Under the term ignition coil breakdown or spark plug tip is understood as a breakdown in the weakest point of the body or wire insulation due to a decrease in resistance, occurring in short periods of time. This is mechanical damage that leads to the appearance of cracks or melting. On the surface of the case, the breakdown site appears as black, burnt-out dots, longitudinal tracks or white cracks. Such spark piercing areas are especially dangerous in humid weather. This malfunction leads not only to failure of the mixture to ignite, but also to complete failure of the ignition module.
Often such places are not difficult to notice visually, but sometimes it is necessary to check the ignition coil, not with a multimeter or oscilloscope, but with a simple device made of two wires. When a damaged area is identified, the part is usually completely replaced, although sometimes it is possible to delay the replacement using electrical tape, sealant or epoxy glue.
Coil overheating
Regardless of the make of the car, be it a VAZ or a BMW, the symptoms are usually the same.
A clear example of this is heating the coil. This happens most often due to melting of the winding inside. Consequently, the device loses its primary characteristics and is unstable. This also affects the behavior of the motor. Usually all this is accompanied by dips in dynamics at speeds above 50 kilometers per hour.
But the cause of a malfunction is not always in the coil. There may well be a short circuit in the circuit, or the problem lies in the fuse box. In this case, you first need to check everything and only then replace the coil with a new one.
What is the advantage of the electronic system
The world's leading manufacturers abandoned the contact system back in the eighties of the 20th century. AvtoVAZ installed these mechanisms until the nineties. Today they are no longer installed on any modern car. And there are four good reasons for this:
- The contacts required regular maintenance. As a result of the action of the spark, they burned out and had to be carefully cleaned.
- The classic system was subject to wear and tear. We had to replace it with new parts every 15 thousand kilometers.
- Due to bearing wear, the engine was unstable.
- The contact system led to stretching of the balancer springs.
These problems arose one after another, leaving the car owner unable to breathe. The spark power regularly decreased, the engine began to work worse, and consumption increased significantly. Modern electronic ignition systems of the VAZ 2106 operate much more stable and durable. The spark is powerful and the fuel mixture ignites better.
Experienced car enthusiasts believe that the most reliable for Zhiguli are the contactless ignition system kits for the VAZ 2106 from SOATE. You can learn more about choosing a specific kit in the following video:
The principle of operation of the ignition coil
How to check the ignition coil?
replacing the ignition coil of a VAZ 2107 The most ordinary coil on its primary winding has 100 - 150 turns of insulated copper wire. Both ends of the conductor are brought out to its body. The secondary winding is made of 30,000 - 50,000 turns and depends on the modification. The diameter of the wire of the high-voltage winding is significantly smaller than that of the low-voltage winding. The plus from the battery is supplied to the primary winding, and the secondary is connected to the terminal on the spark plugs.
To increase the strength of the magnetic field, the wire of both windings is wound onto a ferromagnetic core. On some models, in order to avoid overheating of the wire and metal core, the cavity inside the coil is filled with transformer oil. It not only provides reliable cooling, but is also an excellent insulator.
Ignition coils are divided into three main types:
The use of one or another coil depends on the internal combustion engine ignition system used.
Features of a custom ignition coil
Most often installed on engines with an electronic ignition system. The basic operating principle is the same as the standard ones. By design, it also has low-voltage and high-voltage windings. The difference is the location of the primary winding inside the secondary. Accordingly, the coil has two cores - outer and inner. On the high-voltage winding of such a coil there is a special diode installed that cuts off the high voltage current.
According to the structural features of the core, they are divided into two subtypes:
The second subtype is often connected in a modular manner, 4 pieces each. For individual ignition coils, it is important to synchronize all devices with the engine camshaft. This necessity is caused by the fact that during the passage of one period each coil produces one spark.
Double-lead coils (dual)
The design feature is the presence of an additional pair of leads from the secondary winding. Thanks to this approach, it becomes possible to form a spark simultaneously on two spark plugs. The spark plug of the first cylinder gives a spark at the moment of compression of the fuel mixture, and the second - at the release of exhaust gas. They are used for paired number of cylinders in internal combustion engines. The ignition system is significantly simplified and distributors can be eliminated from it.
Connection takes place in one of the following ways:
On four-cylinder engines, four-terminal ignition transformers can be installed, which are essentially a simple solder of two-terminal ones.
Eight-valve VAZ engines use ignition units with two-channel coils capable of producing a spark for two cylinders simultaneously. But with the advent of 16-valve engines (Priora, Grant, etc.), individual ignition coils (IKZ) began to be used.
