Backstage
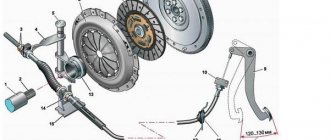
The gearbox is a multi-lever assembly mechanism that connects
the gear shift lever
and the rod that fits the gearbox.
It is located under the bottom of the car, as a rule, near the cardan or under the gearbox lever located in the cabin. In any case, dirt and water get there, which over time deteriorate the quality of lubrication of the rubbing elements of the slide, which is why they begin to wear out, leading to various problems. The average service life of the gearbox linkage will be 120 thousand km, but adjustment may be required during operation. photo gallery:
Backstage device
The design of the rocker depends on the car model, since different families use different types of gearbox controls. Therefore, consider the exact design of the gear lever
in the universal version is impossible, but you can study the approximate average version.
In most cars, the rocker consists of the following elements:
- gearshift lever;
- gear selection system traction;
- gear selector fork pin;
- finger lock;
- drawstring fork;
- yoke fork oil seal.
Gearbox mechanism
Connected together, these parts are responsible for ensuring that the gear shift lever engages the gears in the desired positions.
Design (production) of the rocker mechanism
Despite the apparent simplicity of the rocker mechanism, in order for it to work effectively, a lot of work is required to calculate and design it. The following main aspects are considered:
- productivity and efficiency;
- cost of production and operation;
- fault tolerance and overhaul life;
- accuracy of action;
- safety.
Considering the complexity of the mutual influence of these aspects on each other, the calculation of the crank mechanism is a multi-stage iterative task.
During the design, the following types of calculations and modeling are carried out:
- kinematics calculation;
- dynamic calculation;
- static calculation.
Typically, design and calculation are divided into the following stages:
- Determination of the required law of motion by calculation-analytical or graphic-analytical method.
- Kinematic modeling. Implementation of the general plan, speed plan, graphical modeling of moments of inertia, graph of energy-mass dependencies.
- Force modeling. Construction of a plan of accelerations, diagrams of forces applied to links in several positions.
- Synthesis of rocker-lever mechanism. Plotting graphs of displacement, speed, acceleration using the graphical-differential method. calculation of the dynamics of the rocker mechanism and its dynamic synthesis.
- Checking for compliance with the law of motion. Final profiling of the wings.
- Checking for compliance with health and safety standards.
- Release of drawings.
For a long time, the calculation and design of the rocker mechanism was a very labor-intensive process that required great concentration and care from the designer. Recently, the development of computer technology and software products of the CAD-CAE family has significantly facilitated all routine calculation operations. The designer just needs to select a suitable kinematic pair or link from the library programs supplied by the manufacturer and set their parameters on a three-dimensional model. There are modules on which it is enough to graphically display the law of motion, and the system itself will select and offer a choice of several options for its kinematic implementation.
What kind of backstage could there be?
According to their types, the scenes are divided into:
Visual difference between the standard and short-stroke ones (on the left - short-stroke, on the right - standard)
- Short-stroke. This is the same rocker, only with a reduced stroke due to the length of the handle itself;
- Standard.
Why do you need a short-stroke rocker? This type is used to reduce the distance and time of movement of the gearshift handle when changing gears. This allows you to make gear shifts more precise and much faster.
Also, on some cars, with standard shifters, when switching to 5th gear, the gearshift knob rests on the passenger. Installing a short-stroke one solves this problem.
The short-throw shifter is becoming popular among riders for whom shift speed is very important.
Signs of a malfunctioning rocker
Most often, problems with the rocker are eliminated by adjustment
or
replacing a repair kit
, less often the unit needs to be replaced.
In most car models, the gearbox linkage is a fairly reliable unit that can easily last up to 100 thousand kilometers without repair. The exception is cars that are not initially distinguished by high build quality - anything can happen to them. Wear of the link can be determined by the appearance of such signs as:
- increased play in the gear shift lever;
- problems with gear shifting;
- impossibility of adjusting the mechanism.
If the gears begin to engage excessively slowly, or the wrong gear is engaged that should be engaged, first of all you should try to adjust the drive if it is visually in normal operating condition. If the joints of the hinges work with a lot of play, the link will have to be changed.
The play does not affect the speed of movement and performance of the gearbox, but driving with it is extremely uncomfortable, so it is better to carry out repairs and replacement.
Rocker mechanism
The slide is a straight or curved lever with a slot into which the end of another lever slides. It moves relative to the backstage in a straight line. Rocker mechanisms are swinging, rotating and straight.
Crank and rocker mechanisms are capable of providing high speed linear movement of the executive bodies. A typical example of a rocker-type mechanism is the valve control system in automobile engines, the reverse control device for a steam engine, etc.
Rocker pairs are used in metalworking and woodworking machines, where the working element must make multiple linear movements with a return stroke.
Another area of application is analog computing devices, where rocker pairs help determine the values of the sines or tangents of given angles.
Why does the slide break?
Due to the applied forces on the backstage, it tends to become loose
TOP 5 common reasons for the failure of the scenes:
- from abruptly shifting gears when efforts are made, although you can do without them;
- under operating conditions, load on the mechanism;
- due to the installation of a low-quality part;
- if installed incorrectly (a misalignment of a couple of millimeters is enough), the link will fail after 100 km;
- during use, a displacement is formed (which guarantees incorrect loads on the equipment elements);
How to adjust the gearbox rocker
The linkage is adjusted when the standard one is changed to a short-stroke one or in case of repair. There are several adjustment methods:
- On the first transfer.
