diagnostics
If the VUT malfunctions, the force on the pedals during braking may increase many times over. Driving under these circumstances is unsafe. All symptoms must be immediately diagnosed and the broken unit repaired.
Typically, the vacuum booster is not checked during routine maintenance, so it is important to watch for the following symptoms:
- The pedal became hard. The main indicator that the VUT is worn out or is not working correctly. This may happen gradually or happen suddenly. In addition, the pedal may be positioned higher than usual.
- The braking distance has lengthened. This occurs because it is impossible to obtain the force on the master cylinder rod necessary for the design speed of stopping the vehicle.
- The engine stalls when the brakes are applied. This occurs when the amplifier diaphragm has lost its seal and allows air to leak past the seals. In addition to reduced braking ability, engine stalling can cause major problems on the road.
- The brake system stops working. The failure may be due to a malfunction of the VUT valves.
Unit repair - diaphragm replacement
This operation is unpopular among Zhiguli owners; usually car enthusiasts prefer to change the entire amplifier. The reason is that the result does not correspond to the effort expended; it is easier to buy and install the VUT assembled. If you definitely decide to disassemble and repair the vacuum amplifier, prepare the following tools and consumables:
- assembly spatula, powerful flat screwdriver;
- pliers;
- hammer;
- brush with metal bristles;
- large bench vice;
- repair kit for vacuum amplifiers VAZ 2103—2107;
- silicone sealant.
To carry out repair work, the VUT must be removed from the vehicle, as described in the instructions above. Disassembly and replacement of parts is carried out in the following order:
- Place a mark on the body with a marker, flare the connections with the cover, bending the edges of the shell with a mounting blade.
- Carefully separate the elements, holding the lid with your hands, as there is a large, powerful spring installed inside.
- Remove the rod and seal, remove the diaphragm from the inner housing. When disassembling, lay out all the parts one by one on the table so as not to confuse anything during the installation process.
- Clean the housing and the membrane contact areas with a brush. If necessary, dry the inside of the chambers.
- Reassemble the vacuum booster elements in reverse order, using new parts from the repair kit.
- Aligning the marks on the cover and body, insert the spring and compress both halves in a vice. Roll carefully using a pry bar, hammer and screwdriver.
- Check the tightness of the VUT using a rubber bulb inserted into the hole in the vacuum hose.
After assembly, install the unit on the car, having adjusted the rod extension in advance (the procedure is described in the previous section). When finished, check the operation of the amplifier while running.
Video: how to change the VUT diaphragm on a “classic”
Vacuum brake boosters rarely bother Zhiguli owners with breakdowns. There are cases when the factory VUT worked properly throughout the entire life of the VAZ 2107. If the unit suddenly fails, there is no need to panic - a malfunction of the vacuum booster does not affect the operation of the brake system, only the pedal becomes hard and uncomfortable for the driver.
Brake force animation
A modern car is in most cases equipped with two intermediate systems that work as converters of pressure on the brake pedal into the force of pressing the pads against the discs: hydraulic and vacuum. The fluid circuit performs several functions simultaneously.
Its heart is the brake master cylinder (MBC), whose tasks include:
- Creating high braking force on the calipers by multiplying the pressure on the pedals and transferring it to the place of application.
- Reducing frictional wear of moving parts by replacing mechanical components with hydraulic ones.
- Distribution of braking force between the front and rear wheels.
- Providing design flexibility by creating work circuits that are independent from each other. This reduces the likelihood of brake failure.
- Providing technical simplicity compared to mechanical solutions.
- Simplify maintenance.
However, the speeds and masses of vehicles are so high that the hydraulic system's capabilities are insufficient for the force on the cylinder rod to be considered negligible.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=06Jj1Cy_KxQ
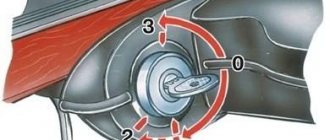
Caliper device
Let's move on. The front axle mechanisms are disk ones, consisting of calipers with the main brake elements - pads, and brake discs.
A caliper is a body with cylinders made in it for the pistons. This model has two of them, one for each block. The support structure is shown in the figure.
The caliper pistons have the form of a glass, which is placed in their cylinders, but they can move along it. To prevent fluid leakage, the pistons are equipped with o-rings.
Pads are small metal plates onto which linings made of friction material are glued.
The brake disc is made of metal for better adhesion to the surface of the pads; its side surfaces are well processed so that there are no protrusions or shells on them.
The VAZ 2107 brakes work like this: the fluid moves into the caliper cylinders, where it begins to push out the pistons. They come out of the cylinders, pressing the pads against the disc.
How to change it yourself
Let's look at how to change the VUT using the example of the VAZ 2110, 2111, 2112. The design of the system is quite monotonous, therefore, after watching the video, you can replace the vacuum brake booster of the VAZ 2114 and many other cars.
