01/19/2022 17,684 Ignition system
Author: Ivan Baranov
As you know, the purpose of spark plugs (SZ) is to ensure the transmission of a spark to ignite the air-fuel mixture. A lot depends on the quality of the SZ, in particular, the stable operation of the engine, as well as the start of the power unit. In this article we will tell you what Russian-made A17DVRM spark plugs are and whether they are as high quality as the manufacturer claims.
[Hide]
Design features of spark plugs
A seemingly simple detail has many nuances. Let's list the main ones:
- The heat value characterizes the rate of heat transfer from the electrodes to the spark plug skirt. During operation, the spark plug must be heated to such a temperature that the carbon deposits on it oxidize without having time to build up, but overheating is also dangerous for it: glow ignition may occur, and the electrodes themselves will begin to rapidly deteriorate. The problem is that the heat load on the spark plug itself is uneven - when driving at low speeds, the heating is much less than when driving with the pedal to the floor. Candles with a standard heat rating in both of these cases will operate at the extreme point of the optimal mode - under- and overheat, respectively.
- The spark gap depends primarily on the power of the standard ignition system and the maximum pressure in the cylinder at the end of the compression stroke: it must be such as to ensure reliable spark breakdown even at low voltage in the network (cranking with a starter on a dead battery). And the difference in this case is obvious: usually the transformation coefficient of the ignition coils is about 2000, that is, when the generator is running, they can produce up to 28 kilovolts, but when starting up - only 14! Consequently, the purchased set of spark plugs must have exactly the same gap as set by the car manufacturer: an increased one means the risk of misfire (but within the capabilities of the coil it will provide a more powerful spark that ignites the mixture better), a reduced one guarantees the possibility of starting with a dead battery, but is fraught with interruptions already from - to reduce spark energy.
- The sticking out of the electrodes also means a lot for the performance of the spark plug in a particular engine. For example, on eight-valve engines, where the spark plug is located on the side of the combustion chamber, increasing the offset optimizes the ignition of the mixture: the area adjacent to the walls of the combustion chamber is less ventilated, while moving the electrodes further ensures that there will be a high-quality, easily ignitable mixture in the spark gap. For VAZ eight-valve engines, where the ventilation of the combustion chamber is structurally deteriorated (the intake and exhaust channels are located in the same direction, and not opposite each other), this is quite sensitive. Spark plugs with electrodes recessed inside are used, as a rule, on multi-valve engines with a minimum volume of the combustion chamber, otherwise they may collide with the valves or piston.
- The number of electrodes in real operation is fundamentally small. Multi-electrode spark plugs theoretically have an increased service life - when erosion destroys one of the side electrodes, a spark begins to strike the other (unlike a common misconception, a spark does not occur simultaneously between several electrodes). In practice, the spark usually “floats” (which is why it seems that there are several of them) - under conditions of poor distribution of the mixture throughout the cylinder, the spark can move from the working area to the “shaded” area, that is, contaminated with residual exhaust gases. As a result, instead of improving the service life, we will get a deterioration in engine performance, which, again, is fundamental for the VAZ eight-valve engine, which already idles disgustingly with the lean mixture prescribed by current economic standards.
Video: Testing spark plugs on a bench.
Something else useful for you:
- Selection of NGK spark plugs: decoding and marking
- What is the heat number of spark plugs: heat number from different manufacturers
- Replacing spark plugs - frequency and replacement procedure
Rear
For clarity, we recommend watching a video about replacing the rear brake pads on a VAZ 2110. This will make it easier to complete the task and have a visual representation of each stage of repairing the brake system.
It will be good if you once installed disc elements on your rear brakes. The beauty of them is that the process of replacing the rear pads will be similar to the front ones.
In some cases, depending on the design of the rear brakes, it may be necessary to completely remove the rotor and caliper. All other activities are carried out in exactly the same way as in the case of the front pads.
The situation is completely different for those who use factory drum braking systems. The work will have to be done delicately, but completely achievable on your own.
