Maybe I'm exaggerating, but it seems to me that every classic encountered such a problem. In the heat, when the car was moving (in my case it was a VAZ 2106), the car began to twitch or completely stall in the most inconvenient places (crossroads, on the highway, etc.). If you open the hood and look at the fuel filter at this time, you could notice that it is empty or there is very little gasoline there; when you try to manually pump gasoline from the fuel pump, you can understand that the fuel pump does not pump gasoline. Everyone solves this problem in their own way, I let the engines cool by 10-15 degrees, then moistened a rag, threw it on the gas pump, successfully started the engine and drove home. (I want to make a reservation right away, I always had a new fuel pump repair kit in the car, I have a DAAZ fuel pump. Pekar g * but there were two of them, the same problems with them.) In general, I removed the fuel pump, took it home, disassembled it, to my To my surprise, everything was fine with it, the diaphragms were not torn, the valves were normal, but since I had a repair kit, I replaced everything with a new one and installed it on the car. The problem has not gone away. Air jams still formed. Then I went to an auto store, bought a fuel pump pusher, it was 8.25 cm long, took off the old one, measured it, its length was 8.2, the difference in principle is not big, I installed a new pusher, drove it, and still the problem did not disappear. I no longer knew what the reason could be, I also went to the auto store, bought a rod with a pusher, removing the old rod with a pusher, I noticed that the rod was cracked, + in addition to all this, there is a 1mm thick gasket between the block and the rod, not order! There should be a gasket with a thickness of 0.27-0.3 mm... Next, installing a new rod + a new pusher that came with the rod, I adjusted the protrusion of the pusher to 1.1 mm (0.8-1.3 seems to be allowed). I installed a new fuel pump (because I had ruined the old one) and that was it, my problems disappeared. I still think that the problem was in the rod and an incorrectly installed gasket, but what’s most interesting is that we drove like this for almost 3 years, with an incorrectly installed gasket. But at the same time, every summer I had to buy a new fuel pump, because this only solved the problem of an air lock...
That's all, if someone solved this problem differently, please leave a comment, I will be very grateful to you
When operating the “seven”, one of the problematic components is the fuel pump. Sometimes its malfunctions have to be fixed urgently, “on the road”. Therefore, it will be useful for every owner of the “Seven” to know how the VAZ 2107 fuel pump (carburetor) works, what its main malfunctions are and how to repair it.
Functions and structure of the VAZ 2107 fuel pump (carburetor)
The fuel pump is a key component of the engine power supply system. The function of the pump is to supply gasoline from the fuel tank to the carburetor float chamber. The fuel pump on carburetor VAZ models is installed on the side of the cylinder block, inside the engine compartment.
The specific design of the pump makes the fuel pump one of the weak points of the power system. Contamination and poor quality gasoline, constant loads leading to natural wear of parts often cause unit failure. As a result, the gasoline supply stops and the engine stops working.
The VAZ 2107 fuel pump consists of the following parts:
- pusher;
- spring;
- balance;
- lid;
- cover screw;
- screw;
- mesh filter;
- membranes (working and safety);
- lower and upper plates;
- stock;
- valves (inlet and outlet);
- manual pumping lever.
The VAZ 2107 fuel pump works like this:
- The reciprocating movements of the pusher are ensured by the joint work of the drive cam and the return spring.
- working membranes move, creating alternately pressure and vacuum in the working chamber;
- when the pressure decreases, the exhaust valve closes, gasoline begins to flow from the gas line through the opening inlet valve;
- as the pressure increases, the inlet valve closes, and gasoline is pumped through the outlet valve into the hose leading to the carburetor.
The principle of operation of the VAZ fuel pressure regulator
To clearly control stable movement in the fuel rail, when the pressure is low, to send an alarm to the electronic control unit, and when the pressure is high, to let fuel flow through the return channel - these are the main tasks of the pressure regulator. Electronics has no logic; it is guided only by dry data. Depending on the car model and the number of special sensors, the source of the malfunction can be more or less accurately localized. In simple injection systems, such as in VAZ cars, diagnostics consists not so much in the ability to correctly read error codes on the diagnostic port, but in knowing the interconnection of system elements.
