Functionally, any car can be considered as a set of passenger and cargo compartments, as well as all the mechanisms and structures that allow the vehicle to move, that is, the body and chassis.
Historically, the engine has been separated into an independent unit, not related to the chassis, although structurally it is also always mentioned in its composition.
What is the name of the chassis of the car?
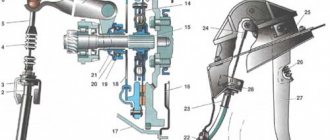
To be more precise, freedom of movement of the body is ensured in relation to the wheels moving on the road surface. Suspension - chassis
car, which can be of two types: Independent - a type of suspension in which the wheels on one axle do not have a rigid connection and change position independently of each other.
Interesting materials:
How to leave a review on YouTube? How to leave a review in bla bla car? How to leave things in the storage room at the station? How to free up space on Mac? How to whiten the insoles of sneakers? How do we relax for the New Year 2022 2020 Ukraine? How do we relax for the New Year 2019 Ukraine? How do we relax for Christmas? How do you vacation in Kazakhstan in December 2022? How to format a flash drive for ps4?
Chassis features
Chassis suspension elements reduce loads and compensate for vibrations when driving on bumpy roads and off-road. The subframe allows you to install the body, engine and other components on the chassis. The front and rear axles transmit rotational motion through the wheels and thus ensure the movement of the vehicle.
The first cars produced in the last century were somewhat different from those that drive on the roads today. All cars - both cars and trucks - used to have a frame on which all the units and components (body, transmission, engine, etc.) were installed. Over time, the frame chassis of the car remained only with trucks and buses. In passenger cars, the functions of the frame began to be performed by the body.
Notes
| Chassis on Wikimedia Commons? |
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
UsefulSee what “Chassis” is in other dictionaries:chassis - 1) car - an assembled set of transmission units, chassis and control mechanisms, i.e. a car without an engine and body. The chassis is not yet capable of moving on its own, but it can be rolled on wheels. In literature often... ... Encyclopedia of technology chassis - uncl., cf. chassis m. 1. In front of all the windows on the second and third floors... there were châssis, or sun umbrellas, made of motley or striped fabric. Academy of Three Noble Arts. // Shtelin 1 147. unit. View of the window frame. In antichambre... ...Historical Dictionary of Gallicisms of the Russian Language chassis - unchanged; Wed [French châssis] 1. The frame or base of various machines, mechanisms and devices. Sh. car. Sh. radio receiver. // The totality of all mechanisms and assemblies mounted on the frame of a car, tractor or other vehicle... Encyclopedic Dictionary CHASSIS - 1) in photography the same as a cassette. 2) in calico-printed manual production, a machine in which. paint is distributed. Dictionary of foreign words included in the Russian language. Chudinov A.N., 1910. CHASSIS see CASSETTE. Dictionary of foreign words,... ... Dictionary of foreign words of the Russian language chassis - CHASSIS, uncl., pl. Legs. The landing gear was set up. Landed on the landing gear (after a jump). General use “chassis” (uncl., cf) frame in a vehicle, etc. ... Dictionary of Russian argot CHASSIS - (French chassis) 1) a set of parts of transport, agricultural and other machines that serve to transmit force from the engine to the propulsion unit, to move the machines and control them. 2) The takeoff and landing device of an aircraft. In seaplanes... ... Big Encyclopedic Dictionary CHASSIS - CHASSIS, uncl., avg. (French chassis) (technical). 1. A frame on which a car body or an airplane body is placed. 2. A device on which fabric with a pattern painted on it is stretched, used. in calico printing production. Explanatory... ... Ushakov's Explanatory Dictionary CHASSIS - CHASSIS, uncl., avg. (specialist.). 1. The main part of a car, tractor or other vehicle is the frame on which the body, engine, and all mechanisms and parts are mounted. 2. Aircraft takeoff and landing device. Remove sh. Release sh. 3. Support... ... Ozhegov's Explanatory Dictionary chassis - tripod, legs Dictionary of Russian synonyms. chassis noun, number of synonyms: 6 • car (12) • ... Dictionary of synonyms Chassis is a ground mechanical device on wheels, not equipped with a cabin, and (or) engine, and (or) body, not intended for operation;. Source: Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated September 10, 2009 N 720 (as amended on October 6, 2011) About ... ... Official terminology |
Engine
An engine is a source of mechanical energy necessary to move a car. In an internal combustion engine, the thermal energy obtained from the combustion of fuel in its cylinders is converted into mechanical work.