To get started, arm yourself with a set of tools, which includes:
- Balloon wrench;
- Jack;
- Pliers;
- Screwdriver;
- Hammer;
- Sharp chisel;
- Open-end, socket and ring wrench sizes 12, 13 and 17 - 3 sizes of each type of wrench.
Now we proceed directly to replacing the rear brake pads.
- Place chocks under the front wheels and remove the rear wheel.
- Unscrew the guides using a 12mm wrench.
- Guides are required for fixing to the axle shafts of the drums.
- It may be quite difficult to remove the drum from its place. This is where you will need a hammer and a wooden stand. Tap the inside of the drum. It is strongly not recommended to hit the drum directly with a metal hammer, as the mechanism may be damaged.
- If the drum cannot be removed even after hammering, treat the contact areas with the hub with WD40 or other penetrating lubricants.
- Then, arm yourself with pliers and remove the springs from the bottom and top of the pads.
- Remove the guide spring located in front.
- This will allow you to completely remove the block.
- When the bar is removed, you can begin to remove the spring from the rear pad.
- Well, now remove both parts of the block. When removing the back one, remember the hook. It comes from the handbrake cable.
- After removing the old block, put a new one in its place. Assembly is carried out in reverse order.
- But there is one caveat - the bushing must be removed from the drive arm, which will greatly facilitate the reassembly process. The upper part of the pads is inserted into the grooves located on the cylinder rod.
- Be prepared for the fact that certain difficulties may arise when installing a new element. The reason is the large output that remains as a result of the operation of old brake elements.
- Take two pry bars and squeeze the two blocks together to bring them as close as possible. At this point the replacement can be considered completed.
- At the last stage, mandatory bleeding of the brake system is carried out. Without it, not a single intervention in the design of car brakes can be done.
As you can see, replacing the pads is not difficult if you act consistently. The best option is to install disc brakes everywhere. They are easier to work with, they are more efficient in their tasks, plus replacement is carried out without any problems, unlike drums.
NGK Iridium Spark Plugs
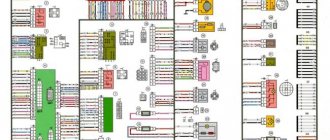
UAZ contact ignition system, composition and general structure, diagrams of the contact ignition system.
procedure for installing the ignition on a UAZ car; wiring diagram for electronic ignition on a UAZ. Iridium ngk spark plugs are considered the best solution, as they have excellent quality. Iridium is a noble metal and the hardest. This metal melts at a temperature of 2450 degrees. If you compare an iridium spark plug with a regular spark plug, it will last you twice as long.
NGK iridium spark plugs have a platinum plate on the middle electrode. It provides high spark plug power even in difficult conditions. These spark plugs have a thin middle electrode and less voltage is required during ignition.
Innovative technologies have developed such a system that electrical charges occur in the annular gap between the middle electrode and the insulator. Thanks to this, soot particles that collect in this area are removed. The self-cleaning effect of such candles extends their lifespan.
Characteristics
Let's start with the main characteristics. The length of the thread of the AU17DVRM spark plug is 1.9 cm; a 16 mm hexagon is used to unscrew and screw the devices into the engine. One of the main characteristics is the gap, which in this case is 1 mm. If we talk about stability, then these SZ cannot boast of it, especially if we compare this brand with the Bosch and NGK brands. If you believe the manufacturer, then SZ AU17DVRM are produced using modern technologies and innovations, which makes it possible to achieve a high quality product.
Non-traditional schemes
Gas-53 diagram - car diagrams. gas ignition circuit 53
Some of the design solutions in spark plugs of an unconventional design can be called conditionally working - by improving one thing, they worsen another. The simplest example is the NGK V-Line series of spark plugs: their central electrode has a groove, so the spark always jumps between the edge of the electrode and the side one. In theory, this improves ignition of the mixture by moving the spark into a better ventilated space and stabilizing the spark point, but the erosion of such a central electrode is accelerated.