The fuel pressure regulator in power systems without a return channel is installed in the fuel tank; such systems are practically not used. The regulator that works with the recirculation system has three pipes.
- Inlet pipe.
- Atmospheric pressure control pipe.
- Fuel return channel pipe.
The regulator is technologically divided into two chambers, one of which is air, the second is fuel. They are separated by a membrane, which is under the action of a check valve spring. In that case. if the pressure in the system exceeds a certain parameter, and it is slightly different for all gasoline engines, then the spring is weakened, the pre-bypass valve opens and excess fuel goes back into the tank, where, passing through the filter, it again enters the fuel rail.
Reasons for the malfunction of the VAZ 2107 fuel pump
- Depressurization of the working chamber due to wear of the sealing gasket. This causes fuel to leak out of the pump or air to be sucked in instead of gasoline.
- Clogged valve channels (intake and exhaust), as a result of which the valves cease to perform their functions. The problem can be prevented by installing a fine filter in the fuel line in front of the fuel pump.
- Wear and distortion of valve parts. The result of the misalignment is the same as when the valves are clogged, but identifying and eliminating the problem is quite difficult.
- Rupture of the working membrane. Pressure drops cease to form in the working chamber, and the pump loses its functionality.
- Damage to the safety chamber. Gasoline begins to enter the engine crankcase, where it dilutes the engine oil. If the problem is not noticed in time, the engine may seize.
Main malfunctions of the regulator
As can be seen from the design of the device, there is practically nothing to break there. Over time, the spring may lose elasticity, and then the pressure will change and the engine will not receive the required amount of gasoline. In this case, the electronic control unit will try to make the mixture as rich as possible, adjusting the ignition timing to the lean mixture, and this already causes incorrect operation of the engine and excessive consumption of gasoline. But the main indicators that the pressure regulator requires at least checking are:
- unstable engine operation at idle;
- the engine often stalls when moving from a stop at minimum or idle speed;
- unstable speed, floating engine speed;
- deterioration in dynamics;
- excessive fuel consumption;
- difficult start-up after a long period of parking;
- power drop.
And it is intuitively clear that the engine is choking, judging by its operation. These symptoms are characteristic not only of the pressure regulator, but if all of them are present in full, then it makes sense to check, and most likely replace the regulator.
Troubleshooting the VAZ 2107 fuel pump
Before checking the fuel pump, it is advisable to stock up on M8 bolts or other products of a similar diameter that can serve as plugs for fuel hoses.
To check the VAZ 2107 fuel pump, you must perform the following steps:
- Loosen the hose clamp that supplies gasoline to the carburetor and remove the hose from the fitting.
- Plug the fuel hose to prevent fuel from spilling out.
- Pump the fuel pump manual drive lever several times. If a stream of gasoline comes out of the outlet fitting, the fuel pump is working. If not, the check should continue.
- Loosen the inlet hose clamp, remove the hose and plug it in the same way as before.
- Close the inlet fitting with your finger and pump the hand drive lever several times. If there is a noticeable vacuum, the problem is not in the fuel pump. If the finger does not “stick”, it is necessary to remove and repair or replace the fuel pump.
Fuel pump and problems associated with it
Natural wear or damage to the diaphragm, loss of spring elasticity, clogged, tarred or stuck valves, clogged filter and loss of tightness - all of the above can interfere with the flow of fuel to the carburetor.
In addition, fuel leakage caused by loss of tightness is fraught with fire hazards and leads to significant fuel losses. It is estimated that the loss of one drop of gasoline per second results in an annual loss of 675 kg.
With the help of modern diagnostic equipment at service stations, it is possible to quite simply determine the performance of the fuel pump by measuring the pressure in the discharge pipeline and the vacuum in front of the fuel pump. This way the condition of the main working parts is revealed: diaphragm, valves, springs.
In “self-service” conditions, we can recommend old, but fairly reliable methods for checking a gasoline pump and troubleshooting its parts without the use of special equipment.
