Checking the ignition system on a VAZ 2106 car
| WARNING The VAZ 2106 is equipped with a contact ignition system. A voltage of approximately 24,000 V is supplied to the high-voltage wires (as an option, a contactless high-energy ignition system can be installed on a VAZ 2106 car - a voltage of approximately 40,000 V). At low current levels, this voltage is not life-threatening, but can lead to electrical injury. Therefore, if you handle a high-voltage wire with the ignition on, use a thick rubber glove or, as a last resort, pliers with insulated handles. |
To check the ignition system on a VAZ 2106 car, you will need: slotted and Phillips screwdrivers, pliers with insulated handles and a tester or 12 V test lamp with two wires connected to it. You can also use a car portable lamp.
RECOMMENDATIONS Before checking the ignition system, place the gear shift lever in neutral and leave the parking brake on.
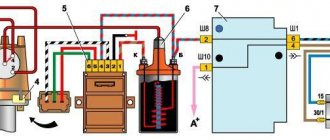
1. With the ignition off on the car, check the integrity and fit of the high-voltage wires in the ignition distributor cover, as well as the fit of the high-voltage wire in the ignition coil. 2. Check the wires going to the ignition coil and their connections. Also check the wire connecting the distributor and the ignition coil.
3. Turn on the ignition on the VAZ 2106 car. Check if current is supplied to the ignition system. Connect one wire of the tester or warning lamp to the “+B” terminal of the ignition coil, and the other to ground. If no current is supplied to the ignition system, then the fault is in the ignition switch or in the wiring from the switch to the ignition coil. In order to get to the nearest car service center, you can apply emergency power to the ignition system. To do this, connect the “+B” terminal of the ignition coil and the “+” terminal of the battery with an additional wire. Fasten the wires securely. Keep in mind that now, in order to turn off the engine, you will need to disconnect the additional wire from the “+” terminal of the battery.
WARNING If strong sparking is noticed when connecting to the “+” terminal of the battery, this method will have to be abandoned - most likely, the wiring is shorted to ground.
5. If there is no spark between the spark plug electrodes, remove the distributor cover. Check if there is a gap between the breaker contacts. To do this, use a special wrench to turn the engine crankshaft so that the top of the ignition distributor shaft cam is strictly opposite the textolite pad of the moving contact lever. The gap between the moving and fixed contacts of the breaker should be 0.35-0.4 mm.
NOTE When using an autotester, the closed state angle of the contacts (UCS) is measured, which should be 55°. The measurement is carried out with the engine running! An approximate value can be obtained by cranking the engine crankshaft with the starter.
6. If the gap (UZSK) does not meet the standard, adjust it and be sure to check the ignition timing.
VAZ models 8 and 16 valves
Despite the similarity in engine design, the ignition system of the 1.5-liter injection 16-valve engine differs from the 1.6 16-valve engine. The 1.6 liter engine uses an electronic contactless ignition system with individual coils on each spark plug. Therefore, there was no need for an ignition module. Such a system is more reliable and cheaper to operate, since if one coil fails, there is no need to replace the entire module.
The 16-valve 1.5-liter VAZ 2112 injection engine used the same non-contact ignition system as the 8-valve engine, but a different ignition module was installed. Its catalog number is 2112-3705010. The design of the module remains the same - two ignition coils (for cylinders 1-4 and 2-3) plus switch keys in a single block.
Vehicle ignition system components
Previously, a distributor of the R-125B brand was installed on the car. This unit was mounted on the machine together with a carburetor marked 2103. The distributor had a special mechanical corrector in its design, and there was no vacuum regulator. The VAZ 2106 is equipped with spark plugs of type A17DV or plugs that have similar technical characteristics. The design of the automotive system uses a VK347 type lock, equipped with an anti-theft device.
The car uses a B117-A type ignition coil, which has an open magnetic circuit and is an oil-filled and sealed system. The VAZ 2106 has a contact ignition, but it is worth noting that sometimes a contactless version is also available. The contact system is considered simpler in its design.