Some of the candles on the market cannot be classified as anything other than “Herbalife” from the car market: all sorts of “pre-chamber”, “torch” and so on candles, at best, work no better than standard ones, at worst, they quickly deteriorate. For example, in the notorious “Bugaets” candles, the soldered skirt not only worsened the ventilation of the spark gap, but also burned out, and sometimes went into “free flight” into the combustion chamber. Of the designs that are workable, but useless in the practice of an ordinary motorist, we note only spark plugs that do not have a side electrode at all - they were originally created to work in ultra-high boost engines in order to avoid overheating of the protruding side electrodes; in a normal city cycle on a “civilian” boost level motor, they They clean themselves disgustingly and guarantee rough idling even on ideal quality gasoline.
Noble metals: practical meaning of application
Wiring diagram of the ignition switch VAZ 2108. ignition switch block VAZ 2109
As we already said in the last paragraph, the transition to a multi-electrode circuit did not bring much practical benefit in increasing the service life of spark plugs. In fact, the fight against the very cause of natural wear of spark plugs, that is, erosion of contacts, was replaced with a palliative - the substitution of “spare” ones. To increase the immediate reliability of the electrodes, the design of the spark plugs was significantly redesigned.
In “platinum” and “iridium” spark plugs, the main feature that catches the eye is a very thin central electrode, which precisely localizes the point of origin of the spark - opposite it, a plaque of the corresponding metal is soldered on the side electrode, and the central electrode is also covered with it.
The advantages of such candles are obvious: the electrodes have a service life that, under normal conditions, is two to three times longer than that of conventional candles. The thin central electrode is perfectly self-cleaning, which also contributes to reliable operation.
The disadvantages, alas, are also significant. The first is the price: a set with the Platinum or Iridium inscription will cost at least two to three times more than regular candles. The second, oddly enough, is tenderness: non-fading carbon deposits instantly kill such candles, and mechanical cleaning is contraindicated for them, just like the old-fashioned burning with a torch. First of all, we are, of course, talking about the notorious ferrocene, which is still not uncommon to encounter.
Gap adjustment
The candles themselves must be carefully cleaned with a rag and make sure that they do not have mechanical damage in the form of cracks, chips or swelling on the porcelain insulator.
During manipulations, care should be taken not to damage anything. The adjustment itself is made by bending or bending the side electrode. You can bend it by lightly tapping it with something hard, for example, with pliers. You can bend the side electrode either with pliers or a flat-head screwdriver.
Interchangeability of spark plugs - table.
26.09.2015
The spark plug is a small, but very important part of any car, because thanks to it, ultimately, an electrical discharge is created, which guarantees a confident start of a cold engine, good throttle response, stable idling, no cylinder misfires, etc.
This is why it is so important to regularly (at every oil change) monitor the condition of the spark plugs and replace them on time. Moreover, it is better to do this replacement according to the manufacturer’s recommendations - with an original part, but, unfortunately, this is not always possible, fortunately there is such a thing as the interchangeability of spark plugs
What can you change for what?! Let's look at the most common types of spark plugs in our country and their analogues.
Spark plug interchangeability table.
Note. * non-standard designation of a spark plug with two “ground” electrodes. n.d. - no data. The completeness and spark gaps of analogue spark plugs may differ.
Now let's look at the table in more detail.
A17DV.
Country of origin: Russia.
On which cars it is used: VAZ 2101-2107 and their modifications until 1988.
Analogues:
- BOSCH (Germany) – W7D;
- NIPPON (Japan) – DENCO W20EP-U;
- NGK (Japan) – BP6ES;
- AC DELCO (USA) – 42XLS;
- BRISK (Czech Republic) – L15YC;
- BERU (Germany) – 14-7DU;
- CHAMPION (USA) – N9Y;
- EYQUEN (France, Italy) – 750LS.
A17DVM.
Country of origin: Russia.
On which cars it is used: VAZ 2101-2107 and their modifications until 1988.
Analogues:
- BOSCH (Germany) – W7DC;
- NIPPON (Japan) – W20EP-U;
- AC DELCO (USA) - C42XLC;
- BRISK (Czech Republic) – L15YC;
- CHAMPION (USA) – N9YC;
- NGK (Japan) – BP6ES;
- BERU (Germany) – 14-7DU;
- EYQUEM (France, Italy) – C62LS.