Replacing the fuel pump VAZ 2107
The easiest way to restore engine operation if the fuel pump breaks down is to replace the latter. Replacing the VAZ 2107 fuel pump is done as follows:
- clean the area where the fuel pump meets the cylinder block using white spirit or WD-40;
- loosen the fuel hose clamps;
- remove the hoses and plug them with M8 bolts or something similar, for example. plastic choppers;
- Using a 13mm wrench, unscrew the two nuts securing the fuel pump to the engine;
- remove the old fuel pump from the studs and install a new one;
- secure the new fuel pump with nuts;
- connect the fuel hoses and tighten the clamps.
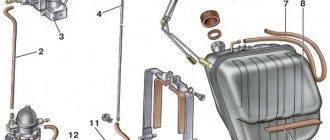
Fuel pump drive
The VAZ 2107 mechanical fuel pump is driven by a pusher and an eccentric. Among drivers, it is customary to call the pusher a rod, although the rod is another part of the fuel pump. The eccentric is located on the intermediate shaft, which operates from the gas distribution mechanism.
The fuel pump drive includes (see figure):
- 1 - pusher;
- 2 — heat-insulating spacer;
- 4 — adjusting gasket;
- 5 - sealing gasket;
- roller (cam).
Device and principle of operation
The operation of the mechanical fuel pump drive is not based on the fact that:
- the oil pump shaft is driven through a timing chain;
- the cam (or eccentric) begins to press cyclically on the pusher;
- The pusher transmits force to the lever and the fuel pump begins to pump fuel.
Drive faults
Problems with the mechanical fuel pump drive lead to interruptions in the operation of the fuel supply system. Actuator malfunctions are most often associated with deformation or excessive wear of the pushrod or cam.
Fuel pump rod bends
The fuel pump pusher is often made of metal that is not strong enough. There are often cases when, after 2–3 thousand kilometers, such a pusher bends and flattens the constant impact of the cam. The length of the pusher should be 82.5 mm. If your fuel pump tappet does not meet this size and is flattened on the cam side, it will need to be replaced.
Repair of fuel pump VAZ 2107
Repairing the VAZ 2107 fuel pump instead of replacing it is a much more rational decision from a financial point of view. To do this, you need to remove the unit. The procedure for removing the fuel pump is described in the previous section “Replacing the VAZ 2107 fuel pump”.
After the fuel pump is removed, you can begin to disassemble it and check the parts for damage or wear.
It's worth starting with gaskets. The thickness of the gasket between the fuel pump and the thermal insulating plastic spacer must be more than 0.3 millimeters. The gasket between the spacer and the cylinder block must be thicker than 0.8 millimeters.
The most common failure of a fuel pump is a rupture of the working diaphragm. To replace it, you need to unscrew the cover bolt and pull out the diaphragm assembly (rod with attached diaphragms). To replace them, simply unscrew the nut on the rod. You should also check the serviceability of the return spring and replace it if necessary.
When the cover is removed, the strainer becomes accessible and should be cleaned of dirt and inspected for damage before reinstalling.
The fuel pump valve channels should be cleaned and checked to see if they are loose in their seats. If play is noticeable, the valve should be replaced. If the cause of the play is a broken seat, the malfunction cannot be eliminated. You only need to replace the fuel pump.
In some cases, the tightness of the working chamber of the fuel pump is broken due to deformation of the cover. In this case, you can try to select and install a whole cover from an old fuel pump.
The fuel systems of classic VAZ models, such as 2106 and 2107, differ in the type of supply of the combustible mixture to the cylinders. For some, the carburetor is responsible for this, for others, the injector. However, the coordinated operation of the power unit for both depends not on the design of the system, but on the serviceability of its elements, and primarily the fuel pump. Every car enthusiast should, if necessary, be able to repair and replace this element with his own hands.
Fuel pump drive
The VAZ 2107 mechanical fuel pump is driven by a pusher and an eccentric. Among drivers, it is customary to call the pusher a rod, although the rod is another part of the fuel pump. The eccentric is located on the intermediate shaft, which operates from the gas distribution mechanism.