VAZ contact ignition requires regular maintenance and monitoring of the condition of the contacts. This type of ignition is considered to be a classic version of the system. The design of the VAZ 2106 spark plugs is non-separable and has a ceramic insulator. The distributor is designed to interrupt low-voltage currents in the primary winding and distribute high-voltage pulses across the spark plugs.
The distributor breaker consists of a cam with four protrusions and a stand on which contacts are located that open during rotation. At the upper end of the cam bushing, a support strip of the advance regulator with weights is soldered. A vacuum regulator is attached to the side of the distributor. The design of the distributor provides for the installation of an interference suppression resistor.
The operation of the contactless system is based on the use of an electrical impulse distribution sensor. It operates using the Hall effect. The sensor consists of a semiconductor wafer, a special chip and a magnet.
Uneven sparking
Electrical power distribution in an automotive system is provided by the rotor. It is sometimes put on the distributor drive. And of course, the cover with the CG and sockets for the armored wires is responsible for the correct distribution.
The current distribution in this case can be represented as follows:
- The current flows through a carbon contact with a spring to the rotor.
- Further along the runner tire to the side contact.
- From here to the armored wires of the engine cylinders.
According to experts, in the correct understanding there is no contact between the spark plug sockets and the rotor. Current transmission with a force of 15-25,000 V occurs through an air gap.
The design of the ignition coil, the principle of its operation and testing
The car coil is a high voltage pulse transformer. A thin wire of the secondary winding is wound around the core of the device. It contains 30 thousand turns. In accordance with the device diagram, a primary winding consisting of thick wire is located on top of the secondary winding. Both windings are connected to the car battery at one of their ends.
The second end of the primary winding is connected to the distributor. The common connection point of the coil windings is connected to the voltage switch. The core plays the role of a magnetic field amplifier. At the moment the circuit breaks, a high voltage is generated in the secondary winding, which is supplied through a wire to the spark plug for breakdown and formation of a spark.
In the process of diagnosing the performance of the coil, the first thing to do is check the voltage supply to it. For this purpose, its supply is turned on and after that a measurement is made between terminal B+ and ground. This value should be 12 V. If voltage is not supplied to the coil, then the reason for its absence should be sought in the lock.
First signs of trouble
The main signs of ignition coil failure are lack of ignition. If it is a single device with a distributor, then in all cylinders; if it is a double or single device, then in those served by it. The absence of a spark is not necessarily a 100% sign of a faulty coil. Perhaps the limiting resistor has burned out, the spark plug is faulty, the high-voltage wire has broken, or there is a malfunction in the ignition system. A comprehensive fault diagnosis is required.
Visual signs that the ignition coil is not working:
- the presence of “breakdown tracks”, oxides on the coil;
- change in dielectric color;
- burning of contacts and connectors;
- traces of overheating on the body;
- increased pollution.
Let's talk in more detail about these and other points indicating that the ignition coil of the VAZ 2106 is in a faulty state.
Presence of interruption tracks in the ignition coil
Let's figure out why the ignition coil breaks. Firstly, over time, as a result of high temperature changes, the dielectric insulation cracks, and salty moisture, which is a conductor, can enter microcracks.
The photo shows a common malfunction - breakdown of the ignition coil of a VAZ 2106
For voltages of more than 15,000 volts generated in the secondary winding, even pure undistilled water acts as a conductor. Secondly, during operation, the physical properties of the dielectric and rubber insulation of the tips of high-voltage wires, especially those of dubious production, change.
High-voltage breakdown can be caused by the installation of non-standard high-voltage wires in which there is no distributed current-limiting resistance. A breakdown can occur as a result of severe contamination or waterlogging. Even in the event of a single breakdown, irreversible changes occur in the structure; further operation is not recommended.
Burning of contacts and connectors of the ignition coil of a VAZ 2106
The big disadvantage, the disadvantage of CG, is the sparking process, which cannot be eliminated in any way. However, significant minimization of sparking can be achieved by connecting a capacitor. Yes, and be sure to set the correct gap.