- Remove the low brake fluid level sensor connector.
- Unscrew the 2 bolts 17 securing the brake cylinder to the VUT body. There is no need to unscrew the lines, just move the cylinder with the tank a little to the side.
- Disconnect the vacuum hose from the check valve. Check the condition of the valve and install it on the new brake booster.
- Unscrew the 4 bolts securing the VUT to the engine shield. The working space in the area of the pedal assembly on the interior side is limited, so an extended socket, extension and ratchet are best suited for unscrewing.
- Disconnect the brake sensor connector.
- Pull out the VUT along with the mounting bracket and the brake pedal.
- Using pliers, remove the locking plate of the brake pedal lever rotation axis.
- Pull out the “finger” that secures the VUT pusher in the lever.
- Unscrew the 2 nuts securing the vacuum body to the bracket.
Choice
We will give some recommendations regarding the choice of a new vacuum amplifier.
Selection criterion
Required parameters
The cost of a good vacuum cleaner is now about 2.5 thousand rubles. These are not the most expensive, but not the cheapest Chinese options. Optimal for VAZ 2109
This packaging, used by a genuine manufacturer, is made of corrugated cardboard
The label should be clearly legible - the production batch number, the production date of the part and the name of the manufacturer itself
You should not buy from market traders. There are many good, trusted spare parts stores in any city. Don’t be shy to ask for certificates, documents for parts
Choosing wisely
Now there are a lot of fakes on the market. Such parts cost the same as the originals, but last much less.
How to check the vacuum brake booster
Checking the vacuum brake booster is a simple procedure that even a novice car enthusiast can handle. To determine if a part is malfunctioning, it does not need to be removed from the machine; all you need to do is perform 3 simple tests that indicate the problem.
Test 1
The car must be started and allowed to idle for about 5-7 minutes. Next, the engine is turned off, and the driver needs to fully depress the brake pedal to create a vacuum in the brake booster. The pedal is then released and pressed down again.
If there is a problem with the vacuum brake booster, the second time you press the brake pedal, the pedal travel will be significantly less than the first time because vacuum can no longer be created. In a situation where the second press does not differ from the first along the pedal stroke, we can conclude that the system is working properly or, if there is no certainty, move on to the next test.
Test 2
When the car engine is turned off, you need to press the brake pedal several times (6-8). Next, the pedal is depressed as much as possible and the engine starts. If there are no problems with the operation of the vacuum brake booster, a vacuum will begin to create in the system. As a result, the membrane presses on the rod, it pulls the pusher, which is connected by a mechanism to the pedal. Accordingly, at this moment the pedal, even if it is pressed all the way, will begin to drop slightly even lower.
Examination
Typically, a vacuum booster is checked for serviceability as follows:
- Without starting the engine, you need to press the brake several times (as when pumping);
- After the 5th – 6th press, lock the pedal in the pressed position, start the engine;
- As soon as the engine starts, the pedal moves forward slightly on its own. This is if the vacuum booster is working properly.
If a vacuum is not created, then the first thing you need to do is check the connections and the hose itself for leaks, as well as the check valve of the VAZ 2110 vacuum tank. Often the reason is a malfunction (ruptures, cracks) of rubber parts that require replacement.
An internal part, such as the diaphragm, may require repair; over time, a hole may appear in it.
The diaphragm is sold as part of a repair kit. The price of the VUT VAZ 2110 repair kit fluctuates around 250-400 rubles.
History of appearance
The automobile industry began to gain momentum at the end of the 19th century. At the dawn of the evolution of self-running crews, little attention was paid to brakes - they were simply not needed. The friction in the transmissions was so great that the vehicles slowed down sufficiently in the absence of traction. However, the power and weight of engines grew, and already at the beginning of the 20th century, many devices designed to stop vehicles were patented.
Some innovations of that period were ahead of their time. For example, four years after the appearance of Karl Benz's car, British engineer Frederick Lanchester patented a disc brake. It took several decades for this invention to become widely accepted.
The first use of air for braking was demonstrated on its model by the Chicago manufacturer Tincher. Pressure was generated by a small pump and could be used for braking, inflating tires, or sounding a horn. The 1928 Pierce-Arrow was the pioneer of vehicles equipped with a modern vacuum brake booster.
However, despite their effectiveness, until the mid-20th century, such systems were offered by automakers only as an option. The fact is that to operate the drum brakes, the force of the foot on the pedal was sufficient. It was only with the spread of a more efficient method of braking using a disc-pad pair that servos became standard equipment. The main dates in the history of the modern vacuum pump can be considered:
- 1920s - Several inventors work on actuators for aviation using vacuum in the intake manifold.
- 1927 - Belgian engineer Albert Devandre invented a vacuum brake servo.
- 1928 - the first production car with VUT.
- Second half of the 20th century - the system becomes commonplace for production models.