A17DVRM.
Country of origin: Russia.
On which cars it is used: VAZ 2104-2111 and all their modifications.
Analogues:
- BERU (Germany) – 14R-7DU;
- BOSCH (Germany) – WR7DC;
- NIPPON (Japan) – W20EPR;
- AC DELCO (USA) – CR42XLC;
- BRISK (Czech Republic) – LR15YC;
- NGK (Japan) – BPR6ES;
- CHAMPION (USA) – RN9YC.
A10.
Country of origin: Russia.
On what vehicles is it used: ZIL-157KD and its modifications.
Analogues:
- BOSCH (Germany) – W9AC;
- AC DELCO (USA) – 46F;
- BRISK (Czech Republic) – N19;
- NGK (Japan) – B4H;
- BERU (Germany) – 14-10A;
- AUTO LITE (USA) – 416;
- CHAMPION (USA) – L90.
A20D.
Country of origin: Russia.
On what vehicles is it used: AZLK, IZH.
Analogues:
- BOSCH (Germany) – W6CC;
- MARELLI (Italy) – 7LPR;
- BRISK (Czech Republic) – L14;
- NGK (Japan) – B7ES;
- BERU (Germany) – 14-6CU;
- AUTO LITE (USA) – 4054;
- CHAMPION (USA) – N3C.
A14B and A14B-2.
Country of origin: Russia.
On which vehicles is it used:
- GAZ-24;
- buses: RAF, ErAZ;
- motorcycles: “Dnepr” and “Ural”.
Analogues:
- BOSCH (Germany) – W8BC;
- AC DELCO (USA) – 43FS;
- BRISK (Czech Republic) – N17YC;
- NGK (Japan) – BP5HS;
- BERU (Germany) – 14-8B;
- CHAMPION (USA) – L92YC;
- AUTO LITE (USA) – 275;
- MARELLI (Italy) – F7NC;
- NIPPON (Japan) – W14FP;
- EYQUEN (France, Italy) – 550S.
A14D.
Country of origin: Russia.
On what cars is it used: GAZ-3102.
Analogues:
- BOSCH (Germany) - W8CC;
- BRISK (Czech Republic) – L17C;
- NGK (Japan) – B5ES;
- BERU (Germany) – 14-8C;
- CHAMPION (USA) – N5C;
- AC DELCO (USA) – 43XL;
- MARELLI (Italy) – CW6L;
- NIPPON (Japan) – W17ES;
- AUTO LITE (USA) – 394;
- EYQUEN (France, Italy) – 600L.
A11 and A11-3.
Country of origin: Russia.
On which cars it is used: GAZ, ZIL, UAZ.
Analogues:
- BOSCH (Germany) – W9AC;
- BRISK (Czech Republic) – N19;
- NGK (Japan) – B4H;
- BERU (Germany) – 14-10A;
- CHAMPION (USA) – L86C;
- AUTO LITE (USA) – 416;
- MARELLI (Italy) – CW4N;
- AC DELCO (USA) – 45F, 420Z;
- EYQUEN (France, Italy) – 406.
A14DV.
Country of origin: Russia.
On what cars is it used: GAZ-14, GAZ-3102 and its modifications.
Analogues:
- BOSCH (Germany) – W8DC;
- AC DELCO (USA) – 43XLS;
- BRISK (Czech Republic) – L17C;
- NGK (Japan) – BP5ES;
- BERU (Germany) – 14-8DU;
- CHAMPION (USA) – N11YC;
- MARELLI (Italy) – CW6LP;
- AUTO LITE (USA) – 55;
- EYQUEN (France, Italy) – 600LS.