The fuel pump drive includes (see figure):
- 1 - pusher;
- 2 — heat-insulating spacer;
- 4 — adjusting gasket;
- 5 - sealing gasket;
- roller (cam).
The pusher is driven by an eccentric located on the shaft of the auxiliary mechanisms
Device and principle of operation
The operation of the mechanical fuel pump drive is not based on the fact that:
- the oil pump shaft is driven through a timing chain;
- the cam (or eccentric) begins to press cyclically on the pusher;
- The pusher transmits force to the lever and the fuel pump begins to pump fuel.
Drive faults
Problems with the mechanical fuel pump drive lead to interruptions in the operation of the fuel supply system. Actuator malfunctions are most often associated with deformation or excessive wear of the pushrod or cam.
Fuel pump rod bends
The fuel pump pusher is often made of metal that is not strong enough. There are often cases when, after 2–3 thousand kilometers, such a pusher bends and flattens the constant impact of the cam. The length of the pusher should be 82.5 mm. If your fuel pump tappet does not meet this size and is flattened on the cam side, it will need to be replaced.
If the fuel pump pusher is flattened on the cam side, it needs to be replaced.
What fuel pumps were equipped with classic VAZ models?
Classic VAZs include all models of the Zhiguli family, produced from 1970 to 2012 and their modifications:
- VAZ 2101;
- VAZ 2102;
- VAZ 2103;
- VAZ 2104;
- VAZ 2105;
- VAZ 2106;
- VAZ 2107.
Depending on the year of manufacture, the engines of these vehicles were equipped with different fuel systems. In all the first Zhiguli models, the fuel mixture was injected into the cylinders using a carburetor, and the fuel was supplied by a mechanical fuel pump. The latest modifications of the VAZ 2104, 2105 and 2107 had an injection system and an electric fuel pump.
Carburetor cars of the Zhiguli family were equipped from the factory with mechanical fuel pumps of the diaphragm type DAAZ 2101 (catalog number 1106010) produced by the Dimitrovgrad Automotive Unit Plant. Thanks to their simple design, reliability and maintainability, they have proven themselves well not only on the “classics”, but also on cars of the Sputnik and Samara families, which were equipped with their modified versions.
Carburetor VAZ 2101–2107 were equipped with DAAZ mechanical fuel pumps
Injection Zhiguli models were equipped with domestically produced electric fuel pumps. They were produced by the Pekar and Utes enterprises under catalog number 21073–1139009. The latest modifications of the Zhiguli were equipped with products (catalog number 2112–1139009). The same devices were installed on all models of the Samara and Lada families.
Injection models of classic VAZs were equipped with electric fuel pumps “Pekar”, “Utes”, “Bosch”
Fuel pressure regulator - signs of malfunction
The control system of any modern engine with an injection system consists of a huge number of sensors that depend on one another, and together they report to the electronic control unit about the condition of the engine. Based on this data, the ECU adjusts the main characteristics of fuel formation, the operation of the ignition system, right down to the operation of the transmission. And if one sensor or regulator gives incorrect readings, the engine will not work correctly. The fuel pressure regulator is also an important element for monitoring engine condition.
Checking, repairing and replacing a mechanical fuel pump
Methods for diagnosing fuel pumps for carburetor and injection engines of Zhiguli are also different. Checking a mechanical pump consists of determining its performance, as well as assessing the condition and performance of its component elements.
How to check the performance of a mechanical fuel pump
The productivity of the DAAZ mechanical pump is 1 liter per minute. To check the amount of pumped fuel you will need:
- a piece of gas-resistant hose (50–80 cm);
- 2 clean containers with a volume of at least 2 liters (plastic bottles are acceptable);
- 1.5 liters of gasoline;
- watch with stopwatch;
- crosshead screwdriver;
- assistant.
- Using a screwdriver, unscrew the screw on the clamp of the pump outlet fitting. We remove the hose from it.
Remove the fuel hose from the outlet fitting
We estimate the amount of fuel pumped by the pump per minute
If the amount of gasoline is less than 1 liter, the fuel pump is faulty.
