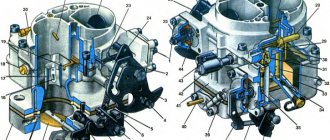
Solex carburetors of the 2108 family have been produced at the Dimitrovgrad Automotive Unit Plant since the mid-1980s. Their development and production were organized specifically for the first series of front-wheel drive “eights”. Thanks to their unique design, reliability and maintainability, these devices even today allow old cars to feel quite cheerful, and their owners can easily and easily assemble or clean the carburetor, reduce fuel consumption, adjust the system and much more.
How does Solex differ from Ozone and Weber?
The main difference between Solex carburetors and devices of previous families is the possibility of installing it on transversely located power units with the float chamber forward. This installation option made it possible to eliminate the leanness of the fuel mixture when the car enters a turn, climbs, or during sudden acceleration.
In addition, Solex has a completely different float chamber design. It has a two-section design, which allows the device to be used both on front-wheel drive cars and on classic cars.
Solex carburetors are reliable and maintainable
What brands and models of cars were installed on?
C were installed not only on VAZs. Other automakers also actively used them for their cars.
Table: modifications and applicability of Solex carburetors
| Modification | Applicability | Engine volume, cm3 | Notes |
| DAAZ-2108–1107010 | VAZ 2108, 2109 | 1,3 | |
| DAAZ-21081–1107010 | VAZ 21081, 21091, ZAZ 1102 | 1,1 | |
| DAAZ-21083–1107010 | VAZ 21083, 21093, 21099 | 1,5 | |
| DAAZ-21083–1107010–31 | VAZ 2108, 2109, 2110, 2111 | 1,5 | Has a semi-automatic starting device |
| DAAZ-21083–1107010–35 | VAZ 2108, 2109, 2110, 2111 | 1,5 | Has a two-level semi-automatic starting device (winter/summer) |
| DAAZ-21083–1107010–62 | VAZ 2109, 2115 | 1,5 | Has an electronic device for controlling the composition of the combustible mixture |
| DAAZ-21083–1107010–05 | VAZ 2109 | 1,5 | |
| DAAZ-21412–1107010, DAAZ-21412–1107010–30 | AZLK 2141, 2141–23 | 1,5/1,8 | |
| DAAZ-1111–1107010 | VAZ 1111, 11113 "Oka" | 0,65/0,75 | |
| DAAZ-21051–1107010 | VAZ 2103, 2105 | 1,5 | |
| DAAZ-21053–1107010 | VAZ 21074, 21061 | 1,6 | |
| DAAZ-21051–1107010–30 | VAZ 2104, 2105 | 1,3 | |
| DAAZ-21053–1107010–62 | VAZ 2107, 21072, 21074 | 1,3/1,5/1,6 | |
| DAAZ-21073–1107010 | VAZ 2121, 21213 "Niva" | 1,6/1,7 |
VAZ 2109: engine and its performance
Engines of different sizes and power can be installed under the hood of a hatchback. The first models were equipped with a four-cylinder, eight-valve engine, the volume of which was 1100 cc. cm. In subsequent models, this figure increased by 1300 cc. cm, and later reached 1500. In the 90s, a model with an injection engine was also released. The VAZ 2109 car, the engine of which is capable of producing 78 hp. strength, works easily and naturally. But the injection engine with a volume of 1596 cc deserves special attention. cm.
What is the difference between modifications 21081 and 21083
If you compare the two main modifications of Solex carburetors (21081 and 21083), used on front-wheel drive Sputniks and Samaras, then visually you will not find any differences between them. The difference exists only in the operating parameters of some of their elements.
Table: comparison of basic calibration data for Solex carburetors 21081 and 21083
| 21081 | 21083 | |||
| For 1st camera | For 2nd camera | For 1st camera | For 2nd camera | |
| Mixing chamber diameter, mm | 32 | 32 | ||
| Diffuser diameter, mm | 21 | 23 | 21 | 23 |
| Air jet of the main dosing system | 165 | 135 | 155 | 125 |
| Fuel jet of the main metering system | 95 | 97,5 | 95 | 97,5 |
| Idle air jet | 170 | 170 | ||
| Idle fuel jet | 39–44 | 39–44 | ||
| Air jet of the second chamber transition system | 120 | 120 | ||
| Fuel nozzle of the second chamber transition system | 50 | 50 | ||
| Economizer fuel jet | 40 | 40 | ||
| Accelerator pump cam number (size) | 4 | 7 | ||
| Throttle valve starting gap, mm | 1,0 | 1,1 | ||
| Air damper starting gap, mm | 2,7±0,2 | 2,5±0,2 | ||
| Needle valve hole diameter, mm | 1,8 | 1,8 | ||
| Vacuum regulator hole diameter, mm | 1,2 | 1,2 | ||
Solex design
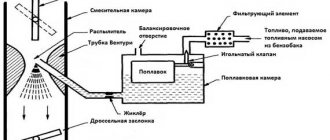
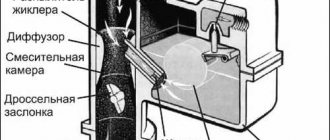
The Solex carburetor serves for precise dosage of fuel during the formation of the fuel-air mixture, as well as timely supply of this mixture to the combustion chambers of the engine. Its design provides two channels for air passage. Throttle valves are installed at the bottom of these channels. Their drive is designed in such a way that when you press the accelerator pedal, the dampers open alternately: first the first, followed by the second.