Experts say that if you increase the gap above standard values, you can get rid of sparking. In other words, if the distributor contacts are burning, increasing the gap will be the optimal measure to eliminate the problem. However, this also has its drawbacks. In particular, the angle decreases, which leads to a decrease in the additional current voltage.
Traces of overheating on the ignition coil body of a VAZ 2106
Another sign by which you can determine the malfunction of the ignition coil of the VAZ Six is the presence of traces of overheating on the short circuit housing. The photo shows what they look like:
This is what signs of overheating look like on the ignition coil housing
Distributor diagnostics
Malfunctions of the ignition system can be caused by a breakdown of a component such as a distributor. Several types of problems may arise in it that can damage the contact ignition of the VAZ 2106. So, if the coil is working properly, then the problem in the operation of the system is due to the fact that the distributor, which has the contact ignition of the VAZ, has broken down.
To check, you need to remove the cover and inspect it. All contacts and contact angle must be free of damage and cracks. After inspecting the cover, you need to check the distributor slider. Sometimes cracks appear on this element as a result of wear, which leads to breakdowns to ground.
After inspecting the slider, the breaker contacts are examined, if necessary, they are cleaned, and the gap between them is checked. It is imperative to inspect the capacitor, since most often it is the one that is faulty, which is the reason for the failure of the vehicle systems. If there is no charge accumulation after applying voltage, the capacitor must be replaced.
When checking the ignition of the VAZ 2106, we must not forget about the spark plugs. The fact is that the normal operation of the system depends on the gap between the spark plug electrodes. The spark plug gap should be 0.4-0.8 mm. Increased play leads to heating of the coil and, as a result, possible breakdown of its windings.
The VAZ ignition relay is designed to protect the system from sudden changes in voltage at the moments of switching on and off. It protects the contacts of the lock and the breaker from burning, thereby ensuring the long service life of these components. The contacts in the VAZ ignition relay open almost instantly, which prevents the formation of sparks during operation.
The advantage that the VAZ ignition relay has over other elements of the system is the ease of its replacement in case of failure. When repairing a car, it is better to have a special manual on hand. As a rule, such a publication, in addition to a textual explanation, contains photographs of vehicle components, which facilitates repairs.
Often the reason for the disappearance of the spark on the spark plugs is a malfunction of the ignition coil (IC). The article describes the device, how to check the ignition coil of a VAZ 2106, its malfunctions and how to eliminate them.
Which ignition is better: contactless or contact?
Contact ignitions are obsolete, but are still used in older cars. On rear-wheel drive VAZ models, contactless was first installed on 2107.
Let's look at the differences between contact and non-contact ignition:
Advantages of contactless ignition:
- since there is no contact group in the distributor, sparking occurs clearly;
- long coil life;
- at medium engine speeds, BSZ creates a spark 4 times more powerful than contact ignition. This is especially useful if the spark plugs are dirty, as a spark will still be produced;
- performs its functions perfectly even in cold weather;
- if the voltage in the electrical network is low, then sparking will still occur;
- thanks to the powerful, stable spark of the candles, the fuel-air mixture ignites faster;
- if BSZ is installed, then fuel consumption decreases and engine power increases;
- improved vehicle acceleration dynamics;
- BSZ is easier to maintain because the device has no moving parts.
Features of the ignition coil device
The VAZ 2106 ignition coil is one of the components of the ignition system, which also consists of a lock, high-voltage wires, a distributor and spark plugs.
The coil is a high-voltage pulse transformer. They consist of a core on which a secondary winding of thin wire is wound. A primary winding made of thick wire is wound on top of the secondary winding. Each of the windings is connected to a battery.
Short circuit device diagram
The core's job is to enhance the magnetic field. When the circuit breaks, a high-voltage current appears in the secondary winding, which is supplied to the spark plug, where a breakdown occurs and a spark jumps.