Applicability of spark plug NGK BPR6ES-11
Suitable for cars and engines
NGK BPR6ES-11 on Mitsubishi
Installed on Mitsubishi cars
Colt CJ1A 1.3i 4G13 after 6.2000 Colt C12A 1.5 G15B with catalyst 8.1984- C52A 1.5i 4G15 83 hp Lancer C61A) 1.3 12V (4G13) to 4.1991 (C12A) 1.5 (G15B) with catalyst 8.1984- Lancer 4WD C77A 1.8i 4G37 Sigma (F16A) Sigma Wagon (F07W) 3.0i SOHC 12V (6G72) Galant E15A 2.0 4G6 3) with catalyst E33A Eclipse D21A 1.8i 4G37 (D32A) 2.0i Turbo 4G63T L200 4WD K33T 2.6 G54B L300 (P04V/W, P14V, P24V/W) 2.4i 4G64 Pajero (L042G) 2.6 +kat (L047G) 2.6 4G 54 with Space Wagon N34W catalyst 2.4i 4G64 produced before May 1992 right-hand drive Mitsubishi Eterna Sava (E32A) 1.8 4G37 Lancer Mirage Wagon 4WD C37W 1.8i 4G37
The main criteria by which selection is carried out
Products from various brands
Modern motors are manufactured with certain design features that provide them with certain technical characteristics. For normal operation of the power unit, it is necessary to install an SZ, with certain parameters corresponding to the type of car engine
When choosing an analogue of SZ, you should pay attention to their main parameters:
- Screw-in dimensions:
- length of the threaded part;
- thread pitch;
- thread diameter;
- turnkey hexagon dimensions.
We recommend: Motor oil ZIC X7 LS 10w-40
Products with overall and connecting dimensions that do not correspond to the engine type cannot be mounted on the power unit. The use of devices with a threaded part that is too long or short, in most cases ends in a major overhaul of the car engine.
- The thermal part of the analogue should be as close as possible to the characteristics of the original. We are talking about the heat number, which reflects the ability of candle products to heat up at different thermal loads of the engine. Please note, when selecting SZ for compatibility, that domestic products are marked indicating the heat number, while foreign ones are divided into cold (having a large heat number) and hot (having a small heat number).
- The distance between the spark plug contacts must correspond to the size specified in the machine manual. An increased spark plug gap will lead to a decrease in spark power, and a reduced gap will lead to breakdowns in the ignition system.
- Number of spark plug electrodes. Many motorists are of the opinion: the more spark plug contacts, the stronger the sparking. This is an erroneous statement; the spark occurs between two contacts. In multi-contact devices, the operating principle is as follows: if one electrode burns, sparking will occur on the second. Such modernization of the SZ design makes it possible to increase their operational period, but does not affect the spark power.
- The material from which the spark plug contacts are made. It is possible to buy iridium, platinum or classic candles. The operational period of the product, the rate of formation and the power of the spark depend on the material of their contacts.
We recommend watching a video about how the SZ marking is deciphered:
Rear
For clarity, we recommend watching a video about replacing the rear brake pads on a VAZ 2110. This will make it easier to complete the task and have a visual representation of each stage of repairing the brake system.
It will be good if you once installed disc elements on your rear brakes. The beauty of them is that the process of replacing the rear pads will be similar to the front ones.
The situation is completely different for those who use factory drum braking systems. The work will have to be done delicately, but completely achievable on your own.
To get started, arm yourself with a set of tools, which includes:
- Balloon wrench;
- Jack;
- Pliers;
- Screwdriver;
- Hammer;
- Sharp chisel;
- Open-end, socket and ring wrench sizes 12, 13 and 17 - 3 sizes of each type of wrench.
Now we proceed directly to replacing the rear brake pads.
- Place chocks under the front wheels and remove the rear wheel.
- Unscrew the guides using a 12mm wrench.
- Guides are required for fixing to the axle shafts of the drums.
- It may be quite difficult to remove the drum from its place. This is where you will need a hammer and a wooden stand. Tap the inside of the drum. It is strongly not recommended to hit the drum directly with a metal hammer, as the mechanism may be damaged.
- If the drum cannot be removed even after hammering, treat the contact areas with the hub with WD40 or other penetrating lubricants.
- Then, arm yourself with pliers and remove the springs from the bottom and top of the pads.