Assessment of the condition and performance of component parts
The following pump elements must be checked:
- intake and exhaust valves;
- mesh filter;
- diaphragms;
- pusher (rod).
Design of the DAAZ fuel pump
- crosshead screwdriver;
- slotted screwdriver;
- key to 10;
- key to 13;
- caliper or ruler.
- Loosen the screws of the clamps of the inlet and outlet fittings of the pump, remove the hoses from them. We place a finger on the outlet fitting, and with the other hand we press the manual pumping lever several times. You should feel the air escaping under pressure with your finger. Next, plug the inlet fitting with your finger and pump it up manually again. A vacuum should be felt at the pump inlet, i.e. the finger should be sucked inside the fitting. If nothing like this happens, the valves of the device are faulty and must be replaced.
Checking the valves consists of determining the air pressure at the outlet fitting and the vacuum at the intake
The mesh filter should not show signs of damage or deformation
If the pump diaphragms are damaged or deformed, they must be replaced.
Removing the pump thermal spacer
The length of the pusher should be 82.5 mm
Do-it-yourself repair of a mechanical fuel pump
It is not advisable to purchase faulty fuel pump parts separately. It is much more profitable to purchase a repair kit, which includes elements that may fail, namely:
- valves;
- set of diaphragms;
- pusher;
- thermal spacer;
- gaskets and washers.
Fuel pump repair kit
Repairing a fuel pump involves dismantling and disassembling it. They are produced according to the same algorithm that was described earlier in the diagnostics section. If, after disassembling the fuel pump body, you find that there is dirty deposits or debris on its walls or on the inner surfaces of the fittings, clean them with carburetor cleaning fluid and a piece of coarse cloth. When removing plaque, use a small wooden spatula and toothpicks. It is highly undesirable to use metal objects for these purposes.
To replace the pump valves, they will need to be removed from their seats. To do this, using a thin slotted screwdriver or knife, you need to knock out three cored areas in each of the sockets, after which the valves will come out of them freely. Having installed new parts in place of the faulty ones, the sockets must be cored again by hitting the edge with a core (screwdriver) in three places.
Replacing fuel pump valves
Important: when replacing valves, do not confuse the intake and exhaust!
In order to replace the diaphragms, you need to unscrew the nut in the upper part of the rod on which they are mounted with a 10mm wrench, then remove them and install new ones in their place in a certain order. The lowest diaphragm is the safety diaphragm. This is followed by a small and large spacer, and on top of them are two other (working) membranes.
As for the thermal spacer, it rarely fails. More often there is a manufacturing defect, which manifests itself in the unevenness of the mating plane to which the pump housing is attached. This may cause oil leakage. To replace the spacer, remove the old one from its seat, remove the old gasket from under it, and install a new spacer with the corresponding gasket from the repair kit.
Installing pump gaskets
The DAAZ fuel pump repair kit includes three gaskets of different thicknesses:
Gasket “A” is installed between the cylinder block and the thermal spacer, and the other two are used to adjust the protrusion of the pusher (rod) above the mating plane of the spacer.
Determination of the protrusion of the pusher
We install the new rod in place, and slowly turn the engine crankshaft (using the wrench on the pulley nut), select the position when the rod is extended to its minimum length. We place gasket “B” on the mating plane of the spacer and measure the amount of rod overhang above it with a caliper. It should be 0.8–1.3 mm. If the offset is greater, instead of spacer “B” you need to install spacer “C”, and if it is less, swap the first and second positions. Having achieved the result, we put the fuel pump in place and secure it with nuts. For greater tightness of the joint, the gaskets can be lubricated with a thin layer of automotive sealant.
How to clean a carburetor
Before you start cleaning the carburetor, you need to carefully prepare: buy a special aerosol cleaner at a car shop, arm yourself with smooth, dry cloths, a tire inflator, remove the carburetor and disassemble it.
Jets—fuel and gas supply channels—are cleaned with compressed air or a liquid cleaner under pressure. Mechanical cleaning with any fleecy or metal objects is prohibited.
When cleaning the jets with compressed air (you can use a tire pump for this), the body of the idle jets, the main metering system (air and fuel), then the valves and channels of the pump sprayer are blown out.
