UAZ-2206, UAZ-3303 with engines UMZ-4178, UMZ-4179, UMZ-4218, ZMZ-4021 and ZMZ-4104 liquid, closed, with forced circulation of coolant by a centrifugal pump.
Cooling system of UAZ-3741, UAZ-3962, UAZ-3909, UAZ-2206, UAZ-3303, general device.
Low-freezing liquid OZh-40 or TOSOL-A40M is used as a coolant in the cooling system; in exceptional cases, the use of water is allowed. At ambient temperatures below minus 40 degrees, coolant-65 or TOSOL-A65M must be used in the system.
The volume of the cooling system, including, on UAZ-3741, UAZ-39094, UAZ-3303 and UAZ-33036 vehicles is 13.2-13.4 liters, on UAZ-3962, UAZ-3909, UAZ-2206 - 14.4- 14.6 liters. On UAZ-37411 and UAZ-33031 vehicles equipped with a pre-heater, the volume of the cooling system, including the heater and preheater, is 13.9-14.1 liters, and on UAZ-39621 - 15.1-15.3 liters.
Diagram of the cooling system of the UMZ-4178, UMZ-4179, UMZ-4218, ZMZ-4021 and ZMZ-4104 engines on the UAZ-3741, UAZ-3962, UAZ-3909, UAZ-2206, UAZ-3303.
For normal engine operation, the coolant temperature must be maintained within the following limits: for UMZ-4178, UMZ-4179, UMZ-4218 engines - 70-90 degrees, for ZMZ-4021 and ZMZ-4104 engines - 80-90 degrees.
This is accomplished by a thermostat, which automatically regulates the amount of fluid flowing through the radiator, and louvres, which regulate the amount of air cooling the radiator. In cold weather, the cooling system must be protected with an insulating cover with a flap valve.
The coolant temperature is controlled by a temperature located on the instrument panel and connected by an electrical wire to a temperature sensor screwed into the thermostat housing. In addition, overheating of the coolant is indicated by a lamp with a red filter installed on the instrument panel and connected by an electrical wire to the one screwed into the upper radiator tank.
The warning light comes on when the coolant reaches a temperature of 91-98 degrees for vehicles operating in temperate climates, and 102-109 degrees for vehicles operating in tropical climates.
The causes of overheating may be: low fluid level in the radiator, weak fan belt tension, significant scale deposits in the engine cooling jacket and radiator, driving with the blinds closed and the insulation cover valve closed. If the warning light comes on, the cause of the overheating must be immediately identified and eliminated.
Water pump.
The water pump is centrifugal type. Its design uses a ball-roller bearing, manufactured integrally with the pump shaft. The bearing has special seals that ensure preservation of the lubricant incorporated during manufacture. The bearing does not require additional lubrication during operation. Coolant leakage through the inspection hole located on the bottom of the pump housing indicates a faulty seal.
Thermostat.
With solid filling, fits in the case. Operating the engine without a thermostat is unacceptable, since when the thermostat is removed, the main flow of liquid will circulate through a small circle of the cooling system, bypassing the radiator, which will lead to overheating of the engine.
Radiator plug.
It hermetically closes the radiator and communicates the cooling system only with the expansion tank through the outlet and inlet valves. The sealing gasket prevents vapors or coolant from escaping through the gap between the radiator neck and the radiator cap locking spring. For normal operation of the radiator cap, it is necessary that the valve gaskets and the gasket between the radiator neck and the lock spring are in good condition.
Fan drive clutch.
Some UAZ-3741, UAZ-3962, UAZ-3909, UAZ-2206, UAZ-3303 vehicles are equipped with a fan drive clutch designed to reduce fuel consumption, reduce fan noise, facilitate warming up a cold engine and maintain engine thermal conditions within optimal limits.
In the gap between the driving and driven parts of the clutch there is a high-viscosity working fluid, through which rotation is transmitted from the clutch shaft mounted on the hub of the cooling system pump pulley to the clutch housing and the fan mounted on it. The clutch is turned on and off automatically depending on the air temperature behind the radiator. The coupling is not dismountable.
It should be borne in mind that the connection between the coupling shaft and the hub has a left-hand thread. For proper operation of the viscous coupling, its outer surface must be kept clean. If the clutch stops turning on or off, it is necessary to inspect it and, if necessary, replace the clutch.
Operation of the engine without the participation of the main elements is impossible; the cooling system is included in this list. Since engine operation and fuel combustion are interconnected, it is not difficult to understand that the result of such a connection is the release of heat. In the combustion chamber this indicator reaches a level of 2000°C. Without removing the temperature and bringing it to the required level, the unit will jam and will not perform the established functions.
