The engine coolant circulation pattern is approximately the same for each vehicle. During operation, an internal combustion engine generates a large amount of heat. To avoid possible problems, this heat must be constantly removed. Due to overheating, even mechanical damage can occur, so if the coolant does not circulate, serious consequences for your car can occur. To avoid such problems, all cooling mechanism components must be configured and operating properly.
Cooling system functions
The temperature in the cylinders during engine operation can reach 800-900 degrees. Even after a few seconds without the cooling devices operating, the motor temperature rises to an unacceptable level. Heat removal processes protect mechanisms and parts that also maintain normal operating condition and speed up the warm-up of the machine.
Vehicle cooling system
However, these are not all the functions that are assigned to the operation of the car’s cooling circuit. More modern developments can perform other tasks that contribute to the normal operation of the motor and increase its service life. Among them:
- Air heating. Most often, this function applies to heating, air conditioning and ventilation devices.
- Oil cooling. Without lubrication, a car can also overheat, and sometimes this happens even from constant operation of the engine, so a coolant comes to the rescue.
- Cooling of gases in the recirculation mechanism.
- Cooling the fluid in the gearbox. Working fluids in an automatic transmission also require a decrease in their temperature.
In order to perform their assigned tasks properly, cooling systems come in different forms. They differ in cooling methods. There are three types of systems:
- Closed liquid system;
- Open air system;
- Combined system.
Auto engine cooling system
The most common cooling method is liquid-based. It ensures uniform distribution of cold and has the lowest noise level during operation.
Air or dropsy
The cooling system of an internal combustion engine is designed to remove excess heat from engine parts and components. In fact, this system is bad for your pocket. Approximately a third of the heat obtained from the combustion of precious fuels has to be dissipated into the environment. But this is the structure of a modern internal combustion engine. The ideal would be an engine that can operate without dissipating heat to the environment, and convert all of it into useful work. But the materials used in modern engine construction will not withstand such temperatures. Therefore, at least two main, basic engine parts - the cylinder block and the cylinder head - have to be additionally cooled. At the dawn of the automotive industry, two cooling systems appeared and competed for a long time: liquid and air. But the air cooling system gradually lost its ground and is now used mainly on very small motor vehicle engines and low-power generator sets. Therefore, let’s take a closer look at the liquid cooling system.
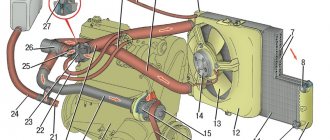
CO components
The operation circuits of cooling mechanisms include many elements. Each of the parts performs its own functions; accordingly, for the ideal operation of all systems, the elements must be in good condition, and they must not be affected by external negative factors. There are times when coolant is not circulating and this is a sign that one of the components is not working properly.
- Radiator. Its task is to reduce the temperature of the refrigerant under a constant flow of cold air. Heat output is increased, thereby increasing efficiency and cooling capabilities, allowing you to get more work done in less time.
- An oil radiator can be installed along with the main one. It is designed to cool the lubricant.
- Another type of device of the same type is a radiator designed to cool exhaust gases. It is necessary to reduce the combustion temperature of the fuel mixture.
- The job of the heat exchanger is to heat the air. The operation of this device will be more efficient if it is installed at the point where the coolant exits the engine.
- The expansion tank helps compensate for the changing volume of coolant as a result of its expansion.
- The circulation and movement of coolant is provided by a centrifugal thrust pump. Such a pump is often called a pump. The operating system may vary depending on the type of device. In particular, there are pumps on a belt, and there are pumps on gears. Some powerful engines require the installation of an additional pump of the same type.
- Thermostat. The purpose of this device is to set the level and amount of refrigerant. All refrigerant is controlled, thereby maintaining the most acceptable temperature conditions. You can find the thermostat in the middle between the radiator and the cooling jacket in the pipe.
- An electrically heated thermostat is also found on powerful engines. Full opening of such a thermostat occurs under heavy load on the internal combustion engine.
- The fan is an important part of the radiator. It increases the cooling intensity and can operate on different drives such as mechanical, electric or hydraulic. Most often, cars are equipped with an electric drive.
- The control system elements have their own purpose and allow you to use the entire system to its full potential. The temperature sensor displays the necessary information on the screen, converting it into a signal.
- The electronic control unit receives signals from the sensor, converts them into execution signals and transmits a coded signal to the same devices.
- Executing devices perform the tasks assigned to them after receiving a certain signal. Among them are: heater, relay, fan control unit, another relay for the engine.
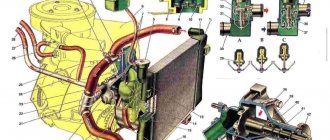
Elements included in the system
The combined closed-type circuit includes a heating system for the vehicle interior. Based on this, we can make the following list of elements included in the cooling system:
- radiators (one for cooling, one for heating);
- fans;
- water pump (pump);
- thermostat;
- temperature sensor.