Reasons for failure
Like all electrical and electronic units, the reel has a certain trouble-free operation life. The average service life of ignition coils is approximately seven to ten years of operation or 150,000 - 200,000 thousand mileage.
There are many reasons for ignition coil failure. The most common is an internal short circuit. When the coil overheats, for example due to increased temperature conditions of the engine (lean mixture, faulty cooling system), the insulation is damaged. The use of worn-out spark plugs, in which an internal gap has arisen due to wear of the conductive glass sealant, also leads to overheating of the coil. In addition, reverse gases and breakdown of the insulator have a detrimental effect on the condition of the rubber tip of the ignition coil.
The photo shows a faulty ignition coil of a VAZ 2106
Let's look at the most common reasons for the failure of the VAZ 2106 ignition coil:
- Natural wear and tear. The device is operated in extreme conditions with large differences in temperature, humidity, and the possibility of ingress of moisture, dirt, and foreign liquids. In this case, large currents flow through the primary winding, and a high-voltage pulse is formed in the secondary winding.
- Electrical breakdown. Let's figure out why the ignition coil breaks. Over time, as a result of high temperature changes, the dielectric insulation cracks, and salty moisture, which is a conductor, can enter microcracks. For voltages of more than 15,000 volts generated in the secondary winding, even pure undistilled water acts as a conductor.
- Overheat. Some vehicles have ignition coils installed directly at or near the top of the engine. If there is no air access to their structure for natural ventilation (this is possible when installing additional equipment), the device may overheat and fail.
- Mechanical load. The coil mount must be standard. Some car enthusiasts neglect these requirements by “hanging” it on homemade structures.
- Wear of spark plugs and high-voltage conductors. Despite the fact that the circuit has a limiting resistance, wear of spark plugs and high-voltage conductors can cause electrical breakdown in them. Then the load current increases and the bobbin may overheat.
- Generator voltage regulator relay malfunction. Sometimes it leads to an increase in the voltage of the vehicle’s on-board network and failure of the electronic amplifier (switch).
- Malfunction of the contact group of the lock, electronic switch. If, during parking, +12 Volts are constantly supplied to the coil in the event of an abnormal closure of the lock contact group, the device may overheat and fail. The same situation is possible if the switch is faulty.
How to check the ignition coil?
Short circuit testing is performed in the following stages:
- visual inspection;
- checking for voltage;
- measuring resistance using an ohmmeter;
- checking for spark.
A visual inspection reveals mechanical damage to the surface, the presence of oil stains, mud deposits, and the reliability of connections and electrical contacts. To check the voltage supply to the unit, you need to turn on the ignition and measure the voltage between terminal “B” and ground with a voltmeter. It should be 12 V. If there is no voltage, then the problem is in the ignition switch.
Instructions for connecting short circuit
To carry out the operation of removing and replacing the short circuit, you need to prepare:
- heads or keys for “8” and “10”;
- extension;
- small wrench or ratchet.
The short circuit is located in the left corner of the engine compartment.
The replacement procedure consists of the following steps:
- First, remove the central high-voltage wire from the ignition distributor (distributor).
- Next, you need to use the key set to “8” to disconnect the supply wires from the short-circuit contacts. To correctly connect the wires after installing a new unit, it is better to remember how they are connected or mark them.
- At the next stage, you need to unscrew the two nuts securing the clamp that holds the short circuit housing.
- After unscrewing the clamp nuts, you can remove the coil.
- Next, a new product is installed, all wires are connected according to the marks.
Assembly is carried out in reverse order.
Photo gallery “Replacing a short circuit on a VAZ 2106”
After installing a new short circuit, you need to check the operation of the internal combustion engine.
Lada Samara, 2113-2115
On carburetor models of VAZ cars of the Samara family (2113-2115), ignition coils 2111.3705 (analogous to Bosch F000 ZS0 211) are installed. These coils have a 3-pin connector and are used for VAZ cars with a microprocessor internal combustion engine control system based on the M7.9.7 controller or its analogues with 8-cl. engines.