The advantage of the UAZ “Bukhanka” car is simplicity, reliability and survivability. This statement also applies to engines and components used in transport. The simplicity of cooling makes it easier to operate and repair. Such features are attractive to users who have long appreciated the car.
Car UAZ-452 “Loaf”:
Types of cooling systems UAZ Bukhanka
The operation of an internal combustion engine involves the generation of heat. For this reason, the cooling system of the UAZ Bukhanka 409 engine is designed to normalize the temperature regime inside the unit. This function is basic, since on modern engines cooling also performs additional tasks.
Overheating of the motor increases mechanical work, leading to loss of power, as it makes the filling of the chamber worse. Overheated parts independently ignite the working mixture, increasing wear, burning oil, reducing the mechanical properties of the material, rendering the engine unusable. Lack of heat causes fuel to condense on the walls and gradually flow into the oil pan. Lubricant dilution increases wear on rubbing parts, reducing engine power.
Motor ZMZ-402:
The difficulty of operating cooling is that the system maintains an acceptable mode, balancing between too little and too much heat. Ideally, the operating temperature is kept within 90°C.
Additional cooling features:
- Maintaining temperature in the stove, ventilation, air conditioning;
- Cooling the motor lubricant;
- Reducing the temperature in the combustion gas recirculation mechanism;
- Reducing the air temperature in the turbocharger of the engine;
- Reducing the temperature of the working fluid in the automatic transmission.
Due to the difficulty of maintaining a constant operating temperature, three types of cooling systems have been developed. Each type is used in proportion to the requirements for the motor and the conditions in which the unit will be operated.
- Liquid cooling (closed, open);
- Air cooling (natural, forced);
- Mixed cooling (hybrid).
Modern schemes, which include the 402 engine cooling system, more often than others use a combined (mixed) temperature reduction. The scheme combines the properties of liquid substance and air, which complement and compensate each other.
Scheme of cooling system UAZ “Bukhanka”:
Installation of a foreign-made viscous coupling on a UAZ
I tried, I even bought it from a Steyr engine, but I couldn’t install it and gave it back. There's a key problem there. that the tolerance for runout of a viscous coupling (especially imported) must be very small, otherwise even a BMW clutch will not last long. Making an adapter will only increase the already existing inherent runout of the pump shaft. It was also not possible to change (replace) the fasteners on the coupling itself, since it is made conventionally non-removable. Therefore, I decided for myself that there was a chance to install a normal viscous coupling. unfortunately, practically none. I installed a BMW clutch two and a half years ago. To do this, I had to replace the pulley hub on the pump. I took this hub itself at disassembly, its internal diameter is slightly smaller than ours, it had to be ground. The impeller is nine-bladed. Everything works perfectly, at +35 degrees in the mountains (2000 m) on long and steep climbs the temperature reached about 90-95 degrees October 2003
This is what a BMW viscous coupling with an 11-blade fan looks like; you just need to remove the fan hub from the water pump and cut the thread to 22x1.5 right.
Operating principle
Cooling is based on the principle of heat extraction by liquid. Afterwards, the substance moves into a device (radiator), where it transfers the accumulated heat to the environment through air, while cooling. Then the working fluid returns to the heated elements and the process repeats. The cooling system of the ZMZ 409, UAZ 402 (421) engines operates on this principle.
When examining the cylinder, it is clear that the product consists of an internal and external part. The gap between these parts is called a jacket; antifreeze moves through this space. You can also read about.