In case of severe contamination, the jets are placed in acetone so that the deposits soften or completely dissolve. Then they should be blown out.
| Hole diameter, mm | First camera | Second camera |
| Main fuel jet | 1,35 | 1,25 |
| Air jet | 1,70 | 1,90 |
| Idle fuel jet | 0,45 | 0,60 |
| Idle air jet | 1,80 | 0,70 |
| Accelerator pump nozzle | 0,50 | — |
| Accelerator pump bypass jet | 0,40 | — |
| Fuel nozzle of enrichment device | — | 1,50 |
| Emulsion nozzle of the enrichment device | — | 1,70 |
| Air jet of enrichment device | 0,70 | — |
Flushing the float system To get to the carburetor float system, you must:
- Remove the air filter and fuel hose clamps.
- Disconnect the cable that controls the starting device.
- Remove the electrical connector on the solenoid valve.
- Then unscrew the fastening bolts and, without turning over, remove the carburetor cover.
It is best to clean the float compartment with a rubber bulb, carefully drawing out any remaining fuel from the chamber. You should not use fluffy rags - they can accidentally clog the jets.
To complete the cleaning, you can wipe the bottom of the float chamber with a stiff brush.
To check how well you have cleaned the float chamber, you need to unscrew the air jets and blow out the emulsion wells. If dirt appears in them, washing should be repeated and checked in the same way.
Flushing the throttle valve
It is produced using a cleaner, which can be purchased at a specialized auto store.
- The throttle valve itself is washed, as well as all accessible elements, channels, valves, etc. Particular attention should be paid to the forced crankcase ventilation channel, since it becomes clogged more often and more severely than other parts.
- After this, the idle speed sensor is unscrewed and the internal elements are washed.
- The procedure is repeated again.
Video: how to clean the throttle valve on a VAZ
Diagnostics and replacement of the electric fuel pump on cars of the Zhiguli family
In injection engines of classic VAZs, the fuel pump may lose its functionality both due to problems with the power supply to it and due to a malfunction of its electric motor. In the first case, the situation can be corrected by diagnosing and repairing the electrical circuit of the device. But if the electric motor of the pump fails, only replacing it will help.
Checking the protection devices for the electrical circuit of the fuel pump on injection VAZs of the Zhiguli family
If there is a problem with the electrical equipment of the fuel pump circuit, it usually does not turn on at all. Turn on the car's ignition without starting the engine and listen. First, you should hear a click from the relay, and then a characteristic “squeal” emitted by the pump’s electric motor. If you don’t hear anything like this, start diagnosing with the electrical circuit of the device.
The pump circuit is connected to the on-board network via a separate relay, and its protection is provided by a fuse. Both of these devices are located in the vehicle's optional mounting block. You will find it under the glove box. It contains 3 relays and 3 fuses. The fuel pump relay (indicated R2 in the diagram) is located in the middle, and the fuse (F3) is to the left of it. We pull the fuse out of its seat and check it by “ringing” it with a tester. If a malfunction is detected, we replace it, not forgetting to comply with the rating (15 A).
You can check the functionality of the relay by installing a known working device in its place. Instead, replace it with the relay located to the right of the one being diagnosed, which is responsible for the radiator fan circuit. If this option does not suit you, turn on the ignition and measure the voltage between the pink wire going to the relay and the vehicle ground. The device should show 12 V. This means that the device is powered. After this, you need to connect the pink wire with the gray one at the relay terminals. So we will connect the fuel pump directly to the battery. If it works (that same “squealing” sound will be heard), simply replace the relay.
The fuel pump relay is located in the middle (R2), and the fuse is located to the left of it (F3)
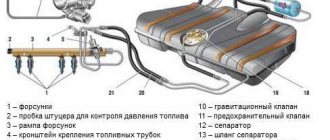
Checking the fuel pressure in the system
The main indicator of the operation of a fuel pump is the pressure it creates in the system. If the device turns on, pumps fuel, but the engine runs intermittently, take the time to check the pressure. To do this, you will need a pressure gauge with a measuring range of 5–7, equipped with a gas-resistant hose and a threaded fitting (if there is no special one, you can use a regular tire pressure gauge). The sequence of actions is as follows:
- On the fuel rail we find a fitting closed with a plastic cap. Unscrew the cap and connect the pressure gauge hose to the fitting. If your device is not equipped with a special threaded fitting, the hose can be secured to the “nipple” using a small clamp.