The radiator plays a major role in the cooling system. It is made of two tanks, which are combined by many welded or drawn brass tubes. Tubes are less commonly made from aluminum, as their strength is lower. The tubes can be straight or tape, with an elliptical cross-section. Thanks to this structure, they can more easily withstand the pressure of frozen liquid. To increase the heat transfer area, the tubes pass through a stack of plates. The lower tank has a valve for draining liquid. In the upper tank there is a neck or pipe leading to the expansion tank. It is closed with a plug, inside of which there are inlet and outlet valves.
There is a temperature sensor on the side of the radiator that indicates the coolant temperature. A fan is installed in the center to blow over the radiator. It can receive a drive in three ways:
- Directly from the crankshaft.
- Through the coupling.
- From an electric motor.
A water centrifugal pump circulates liquid throughout the system. Mounts directly to the crankshaft. With high engine power, the oil is cooled by installing an oil cooler on the main one.
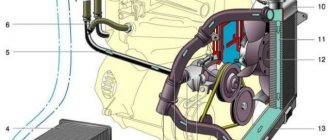
Coolant circulation diagram
- The coolant circulation circuit consists of a large circle and a small one. While the engine is cold, the coolant does not circulate only in a large circle. The small circle is limited by the cooling jacket and radiator. The thermostat does not open until the engine warms up and the temperature reaches the required level. Also, during circulation in a small circle, the thermostat closes the fluid flow to the radiator.
In general, this is what the internal combustion engine of a car looks like:
- The small circle provides for a smaller amount of liquid circulating in the cooling circuit. This is why the engine can heat up faster. After reaching the critical point, the thermostat opens and the hot liquid enters a large circulation circle. Its movement occurs from top to bottom. Excess heat as a result of blowing is removed from the engine to the outside. The thermostat's job is to react to the coolant temperature and protect the engine from overheating.
- Then the coolant is supplied directly to the engine. It heats up faster, thus warming up the engine. The operation of the radiator becomes necessary only when the liquid reaches a certain temperature. When the coolant temperature becomes high, the thermostat opens and the coolant then flows through a large circulation circle.
Fluid replacement and flushing
If you have not had to replace any component in the cooling system before, then the instructions recommend changing antifreeze at least every 5–10 years. If you have never had to add water to the system from a canister, or even worse, from a roadside ditch, then when replacing the fluid, the system does not need to be flushed.
To remove coolant, there is a drain hole with a plug at the bottom of the radiator.
To remove coolant, there is a drain hole with a plug at the bottom of the radiator.
But if the car has seen a lot in its lifetime, then when replacing the fluid it is useful to flush the cooling system. Having opened the system in several places, you can thoroughly rinse it with a stream of water from a hose. Or simply drain the old liquid and fill with clean, boiled water. Start the engine and warm up to operating temperature. After waiting until the system cools down, so as not to get burned, drain the water. Then purge the system with air and add fresh antifreeze.
Flushing the cooling system is usually started in two cases: when the engine overheats (this manifests itself primarily in the summer) and when the stove stops heating in winter. In the first case, the reason lies in the radiator tubes overgrown with dirt on the outside and clogged on the inside. In the second case, the problem is that the heater radiator tubes are clogged with deposits. Therefore, during a scheduled fluid change and when replacing cooling system components, do not miss the opportunity to thoroughly rinse all components.
Tell us what cooling system malfunctions you have encountered. And I wish you a hot heater in winter and good cooling in summer.
Engine cooling system: how does it work and is it necessary to flush it in winter?
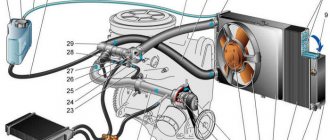
Using a “large” circle
The cooled antifreeze is re-entered into the engine by pumping it through the water pump. However, a situation may arise in which this is not enough for normal cooling. Fans will come to the rescue, and their activation will be ensured by a special sensor. It’s called the “fan switch” and is located under the radiator. When its contacts close, these devices turn on, providing additional forced cooling.
After a while, the antifreeze temperature drops and the fans turn off. A figure around 90 degrees is considered conditionally acceptable for most internal combustion engines, although some thermostats are designed to maintain 87 degrees. The efficient operation of the entire cooling system as a whole is achieved by using the above-described scheme. When the engine is not warmed up, heat removal is not required. But in further work it will be necessary to include additional equipment in the cooling process.
Water circulation as an engine
The pool is quite simple.
Swimming pools, whether they are in the ground or above it, are designed exactly the same and work according to absolutely the same principle. Hoses, filters, motors are also used the same in both places.
Water reservoir. The walls of the pool are plastic structures that create the shape of the pool; the inside is blue or any other with or without a pattern.