Review of faults and methods for repairing them
The morally outdated UMZ 417 engine does not bend the valve, but causes several other troubles:
| Oil consumption | maximum 0.6 l/1000 km |
| What kind of oil to pour into the engine by viscosity | 5W30, 5W40, 0W30, 0W40 |
| Which engine oil is best by manufacturer | Liqui Moly, LukOil, Rosneft |
| Oil for UMZ 417 composition | synthetic in winter, semi-synthetic in summer, mineral |
| Engine oil volume | 6 l |
| Operating temperature | 90° |
| ICE resource | stated 150,000 km |
| Adjustment of valves | adjusting screws |
| Cooling system | forced, antifreeze |
| Coolant volume | 10.7 l |
| water pump | with plastic impeller |
| Spark plugs for UMZ 417 | BCPR6ES from NGK or domestic AU17DVRM |
| Spark plug gap | 0.8 mm |
| Timing drive | gear wheel |
| Cylinder operating order | 1-3-4-2 |
| Air filter | Nitto, Knecht, Fram, WIX, Hengst |
| Oil filter | with check valve |
| Flywheel | universal for ADS oil seal, lever and petal clutch |
| Flywheel mounting bolts | M12x1.25 mm, length 26 mm |
| Valve stem seals | manufacturer Goetze, light intake |
| Compression | from 13 bar, difference in adjacent cylinders maximum 1 bar |
| XX speed | 750 – 800 min-1 |
| Tightening force of threaded connections | spark plug – 31 – 39 Nm |
| Water in cylinders | cylinder head gasket torn | gasket replacement |
| Oil leak | cylinder head tightening loose | tightening the nuts periodically |
| Oil loss, increased pressure in the crankcase | loss of tightness of the rear crankshaft seal | replacing the packing of a cord impregnated with graphite lubricant |
The rear crankshaft oil seal is generally a weak point, so after the 421 engine comes out, a rubber oil seal is used in this unit, rather than an impregnated rope cord. This modernization increases the service life, since replacement is carried out much less frequently.
Design of the UAZ “Bukhanka” cooling system
The cooling system diagram of the UAZ Bukhanka is simple and typical for other engines. The design is closed, the circulation of the cooling liquid is forced.
Motor UAZ-409:
The elements of the mechanism include:
- Radiator;
- Forced cooling fan;
- Pump for pumping liquid;
- Thermostat;
- Cooling core jacket;
- Pipes;
- Coolant temperature sensor;
- Expansion tank;
- Stove with fan.
Radiator and fan
Antifreeze, having passed through the power plant, needs to reduce the temperature. For this purpose, a radiator is used, which performs the function of a cooler by breaking the flow into parts, increasing the blowing area. Initially, the cooling radiator of the UAZ Bukhanka engine 409 is made of copper with three rows of cells. Sometimes, to increase thermal output, the user replaces the product with aluminum. The radiator itself is cooled by the flow of air that blows over the car while it is moving. In a stationary position, or when moving slowly, the running power unit does not receive enough airflow. For this purpose, a fan is provided in the design.
The UAZ Bukhanka car fan is of forced type, which means that when the engine is running, the mechanism operates constantly. The product is driven by the crankshaft through a pulley, regardless of whether the motor is loaded or not. Sometimes users upgrade the unit by installing an electric fan that turns on when the liquid reaches the desired temperature. This saves fuel and adds horsepower to the engine.
Cooling system of UAZ “Bukhanka”:
Characteristics, types and applicability of UMZ-4218 engines
In the early 90s, the Ulyanovsk Automobile Plant began to feel an acute shortage of powerful and reliable engines that could provide new UAZ vehicles with better speed characteristics and cross-country ability. By 1993, based on the UMZ-4178 unit, a new UMZ-4218.10 engine was developed and put into production, which was distinguished by its large volume and torque for passenger cars. However, this unit had a number of “childhood diseases” that were “cured” with the subsequent modification - UMZ-421.10. Subsequently, on the basis of the new engine, a whole family of power units was created, which today are used in UAZ and GAZelle vehicles.
Almost all car enthusiasts know that their car has an engine cooling system. UAZ Bukhanka or 452 is equipped with a simple power unit design, and therefore the rest of the systems have simple design features.
water pump
The water pump on the UAZ Bukhanka car is mechanically driven, centrifugal type. The purpose of the device is to force antifreeze to move through the pipes and voids of the engine. The pump transports the fluid flow to the radiator, where the substance is cooled and back to the cylinders. Malfunctions in the pump will lead to overheating of the motor and serious damage, so the unit requires maintenance. The pump elements are as follows: aluminum frame, impeller, seal. The impeller, rotating, creates a centrifugal force that throws the liquid towards the walls of the frame. The job of the seal is to contain the coolant and prevent leakage at the joint.
Maintenance regulations for UMP 417
Due to design flaws and obsolescence, the UMZ 417 engine has to be serviced between major overhauls and consumables must be replaced within the following periods:
- oil and oil filter - 7.5 - 10 thousand mileage;
- valve clearance adjustment - 15 thousand km;
- air filter - after about 2 years;
- exhaust manifold - 2 years;
- fuel filter - 30 thousand mileage;
- spark plugs and battery - 60 thousand km;
- crankcase ventilation – 3 years;
- coolant - 40 thousand mileage.
Since the camshaft is located at the bottom, the timing drive is carried out by a gear wheel. Such an internal combustion engine device is more reliable in comparison with belt and chain drives, but is already obsolete at the time of development.