- Remove the guide spring located in front.
- This will allow you to completely remove the block.
- When the bar is removed, you can begin to remove the spring from the rear pad.
- Well, now remove both parts of the block. When removing the back one, remember the hook. It comes from the handbrake cable.
- After removing the old block, put a new one in its place. Assembly is carried out in reverse order.
- But there is one caveat - the bushing must be removed from the drive arm, which will greatly facilitate the reassembly process. The upper part of the pads is inserted into the grooves located on the cylinder rod.
- Be prepared for the fact that certain difficulties may arise when installing a new element. The reason is the large output that remains as a result of the operation of old brake elements.
- Take two pry bars and squeeze the two blocks together to bring them as close as possible. At this point the replacement can be considered completed.
- At the last stage, mandatory bleeding of the brake system is carried out. Without it, not a single intervention in the design of car brakes can be done.
How to check spark on a spark plug
If you experience unstable engine operation, it begins to “triple”, it is quite possible that it is time to change the spark plugs, or the PVN, or the ignition module needs to be replaced. So, first, let's check the spark plugs of the VAZ 2114, most often the reason is in them.
- We remove the PVN tips from the spark plugs
- Unscrew all 4 spark plugs (you will need a 21 key)
- We put the tip on the spark plug and lean it against the metal (possibly against the body of the engine block)
We start turning the starter and look at the spark plug, if there is a spark, then the spark plug is working. We do the same actions with other candles.
Author Auto mechanic
- Fuelfree fuel saver: scam or truth? (+ real reviews) — 04/26/2020
- Infiniti QX50 (infinity qx50) 2018-2019: review, prices and reviews - 04/26/2020
- Tire markings and full explanation of their designations - 02/04/2020
- Rating of the best crossovers up to 2,000,000 in 2022 - 02/01/2020
- How to pass the traffic police exam the first time: tricks and tips from the inspector - 01/16/2020
View other articles
Pros and cons of iridium spark plugs
Companies that produce vehicles do not forget to work on improving the operation of such an important part as the spark plug. The technical characteristics of the candles and their service life depend on the quality of the material used.
Innovative technologies have made it possible to use iridium in candles. Its alloy is used in the manufacture of central electrodes for spark plugs. The core in iridium spark plugs is small, smaller than in similar spark plugs. The use of such spark plugs allows the engine to develop maximum permissible power.
Laser welding is used to weld the iridium tip to the electrode circumference. This candle is very reliable.
Iridium spark plugs improve engine economics. The smaller the center electrode of the spark plug, the better the engine performance.
The advantages of such candles are obvious. Their advantages:
- The power of the engine used is increased by up to four percent.
- The engine starts easily and simply even at low temperatures.
- Less fuel is consumed. Save up to seven percent.
- The service life of candles increases almost three times.
They also have their disadvantages.
The number of electrodes does not determine the quality
A spark plug with three electrodes does not produce three sparks - the breakdown follows the path of least resistance, on one of them. Which one will work at the moment is determined by production, amount of soot and other factors. Electrodes that are not involved in generating a spark will, on the contrary, interfere with the uniform distribution of the flame, plus, they will make it difficult to cool the thermal body of the spark plug with the combustible mixture. Therefore, replacing a spark plug with one electrode with a three-electrode one is not always justified. The only plus is that the service life of parts with several electrodes is longer, due to their “shift” operation.
Plugs with copper electrodes (both or at least one) are better, the spark quality is higher, and cooling is faster!
Source
Choosing spark plugs for VAZ
Let's talk about spark plugs using a specific example - the 16-valve VAZ-2110 engine, which is equipped from the factory with A17DVRM spark plugs from the Engels plant. The same plant, by the way, produces original spark plugs for other Russian conveyors: the “EZ” marking can be seen on Renault Original spark plugs, for example. For convenience, we will focus on these candles.