Dry and oil-filled
They belong to classic ignition coil systems, where the internal space is filled with transformer oil. When large currents pass through the conductors, they begin to heat up; in this case, the oil acts as a coolant. The housings of such coils are usually made of metal, although this is not always advisable.
In view of this, recently most automakers have begun to use a different type of design - a dry transformer. They feature a layer of epoxy resin as a casing, which protects the windings from damage from dirt and high humidity, and also serves as cooling.
Regardless of the type of coils, during testing, the main technical parameter that you need to pay attention to is the winding resistance readings. You can measure it using a conventional multimeter or ohmmeter
Professional testing
You will need professional grade equipment.
The optimal solution would be to designate a separate stand for checking coils. This way it will be possible to set different speed modes for the rollers, simulating different types of work. When interacting, you need to ensure that a spark is constantly maintained, regardless of the operating mode. Before carrying out the test, you need to make sure that this power supply is connected correctly, otherwise you may receive unreliable data, which will prevent the determination of problems.
A reel is a small component of vehicles. Even small deviations from normal performance can lead to serious engine problems.
Author of the article Shamraev Nikolay Pavlovich Rate the article (votes: 41, average: 4.8 out of 5) We recommend reading How to check a thyristor with a multimeter How to check a thyristor and triac Ku202N with a multimeter How to make a sword How to make a sword out of wood with your own hands Comments on the article
Briefly about ignition coils
The main symptoms of a malfunction of the DPD on a VAZ-2114
There are two types of coils - single-spark and double-spark. Regardless of the type, the principle of operation does not change and consists of electromagnetic induction of current, which is supplied to the spark plug in the form of a short pulse. This is enough to form a spark and ignite the mixture in the combustion chamber.
To understand what are the main signs of faulty ignition coils, you need to understand what they consist of. There is nothing complicated here. There is a primary and secondary winding. The secondary winds the core and is made of small-section wire, the primary is wound on top and has a thicker wire.
For both single- and double-spark coils, breakdowns are usually similar. Let's see what they are.
Selecting a multimeter
As a rule, in specialized services the device model MAS 838 is often found. It has the ability to measure a regular microcurrent of 200 µA. The display is backlit, so when carrying out this process in an unlit garage, you do not need to use a flashlight.
To run the process itself, specific accuracy is not required. Therefore, there is no point in purchasing an expensive model. It’s better to just buy the basic package, which is included in all standard devices.
HOW TO TEST IGNITION COILS
Method #1: Spark Test the Ignition Coil
Engine timing faults signs of malfunction
Testing the ignition coil with a spark
- Stop the engine and open the hood.
Depending on the make of the car, the coils may be located in different places. On engines without an ignition distributor, the spark plugs are connected directly to the coils. The surest way to find the coils is to follow the wires that go from the ignition distributor in the opposite direction. Protect exposed skin and eyes and only use tools with insulated handles. - Disconnect one high voltage wire from the spark plug. A separate cable leads to each candle. If you have stopped the engine recently, it will likely be very hot. To avoid injuries and burns, wait 10-20 minutes and start working.
- Remove the spark plug using a spark plug socket. Do this carefully, making sure that no debris gets into the spark plug hole. If dirt or debris gets into the spark plug hole, it can damage the engine. And removing debris from the cylinder is a rather complicated operation. So be extremely careful at this point.
Reconnect the previously pulled wire back to the spark plug. The spark plug must be connected to the ignition distributor, but not screwed into the engine. Use only insulated-handled pliers to hold the candle to avoid electrocution.
Touch the threaded side of the spark plug to bare metal. Touch the threaded part of the spark plug to a bare area of your car. This could be the engine or an area that is missing paint.
Ask a helper or friend to turn on the ignition. When the ignition is turned on, all electrical systems of the car begin to work, and if the ignition coil is working properly, then voltage will be supplied to the spark plug.
Make sure you see blue sparks flying. If you don't see a blue spark, then the problem is obvious. Your coils are not functioning and need to be replaced. If the spark is orange, this means that insufficient voltage is being supplied to the spark plug. The reasons may be: low current, poor contact or damage to the coil.
Reinstall the spark plug and reconnect the wire. Turn off the ignition and reassemble in reverse order.
This is the first way to check the ignition coil yourself. Be careful when working with voltage and follow all safety regulations.
Method # 2. Testing ignition coils by measuring resistance
Testing ignition coils by measuring resistance
Remove the coil from the car. This is the surest way to ensure that the coil is working properly. To do this, you need a device for measuring electrical resistance - an ohmmeter. Using an ohmmeter, you can accurately determine the current condition of the ignition coil. In order to remove the ignition coil, you need to: disconnect the wires from the ignition distributor, and unscrew the fastenings of the coil itself with a wrench. This must be done with the ignition off.