Thermostat
The element takes pride of place in the cooling of the power plant. The purpose of the product is to ensure circulation of the cooler, switching the movement between a small and large circle of circulation. To ensure that the processes on a cold engine are not disrupted and the engine quickly warms up to operating condition, the thermostat moves to the closed position. After heating the liquid in a small circle to 80°C, the mechanism opens, creating circulation through the radiator.
The thermostat is equipped with a solid filler and is placed in the motor housing. Operating a power plant without a mechanism can result in engine failure. The liquid will circulate in a small circle, without cooling in the heat exchanger, which will ultimately lead to overheating and jamming of the motor.
Engine tuning options
Since the UMZ 417 carburetor engine has a heavy piston system, tuning is carried out according to the following scheme:
- boring of exhaust seats up to 39 mm and use of valves from 412 internal combustion engines;
- installation of a 51 mm exhaust pipe;
- Replacing the stock camshaft with a city camshaft to increase torque at low speeds.
An important feature of this power drive is that it is limited to 100 hp. With. potential, so even if you replace the carburetor with an injector, tuning will not bring the expected increase in power. Experts recommend a swap for the UMZ 417, that is, replacing the entire internal combustion engine.
Thus, the UMZ 417 motor was copied from the 402 power drive of the Zavolzhsky Motor Plant with minor changes. Even with existing shortcomings, the internal combustion engine serves regularly in UAZ all-wheel drive buses, trucks and SUVs, that is, in very difficult operating conditions.
Cooling jacket and tubes
The space between the double walls of the combustion chambers of the UAZ car engine is located inside the power plant and the core head. Visually, it represents recesses designed to move fluid and remove heat during engine operation. Antifreeze is transported to the heat exchanger and back through pipes. Malfunctions in the elements lead to overheating of the motor and loss of operation of the unit.
Long-term operation of the engine clogs the cavities and impairs the passage of antifreeze. This is typical when the engine is running on water, since the substance is prone to scale formation and, consequently, a reduction in the cross-section of the holes and corrosion. Destruction of the cylinder walls leads to leaks and liquid entering the cylinder, and this is a major repair of the unit. In order to prevent breakdowns, it is recommended to operate the engine with antifreeze that is neutral to the engine materials, and replace the substance within the prescribed time frame.
Advantages and disadvantages
The disadvantages include the attachments - the complex design of a two-chamber carburetor and the low resource of the pump impeller made of polymer material. Due to the use of an asbestos cylinder head gasket, antifreeze often penetrates into the cylinders. Due to strong vibrations, the cylinder head nuts and covers spontaneously unscrew and oil leaks occur.
That is why the manual contains maintenance operations for periodically tightening the nuts and adjusting the valve clearance with your own hands.
On the other hand, the advantages of the design of the ICE 417 and all its modifications are:
- reliable, albeit obsolete, gas distribution system;
- high reliability and service life;
- reduction of owner costs when using low octane gasoline;
- independent overhaul and mechanical boost.
Unfortunately, tuning can add power within 30 hp. With. without installing a turbine.
Heat meter
Temperature meter UAZ Bukhanka, a part that displays information about the degree of heating on the instrument panel. Since forced ventilation of the radiator is installed on the motors used, the sensor does not control the switching on of the product.
If the motor has been rebuilt and an electric fan has been installed, the temperature sensor reads information about the temperature conditions. Afterwards, the information is transmitted to the control unit, which analyzes and regulates the degree of heating. The meter is installed on the engine thermostat; product malfunctions lead to overheating of the unit and breakdown.
Heating degree meter, motor ZMZ-406:
Fan cooling system indication diagram
In general, everything is simple, any two-color LED, according to your taste (in terms of size), from RingBright, with a diameter of 8 mm. Using this diagram, you can connect both electric fans and an electric coupling. Instead of a fan switching unit, you can use a fan switching sensor from a classic Lada, for example. In principle, it is logical to switch the orange wire going to the LED from the toggle switch to pin 85 of the relay, then the red indicator will light up not only when the fans are forced to turn off, but also when the relay malfunctions. Sensor switching temperature: VAZ-2108 - 94-99 degrees, AZLK-2141 - 82-87 degrees. Installation of a “double” electric fan
Expansion tank
First of all, the expansion tank stores a supply of antifreeze. A certain volume of fluid must always be in reserve to maintain normal engine operation. In addition, vapors and gas are released into the tank, which accumulates in the system during operation. The expander is connected to the atmosphere by a valve installed in the lid. The valve is configured in such a way that there is always excess pressure in the system. This allows the engine to operate at high temperatures, but without the antifreeze boiling. Excess pressure is released from the valves into the atmosphere.