EZ A17DVRM
The main advantage of these spark plugs is the consistency of quality: it is difficult to find large differences in resistance or spark gap size in the original set. It’s not for nothing that we mentioned the word “original” - alas, the market is flooded with either fakes or rejects going on sale. The spark plugs have a good reserve of stopping sparking; with a standard ignition system, they can withstand cranking when the voltage drops to 6V without stopping sparking. They operate stably even at maximum load conditions - misfires, which can be “caught” by a sensitive gas analyzer, are minimal.
As for the resource, they answer their task - to work from maintenance to maintenance - with confidence. Considering their low price and prevalence, they are clearly worthy of recommendation.
EZ T17DVRM
Three-electrode version of the already familiar A17DVRM. The theoretical gain in resource also brought its own disadvantage: the parameters of the spark plugs “float” more, and this is, first of all, an unstable gap, hence some deterioration in motor characteristics. But it should be noted that this deterioration can only be “caught” on a measuring stand; in real operation, it cannot be said that three-electrode spark plugs from Engels will be worse than single-electrode spark plugs.
Denso W20EPR-U11
Excellent candles from one of the world leaders in their production: high and stable manufacturing quality, reliable operation in any mode and a good service life. The spark plugs confidently withstand voltage drops at startup down to 6.5 V (unexpectedly losing to domestic ones!), and misfires with them are minimal.
Their design uses the same solution as the NGK V-Line series, but exactly the opposite: the groove is stamped into the side electrode. This is definitely more profitable in terms of production, since there is no need to strictly orient the side electrode relative to the central one, but there is obviously less practical benefit from such a design.
Brisk LR15YCY-1
Plugs with an increased reach of the central electrode, as expected, did not show an increase in motor performance on a 16-valve engine: this solution would be more “workable” on an eight-valve engine. By all indicators, this is a strong “middle peasant”, but the price is significantly higher than that of competitors with the same qualities. Let us only note the good result for starting on a dead battery: 6.2V is an excellent result... but the original spark plugs from Engels are cheaper and, oddly enough, better than the Czech ones.
NGK BPR6ES-11
The company's marketers clearly made a mistake in classifying these spark plugs as the V-Line series: their central electrode does not have a groove. Let’s say right away: the original kit is a strong “average” product that doesn’t stand out in any way, but doesn’t fail the tests either. I definitely don’t like the noticeable roughness of the workmanship - even the Made in France marking is always printed unevenly, and the side electrode is usually soldered unevenly. One gets the impression that the manufacturing technology was deliberately cruder for the sake of low cost, but these candles could have been better.
The main disadvantage of NGK is not themselves, but the monstrous number of fakes on the market. Just type “spark plug” in a search on Ebay or AliExpress without specifying the brand, and a multi-page list of “NGK type” from China will immediately appear.
Bosch WR7DPX
We will leave these candles out of the rating, given how much more expensive the Platinum series is than its counterparts that do not contain precious metals. However, it is these spark plugs that demonstrate the best results in all motor tests - this is primarily due to the thin central electrode, completely hidden in the insulator: the engine starts when the voltage in the on-board network drops below 6V, which is not available to other plugs, minimal toxicity clearly indicates the smallest amount of misfires.
You will have to try to overheat the central electrode at maximum loads - the design guarantees reliable heat transfer from it to the insulator and then to the skirt. This means that this spark plug can be recommended to both owners of traveling cars and lovers of aggressive driving. Unless, of course, the price stops it.
Rating of the best spark plugs
They are divided into several categories:
- Budget - up to 200 rubles;
- The average price range is from 200 to 500 rubles;
- Premium – from 500 rub.
BRISK L15Y
This type of spark plug has one central electrode made of a special nickel-based alloy. This allows the spark plugs to work perfectly on engines without catalysts. Has 1 side electrode. The electrodes are resistant to carbon deposits. The outside of the candle is galvanized with zinc for protection.
Characteristics:
- external thread – 14 mm;
- thread length – 19 mm;
- wrench – 16;
- distance between electrodes – 0.7 mm;
- heat number – 15 units.
Price – about 50 rubles. for 1 piece
Heat number - what is important to know
Heat number is the ability of candles to accumulate heat.