The specifications for your ignition coil model are required. Each car has its own coil characteristics. If your measurement showed different indicators than those indicated in the specifications, then your coil probably requires repair or replacement.
Touch the ohmmeter probes to the contacts of the primary winding of the coil. Touch the two side contacts at the same time. On the distributor side, the coil has three contacts: one in the center and two on the sides. Turn on the ohmmeter and measure the readings.
We measure the resistance value of the secondary winding. Touch the probes to the central contact and one of the side ones.
Compare your performance with factory specifications. The ignition coil is very sensitive. If the readings differ from the factory values, the coil should be replaced, as it is damaged and does not work correctly.
The resistance of the primary winding should be in the range of 0.7-1.7 Ohms. And the secondary is in the range from 8-15 kOhm. These are the two easiest ways to check the ignition coil yourself and at home. To check the coil you will need:
- Wrenches, in particular spark plug pullers
- Screwdriver
- Insulated pliers
- Candles
- Ignition
- Ohmmeter or multimeter
Three diagnostic methods
Next, consider three proven methods for checking the ignition coil.
Visual testing method
The strength of the visual testing method (known as the “spark test”) is its ease of implementation. It does not require any equipment and can be performed even on the road. The main disadvantages are reasonably considered to be low accuracy, high labor intensity, and the risk of electric shock.
This method will require a working spark plug and pliers, and you may need a socket wrench.
It is advisable to start work no earlier than a quarter of an hour after turning off the engine, so that it has time to cool down.
First, the wire of the first spark plug is removed and the control spark plug is connected to it. Holding the spark plug by the insulator with pliers, we touch the threaded part of the skirt to the uninsulated metal section of the engine housing. When the engine is running and the coil is working properly, an intense purple spark jumps between the electrode and the housing. To minimize risks, you can not start the engine, but turn on the starter for a couple of seconds.
The conclusion that the coil is faulty is made if the spark is weak or has a pronounced yellowish tint. The absence of a spark indicates a coil failure or a complete lack of contact.
If the engine has several coils, the control procedure is performed for each of them.
If there is no spare working spark plug, a spark plug that is unscrewed from one of the engine cylinders is used as a visual indicator.
A voltage of several kilovolts is applied to the spark plugs. Taking this feature into account, when using the visual inspection method in any form of its implementation, be careful and do not touch unprotected parts of your body to uninsulated parts of the on-board electrical wiring.
Second
This method of identifying problems is similar to the “scientific poking” method. This test of the ignition coil involves disconnecting the terminals one by one while the engine is running. Although this method may seem barbaric to many, it helps to quickly identify a faulty coil.
By disconnecting the wire from the coil, the discharge will stop flowing into the fuel combustion chamber and engine operation in this cylinder will be disrupted. A failure can be easily determined by the sound and rhythm of the motor. If there is no change in engine operation when the next coil is turned off, this is a faulty part.
The third is the scientific way
To check the ignition coil, you will need a multimeter. Remove all coils and check the resistance using a tester. The resistance value is affected by corrosion on the contacts, so before checking, clean the elements from dirt, oil residues and other formations that interfere with accurately determining the characteristics of the element.
To measure the resistance on the primary winding, the probes of the device must be installed on both contacts. In this case, the multimeter must be set to 20 ohms.
Depending on the car models and the type of coil, this value can range from 0.4 to 2 ohms.
However, all four coils (assuming your internal combustion engine has 4 cylinders) should have approximately the same resistance.
To measure the secondary winding, connect the first probe of the device to one of the contacts, and the second to the spring that goes to the coil. Since the resistance value on the secondary winding can be from 6 to 10 kOhm, the multimeter flag should be set to 20 kOhm. Thus, you can easily identify the faulty coil and replace it.
It is worth noting that the resource of this element is 60-70 thousand km. According to the experience of many car enthusiasts, original spare parts installed on a car by the manufacturer can withstand more than 100 thousand, so purchase quality parts from reliable suppliers.
Video: How to identify a faulty ignition coil
Symptoms of a faulty ignition coil
Signs of a malfunction of the ignition coil are that the engine periodically “trips” (triggering is especially important in rainy weather, and when starting the engine “in cold weather”), “failures” occur when accelerating the car, when visually inspecting the coil, “paths” of electrical breakdown are observed, burning of contacts, signs of thermal overheating, the presence of a large amount of dirt and debris in the coil body and other, smaller faults. The most common cause of coil malfunction is a break in its primary or secondary windings. In some cases, their insulation is simply damaged. At the initial stage, the coil will work more or less normally, but over time the problems will worsen and the symptoms described above will appear to a greater extent.