Disadvantages of the UAZ Bukhanka cooling system
Despite the fact that the design of the cooling system of the ZMZ-409, UAZ-402 (421) engines is simple and reliable, the mechanism has inherent disadvantages. First of all, this refers to the quality of manufactured spare parts. Installation of insufficiently processed and adjusted parts reduces reliability and leads to breakdowns. In addition, on motors the fan speed is related to the pulley speed, which is not enough during hot periods. You can compensate for the lack of airflow by increasing the radiator capacity. However, the enlarged radiator is closed in cold weather, otherwise the engine will freeze. There are also complaints about the stove. The device requires additional pumping, without which there is not enough heat.
The problems can be resolved if the cooling is upgraded. The work includes replacing the radiator with a mechanism with a large number of sections. Installation of the second stove and other manipulations.
The engine cooling system is liquid, closed, with forced circulation of coolant by a centrifugal pump.
The coolant is supplied to the cooling jacket of the cylinder block.
Low-freezing liquid OZh-40 “Lena”, TOSOL-A40M or water are used as a coolant.
At ambient temperatures below minus 40 °C, coolant-65 “Lena”, TOSOL-A65M should be used.
For normal engine operation, the coolant temperature must be maintained within 70–90 °C. This is accomplished by a thermostat, which automatically regulates the amount of fluid flowing through the radiator, and louvres, which regulate the amount of air cooling the radiator.
In cold weather, the cooling system must be protected with an insulating cover with a folding valve.
The coolant temperature is controlled by a temperature gauge located on the instrument panel and connected by an electrical wire to a temperature sensor screwed into the thermostat housing.
In addition, overheating of the coolant is indicated by a lamp with a red filter installed on the instrument panel and connected by an electrical wire to a temperature sensor screwed into the upper radiator tank.
Signal lamp
lights up when the coolant reaches a temperature of 91–98 °C.
The causes of overheating may be: low fluid level in the radiator, weak fan belt tension, driving with the blinds closed and the insulation cover valve closed.
If the warning light comes on, the cause of the overheating must be immediately identified and eliminated.
Pump 421.1307010–01
– centrifugal type, driven by a V-belt from the crankshaft pulley.
The pump design uses a ball-roller bearing, manufactured integrally with the pump shaft.
The bearing has special seals that ensure preservation of the lubricant incorporated during manufacture. The bearing does not require additional lubrication during operation.
Thermostat
– with solid filling, placed in the case.
Operating the engine without a thermostat is unacceptable, because when the thermostat is removed, the main fluid flow will circulate through a small circle of the cooling system, bypassing the radiator, which will lead to engine overheating.
When servicing the engine cooling system of model 414 and model 4178 (pre-1999* production), it is necessary to take into account their design features: *
By the end of 1999, it is planned to completely switch to the production of model 4178 engines with coolant supplied to the cooling jacket of the cylinder block - coolant is supplied to the cylinder head;
– the pump (21–1307010–52) of the cooling system has two ball bearings. Lubricate the bearings according to the instructions in the lubrication table.
Lubricate the bearings through the grease nipple until the grease comes out of the inspection hole. Remove excess grease, as it can get on the fan belt and damage it;
– the coolant temperature control sensor is screwed into the cavity of the cooling system pump;
– The thermostat is installed in the outlet pipe.
Avoid getting coolant into the oil when removing the head or for other reasons, as this causes resinization of the oil, which can lead to coking and loss of mobility of the pushers, resin deposits and blocking of small holes supplying lubricant to the rubbing surfaces.
Maintenance of the cooling system involves removing scale and sediment from it, adjusting the tension of the fan belt, and also flushing the radiator from the outside.
Every three years or every 60,000 km (whichever comes first), flush the cooling system and replace the coolant with new one.
Flush the cooling system as follows:
– fill the system with clean water, start the engine, let it run until it warms up, with the engine idling, drain the water and turn off the engine;
– After cooling the engine, repeat the above operation.
Rice. 1. Flushing the cooling system
If there is significant deposit of scale and sediment, remove them from the cooling system by flushing with a strong stream of clean water.
Wash the engine separately from the radiator (Fig. 1) so that rust, scale and sediment from the engine cooling jacket do not clog the radiator.
Before flushing the engine, in this case, remove the thermostat and disconnect the hoses from the radiator.
