Anti-lock braking system (ABS) is a system that prevents the wheels from completely locking during emergency braking. This solution is one of the first electronic active safety systems that began to be universally installed on cars.
Today, such a system is an integral part of almost any modern car, even in the budget segment. Also in developed countries, the mandatory presence of ABS in a car is enshrined at the legislative level.
At the same time, many drivers know that the car has this system, but do not fully understand what ABS is and how this solution works. In this article we will look at how ABS works, what it is, as well as what functions such a system performs and why it is important to monitor the serviceability of the ABS in a car.
What is ABS in a car in simple words
ABS in English means Anti-Lock Breaking System. This is a security system designed to perform 3 main tasks:
- prevents wheel locking when braking;
- provides traction when cornering when you press the brake pedal;
- reduces braking distance.
ABS is most effective when cornering in difficult road conditions (for example, heavy rain or snow). The system is designed to eliminate the need for so-called impulse braking and distribute the braking force throughout the braking system so that no wheel locks.
Therefore, it is able to maintain the degree of slip of each wheel in the range from 10 to 40% (full locking occurs at 100% degree of slip): only in this case can the driver correct the trajectory if he has to press the brake pedal in a turn. Constantly monitoring traction is also useful when braking on a straight road. Wheel locking on dry asphalt will damage the tire, and on wet asphalt it will almost double the braking distance.
A car with locked wheels slides straight when turning. ABS is designed to prevent this and maintain an optimal level of slip at each wheel (10-40%), giving the driver the opportunity to correct the trajectory.
ABS is such a popular technical innovation that almost every driver has heard of it. Not surprising: it began to be introduced before World War II, and began to be used on airplanes in the 1950s. It first appeared as standard equipment in a passenger car in 1978 on board the Mercedes W116, and 3 years later in trucks of the German brand. Then it began to be used on motorcycles and buses, and later other cars began to be equipped with ABS.
Story
This development was first presented to the public in the 1950s. However, it could not be called a concept, because this idea was developed at the beginning of the twentieth century. Thus, engineer J. Francis in 1908 demonstrated the operation of his “Regulator”, which prevented wheel slipping in rail vehicles.
A similar system was developed by mechanic and engineer G. Voisin. He was trying to create a braking system for airplanes that independently adjusted the hydraulic action on the braking elements so that the wheels of the aircraft would not slip on the runway as a result of braking. He carried out experiments with modifications of such devices in the 20s of the twentieth century.
Early systems
Of course, as in the case of all first developments of any inventions, initially the system that prevented blocking had a complex and primitive structure. Thus, the aforementioned Gabriel Voisin used a flywheel and a hydraulic valve connected to the brake line in his developments.
The system worked on this principle. The flywheel was attached to the drum on the wheel and rotated with it. When there is no skidding, the drum and flywheel rotate at the same speed. As soon as the wheel stops, the drum slows down along with it. As the flywheel continued to rotate, the hydraulic line valve opened slightly, reducing the force on the brake drum.
This system has proven to be more stable for the vehicle, since in the event of a skid, the driver instinctively presses the brakes even harder, instead of performing this procedure smoothly. This development increased braking efficiency by 30 percent. Another positive result is fewer burst and worn out tires.
However, the system received due recognition thanks to the efforts of the German engineer Karl Wessel. Its development was patented in 1928. Despite this, the installation was not used in transport due to significant shortcomings in its design.
A truly working anti-skid brake system was used in aviation in the early 50s. And in 1958, the Maxaret kit was installed on a motorcycle for the first time. The Royal Enfield Super Meteor was equipped with a working anti-lock braking system. The operation of the system was monitored by the Road Laboratory. Studies have shown that this element of the braking system will significantly reduce motorcycle accidents, most of which occur precisely due to skidding when the wheel locks during braking. Despite such indicators, the chief director of the technical department of the motorcycle company did not approve the mass production of ABS.
In cars, a mechanical system that prevents wheel slipping was used only in some models. One of them is the Ford Zodiac. The reason for this situation was the low reliability of the device. Only since the 60s. The electronic anti-lock braking system found its way into the famous Concorde aircraft.
Modern systems
The principle of electronic modification was adopted by an engineer at the Fiat research center and called the invention Antiskid. The development was sold to Bosch, after which it received the name ABS.
In 1971, automobile manufacturer Chrysler introduced a complete and effective system that was controlled by a computer. A similar development was used a year earlier by American Ford in its iconic Lincoln Continental. Gradually, other leading automakers took up the baton. By the mid-1970s, most rear-wheel drive cars had electronic anti-lock braking systems on the drive wheels, and some cars were equipped with a modification that worked on all four wheels.
Since 1976, a similar development began to be used in freight transport. In 1986, the system was called EBS, as it worked entirely on electronics.
Why do you need ABS and its diagram?