An operating temperature of several thousand degrees and an electrical voltage of 30,000V makes this indicator extremely important. Candles are divided into two types: cold - the heat number is high; hot - small.
Domestic candles have gradations: 8, 10, 11, 14, 17, 20, 23 and 26; imported ones do not support uniform standards.
Different engines create unique thermal loads. When choosing an analogue candle, you need to take this into account.
Interchangeability of spark plugs
Table 1. Summary table of interchangeability of hot spark plugs.
| RUSSIA | A11 A11-1 A11-3 | A11P | А14В А14В-2 | A14VM | A14VR | A14D | A14DV | A14DVR | A14DVRM |
| AUTOLITE | 425 | 414 | 275 | 275 | — | 405 | 55 | 4265 | 65 |
| BERU | 14-9A | 14R-9A | 14-8B | 14-8BU | 14R-7B | 14-8C | 14-8D | 14R-8D | 14R-8DU |
| BOSCH | W9A | WR9A | W8B | W8BC | WR8B | W8C | W8D | WR8D | WR8DC |
| BRISK | N19 | NR19 | N17Y | N17YC | NR17Y | L17 | L17Y | LR17Y | LR17YC |
| CHAMPION | L86 | RL86 | L92Y | L92YC | — | N5 | N11Y | NR11Y | RN11YC |
| EYQUEM | 406 | — | 550S | C32S | — | — | 600LS | — | RC52LS |
| MAGNETI MARELLI | FL4N | FL4NR | FL5NR | F5NC | FL5NPR | FL5L | FL5LP | FL5LPR | F5LCR |
| NGK | B4H | BR4H | BP5H | BP5HS | BPR5H | B5EB | BP5E | BPR5E | BPR5ES |
| NIPPON DENSO | W14F | W14FR | W16FP | W16FP-U | W14FPR | W17E | W16EX | W16EXR | W16EXR-U |
Table 2. Summary table of interchangeability of medium candles.
| RUSSIA | A17B | A17D | A17DV A17DV-1 A17DV-10 | A17DVM | A17DVR | A17DVRM | AU17DVRM |
| AUTOLITE | 273 | 404 | 64 | 64 | 64 | 64 | 3924 |
| BERU | 14-7B | 14-7C | 14-7D | 14-7DU | 14R-7D | 14R-7DU | 14FR-7DU |
| BOSCH | W7B | W7C | W7D | W7DC | WR7D | WR7DC | FR7DCU |
| BRISK | N15Y | L15 | L15Y | L15YC | LR15Y | LR15YC | DR15YC |
| CHAMPION | L87Y | N4 | N9Y | N9YC | RN9Y | RN9YC | RC9YC |
| EYQUEM | 600S | — | 707LS | C52LS | — | RC52LS | RFC52LS |
| MAGNETI MARELLI | FL6NP | FL6L | FL7LP | F7LC | FL7LPR | F7LPR | 7LPR |
| NGK | BP6H | B6EM | BP6E | BP6ES | BPR6E | BPR6ES | BCPR6ES |
| NIPPON DENSO | W20FP | W20EA | W20EP | W20EP-U | W20EXR | W20EPR-U | Q20PR-U |
Table 3. Summary table of the interchangeability of cold candles.
| RUSSIA | A20D A20D-1 | A23-2 | A23B | A23DM | A23DVM |
| AUTOLITE | 4054 | 4092 | 273 | 403 | 52 |
| BERU | 14-6C | 14-5A | 14-5B | 14-5CU | 14-5DU |
| BOSCH | W6C | W5A | W5B | W5CC | W5DC |
| BRISK | L14 | N12 | N12Y | L82C | L12YC |
| CHAMPION | N3 | L82 | L82Y | N3C | N6YC |
| EYQUEM | — | — | 755 | 75LB | C82LS |
| MAGNETI MARELLI | FL7L | FL8N | FL8NP | CW8L | F8LC |
| NGK | B7E | B8H | BP8H | B8ES | BP8ES |
| NIPPON DENSO | W22ES | W24FS | W24FP | W24ES-U | W24EP-U |