To better clean the cooling jacket of the cylinder block, unscrew the drain cock along with the fitting from the cylinder block.
Flush the cooling jacket until the water leaving the engine is clear. Do not use alkaline solutions to wash the cooling jacket, as they cause corrosion of the cylinder head and block.
Rinse the radiator with the cap closed, first supplying water to the upper pipe to remove sediment from the lower tank first, and then to the lower pipe.
Flush until the water coming out of the upper tank is clear. At the same time, rinse the radiator core with a stream of water and blow out compressed air.
If there are significant scale deposits in the radiator tubes, do the following:
1. Remove the radiator from the car and fill it with a 10% solution of sodium hydroxide (caustic soda), preheated to a temperature of 90 °C.
2. After 30 minutes, drain the solution from the radiator.
3. Rinse the radiator with hot water in the direction opposite to the coolant circulation in the engine (see Fig. 1) for 30–40 minutes under a pressure of no more than 49 kPa (0.5 kgf/cm2).
Rice. 2. Checking the fan belt tension
Adjust the fan belt tension by turning the generator.
The normal deflection of the belt should be 8–14 mm when pressed with a force of approximately 4 kgf (Fig. 2).
Check the operation of the thermostat simultaneously with flushing the cooling system, as well as in the event of systematic overheating of the engine (if the power supply and ignition systems are working properly).
To check, place the thermostat together with a thermometer in a vessel with water heated to a temperature of 90–100 °C.
Then, as the water gradually cools, monitor the temperature of the beginning (80±2) °C and the end of closing (70±2) °C of the thermostat valve.
Replace the faulty thermostat with a new one.
When checking the thermostat, pay attention to the cleanliness of the valve disc. Remove scale and dirt from the surface of the thermostat with a wooden spatula, then rinse in water.
You can also check the serviceability of the thermostat by heating the inlet pipe of the upper radiator tank when the engine warms up.
If the thermostat is faulty, the pipe warms up immediately after starting the engine; if it is working properly, it will warm up after the water temperature in the block reaches 60–70 °C (according to the coolant temperature indicator on the instrument panel).
Check the blinds for complete opening with the drive handle pushed in all the way.
If the blinds do not open completely, adjust them as follows:
1. Loosen the screw securing the drive rod in the articulated coupling of the lever located on the blinds.
2. Open the blinds completely by turning the drive lever counterclockwise.
3. Push the blind drive handle all the way.
4. Secure the drive rod in this position in the articulated coupling of the lever.
5. Close and open the blinds several times in a row, then check the complete opening of the blinds with the handle pushed in all the way and their complete closing with the handle pulled out.
If the drive handle moves with great force, lubricate the axes of the blinds and the rod.
Lubricate the valve axes with motor oil, and the rod, after removing it from the shell, with Litol-24 lubricant.
The rod can be lubricated with an easily penetrating lubricant consisting of 60% colloidal graphite concentrate in mineral oil and 40% white spirit. Apply lubricant to the rod casing.
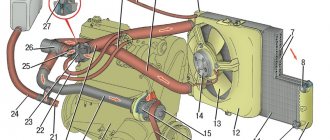
Rice. 3. Fan drive clutch
Engines of models 4218 and 4178 can be equipped with a viscous fan drive coupling (Fig. 3), which reduces fuel consumption, reduces fan noise, and also helps warm up a cold engine and maintain engine thermal conditions within optimal limits.
The outer surface of the coupling should be kept clean to ensure the removal of heat generated during the operation of the coupling and the normal operation of the bimetallic valve spring.
The clutch is turned on and off automatically.
If the clutch stops working, disconnect the clutch from the hub (the connection between the clutch and the hub has a left-hand thread), remove the fan, unscrew the two fan mounting studs from the clutch body, drain the working fluid through the holes in the studs and thoroughly rinse the inner cavity of the coupling with gasoline.
Let the gasoline drain completely, then pour 40 g of polymethylsiloxane liquid PMS-10000 TU 6-02-737-78 into the coupling through one of the holes. The second hole should be open for air to escape.
After this, screw the studs into the housing, secure the fan and install the coupling on the hub of the cooling pump pulley.
Drain the liquid from the engine cooling system through two taps. One of them is located on the lower radiator tank, the other on the cylinder block. When draining, remove the radiator cap.
The importance of the cooling system on all vehicles is endless. The main purpose of this system is to remove high temperature from the engine in order to prevent it from rising above a critical level. After all, an increase in temperature above normal will lead to irreparable consequences that will entail the need for major repairs. But let’s not talk about sad things and let’s look at what the cooling system on the UAZ Patriot is, what its features are and what it consists of.
