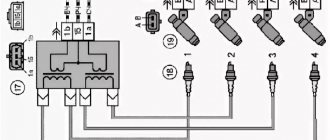
Ignition module
As mentioned above, the “ten” has 4 engine types: 16 and 8 valve internal combustion engines, as well as with a volume of 1.5 and 1.6 liters. This will lead to differences in the ignition modules. Depending on the installed engine with a certain volume, its own ignition module will be installed.
Differences
The main differences between the modules will be the size and mounting holes. In a 1.5 liter internal combustion engine, the ignition module is larger in size in contrast to the 1.6 liter engine. The cost of the modules depends on the manufacturers, but it should be noted that the MZ from a 1.5 liter engine is always more expensive than a 1.6 liter one.
16 valve MZ
In a 16-valve internal combustion engine, the ignition module is installed on the valve cover near the oil filler neck.
8 valve MZ
The MZ on an 8-valve engine is installed on the front of the cylinder block between the dipstick and the breather.
Checking the ignition module (coil)
© Mikhail Ukhanov, aka miha
The ignition module belongs to groups of actuators, the performance and “performance” of which is not checked or controlled in any way, because there is no feedback and the ECU simply sends control signals to them. Diagnostics of the operation of the IM can be carried out by the ECU only indirectly. And the normal operation of the engine depends on the performance of the IM, and the ignition module, in particular. Another catch is that the performance of the modules is very relative - like any other IM, it can have not two stable states of working/not working, but many more intermediate, “semi-working” states, in which the car “seems to be working, but not as necessary". For example, the MZ can “mope” only at certain speeds, at a certain temperature...
Therefore, the question arises about high-quality and unambiguous verification. At the Rostov car service center “Injector”, Mikhail Ukhanov (aka miha) and Tom (aka Igor Semenov) developed their own version of a device for checking ignition modules, allowing this to be done.
The technique is quite simple if you understand the essence of the process. We have a generator with a variable frequency, on average from 3 to 30 Hz. and variable output pulse duration, from 1 to 5 ms.
A fully functional module (one channel) is capable of delivering 13mm to the arrester. a full-fledged spark, with a core accumulation time of 2 ms., of course, on a charged battery about - 12.6 v.
- If the coil has a clear interturn breakdown, there will be no spark at the spark gap or it will be intermittent.
- If the breakdown is insignificant or there is a breakdown of the insulation to ground, as well as a wire with a break or high resistance, we have in mind a seemingly normal spark, but if we close the ends of the spark gap one by one with a probe connected to ground (in this case, the MC must be installed on the machine), a spark will disappear or become intermittent (because it will go to ground through places where the insulation is broken (through the MH housing), sometimes an external breakdown of the coil is visible through a crack in the housing.
- If we short one end to ground, the energy of the coil, with good insulation, will reach the spark gap and we will see a spark, and if there is a defect, then, as we know, electricity will flow through the least resistance, in this case the spark will jump anywhere before reaching the spark gap.
The photos below show how it all works. My 12 turned up very opportunely...
| The check can be done directly on the car. Thank God, no flaws were found in my module | ||||