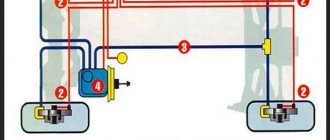
Many car owners, although they have heard about this system, have no idea how ABS works on a car. Each wheel has a sensor that transmits information to the controller about the current speed of rotation of the wheel. A modern ABS system consists of the following components:
- pressure modulator with electronic controller and pressure-regulating valves (previously modulators and controllers were separate components);
- wheel speed sensors (one for each wheel).
Sensors mounted on the wheel hubs constantly monitor the slippage of each wheel and immediately inform the ABS control unit if there is a tendency to lock up. Using a modulator, it distributes pressure from the master cylinder in such a way as to maintain the movement of the wheel. This element reduces the pressure as wheel slip increases and increases it again when traction is restored. The driver perceives the operation of ABS by the characteristic vibration of the brake pedal. Do not under any circumstances release the pressure at this point; on the contrary, it should be increased in order to utilize the potential of the ABS.
How effective are anti-lock brakes?
It doesn't take a genius to figure out that if the aviation industry and car manufacturers have adopted ABS, it's probably a good thing. The fact that it is a required feature on all new cars sold indicates that the government and other regulators have confidence in the system.
Here are four benefits of ABS:
- Vehicles equipped with ABS are less likely to be involved in a fatal accident.
- ABS reduces the likelihood of frontal collisions on wet and dry roads
- Cars with ABS rarely leave the road.
- In an emergency situation, a car with ABS tends to provide more steering control than a car without ABS.
Why does the ABS light come on?
There are several reasons why the ABS light came on:
- damage to wires;
- dirt getting into the ABS sensors, turning them off or breaking;
- defect of the ring gear located on the wheel hub.
Sometimes the reason lies in the fact that the electrical unit in the car, designed for convenient control of the system, does not function properly.
Braking performance
The ABS system not only shortens braking distances, but also provides maximum control over the vehicle. Compared to a car not equipped with this system, a vehicle with ABS will definitely brake more effectively. There is no need to prove this. In addition to the shorter braking distance, the tires in such a car will wear out more evenly, since the braking forces are distributed evenly to all wheels.
This system will be especially appreciated by drivers who often drive on roads with unstable surfaces, for example, when the asphalt is wet or slippery. Although no system can completely eliminate all driver errors and protect against emergency situations (the driver’s attentiveness and foresight has not been canceled), ABS brakes make the vehicle more predictable and controllable.
Given the high braking performance, many experts recommend that beginners get used to driving vehicles with an ABS system, which will increase safety on the road. Of course, if the driver violates overtaking rules and speed limits, the ABS system will not be able to prevent the consequences of such violations. For example, no matter how effective the system is, it is useless if the driver has not changed his car for the winter and continues to drive on summer tires.
How ABS works on a car
It is not difficult to understand the principle of operation of ABS on a car. Fluid plays an important role in the braking system. It is with its help that the force is transmitted to the brake pads. The harder you press the brake pedal, the more pressure the fluid puts on the pads, increasing braking force. To prevent wheel locking, ABS regulates brake fluid pressure. If during braking the controller receives a signal from at least one of the wheels that its speed has decreased, then ABS reduces the pressure in the brake system for this wheel. When the wheels begin to rotate at the appropriate speed, ABS increases braking force, allowing you to maintain 10-30 percent slip.
The main function of ABS is to maintain an adequate degree of braking impulse when one wheel loses traction. This allows the car to maintain a sufficient level of controllability. During braking, ABS controls wheel rotation. If the brake is applied hard enough to cause one wheel to spin slower than the others, the pressure in that wheel's system is reduced until it starts spinning again.
The speed of rotation of all wheels is measured by the ABS system, which does not intervene in the brake system until it receives a signal that the driver has applied the brakes. When you apply the brakes, the ABS system detects slippage and uses solenoid valves to modulate the pressure in the circuit of a specific wheel or wheels.
ABS has a fairly strong effect on stopping distance, although not always. Tests show that cars with ABS can stop several tens of meters faster than cars without it. This result can be achieved by following certain operating principles.
First, when braking in difficult conditions, apply as much force as possible to the brake pedal and hold it until the car stops. Pulse braking is not recommended - it disrupts the smooth operation of the entire system and increases the braking distance. Secondly, if you approach an obstacle while braking, drive through it with the brakes on. This increases vehicle control and prevents wheel locking.
Generations of anti-lock braking system
ABS warning light
It took 14 years of effort by a huge number of engineers to create the ABS system. ABS has been produced since 1978, its creator is Bosch.
The first generation of the system (1970) was called ABS-1. This electromechanical product was not reliable and durable due to the thousands of analog components that were used in the ECU. Although the main function of ABS was fulfilled, the product was not suitable for mass production.