Pressure connection
The pressure in the ramp should be 2.8–3.2 atmospheres
When removing the vacuum hose from the regulator, the pressure should drop by 0.2–0.7 atmospheres
Replacing the fuel pump on injection Zhiguli cars
You can replace the fuel pump either as an assembly (install a new fuel module) or separately (change only the pump). The cost of a new domestically produced module with a fuel level sensor is 2800–3000 rubles. The production pump itself will cost 500 rubles less.
Replacement Tools:
- slotted and Phillips screwdrivers;
- key to 10;
- key to 7.
Work order:
- Disconnect the negative terminal from the battery.
- Open the gas tank cap.
- Using a slotted screwdriver, remove the rubber apron from the neck of the tank. Disconnect the safety valve tube from it.
Use a slotted screwdriver to pry off the apron
Unscrew the screws securing the gas tank trim
Unscrew the tank clamp bolt
Disconnect the electrical wiring, fuel line hoses, unscrew the nuts securing the fuel module cover
Removing the fuel module from the gas tank
Disconnect the fuel filter
Disconnect the pump power cables
Use a screwdriver to move the clamps and remove the pump from the casing.
Disconnect the tube from the outlet fitting
After installing the pump, it is advisable to check the pressure in the system as described above.
Replacing the fuel pump in cars of the Zhiguli family does not require the car owner to have extensive knowledge in the field of auto repair, and does not take a lot of time and money. It can be done without any problems in a garage, or right on the street. However, if you do not have the necessary tools or the desire to do this yourself, it is better to turn to specialists.
Fuel pressure sensor VAZ 2105 injector
- To the beginning of the forum
- Forum Rules
- Old design
- FAQ
- Search
- Users
I measured the pressure in the fuel rail (21053 engineer): 1. Only the fuel pump without the engine 2.8 2. I start the engine and at idle 2.4 3. I remove the flexible hose from the pressure regulator (to the receiver) pressure 2.8
Are these normal readings, or do I have problems with the fuel pump (in the murzilka it says there is no change in pressure)
Tell me what indicators should be for an engineer. classics? (data from 21073 engineer -> suitable)
Thank you in advance, Konstantin
Judging by the Murzilka it should be 2.8 at XX, and with the hose removed 3.3 (approximately)?
It confuses me that 2.8 is when I remove the hose from the regulator, but on XX I have 2.4. This is fine ?
That's exactly what happened to me. During the operation, two pressure regulators and two pumps were used (one Czech, the other Bosch), the readings were the same.
The prerequisites are there, the car is slowly picking up speed, i.e. I’m easily overtaken by the carburetor classic (on third) + increased fuel consumption (10-11 liters in the city), although maybe I’m worrying about fuel consumption in vain.
I suspected the fuel pressure regulator and checked the pressure (I bought a new pressure gauge to measure it), the regulator seems to be in order, but I don’t like the pressure.
I'll check the pressure with another pressure gauge (I'll pick up a different company) and suddenly the pressure gauge is defective.
But I want to know how the pressure behaves on YOUR working machines, because... Murzilka tells me about the need to sequentially replace the fuel pump grid and then the pump itself, I just don’t have another working pump to test yet, buy a new pump and then understand that everything was fine with me, probably not a very good idea.
Help, give me pressure readings from a working machine (I think there are some)
the car slowly picks up speed, i.e. me easily
outperforms the classic carburetor (in third) + increased fuel consumption (10-11l in the city)
What about pressure? what should it be on XX?