Cars use internal combustion engines with spark ignition and self-ignition, as well as electric ones.
Specification
When describing the chassis for a ground vehicle, special terminology is used:
- geometric dimensions of the platform;
- wheel formula;
- wheelbase;
- front and rear wheel tracks;
- ground clearance;
- front axle load;
- load on the rear axle (or bogie);
- wheel size;
- tire size.
When describing the geometric dimensions, the length, width and height of the structure are determined by the frame, or the outer parts of the suspension. So, for example, for KAMAZ 63501 it will look like this:
- dimensions - 9930x2470x1240 mm;
- wheel formula “8x8”, which means eight wheels, four axles and all driven;
- wheelbase - 1940+3690+1320 mm;
- track - 2050 mm;
- ground clearance - 390 mm.
For a Renault Logan passenger car, this description will look slightly different:
- dimensions - 4300x1733 mm;
- wheel formula “2x4”;
- wheelbase - 2634 mm;
- track - 1480 mm;
- ground clearance - 155 mm.
Features of the chassis design for vehicles moving in the aquatic environment and in aviation
For vehicles whose main operating environment is water, a chassis similar to classic designs for land transport does not exist.
However, using the definition of one of the purposes of this design as a driving device that converts engine torque into forward motion of a vehicle, it can be assumed that the driving mechanisms of old wheeled steamers are such a chassis for water transport.
In modern conditions, transom wheels are actively used on small displacement boats. Their device is quite simple. This is a wheel with a pneumatic tire that has a rotation bearing that fits onto the swing arm. This lever is a rigid post. When locked in the lower position, these transom wheels allow the boat to move along the coastal surface. After entering the water, the wheels on the levers turn to the upper position and do not interfere with further movement through the water.
Enthusiasts are constructing small vehicles of the Sarmat type, which, thanks to especially large pneumatic wheels, stay afloat and are able to move in the aquatic environment.
Typical representatives of the “amphibious” class, that is, vehicles capable of moving both on land and on water, are mass-produced floating all-terrain vehicles and swamp vehicles. They can be wheeled, such as the floating wheeled chassis BAZ 5937 or ZIS-485 (BAV), or tracked, such as the TM-140 or MLTB.
ZIS-485(BAV)
Distinctive features of the chassis design for these machines are the presence of special floats and complete sealing of the body and machine components. In addition, they are equipped with an additional jet engine for more energetic movement through the water.
The design of the landing gear of modern aircraft is designed to ensure the movement of the aircraft around the airfield and to minimize the impact energy when the aircraft wheels touch during landing.
For these purposes, the front strut is rotatable, and the main wheels are equipped with brakes that can be released asynchronously in order to ensure effective turning.
The racks act as load-bearing structures and at the same time are shock-absorbing devices. For structural strength there is a system of levers and supports. In addition to wheels, aircraft can be equipped with skis for landing on snow and floats for landing on water.
Factors influencing changes in vehicle chassis design
Land vehicle chassis have changed since their invention and installation on carts. At first, this concerned lightening the wheel design. Cuts were made in the wooden circle to facilitate the structure. With the advent of metal spokes, they began to be installed in wheels. With the invention of bearings, they began to be installed on axles to facilitate wheel rotation and increase the service life of the wheel axle.
The body of carriages was initially suspended on belts or chains. Then they began to install sprung suspension in the form of springs on them, which began to be installed on other carts if the owner expressed such a desire. At the beginning of the 19th century, the spring was invented. They immediately began to be installed on carriages and other vehicles. During the period of undivided dominance of horse-drawn transport, many parts of the vehicle chassis were made of wood.