Installing an electric fan to cool the radiator
At the beginning of winter I installed an electric fan... Among all the fans with brackets (the motors are all the same, only the Tenth, Nivsky and Volgovsky propellers have more blades), the choice fell on 2106. The Volgovsky one has a very wide bracket, the radiator would have to be moved far forward or the bracket cut , Okovsky and Vosmerochny had to be installed vertically, and this also complicates the mounting.
During installation, I dismantled the original fan and casing. Using the upper mounting rods, I moved the radiator as far as possible from the engine. In this position, the new fan and shroud fit almost perfectly. I drilled one additional hole on the casing so that the 2 holes on the fan casing coincided with the standard mounting holes from the old casing on the radiator. This is on the side of the casing where the motor is mounted. To the other side of the casing I screwed a suitable corner with holes drilled so that they again coincided with the standard ones on the radiator. I secured it with the same bolts that the standard casing was screwed on. The crankshaft pulley does not interfere with the new design. As a temperature sensor I used a Zhigulevsky one (92-87), screwed in through an appropriate adapter instead of the standard emergency temperature sensor. True, it is necessary that the emergency sensor is not screwed into the top of the radiator, as in older models, but from the side, on the engine side. I used the electrical connection diagram as in a classic Zhiguli. It works for six months without problems. I didn’t notice much of a difference in operation, except that it began to warm up faster and held the temperature better in winter. I installed a fan from 2106. And 1 (ONE PIECE). It fit right in instead of the standard one and the diffuser. Moreover, it was necessary to file the corner of the diffuser in one place and drill two holes in it. I had to slightly lengthen the frame on which the fan is mounted. Everything turned out to be quite simple and took half a day. I've been driving like this for a year. There have been no problems yet. In general, the fasteners are not a problem. I lengthened the frame with a plate that is used to press the rubber mudguards in Zhiguli cars. There's even a hole in it. If you imagine a Zhiguli fan, it has a diffuser on the left with two holes for attaching to the radiator. I used one, re-drilled the second. On the right there is one hole for fasteners. This plate is screwed there at an angle so that it reaches the standard diffuser mounting hole. Yes, the overheating sensor is a little in the way, the diffuser will need to be slightly filed. You may have to tilt the radiator forward a little, I don’t remember. There remains a frighteningly small gap between the axis of the pump pulley and the device, but it turned out to be enough. When I installed it, I didn't remove the radiator.
Device Features
The cooling system on each car is a separate unit, which consists of main components. These main components on the UAZ Patriot car include the following elements:
- radiator;
- water pump;
- thermostat;
- expansion tank;
- coolant;
- fan;
- hoses and tubes.
UAZ vehicles of Euro-3 and Euro-4 environmental standards are equipped with closed-type cooling systems, the functioning of which is ensured by the circulation of antifreeze or antifreeze. This liquid is the main reagent that removes heat from the engine.
The cooling system also includes heater radiators and an electric pump that supplies fluid to these products. The UAZ Patriot Euro-3 is equipped with one heater radiator, and its descendant Euro-4 is already equipped with two devices. The photo below shows a diagram of the design of the cooling system, which displays a complete list of working elements.
The diagram displays not only a list of the main elements of the unit, but also the path of fluid passage. Thanks to such a diagram, you can roughly imagine the structure of the system and the principle of its operation. If we touch on the principle of operation of the unit, it is as follows:
- Since the system is closed, pressure is created in it. Pump 16 is directly involved in creating pressure.
- The pump operates thanks to the torque from the SUV engine shaft.
- The pump directs the liquid into a special jacket, where heat is transferred from the engine to the coolant.
- From the jacket, the liquid enters an element such as thermostat 6, which is involved in the distribution of cold and hot liquid flows. If the fluid is at a high temperature, the thermostat directs it to the radiator for cooling, and if it is cold, then to the water pump.
Thus, the cooling system of the Patriot engine and, in fact, most modern vehicles operate. Therefore, this scheme is appropriate for other cars.
If it is necessary to increase the temperature in the cabin, the driver activates a special heater switch, thereby opening coolant access to heater radiators 1 and 2. Pump 3 begins to pump pressure into the cabin heating structure, thereby accelerating the circulation of liquid through the radiators. The diagram displays all the processes, so understanding it will not be difficult.
