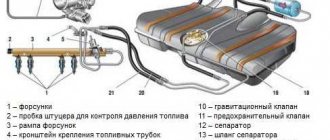
How to independently measure the pressure in the fuel rail of a car and why is it necessary????
Checking the fuel rail pressure is a standard procedure in a long chain of diagnosing engine and fuel system malfunctions.
Often this check is carried out in cases where the engine runs unevenly and there are dips during acceleration. This is one of the mandatory check points if the car jerks during acceleration. I described this in the article “Why does a car jerk during acceleration and acceleration.” Also, this diagnosis is performed in cases where the car has increased fuel consumption.
Cleaning the diesel engine fuel system
When using diesel fuel of inadequate quality with a high content of sulfur elements, the working parts of the fuel system become covered with harmful deposits and become inoperable. In particular, the injector holes become clogged with build-up that has hardened under the influence of high temperatures. Under the influence of the listed factors, the following occurs: a decrease in the throughput of the nozzles, a change in the direction of the spray pattern, etc. The car owner faces a natural problem of how to pump the fuel system of a diesel engine.
It is best to entrust system cleansing activities to professionals. If special equipment is available, the injectors are dismantled and checked on diagnostic stands. However, this method is highly labor-intensive with significant material costs.
Experienced drivers flush the fuel system of a diesel engine with their own hands in a garage. At the same time, they use a simplified technique - adding a special liquid to the fuel tank. This procedure is recommended to be carried out every 3 – 5,000 kilometers.
The most popular cleaning products for diesel injectors among car owners are:
- Laurel.
- Liquid moly.
- High Gear.
When choosing the best cleaner for the fuel system of your car, you need to study the features of each product and read consumer reviews. Thanks to timely maintenance of a diesel engine, the service life of your vehicle is significantly increased and the technical characteristics of your vehicle are improved.
Preparing for measurements
We string a hose onto the inlet fitting of the pressure gauge and secure it with a clamp - we must avoid pressure losses during measurements.
Then you need to remove the cap from the fuel rail. There will be a nipple under it - remove that too. Be careful - if you recently started the car, there will be residual pressure in the fuel system and gasoline may spill out, so have a cloth ready and try to protect your eyes.
When you have removed the plug and nipple, install the second end of the hose that goes to the pressure gauge. We also fix everything with clamps.
Fuel pressure regulator repair
After the diagnostics of the system is completed and the sealing ring is inspected, the umbrella is unscrewed from the fitting. You can unscrew it using the metal valve cap. The pressure gauge hose is then connected to the fitting, then the entire structure is secured using clamps. Pressure measurements are carried out only when the engine is running. Standard pressure readings should be 2.9-3.3 kg/cm2. Then the hose is carefully disconnected from the fuel pressure regulator, and the pressure gauge readings are recorded: the pressure should increase to 70 kPa from 20 kPa.
The fuel pressure regulator is changed if the readings remain too low or zero. Replacing this part is not difficult: you can do it yourself in a regular garage. Before starting the procedure, all pressure is released from the engine power system. To do this, unscrew the nut securing the fuel pipe, after which the bolts that secure the regulator itself to the fuel rail on most cars with injection engines are unscrewed.
Subsequently, the regulator fitting is carefully removed from the hole in the fuel rail, after which the RTD is completely dismantled. Before this, the fuel pipe is completely disconnected. The last stage is the installation of a new or working regulator into the ramp, after which the functionality and serviceability of the entire fuel system is checked using a pressure gauge.
Before installing a new fuel pressure regulator, experts recommend lubricating the O-rings with gasoline: this will make installation of the new part easier. A similar procedure is performed when replacing the o-rings themselves.
Measuring process
Fuel pressure must be measured in 4 operating modes, that is, 4 different measurements will be required.
With the ignition on
When the ignition is turned on, the fuel pump must supply the system with the fuel needed to start the engine. Therefore, we simply turn on the ignition and look at the readings. The pressure must be above 3 atmospheres.
Idling
Just start the engine and look at the pressure gauge readings. Normal pressure is 2.5-2.7 atmospheres.