Each of the chambers at the bottom has a narrowing into a cone - a diffuser, in which a vacuum is created during engine operation. Under its influence, fuel from the float chamber is sucked into the chamber. The required level of gasoline in the float chamber is maintained thanks to a special mechanism consisting of two floats and a locking needle.
The Solex carburetor consists of two main parts: the cover and the body. The cover contains fittings for fuel hoses, a flange and studs for attaching the air filter. The housing design includes:
- float chamber;
- primary and secondary mixing chambers with diffusers;
- air and fuel channels;
- accelerator pump;
- emulsion wells;
- economizer;
- econostat;
- throttle valves and their drive mechanism.
The parts are connected to each other with five screws.
The Solex carburetor consists of two parts: the cover and the body
Basic systems, mechanisms and devices of the Solex carburetor
The Solex carburetor includes the following systems, mechanisms and devices:
- idle system;
- dosing systems of the primary and secondary chambers;
- transition systems of the primary and secondary chambers;
- float mechanism;
- econostat;
- power mode economizer;
- forced idle economizer (EFH);
- starting device;
- accelerator pump;
- throttle valve drive mechanisms.
Why are there wires on the carburetor?
The Solex carburetor is not a purely mechanical device. One of its parts has an electromechanical design. This is a solenoid valve. It serves to stop the fuel supply to the carburetor when the engine is braking, as well as turning off the ignition. This solution allows you to save from 300 ml to 1 liter of fuel per 100 km.
The valve is connected by wire to the EPHH control unit
The solenoid valve is actuated by the EPHH unit. It is connected to terminal “K” of the ignition coil, as well as to a special contact of the quantity screw, which closes to ground when the gas pedal is released. This allows it to read the crankshaft speed and send a corresponding signal to the valve.
The EPHH unit is located in the engine compartment
Both the valve and the quantity screw contact are connected to the EPHH unit using wires. There are no other electrical devices in the carburetor.
The quantity screw contact is connected to the EPHH control unit
Tuning: basic description
Tuning a carburetor engine primarily involves boring the cylinder block. This is done in order to increase the combustion chamber, and, accordingly, the pressure inside it.
Also, lightweight parts are installed, which make it possible to reduce the weight of the motor, which will increase acceleration dynamics.
Signs of carburetor malfunction
Signs of a malfunctioning Solex carburetor are:
- inability to start the power unit;
- complicated starting of a cold or hot engine;
- unstable idle;
- idle speed is too high or too low;
- increased gasoline consumption;
- reduction in engine power characteristics;
- jerks and dips when pressing the accelerator pedal sharply.
Let's take a closer look at each of the symptoms in the context of possible malfunctions.
The engine does not start at all or starts but immediately stalls
If a vehicle's engine does not start (with a known-good ignition system), it is possible that fuel is not getting into the cylinders. To check whether it enters the intake manifold, you need to remove the air filter housing and turn the throttle valve drive sector 2-3 times, observing the “spouts” of the sprayer. The fuel from them should spray out in thin but continuous streams. If this does not happen, it is worth checking the operation of the fuel pump, as well as the condition of the carburetor strainer.
It is also possible that the fuel valve needle may jam in the closed position, blocking the flow of gasoline into the float chamber. In order to return the needle to its normal position, it is enough to gently hit the carburetor body with something (for example, a key). In the future, the needle valve will need to be replaced.
If the engine starts and immediately stalls, this may be the result of a lean fuel mixture or a faulty solenoid valve. In the first case, it is necessary to check the intake pipe for leakage of foreign air, and also adjust the quality of the mixture.
To check the solenoid valve in this situation, disconnect the power wire from it, turn on the ignition and touch its contact with the tip of the wire several times. When touched, a characteristic click should be heard, indicating that the electromagnet is triggered. It would not be superfluous to unscrew the valve, inspect and clean its nozzle with a stream of air, and also check the condition of the rubber gasket.
Difficulty starting a cold engine
Typically, problems with starting a cold power unit occur due to incorrect adjustment or malfunction of the starting device. If during start-up the air damper does not completely close the channel, this leads to an excessively lean fuel mixture. At the same time, the engine “grabs” in places, but still stalls. Incomplete opening of the damper, on the contrary, leads to over-enrichment of the combustible mixture, which increases gasoline consumption and may also cause detonation.
This problem is eliminated by adjusting the starting device.
Difficulty starting a warm engine
The main reason for the difficulty of starting the engine “hot” is also the over-enrichment of the mixture. It can be caused by incorrect adjustment of the starting device, as well as an excessively high level of gasoline in the float chamber. In the latter case, fuel is overfilled, which, again, leads to an increase in its consumption.