There are several typical signs of an ignition coil breakdown. It’s worth mentioning right away that the malfunctions listed below can be caused by other reasons, so diagnostics should still be carried out comprehensively, including checking the condition of the ignition coils. Thus, symptoms of breakdown can be divided into two types - behavioral and visual. Behavioral ones include:
- The engine begins to "trouble". And over time, the situation gets worse, that is, the “tweaking” is expressed more and more clearly, the power and dynamics of the engine are lost.
- When trying to accelerate quickly, a “failure” occurs, and when idling, the engine speed does not increase sharply. There is also a loss of power under load (when transporting heavy loads, driving uphill, and so on).
- “Tripping” of the engine more often occurs in rainy (humid) weather and when starting the engine “cold” (especially typical for low ambient temperatures).
- In some cases (on older cars), the smell of unburned gasoline may appear in the cabin. On newer cars, a similar situation may occur when, instead of more or less clean exhaust gases, the smell of unburned gasoline is added to them.
When dismantling the ignition coil if it malfunctions, you can observe visual signs that it has completely or partially failed. So, these include:
- The presence of “breakdown tracks” on the coil body. That is, characteristic dark stripes along which electricity “strikes”. In some particularly “neglected” cases, scale occurs on the tracks.
- Change (turbidity, blackening) in the color of the dielectric on the ignition coil body.
- Darkening of electrical contacts and connectors resulting from their burning.
- Traces of overheating on the coil body. Usually they are expressed in some kind of “drips” or changes in the geometry of the body in some places. In “severe” cases, they may have a burning smell.
- High contamination on the coil body. Especially near electrical contacts. The fact is that electrical breakdown can occur precisely on the surface of dust or dirt. Therefore, it is advisable to prevent such a state.
The main sign of a coil malfunction is the lack of ignition of the fuel mixture. However, this situation does not always arise, since in certain cases part of the electrical energy still goes to the candle, and not just to the body. In this case, it is necessary to conduct additional diagnostics.
Well, on modern cars, in the event of a breakdown of the ignition coil, the electronic engine control unit (ECU) will notify the driver about this by activating the Check Engine lamp on the dashboard (and a misfire diagnostic code). However, it can also light up due to other faults, so this requires additional diagnostics using software and hardware.
The symptoms of malfunction described above are relevant if the engine has individual ignition coils. If the design provides for the installation of one coil, common to all cylinders, then the engine will stall completely (this, in fact, is one of the reasons why several individual modules are installed on modern cars).
Oscilloscope testing
The most extensive information is obtained after testing the ignition system with an oscilloscope, the results of which are displayed on the monitor of a personal device (PC or tablet).
It records, in the form of an oscillogram, changes in parameter values not only of the coil, but also of the entire group of engine systems. Distortion of the graph occurs under the influence of certain characteristics by which one can judge the serviceability of a particular section:
- Advanced ignition (angle);
- Number of revolutions per minute (crankshaft rotation);
- Throttle position (travel angle);
- Pressure;
- Proportions of the fuel mixture (lean or rich);
- Others.
Using a motor tester based on a digital oscilloscope, the following problems are identified:
- Opening the high-voltage circuit connecting the sensor to the spark plugs. The spark gap may decrease, which will negatively affect the transistor and insulation;
- An increase in resistance in this area, accompanied by a drop in voltage. This happens when wires that are too long oxidize and age. The graph clearly shows how the voltage at the beginning of the spark is greater than at the end of the spark;
- A break in the wire between the sensor and the coil. An additional spark gap (between the ends of a broken wire) leads to an increase in voltage and damages the winding;
- Interturn breakdown. It also absorbs some of the energy, especially when the load on the engine increases. Therefore, the engine loses power during acceleration and increasing speed;
- Spark plug electrode gap. A change in its value leads to a voltage drop and misfire;
- Reduced compression in cylinders. They focus on reducing the sparking voltage due to a decrease in the discharge pressure of the pistons in the cylinder chambers.
All of the above changes are accompanied by an insulation breakdown and a voltage drop in the ignition system circuit. These explain the misfires, over-gassing and failures of ignition.
Symptoms of malfunction and common causes of failure
The ignition coil, like an unregulated transformer, does not contain moving parts, and therefore has high operational reliability. Cases of its failure, which rarely occur in practice, are externally manifested in the fact that the engine
- begins to “triple”, and this effect may partially disappear after warming up, but its intensity increases over time;
- gives interruptions during rain and high air humidity;
- in winter, before the warm-up is completed, “dips” are observed, which decrease when the operating temperature is reached;
- reacts “failure” to a sudden supply of gas.