The water in the pool must be constantly circulating. Water circulation is ensured by a pump motor. At night, when the water temperature drops and there is no sunlight, the pump
can be turned off.
Usually a timer is set for this. The timer must be of appropriate power and suitable for outdoor use.
If you have a water heater or thermopump (heat pump) installed, then you cannot turn off the pool at night; the motor must run 24
hours a day.
Due to circulation, water is purified. The acidity of the water and the presence of chlorine in it are checked every few days using a test.
The water in the pool flows into a white rectangular window, which absolutely all pools have. Behind this window there is a round box with a filter basket.
The pictures were taken at different pools, but all the details of the device are the same in almost all houses
The water passes through this first filter, leaving leaves and large debris in the basket. From time to time the box needs to be opened and accumulated debris removed. If there is a lot of debris, the water will not flow well, the motor will work with overload, and the circulation and purification of the water will be insufficient.
Then the water enters the pump motor. If you open the top transparent plastic cover, you will see a filter basket very similar to the previous one. If something slipped through the first filter, it will linger here. You also need to check the cleanliness of this filter from time to time. Next, the water enters the filter barrel. The structure of the barrel is very simple - it can be filled with very fine sand or something artificial that replaces sand. The water passes through sand or its substitute, is filtered and then returns clean to the pool.
Not far from the white rectangular box where the water from the pool enters, there is also a small round outlet from where the purified water flows back into the pool. The white plastic tip is adjustable to direct the water stream.
The water flies out with decent pressure and you need to install the outlet hole so that the jet under pressure does not hit above the surface of the water, but at the same time seems to rest against it. The stream of water should not fly out strictly perpendicular to the walls of the pool. It should be directed in the direction opposite to where the water leaves the pool for filtration (the rectangular hole on the wall of the pool is always not far from the outlet).
If the stream hits a little to the side, resting against the surface, but without reaching it, then the water in the pool will not move quickly, but will move in a circle. If the pool is not of the correct cylindrical shape, then it will be a little slower, but the water will still move along the surface. In this case, debris from the surface will fall into the first filter basket, and the water purified by the filter will be better mixed with the rest of the pool water.
At the outlet of the filter, some systems have a chlorine distributor. In other pools, chlorine tablets are placed in a float, which dangles freely on the surface of the water all the time. If the distributor is located at the outlet of the filter, then the amount of chlorine in the pool is easier to control.
You can twist it, do less or more. If you want to open the dispenser cap and add chlorine tablets, you need to turn off the pump motor! Otherwise, there will be a severe burn and even poisoning from the vapors and high concentration of chlorine in the distributor!
To switch the position of the handle on the filter barrel in any way (filtration, circulation, reset, etc.), the motor must be turned off!
If you want to open the chlorine distributor cover, you need to turn off the motor!
If you remove the transparent cover from the pump motor, the motor must be turned off!
All working components of the pool - pump motor, filter, chlorine distributor - can be placed outdoors. They are not afraid of either rain or wind. For the winter, everything is disassembled and partially taken to a warm room.
That's all the structure of the pool is.
All about the pool on your site:
Video “Design and principle of operation of the cooling system”
This video shows how antifreeze circulates in the cooling system.
One of the special liquids that is designed to ensure the correct operation of car mechanisms is antifreeze.
If you do not properly treat the quality and level of antifreeze in the tank, this can lead to quite serious malfunctions, both individual parts and complete machine components.
The principle of operation of antifreeze. The engine cooling process involves circulating coolant through a specific circuit of hoses and tubes. In a situation where the engine has not yet warmed up to the required temperature, the antifreeze pump will only circulate in a small circle, which includes the cylinder block, cylinder head and stove. If the antifreeze is already heated to a temperature of 90-100 degrees Celsius, the thermostat opens, and the coolant goes through the same circle, but with the radiator captured.
As the antifreeze warms up, its volume increases to 5%, which is returned back to the tank. Once the antifreeze cools, it is sent back to the engine. This operating principle makes it possible to prevent the occurrence of air and steam plugs.
If the antifreeze level has decreased, then there may not be enough of it to cool the engine. As a result, situations arise when air-steam plugs appear in the system, which necessarily disrupt the functioning of the system.
The result of such a situation is excessive heating of the head, its destruction, the occurrence of various types of defects in the oil supply channels, an increase in fuel consumption and a decrease in machine power.
With an increased amount of antifreeze in the tank, the pressure throughout the system will increase. The consequence of this may be a leak in the radiator, tank cap or hoses.
Dependence of antifreeze volume. The level of engine cooling fluid depends on several parameters, which include:
- Ensuring the integrity of the gasket itself, cylinder head, radiator, tank, tubes and hoses;
- Correct operation of the radiator and tank valves;
- Proper operation of the fuel ignition system;
- Correctly selected brand of antifreeze.