“Overfilling” is a fairly common phenomenon for Solex. If, looking at the gasket between the carburetor and the cover, you find that it is wet, and there is a persistent smell of gasoline in the engine compartment, there is an “overflow”. It may occur due to:
- incorrect setting of the float mechanism;
- problems with the fuel valve needle (needle sticking in the open position);
- float damage;
- the float hitting the chamber wall.
To eliminate this problem, it is necessary to disassemble the carburetor, check the valve and adjust the float mechanism.
Unstable idle
Normal idle speed of the power unit is one of the main criteria for assessing the performance of the carburetor. Its violation may be caused by:
- contamination of jets and XX channels;
- breakdown of the solenoid valve;
- malfunction of the EPHH control unit;
- damage to the rubber seal (ring) of the fuel quality screw.
Clogged nozzles can be eliminated by washing and purging them. The faulty valve, EPHH block and seal must be replaced.
Idle speed too high or too low
Engine speeds that are too high or too low when idling may result from:
- contamination of the air or fuel nozzle channels;
- suction of excess air;
- improper adjustment of idle speed (quality-quantity);
- too high or low level of gasoline in the float chamber;
- incomplete opening or closing of the air damper.
This malfunction can be eliminated by adjusting the carburetor after cleaning and flushing it.
Increased fuel consumption
The following carburetor malfunctions can lead to excessive fuel consumption:
- malfunction of the storage economizer system;
- incorrect adjustment of the composition of the combustible mixture;
- clogging of air jet channels;
- incomplete opening of the air damper;
- The fuel level in the float chamber is too high.
The problem of increased fuel consumption is solved by diagnosing and adjusting the carburetor.
Reduced engine power
A decrease in the power performance of the power unit is caused by a lean fuel mixture. At the same time, the car takes a long time to accelerate, and when you sharply press the accelerator pedal, the engine “chokes” and short-term dips appear.
The reasons for this phenomenon may be:
- incorrect adjustment of the mixture composition;
- air leak;
- low level of fuel mixture in the float chamber.
Dips, jerks
The occurrence of jerks and dips under engine load occurs due to:
- clogged strainer on the carburetor inlet fitting;
- clogging of the fuel nozzle;
- air leak;
- low fuel level in the float chamber;
- accelerator pump malfunction.
Do-it-yourself installation algorithm
VAZ 21093 carburetor tuning
Here's what to do:
- Take two Solex carburetors;
- Bring them into proper condition and equip them with a repair kit;
- Purchase two manifolds from the Oka car, which will serve as the basis for the intake tract (you also need to make an adapter manifold yourself).
Note. You can install two carburetors on the “nine” without installing an adapter, but then you will have to cut a lot, connect, etc.
- Next, you need to synchronize the operation of the carburetors by opening the dampers on both of them.
Advice. It is advisable to use rods from Ozone as a drive for the dampers, but not cables from Tavria, which stretch.
- After installing the carburetors, we connect the fuel hoses and two return lines through tees;
- Be sure to plug the fitting on one of the collectors;
- We start the car (half a turn) and check everything.
The best tuning of the Solex carburetor for VAZ 21093
Pros and cons of a double carburetor on the “nine”
| Instant effect | High price for both carburetors and associated components |
| Increased acceleration from standstill to 100 km/h | Risk of engine damage (applies mainly to older VAZ 2109 models) |
| Stable operation at high and low speeds | |
| Increasing the maximum speed to 160 km/h (read more about increasing the maximum speed in the article on our website) |
Tuning carburetors on a VAZ 2109 is a responsible but entertaining process. Before carrying out it, it is recommended to study useful photos - materials, diagrams and drawings, watch a video review, and leaf through the instructions. As a result, we carry out modernization with our own hands, which will definitely come in handy.
How to reduce fuel consumption on a Solex
If you notice that the engine begins to consume more fuel than it should, do not be lazy to check it. The rated fuel consumption for any vehicle can be found in its operating manual. It should be borne in mind that the amount of fuel consumed can be influenced by many factors, from the quality of the gasoline itself to the tire pressure, so before checking, take the trouble to diagnose the ignition system and also adjust the valves.
Flow check
Required tools:
- clean empty plastic bottle (2 l);
- a piece of gas-resistant hose (50–80 cm) with a clamp of the appropriate diameter;
- gasoline (1–2 l);
- marker;
- crosshead screwdriver.
Check procedure:
- We are looking for a flat section of the road (3 km) with good surface and low traffic intensity.
- Warm up the engine to operating temperature and turn it off.
- Using a screwdriver, loosen the clamp screw on the suction fitting of the fuel pump.
- We put one end of the prepared piece of hose onto the fitting. We fix the connection with a clamp.
- We pour a certain amount of gasoline into the bottle, measuring it out into 50 or 100 ml portions and making the appropriate marks on the bottle with a marker. We will use them to determine consumption.
- We lower the other end of the hose from the gas pump into the bottle.
- We start the engine and move along the road section at a speed of 60–70 km/h in fourth gear.
- After driving 3 km, we stop, look at the bottle, estimate the consumption and compare it with the passport data.