Mechanical damage to the coil occurs due to impacts on the housing and due to destruction of the insulation as a result of natural aging and when oil gets on it.
The most common cause of coil failure is exposure to moisture in the summer and anti-icing agents in the winter, penetrating into the engine compartment and causing corrosion of the contacts.
Overheating and excessive vibrations during abnormal engine operation negatively affect the reliability of the coil.
From the above list it is clear that the car owner is able to reduce the likelihood of coil failure by properly operating the car and maintaining it in good condition. But failure of this node cannot be completely ruled out.
The on-board computer indicates a coil failure by turning on the Check Engine light. It is triggered for other reasons. Therefore, additional tests are required to accurately localize the fault. Testing is possible without the use of complex professional diagnostic equipment.
Natural wear and tear
The ignition coil is designed for a long service life. There are often cases when an element worked even after a run of 150–200 thousand kilometers without a single replacement. But with every kilometer, the life of the coil decreases. The installation of low-quality spark plugs or careless cleaning of the engine compartment can contribute to the breakdown. At one point, the part may simply not withstand the load.
Checking the ignition coils
There are several ways to test the ignition coil. This is replacing the faulty coil with a coil from another cylinder, checking the resistance of the coil windings, measuring the supply voltage and checking the high voltage. Let's take a closer look.
Replacing coils
Replacing the ignition coil with one from a different cylinder is the easiest way to start diagnosing and works very well on any vehicle.
In the case of a faulty ignition coil, you will usually have a misfire on a specific cylinder. Let's say you have a misfire in cylinder 3.
Simply remove another coil, for example from cylinder 2, and replace it with the coil from cylinder 3. Now, if you have a diagnostic scanner or an ELM327 adapter, you can erase OBD2 errors. If not, remember what error code you had.
Now start the car and let it run for a few minutes. If the ignition coil was indeed faulty, you will now see the error code “P0302. Misfire in cylinder 2” because the faulty coil from cylinder 3 was installed on cylinder 2. Now you need to remove the faulty coil from cylinder 2 and replace it with a new one.
If you change the coils and the misfire remains in cylinder 3, then the problem is not in the coil. In this case, there may be a problem with the ignition module, a problem with the coil connector or wire, with the spark plug, with the fuel injector, or an engine mechanical problem in that cylinder.
Visual inspection
Carefully inspect the coil for signs of cracks, burns, melting, or leakage currents. Check the condition of the spring inside the cap. This often indicates a problem with the coil, so check carefully.
Checking the windings with a multimeter
We will check the electrical resistance of the primary and secondary windings. The main problem is that you cannot simulate the load or measure the coil while it is running. Therefore, faulty coils may still pass this test, but will still be bad.
Find the rated resistance values of your car's ignition coils in the repair manual or on the Internet. If there is no data, you can compare the readings with a known-good coil from another cylinder.
The numbers will be approximately like this:
Remove the coil from the engine. To do this, disconnect the electrical connector and unscrew the fastening bolts.
We will need to check first the resistance of the primary and then the secondary winding. We turn on the multimeter to measure resistance (Ohm) within a range of up to 200 Ohm and connect it to the terminals of the primary winding. Typically these will be the outermost pins 1 and 3 on the connector.
Then we repeat this operation with the secondary winding. Only this time we switch the multimeter to the limit of up to 200 kOhm. We connect one measuring wire to the middle plug on the connector, and the second to the terminal on the spark plug.
If the reading is outside the normal resistance range, the ignition coil will need to be replaced.
Checking the secondary winding of a coil with a diode
In this case, it is useful to do the following. Switch the multimeter to measure direct voltage (DC). Connect it in series between the secondary winding of the ignition coil and the battery. If the battery is connected in the diode direction, the multimeter should show voltage.
After changing the polarity of the connections in the diode blocking direction, the voltage should not be displayed. If there is no voltage in any direction, we can assume that there is a break in the secondary winding. If there is voltage in both directions, then the high-voltage diode is faulty.
Replacement
Individual ignition coils should be replaced with similar models, otherwise there may be problems with ignition timing. It is also advisable to install dual and common ignition coils in accordance with reference data and equipment catalogs, especially since there are not many standard sizes of ignition coils.
Experienced auto electricians often replace the ignition coils of imported cars with domestic Zhiguli ones, and quite successfully. This does not in any way affect the driving performance of the car.
A factory coil from Lada costs two to three times less than a second-hand original or a new Chinese one. If there is a problem with the ignition coil, you can scour the Internet and find what can replace it. Only in this case, in most cases, you have to reconnect the connector to the coil. It is better to entrust this to a specialist.