- In reverse gear.
You need to adjust the rocker with the engine turned off and the parking brake applied. Before you perform any actions related to disconnecting all the parts, make notes, they will be useful for later reassembling everything correctly. Otherwise, changes in the operation of the mechanism may occur.
To adjust, you need to loosen the clamp
To proceed directly to the adjustment itself, you need to loosen the clamp that directly holds the shift lever itself with the rod. Small turns or movement of the hub along the traction lever changes the clarity of the choice and the inclusion of certain gears. After each test, tighten the clamp and check your result.
To adjust the reverse gear, you need to gradually loosen the clamp and move the gearshift lever to a position that corresponds to the ideal engagement of the reverse gear. After adjustment, tighten the clamp back.
To adjust first and second gears, turn the lever clockwise. For the third and fourth speeds, you need to adjust the movement of the lever along the rod forward, in the direction of movement of the machine. However, it is not recommended to rotate it about its axis! To adjust the rocker in fifth and reverse gears, turn the lever in the opposite direction.
If there are problems with shifting first, third, fifth and reverse gears, the lever moves back. You need to do it until you achieve the desired result.
In vehicles where the role of the rocker is performed by cables, and not by a lever, adjustment occurs according to a different algorithm:
- First, move the gear lever to the neutral position.
- Then the gearshift lever boot is removed.
- The cables are tightened. Several nuts are used for tensioning. You need to loosen the far nut, which is located on the cable side. Initially, unscrew the nut 3 turns. Then we tighten the nut, which is located on the reverse side, 3 turns. All fasteners should be locked.
- Then the operation of the gear selector is monitored.
Most likely, the process may differ in different models of machines, but the principle of operation does not. Therefore, before starting work, you should familiarize
with instructions specifically for your car model.
If the adjustments made do not produce results, you need to think about repairs. Most likely, in the gear shift drive, the bushings and ball joints wear out, and the cables also stretch (according to the device). If there are no significant intentions to change the assembly, then you should think about purchasing a repair kit that is suitable for your car and replacing the problematic part.
Types of rocker mechanisms
Based on the type of moving link of the lever circuit, the following types of rocker pairs are used in installations and moving units:
- Creeper. A lever system consisting of four links. The main parts are a rocker and a slider with a fixed guide. It gives the slider a single degree of freedom to perform linear movements. The swing of the backstage is converted by the device into linear movement of the slider. The kinematic scheme is reversible; reverse transformation of motion is also possible.
- Crank. The crank-rocker mechanism is built according to a four-lever kinematic scheme. Transmits the rotation of the crank to the rocker, which also rotates or swings. Common in industrial installations, for example, in slitting and planing machines. For them, a crank-rocker mechanism with a rotating rocker is used. This design provides a very high forward speed and a slow return. Also used in packaging installations.
- Two-stage. The kinematic four-link design has a pair of scenes. Rotation or swing is transmitted through an intermediate lever. The gear ratio is constant and always equals one. Used in compensating couplings.
- Koromyslovy. It consists of a rocker arm, a rocker and a connecting rod connecting them. Allows the symmetry axes of the motion zones, driving and driven links to be positioned at an angle of about 60°. Finds application in automated production lines
Less commonly used in vehicles and some measuring instruments is a somewhat unique rectilinear guide or conchoidal mechanism.
How much does Kulisa cost?
The average price of a standard rocker will be around 500 rubles for a domestic car and about 1000 for a middle-class foreign car. Short-stroke ones, due to the fact that this is considered tuning, will cost more.
| Model | Price, rubles | |
| Short stroke | Standard | |
| VAZ 2110 | 450 | 340 |
| VAZ 2114 | 600 | 480 |
| VAZ 21099 | 440 | 470 |
| Priora | 550 | 500 |
Related terms
- Manual transmission (manual transmission)
Spare parts and repair kits
AvtoVAZ does not offer ready-made repair kits for repairing gear selection mechanisms: you can purchase a repair kit for the Priora gearbox rocker from third-party manufacturers or assemble them yourself.
List of parts for each box that most often fail:
| checkpoint | Detail | vendor code | Quantity | Price, rubles per piece |
| 2110 and 2170 | Gearbox ball lever support cage | 2110-1703190/86/91 | 1 | 500 |
| Lever axis | 2110-1703219 | 1 | 80 | |
| Lever axis bushing | 21100-1703226-00 | 2 | 7 | |
| Remote gearshift lever axis bushing | 2110-1703227 | 1 | 40 | |
| Overlay | 2110-1703317 | 1 | 60 | |
| 2180 | Gearbox ball lever support cage | 2110-1703190/86/91 | 1 | 500 |
| Lever axis | 21700-1703219 | 1 | 80 | |
| Thrust washer | 21700-1703371-00 | 2 | 20 | |
| Bushing (spacer, gasket) of the hinge | 21700-1703226-00 | 2 | 20 | |
| Remote bushing | 11180-1703227-01 | 1 | 45 | |
| 2181 | Rocker assembly with lever | 21901-1703010-20 | 1 | 2000 |
| Transmission shift cables (set) | 21901-1703113-00 | 1 | 4000 |