Thank you ! I understand that my pressure is below normal, I will try to replace the fuel pump grid and then the pump itself.
you have nothing else to do?
pressure at xx 2.2-2.4 normal when removing the RDT hose 2.8-3 when over-gasping 2.8-3 when compressing the return line more than 4 ideally 6
besides, the pressure created by the pump does not affect the speed and dynamics
you have nothing else to do?
pressure at xx 2.2-2.4 is normal
when removing the hose RDT 2.8-3
it diverges from the Murzilka and everything turns out fine for me?
Source
Carburetor adjustment
After cleaning and repairing the carburetor, it should be adjusted.
How to set the fuel level
- First you need to adjust the float, which primarily affects fuel consumption.
- Unscrew the screws securing the cover and, for convenience, place it vertically. Make sure that the needle lightly touches the float.
- Check that the gap between the cover with the gasket installed on it and the bottom of the float is 6.2 ± 0.25 mm. If there is a discrepancy, correct it by moving the float tongue.
- After this, check the movement of the float. Its value should be 8±0.25 mm.
Video: how to adjust the fuel level in a VAZ carburetor
Adjusting the starter
- To do this, the carburetor must be installed on the engine, but not covered with an air filter. After this, pull out the choke as much as possible.
- Then you need to warm up the engine and use a screwdriver to open the air damper a third. The throttle linkage must be adjusted to 3200–3400 rpm.
- Then lower the throttle and reduce the speed to 2800–3000 per minute.
Do not overlook the hole for the plug - it must be clamped so that rarefied air is formed under the diaphragm of the starting device.
Idle adjustment
Performed with a warm engine. Only the quality screw is engaged.
- Using the quality screw, we accelerate the engine speed to the maximum level.
- After this, use the quantity screw to increase the rotation speed by 100–150 revolutions and, without stopping the engine, reduce the speed by the same number, but using the quality screw.
This operation completes the engine adjustment and ensures high-quality and stable operation with the minimum permissible amount of carbon monoxide.
Using the quality screw, you can lean or enrich the fuel mixture - it is responsible for the supply of gasoline, and tightening it leans the fuel mixture, and unscrewing it, on the contrary, enriches it.
When and why you need to change/clean the fuel pump screen
Let's start with the fact that general problems with the fuel system (fuel pump in particular) should be divided into the most common groups:
- the fuel pump mesh and fuel filter are clogged;
- the fuel pump itself has failed;
- injector problems;
Let us add that we should also not exclude the possibility of air leaks, that is, airing of the power system. Another culprit of problems may be the pressure regulator in the fuel rail. In this case, engine malfunctions may be partially similar to some of the symptoms mentioned above. For example, a slight ingress of air into the fuel system results in the engine not starting for a long time after parking.
We also recommend reading the article on how to determine airing of the power system using the example of a diesel engine. From this article you will learn how to check the fuel system for leaks yourself.
Let's go back to the fuel pump. Its malfunction means that the performance of the fuel supply system is reduced. If the fuel pump breaks down, then the car becomes unsuitable for normal use. Signs of a fuel pump malfunction are as follows:
- It is impossible to start the engine, the fuel pump does not pump;
- the engine starts, but runs with serious interruptions;
In this case, the service often recommends diagnosing, repairing or replacing the fuel pump. It should also be taken into account that the fuel pump mesh filter may become clogged inside the device. Let us immediately note that it is impossible to accurately answer the question of when to clean the fuel pump stack. Some car enthusiasts clean/replace the fuel pump mesh as needed or as a preventative measure every 50-70 thousand km. mileage, while others are faced with the need to clean the fuel pump grid for the first time at mileages of 150 thousand km or more. and more. Let us add that the operating manual for some models specifically states that it is recommended to replace the fuel pump stack once every 120 thousand km.
It should be added that the loss of dynamics and the appearance of symptoms of a clogged mesh occurs gradually. For this reason, each driver decides to clean the fuel pump himself. On powerful naturally aspirated engines, the gradual deterioration in acceleration is not felt as strongly as compared to highly accelerated engines with a small displacement. For this reason, many owners of large-volume trucks begin to solve the problem after noticeable complications appear. Also, the condition of the pump grid is greatly influenced by the quality of the fuel being filled and a number of other factors and individual operating conditions, which we will talk about a little later.