Correctly fixed hoses using clamps of the required size;
If there are defects in either the cylinder head or the gaskets, the cooling liquid will penetrate either the cylinders or the oil. A sign of this will be thick white smoke in the first case, and bubbles in the oil in the second.
If the gasket is broken, then both of these signs will be present at the same time. In addition, the car owner will pay attention to an increase in fuel consumption, as well as a decrease in engine power.
If there is damage to the valves of the tank or radiator, the boiling point of the antifreeze will be reduced, which will certainly lead to the appearance of plugs. A mixture that is too rich, on the contrary, will lead to the need to use increased force to press the gas pedal.
Checking the antifreeze level. To correctly check the antifreeze level, you need to perform the steps in this order:
- Remove the reservoir cap with the engine cold;
- Inspect the lower edge of the outlet to which the expansion tank hose is attached. The fluid level must correspond to this;
- When inspecting the expansion tank itself, the location of the antifreeze level should be exactly between the minimum and maximum.
Bottom line. Checking the coolant in the car's tank should be carried out as often as possible, at least twice a week. Timely addition of antifreeze ensures proper engine cooling.
Hello everyone, my dear readers! Even a high school student today knows that a modern car is equipped with several key systems. Some are responsible for power, another for lubrication, and the third for cooling from overheating. I propose to dwell in more detail on what kind of coolant circulation scheme is provided - the understanding of the importance of cooling in general will depend on this.
How to systematize knowledge and gain practical skills on the topic?
The licensed educational product “Automotive Fundamentals” on the LCMS ELECTUDE platform will help you study the topic “Lubricating and Cooling Systems” in detail.
A video review of this training product is available for you right now:
A huge advantage of using the platform is that you not only consistently receive the necessary set of knowledge, but have the opportunity to work with devices in practice, hone your diagnostic and repair skills (the platform has a built-in simulator).
The platform is adaptive for both classroom and distance learning. It is very convenient that the system has a well-thought-out test system. You can not just study the material, but monitor how it has been learned and what real progress has been made in studying the engine cooling system.
A2038301896 Mercedes-Benz Mercedes c class w203 engine water circulation pipe
Original number: A2038301896 Mercedes-Benz
We searched: A2038301896
Warehouse Russia & Belarus
Used A2038301896 Mercedes-Benz Mercedes c class w203 engine water circulation pipe in Ufa — 3 offers found at prices starting from RUB 650. up to 1090 rub.
Expansion tank cap
Another irreplaceable component of the system is the plug. There are two types of construction - sealed and non-sealed. If the latter is used on the car, the expansion tank plug has only a drainage hole through which the pressure in the system is balanced.
But if a sealed system is used, then there are two valves in the plug - an inlet (takes air inside from the atmosphere, operates at a pressure below 0.2 bar) and an outlet (operates at a pressure above 1.2 bar). It removes excess air from the system.
It turns out that the pressure in the system is always greater than in the atmosphere. This allows you to slightly increase the boiling point of the antifreeze, which has a beneficial effect on engine performance. This is especially good for driving through traffic jams in urban environments. An example of a sealed system is VAZ-2108 and similar cars. Unsealed - models of the classic VAZ series.
Washing process
First of all, before flushing, all coolant is drained through the drain plug on the radiator, located at the very bottom, and on the cylinder block to remove any residue.
It is important to remember that draining the fluid should only be done on a cold engine!
After draining, the plugs are tightened again and water with citric acid or, better yet, a special cleaning liquid is poured into the expansion tank.
The process of pouring PRESTONE Super Radiator Flush into the expansion tank
Next, the engine starts and idles for 15 minutes. In this case, care should be taken to open a large circulation circle. Also, when washing, do not forget that the cabin stove should operate in maximum heating mode. When the unit has cooled down, the liquid can be drained by opening the radiator and cylinder block plugs. It is recommended to repeat this process until clean liquid without visible contaminants flows out when draining.
Filling with new coolant can be done immediately after flushing is completed. Pour antifreeze or antifreeze into the expansion barrel carefully and slowly to avoid the formation of air locks in the system.
When pouring antifreeze or antifreeze, use a funnel - this will prevent coolant from getting on engine parts.
When the tank is almost completely filled, you need to close it and start the internal combustion engine for a few minutes so that the liquid spreads evenly throughout the system. Next, after turning off the unit, antifreeze or antifreeze is added to the level between the maximum and minimum marks on the barrel.
In conclusion, it is worth saying that there is no fundamental difference in the use of antifreeze or antifreeze. However, in many countries around the world, car manufacturers have long stopped using antifreeze, since its effectiveness is somewhat lower. Modern antifreeze is manufactured using the latest technologies and better protects the engine from overheating and the cooling system lines from contamination.