Second generation (1978). ABS-2 from Bosch first began to be installed as an option in Mercedes-Benz S-Class cars, and after some time in BMW 7 Series limousines. The number of components was reduced to 140, and the weight of the hydraulic unit was 6.3 kg.
In subsequent generations of ABS, Bosch engineers relied on improving the system and reducing its size. So, in 1980, ABS-2E was released, in which the mass of the hydraulic unit was already 4.9 kg, and the number of components was reduced to 40. In 1995, ABS 5.3 appeared with a mass of the hydraulic unit of 2.6 kg and 25 components. In 2003, ABS 8 was released, in which there were 16 components, and the weight of the hydraulic unit was reduced to 1.6 kg. Since 2010, Bosch has been releasing the 9th generation of the ABS system, which is distinguished by its compact dimensions and hydraulic unit weighing only 1.1 kg.
How to check ABS on a car
There are various instructions for checking the ABS sensor. The first sign that something is wrong with your car is a flashing ABS warning light. Depending on the vehicle model, the indicator may be orange or red. If we start the car, it should light up for a moment and then go out after starting the engine. This means everything is fine. It's worse when the light bulb stops burning or doesn't go out. The absence of a light signal may have a trivial reason, which is a burnt out light bulb.
But we never know, maybe the problem is more complex, the brake system has failed. The vehicle's control system may be damaged. One sign of a problem will be the indicator light turning on and off. Typically, a brake system failure does not mean that the car will not brake at all. This only means that during heavy braking the system will not help the driver.
We can feel this when braking hard on a slippery surface, it is important not to panic at this moment. This seems like a dangerous situation because we are used to our smart car helping itself and not locking the wheel. Most failures and malfunctions are related to one of the sensors. Repairing a car's ABS and replacing this system is not difficult, does not take much time, and is inexpensive. On some (older) models we can check the brake system ourselves.
Under the console there is a drawer containing the system. There are four cables coming out of the box, two of which come from the front wheels and two from the rear. On the wires with the engine running, you need to check the resistance using an ohmmeter. In a properly functioning cable it should be 1000 ohms. If the indicator is different, it is better to sign up for the service. The method works for almost all models, and if you do not have the appropriate equipment, you should immediately go to a service station.
Connecting to the computer takes some time, but thanks to this we will find out whether the sensor or one of the cables is faulty. This is worth taking care of, especially in winter, when a well-functioning brake booster system is especially important. Lack of ride assistance also causes winter tires to wear out faster.
What types of malfunctions are there?
As for the reliability of the anti-lock braking system, it is one of the most reliable car systems. Its elements rarely fail, and most often this is due to violation of the rules of operation and maintenance. All electronic parts are reliably protected from overloads by fuses and relays, so the control unit will not fail.
The most common system malfunction is the failure of wheel sensors, since they are located in places where it is extremely difficult to prevent water, dust or dirt from getting on them. If the hub bearing has too much play, the sensors will malfunction.
Other problems are more related to related vehicle systems. An example of this is a decrease in voltage in the electrical network of a machine. In this case, the ABS will turn off due to the triggered relay. The same problem can occur during power surges in the network.
If the anti-lock braking system turns off on its own, there is no need to panic - the car will simply behave as if it did not have ABS.
Repair and maintenance of the brake system of a car with ABS has its own characteristics. For example, before changing the brake fluid, you need to press the brake several times with the ignition off and release it (about 20 times). This will relieve pressure in the valve body accumulator. Read about how to properly replace the brake fluid and then bleed the system in a separate article .
The driver will immediately know about an ABS malfunction by the corresponding signal on the dashboard. If the warning light comes on and then goes out, you should pay attention to the contact of the wheel sensors. Most likely, due to loss of contact, the control unit does not receive a signal from these elements and signals a malfunction.
How often to diagnose a car's ABS
As you can imagine, it is very important that each sensor works correctly and transmits data to the main unit of the ABS system. In order for the system to work correctly, it is necessary to constantly carry out ABS diagnostics, in which the sensors are first checked.
Problems with the sensor are very different, the most common are: an incorrectly transmitted pulse or interruption of the signal from the sensor to the device. After this, the system stops performing the specified functions, so when you press the brake pedal, the wheels are blocked. If the indicator on the panel lights up, contact your service center immediately.
EBD (Electronic Brake Force Distribution) - brake force distribution system.
In most modern cars, ABS works in conjunction with EBD (Electronic Brake Force Distribution) - a brake force distribution system. Brake force distribution is a software extension of the anti-lock brake system. In other words, the system uses the structural elements of the ABS system in a new way. The EBD system allows you to effectively brake in different road conditions, taking into account sections of the road with heterogeneous surfaces, vehicle load and the technical condition of the tires. EBD distributes braking forces to each wheel individually to ensure optimal traction. The fundamental difference between EBD and other systems from basic ABS is that they help the driver control the car all the time, and not just during emergency braking. The principle of operation of the brake force distribution system The operation of the EBD system, like the ABS system, is cyclical. The work cycle includes three phases:
- pressure retention;
- pressure release;
- increase in pressure.