On UAZ Patriot Euro-3, the cooling system is supplied from the factory with A40M or A60M antifreeze. Patriots of the new standard are filled with both antifreeze and antifreeze. The difference between these liquids lies in the composition and does not play a big role in the process of heat removal.
Fan
A radiator is a container in which liquid is cooled. But it is impossible to cool the liquid without such an element as a fan, so its presence is mandatory. The fan serves in the cooling system to increase the intensity of the coolant temperature reduction in the radiator. In Patriots, the fan is driven by a belt drive from a viscous coupling. This type of device drive is hydraulic, as it is controlled by fluid in a fluid coupling. But such a fan has many disadvantages, so SUV car owners often resort to engine conversion by In particular, the disadvantages of the hydraulic drive of the device include the following factors:
- The load on the engine increases as the viscous clutch is driven by the crankshaft.
- Instability of fan operation, since the speed of rotation of the blades directly depends on the number of revolutions of the crankshaft.
- Inability to turn on the fan when necessary.
Therefore, in frequent cases, drivers install electric fans, which are very popular in the system.
Unfortunately, even modern SUVs from the Ulyanovsk plant are equipped with radiator cooling fans, which are driven by a viscous coupling. The disadvantages of a viscous coupling include the high cost of the product, since the unit is a whole unit.
In conclusion, it should be noted that the high temperature removal system of a car is very important for it, be it a diesel engine or a gasoline one. After all, in any case, they need to remove high temperature in order to avoid the possibility of engine jamming. Therefore, it is very important for every owner of any car to monitor the proper operation of this unit in order to prevent malfunctions. Otherwise, untimely stopping of the engine when the temperature rises above 100 degrees can be fatal for both the engine and the driver.
You can check your BMR and if you need to reduce it!
from the book by E.N. Orlova and E.R. Varchenko "UAZ Cars" maintenance and repair
Cooling system.
Cooling system
(Fig. 25) liquid, closed, with forced circulation. Rice. 25 Engine cooling system diagram 1 - heater radiator 2 - heater valve 3 - cylinder head 4 - water distribution pipe holes 5 - gasket 6 - water distribution pipe 7 - thermostat 8 - outlet pipe 9 - filler neck 10 - blinds 11 - plug 12 - mark minimum 13 - tank 14 - cooling system pump 15 - impeller 16 - pulley 17 - fan 18 - radiator 19 - radiator drain valve 20 - inlet pipe 21 - cylinder block 22 - cylinder block drain valve
Low-freezing antifreeze A-40 is used as a coolant. At ambient temperatures below minus 40 C, antifreeze A-65 is used. Water may be used.
For normal engine operation, the coolant temperature must be maintained within 80...90 C. This is achieved using an automatically operating thermostat and shutters controlled by the driver.
To monitor the coolant temperature, there is an electrical indicator in the instrument panel, the sensor of which is screwed into the cavity of the water pump bracket. In addition, overheating of the coolant is indicated by a warning lamp with a red filter installed on the instrument panel and connected by an electrical wire to a sensor screwed into the upper radiator tank. The control lamp lights up when the coolant reaches a temperature of 92...98 C. When the control lamp lights up, it is necessary to open the radiator shutters.
Rice. 26 Engine cooling pump 1 - nut 2 - shaft 3 - pump housing 4 - lubricant outlet inspection hole 5 - grease fitting 6 - spacer sleeve 7 - sealing washer 8 - rubber seal 9 - spring 10 - impeller 11 - impeller fastening bolt 12 — control hole for fluid outlet 13 — bearings 14 — fan shaft hub 15 — belt 16 — pulley 17 — fan 18 — bolt
Installation of SHAAZ radiator on UAZ-3160
There are new radiators from the SHAAZ plant for the 3160. Their heat output is 62,000 kcal/hour, versus 35,200 kcal/hour for the 3741sh radiators (our “native”). Attention!
As of August 2004, in the catalog of JSC SHAAZ, the figure for 3160 is
37000.
Tubes, when new, cost about 1.5 times more often, and the plates are straight and shorter (ours are corrugated and long) - better “air permeability” and heat transfer the plate itself - because a long plate dissipates heat worse.
Questions: 1. Do they fit without modifications?
There is only one change - instead of the standard lower bolts, regular ones are installed (new radiators have threads on the radiator).
You also need to slightly move the lower pump hose down. 2. Is there any difference in size?
No width or thickness.
The height of the “honeycomb” is about 5-7 cm (due to the absence of lower “legs”, the radiator itself seems to have “lengthened”. The hole for the handle is now in the lower tank. 3. Is it really better to cool?
Yes, indeed. The design is better .