To make the ignition coil last longer, follow these rules:
- Wipe high-voltage wires regularly (preferably at the end of the seasons);
- Make sure that the reel does not get wet or oily liquids;
- check the quality of the coil connector, it should not spark or get hot;
- change spark plugs regularly;
- it must be firmly fixed in place, and not dangle;
- at the slightest suspicion of a malfunction of the ignition coil (misfire, etc.), it should be tested immediately.
Remember, a faulty ignition coil leads to uneven operation, increased loads, and mechanical beats, which ultimately reduces engine life.
Video - VAZ ignition coil and its possible malfunctions:
The principle of operation of the ignition coil
The most ordinary coil on its primary winding has 100 - 150 turns of insulated copper wire. Both ends of the conductor are brought out to its body. The secondary winding is made of 30,000 - 50,000 turns and depends on the modification. The diameter of the wire of the high-voltage winding is significantly smaller than that of the low-voltage winding. The plus from the battery is supplied to the primary winding, and the secondary is connected to the terminal on the spark plugs.
To increase the strength of the magnetic field, the wire of both windings is wound onto a ferromagnetic core. On some models, in order to avoid overheating of the wire and metal core, the cavity inside the coil is filled with transformer oil. It not only provides reliable cooling, but is also an excellent insulator.
Ignition coils are divided into three main types:
- individual;
- two-terminal;
- classic (dry or oil).
The use of one or another coil depends on the internal combustion engine ignition system used.
Features of a custom ignition coil
Ignition system diagram.
Most often installed on engines with an electronic ignition system. The basic operating principle is the same as the standard ones. By design, it also has low-voltage and high-voltage windings. The difference is the location of the primary winding inside the secondary. Accordingly, the coil has two cores - outer and inner. On the high-voltage winding of such a coil there is a special diode installed that cuts off the high voltage current.
According to the structural features of the core, they are divided into two subtypes:
- compact;
- rod.
The second subtype is often connected in a modular manner, 4 pieces each. For individual ignition coils, it is important to synchronize all devices with the engine camshaft. This necessity is caused by the fact that during the passage of one period each coil produces one spark.
Double-lead coils (dual)
The design feature is the presence of an additional pair of leads from the secondary winding. Thanks to this approach, it becomes possible to form a spark simultaneously on two spark plugs. The spark plug of the first cylinder gives a spark at the moment of compression of the fuel mixture, and the second - at the release of exhaust gas. They are used for paired number of cylinders in internal combustion engines. The ignition system is significantly simplified and distributors can be eliminated from it.
Connection takes place in one of the following ways:
- the two contacts of the spark plug and the coil are connected using high-voltage wiring;
- the first contact is directly put on the spark plug, the second is connected with a high-voltage wire.
On four-cylinder engines, four-terminal ignition transformers can be installed, which are essentially a simple solder of two-terminal ones.
Eight-valve VAZ engines use ignition units with two-channel coils capable of producing a spark for two cylinders simultaneously. But with the advent of 16-valve engines (Priora, Grant, etc.), individual ignition coils (IKZ) began to be used.
Dry and oil-filled
They belong to classic ignition coil systems, where the internal space is filled with transformer oil. When large currents pass through the conductors, they begin to heat up; in this case, the oil acts as a coolant. The housings of such coils are usually made of metal, although this is not always advisable.
In view of this, recently most automakers have begun to use a different type of design - a dry transformer. They feature a layer of epoxy resin as a casing, which protects the windings from damage from dirt and high humidity, and also serves as cooling.
Regardless of the type of coils, during testing, the main technical parameter that you need to pay attention to is the winding resistance readings. You can measure it using a conventional multimeter or ohmmeter
Ignition coil
The ignition coil is an important part of the vehicle's starting system. Without its use, it is impossible to get the engine to start.
It is impossible to start the engine without a battery, since the first spark will not form.
The structure of this part is quite simple, but from time to time, like other parts and elements of the car, it fails. The cause may be a malfunction or a certain manufacturing defect. The operation of the coil is not limited to standard engine starting. If the device suddenly fails while the engine is already running, this will automatically lead to its complete stop.
Knowing the answer to the question of how to check the ignition coil is a simple and sure way to identify a faulty part and understand whether it needs to be replaced or not.
Purpose
The main purpose of ignition coils is to transform low-voltage electrical current, which is obtained from the battery or generator, into a special electrical impulse with a sufficiently high voltage. Due to this process, the spark plugs produce the spark necessary to start the engine.
Principle of operation
The operating principle of the described device is quite simple. A low-voltage voltage is supplied to the primary winding of the coil, creating a magnetic field. Sometimes such voltage is completely cut off by a breaker, thereby contributing to a sharp reduction in the magnetic field and the formation of optimal electromotive force in the turns of the ignition coil.