This trend continued during the production of the first self-propelled wheelchairs. However, with the development of road transport, the approach to ensuring driver safety while driving has changed. Wooden parts were replaced with metal ones. The smooth ride on the first car models was ensured by springs and springs. With the advent of shock absorbers, they began to be installed in car suspensions.
On modern cars, all power elements of the vehicle chassis structure are made of high-quality steel. Rubber or plastic bumpers are installed in the spring mounting elements and springs, and some suspension elements, such as ball joints, are covered with rubber boots.
Further development of chassis elements will lead to the use of new structural materials in the design, such as composite materials and nano-materials, which will be able to restore their structure. And in the suspension system the connection will undergo a change, i.e. transition from mechanical suspension linkage to magnetic and electromagnetic suspension.
WHAT IS A CHASSIS NEEDED FOR?
Thanks to the chassis and suspension elements that are part of the chassis, loads are reduced and vibrations are compensated when the vehicle moves on uneven roads and off-road. Thanks to the subframe, which is part of the chassis, engineers were able to install a body, power unit, transmission and other units on the chassis. Due to the front and rear axles, the vehicle moves through the transmission of torque to the wheels.
Once upon a time, all cars (both cars and trucks) had a frame, which cannot be said about today's cars. The body, engine, transmission, as well as chassis attachments were installed on the frame. Over time, car manufacturers realized that there was no need for a frame for passenger cars, and a modified body began to perform all the functions of the frame. And the frame became the lot of heavy SUVs (frames) and trucks.
Advantages and disadvantages of ground vehicle chassis
Modern vehicles, be it a car, a tractor or a special self-propelled device, are equipped with a chassis that is equipped with the latest design ideas.
A positive quality of the chassis of modern cars is their high reliability and service life of the units, which allows them to operate for tens of thousands of kilometers without replacement. And using the ground as a support allows vehicles based on this chassis to move huge loads over long distances with low fuel consumption and optimal speed.
The main disadvantage of ground vehicle chassis is the lack of versatility when moving from one environment to another.
Truck chassis
The most common are spar frames. They consist of two longitudinal beams connected by cross members. The shape of such beams can be completely different: tubular, X- or K-shaped. In the most loaded part, the frame has an increased channel section. The parallel spars design (beams are located at equal distances along the entire length of the chassis) is used on trucks.
In off-road passenger cars, side members can be used that have some divergence of the axes in both the horizontal and vertical planes. The spinal frame consists of one load-bearing longitudinal beam onto which cross members are attached. Often this beam has a circular cross-section, so it can accommodate transmission elements. This frame provides greater torsional resistance than side members. Also, the use of a backbone type chassis involves the use of independent suspension on all wheels. The fork-spinal frame has a branching longitudinal beam in the rear or front part. That is, it combines spars and a center beam. Other types of chassis frame are not used for trucks.
CHASSIS SYSTEMATIZATION
Thus, we can distinguish two different chassis schemes.
- Frame chassis, which in general consists of several strong beams on which all components of the car are installed. This design allows cars to carry huge loads and easily handle different dynamic loads.
- Load-bearing body. In pursuit of reducing the weight of passenger cars, all functions of the frame were reassigned to the body. This frame does not allow moving huge loads, but at the same time provides greater comfort and speed.
Depending on the purpose of the car, the following types of structures can be used:
- spar;
- spinal;
- peripheral;
- fork-spine;
- lattice.
Device
So, the chassis refers to the combination of the supporting part and some key components that allow the vehicle to move independently. All types of structures are divided into two categories.
The first category includes all cars with a frame structure. In this case, the car trolley consists of a frame to which all units, mechanisms and structures are attached. Such cars are heavy and have maximum strength. This design is mainly used in trucks and full-fledged SUVs.
The second category includes the type of chassis, which is immediately part of the car body. The supporting body is not as strong as in the case of a full frame, but it is very light, which is of great importance for passenger cars. Only with this modification of the chassis is it possible to create the lightest possible supercars.