Using data from wheel speed sensors, the ABS control unit compares the braking forces of the front and rear wheels. When the difference between them exceeds a specified value, the brake force distribution system algorithm is activated. Based on the difference in sensor signals, the control unit determines the start of blocking of the rear wheels. It closes the intake valves in the brake cylinder circuits of the rear wheels. The pressure in the rear wheel circuit is maintained at the current level. The front wheel inlet valves remain open. The pressure in the front wheel brake cylinder circuits continues to increase until the front wheels begin to lock. If the rear axle wheels continue to lock, the corresponding exhaust valves open and the pressure in the rear wheel brake cylinder circuits decreases. When the angular speed of the rear wheels exceeds the specified value, the pressure in the circuits increases. The rear wheels are braking. The operation of the brake force distribution system ends when the front (drive) wheels begin to block. At the same time, the ABS system is activated.
EBD will also help distribute the braking force in the event of sudden braking in a turn, preventing the car from skidding and drifting, and losing its trajectory. When turning, the outer wheels are more heavily loaded relative to the turn, and the load on the inner wheels is reduced, thereby putting the car at risk of skidding or losing its trajectory and spinning out of the turn. In this case, EBD will reduce the braking force on the outer wheels, thereby preventing them from locking. The car becomes controllable, and the level of traffic safety increases significantly. With the EBD system you can safely brake in turns and on mixed surfaces. Based on the difference in rotation speeds, the electronics will “understand” that the wheels have reached areas with heterogeneous surfaces and will reduce the braking forces on the wheels that have better traction. By the way, the intensity of deceleration in this case will decrease and will be determined by the friction force of the wheel (wheels) that has the worst grip. Also, the EBD system takes into account the vehicle load when braking.
The braking force between the front and rear wheels is optimized, resulting in the fastest braking possible. For example, when braking a vehicle with more than one person inside, EBD increases braking force to the rear wheels compared to when only the driver is inside, while improving braking performance compared to a vehicle without EBD.
Thus, the operation of EBD helps to reduce the braking distance and the ability to control the car in emergency situations.
Is it possible to disable ABS on a car?
It is worth knowing that the location of the fuse box may vary. Sometimes they can be found under the hood, in other cases they end up in the cabin. Sometimes different fuses are present in the same car in different places. In this case, it is worth disconnecting through the component located in the cabin.
In addition, please note that disabling ABS may negatively affect individual components of the machine. In any case, disabling this system should be considered a temporary measure. The most accessible way to disable ABS is to pull out the corresponding fuse from the block.
Advantages and disadvantages of the system
There is no need to talk much about the advantages of the anti-lock braking system, since its main advantage is in stabilizing the car in the event of wheel slippage during braking. Here are the advantages of a car with such a system:
- During rain or on ice (slippery asphalt), the car shows greater stability and controllability;
- When performing a maneuver, you can actively use the brakes for better steering response;
- On a smooth surface, the braking distance is shorter than that of a car without ABS.
One of the disadvantages of the system is that it does not cope well with soft road surfaces. In this case, the braking distance will be shorter if the wheels are locked. Although the latest modifications of ABS already take into account the characteristics of the soil (the appropriate mode is selected on the transmission selector) and adapt to the given road situation.
In addition, the operating principle of ABS and its advantages are described in the following video:
Working principle of ABS
Is ABS useful?
First of all, ABS is lightning fast. Thanks to vigilant sensors, it constantly monitors the rotation speed of all wheels and immediately reacts to increased skidding. This allows you to safely navigate difficult turns, and on a straight road (also dry, with varying degrees of grip) it significantly reduces the braking distance. Some experts have calculated that a car without ABS will brake 45 m further on wet pavement than a car with ABS! In the absence of precipitation, the differences are within a few meters.
In some situations, ABS increases braking distance, for example, when there is a loose layer (snow, sand, leaves) on a surface with good grip. On a car without ABS, the locked wheels break through the loose layer and an increase in braking force occurs; if the system is working, the car remains on the layer with less grip longer.
Will ABS reduce braking distance during an emergency stop?
A common misconception is that ABS helps reduce braking distances. That's not what it's designed for. Instead, it reduces the likelihood of skidding even when performing excessive evasive maneuvers.
“ABS should maintain steering control, but it should not be assumed that a vehicle with ABS will stop in a shorter distance.”
If anything, intermittently applying and easing the brakes could actually increase stopping distance. Therefore, it is very important to keep your distance from cars in front and obey speed limits.