According to the law of physics on electromagnetic induction, the indicator of the generated electromotive force is directly proportional to the number of turns of the circuit. It is for this reason that a high voltage pulse appears in the secondary coil, where there are more turns. It passes through high-voltage wires and is supplied to the spark plug. Thanks to this impulse, which is transmitted by the coil, a spark appears between the electrodes of the spark plug, igniting the air-fuel mixture.
In older car models, the voltage from the ignition coil was transmitted to the spark plugs via an ignition distributor. Such a scheme was not reliable, because the spark plug ignition coils of more modern cars are combined into a special system and distributed strictly one for each spark plug.
Types of coils
At the moment, there are three main types of ignition coils. Each of them is characterized by its own design features and requires more careful consideration:
- classic ones, which are used on cars with ignition systems with a distributor;
- two-terminal - used in a standard ignition system with direct supply of electrical voltage;
- individual - in this system there is one coil for each candle.
All three types are similar in design, with the exception of some nuances. The classic version consists of two windings - secondary and primary. The second one is placed inside the first one. The difference between the windings is the number of turns of wire used, as well as the thickness of the wire.
In the inner part of these windings there is a core made of a ferromagnetic alloy. Each winding has two terminals. In the primary, they are both input. In the secondary, one terminal is the output, and the second is connected to the primary winding. All of the above elements are placed in a sealed housing. As for the leads, they go out onto the housing cover.
The two-terminal coil differs from the classic version in the presence of two cores - the internal one, which is placed in the windings, and the external one, which is located above them. Instead of one high-voltage terminal of the secondary winding, such a coil has only two of them.
As for the individual coil, it differs in that not the primary, but the secondary winding is placed on top. In this case, its high-voltage terminal is connected to a special tip that is put on the spark plug terminal.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=4wHGBUx6x3M
All types of coils are non-separable and cannot be repaired. These elements must be checked and replaced in a timely manner.
This is very important, since a break or short circuit of the windings can cause malfunctions and also lead to complete inoperability of the engine.
Summarizing
Any malfunction in the ignition coil always has a bad effect on the functioning of the entire vehicle as a whole. Ultimately, this leads to a reduction in its service life. To properly care for your own car, you need to know a lot. We need to treat this with full responsibility. And it is imperative to carry out a diagnostic procedure for checking the ignition coil, because almost the entire operation of the vehicle depends on this element. From our article you learned how to check the ignition coil with a tester or multimeter.
If the owner does not have any knowledge and experience (or has it, but not enough to carry out serious checks), it is best to entrust the solution to this problem to a specialist. Although today you can find a lot of information on literally any issue on the Internet. Therefore, if you have basic knowledge and have read the video and instructions for it, you can try to check the ignition coil manually. Moreover, all the main points of the process are described in detail in the video. If you still have doubts, you can order a service from a professional. The choice is always yours!
The reel is a very interesting transport component. Even the slightest deviation from normal performance can cause engine problems.
Sources
- https://elm327.club/diagnostika-avto/diagnostika-katushek-zazhiganiya.html
- https://instanko.ru/izmereniya/kak-prozvonit-katushku-zazhiganiya-multimetrom.html
- https://uremont.com/publications/articles/kak-proverit-katushku-zazhiganiya
- https://tolkavto.ru/remont-i-obsluzhivanie/elektrooborudovanie/osnovnye-simptomy-neispravnosti-katushki-zazhiganiya.html
- https://prometey96.ru/obsluzhivanie/kak-proverit-katushku-zazhiganiya-multimetrom.html
- https://topmekhanik.ru/kak-proverit-katushku-zazhiganiya-iskroj-i-multimetrom/
- https://msmetall.ru/instrument/prozvon-katushki.html
- https://autolirika.ru/remont/kak-proverit-katushku-zazhiganiya-multimetrom.html
- https://voditeliauto.ru/poleznaya-informaciya/to-i-remont/proverka-katushki-zazhiganiya-multimetrom.html
Causes of ignition coil failure
Let's look at the reasons why the ignition coil fails.
Natural wear and tear
Like all electrical and electronic units, the reel has a certain trouble-free operation life. The average service life of ignition coils is approximately seven to ten years of operation or 150,000 - 200,000 thousand mileage. The device is operated in extreme conditions with large differences in temperature, humidity, and the possibility of ingress of moisture, dirt, and foreign liquids. In this case, large currents flow through the primary winding, and a high-voltage pulse is formed in the secondary winding.
Electrical breakdown
Let's figure out why the ignition coil breaks. Firstly, over time, as a result of high temperature changes, the dielectric insulation cracks, and salty moisture, which is a conductor, can enter microcracks. For voltages of more than 15,000 volts generated in the secondary winding, even pure undistilled water acts as a conductor. Secondly, during operation, the physical properties of the dielectric and rubber insulation of the tips of high-voltage wires, especially those of dubious production, change. High-voltage breakdown can be caused by the installation of non-standard high-voltage wires in which there is no distributed current-limiting resistance. A breakdown can occur as a result of severe contamination or waterlogging. Even in the event of a single breakdown, irreversible changes occur in the structure; further operation is not recommended.
Overheat
Some vehicles have ignition coils installed directly at or near the top of the engine. If there is no air access to their structure for natural ventilation (this is possible when installing additional equipment), the device may overheat and fail.
Mechanical load.
The coil mount must be standard. Some car enthusiasts neglect these requirements by “hanging” it on homemade structures.
Wear of spark plugs, high-voltage conductors
Despite the fact that the circuit has a limiting resistance, wear of spark plugs and high-voltage conductors can cause electrical breakdown in them. Then the load current increases and the bobbin may overheat.
Generator voltage regulator relay malfunction
Sometimes it leads to an increase in the voltage of the vehicle’s on-board network and failure of the electronic amplifier (switch).
Malfunction of the contact group of the lock, electronic switch
If, during parking, +12 Volts are constantly supplied to the coil in the event of an abnormal closure of the lock contact group, the device may overheat and fail. The same situation is possible if the switch is faulty.
To prevent premature failure, all possible causes of malfunction of the ignition coil in the car should be eliminated as much as possible.
Checking the voltage on the coil windings
Adviсe
In order for the coil to work longer, follow the rules:
- install the device on standard mounts;
- do not clutter the device area, ensuring good ventilation;
- keep the body clean;
- check spark plugs and high-voltage wires promptly (before the start of each operating season).
1200 rub. for the photo report
We pay for photo reports on car repairs. Earnings from 10,000 rubles/month.
Write:
The term breakdown of an ignition coil or spark plug tip means a breakdown in the weakest point of the housing or wire insulation due to a decrease in resistance, occurring in short periods of time. This is mechanical damage that leads to the appearance of cracks or melting. On the surface of the case, the breakdown site appears as black, burnt-out dots, longitudinal tracks or white cracks. Such spark piercing areas are especially dangerous in humid weather. This malfunction leads not only to failure of the mixture to ignite, but also to complete failure of the ignition module.
Often such places are not difficult to notice visually, but sometimes it is necessary to check the ignition coil, not with a multimeter or oscilloscope, but with a simple device made of two wires. When a damaged area is identified, the part is usually completely replaced, although sometimes it is possible to delay the replacement using electrical tape, sealant or epoxy glue.
Checking the ignition coil
There are two reliable ways to check IKZ: visual inspection and checking with a multimeter.
It should be noted that the IKZ check is similar for all Lada cars with a 16-valve engine, i.e. the check on cars such as LADA Vesta and X-ray will be the same.
In order to check the ignition coil, it must be removed from the car.
Removing IKZ:
- Disconnect the negative terminal from the battery.
- Remove the decorative plastic trim.
- We unscrew the coil we need with a “10” or Torx E8 head.
- Remove the coil plug and remove it.
Visual inspection
After the coil is removed, it must be carefully inspected. The rubber tip should not have tears or cracks. The plastic part must not be melted or cracked. The contact spring must be in the correct shape without oxidation or rust.
Cracks in the coils or tears in the rubber cap will direct the spark to the engine body, therefore, no current will be supplied to the spark plug, which will lead to misfires.
If such visual faults are detected, the coil must be replaced.
Checking with a multimeter
Testing with a multimeter is divided into two stages. Checking the resistance of the IKZ itself and checking the control voltage of the IKZ (checking the voltage on the IKZ power supply block).
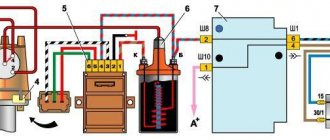
Let's start by checking the voltage at the IKZ power supply.
To do this, set the switch on the multimiter to constant voltage.
Turn on the car ignition
On the block in connector number 3 we take a measurement (we connect one multimeter probe to the motor body and the other to pin number 3) the voltage should be at least 12 volts. If the voltage is less, this means that the battery is discharged or the ECU controller is faulty.
Candles
As is known, it is these elements that play a key role in the ignition of a combustible mixture. The spark plugs are supplied with voltage from the ignition coil. Therefore, it is not surprising that due to low-quality elements, the ignition coil requires repair. You should not buy cheap analogues. Such spark plugs can greatly damage the ignition system, in particular the coil.