When the return line is turned off
Almost all modern cars have a fuel pressure regulator. It is aimed at preventing excessive pressure from being created in the system. When the limits are reached, it resets the pressure to normal. We clamp the return pipe and get the result on the pressure gauge.
It should be about 7 atmospheres. If you have a 6 atmosphere pressure gauge, the needle should be “filled up”.
Under loads
And one more stage of measurement is the measurement of pressure drops under loads. Just apply the throttle (you can just “tug” the throttle cable if you have a mechanical one) and observe the changes.
During recharging, the pressure should be about 3 atmospheres, and then drop to the idle value - that is, up to 2.5 atmospheres.
The main symptoms of fuel pressure regulator problems
When diagnosing the engine power system, it is necessary to take into account the signs of a malfunction of the fuel pressure regulator. The main symptoms associated with RTD problems are a decrease in engine power and its inability to reach the required speed. Signs of a malfunction of the fuel pressure regulator and, accordingly, the engine are as follows:
- The engine idles unsteadily and stalls.
- Fuel consumption increases, power decreases.
- The engine responds slowly to the accelerator pedal.
- When accelerating the car and when changing the throttle, jerks and dips appear.
- The car does not gain speed and does not accelerate.
Important to remember
When you check the fuel pressure with the ignition on, note that after the ignition is turned off, the pressure in the rail drops to 0.7-1 atmosphere and remains at this level. If it drops to 0, the problem is in the fuel pressure regulator.
Try increasing the number of revolutions to 3000 - if the pressure gauge needle does not stay constant, but falls, this may mean that it is time to change the fuel pump.
If the pressure builds up for a very long time or is lower than required, the fuel filter, fuel pump filter or fuel line may be clogged.
I hope you found it interesting and will take note of this. Subscribe to the channel and give it a thumbs up to see even more interesting articles on automotive topics in your feed every day.
Source
How to measure cylinder pressure
Compression readings are taken using a special device - a compression meter. The compression gauge works on the principle of a pressure gauge: an adapter with an injector or glow plug tip design is designed to be installed in the cylinder head and has a shut-off valve that prevents pressure loss during measurements. Simple devices are equipped with a regular scale with an arrow, more precise professional devices are electronic digital or synchronized with a computer.
Attention! The compression meter must be calibrated with an accuracy of 0.1 kgf/cm² - otherwise the measurement results will not meet the standards.
Before the measurement, the diesel engine is warmed up at maximum speed to the operating oil temperature, the operation of the starter and the state of charge of the battery is checked at 100%. Each cylinder is measured separately.
- Remove the glow plug or injector from the block head (depending on the type of diesel unit);
- the compression gauge adapter fitting is inserted into place of the spark plug (injector), making sure that the standard connection is tight;
- turn on the ignition without starting the engine until the starter turns - the primary revolution of the crankshaft (rotation speed must be at least 200 rpm);
- take the measurement result (at the top dead center of the cylinder stroke);
- measure compression in the remaining cylinders in a similar way;
- check the compression indicators of all cylinders;
- then about 50 ml of oil is injected into each cylinder;
- the crankshaft is turned as many times as possible using the starter with the injectors (candles) removed;
- install the injectors in place and take new measurements on each cylinder again;
- check the difference in readings with the first measurement.
Learning Common Rail: all the way
The first production cars with this system, developed by , appeared in 1996. It gets its name from a single ramp from where fuel is supplied to the injectors. The main advantage of the system is a sufficiently high fuel pressure in all engine operating modes, which contributes to better mixture formation in the combustion zone and complete combustion. While maintaining the moderate appetite of its predecessors, the CR diesel better meets environmental standards, and such a car is often more dynamic than a gasoline car and is almost as quiet.
The heart of the system is the high-pressure fuel pump, a compact device with one, two or three plungers and a mechanical drive. The injection pump housing is made of aluminum alloy, the plunger sleeves are steel. To prevent the pump from wasting fuel at idle and at low loads, on some three-piston pumps one section is automatically turned off, while double-piston pumps are regulated by dosing devices. To the fuel injection pump itself, fuel is supplied from the tank under a pressure of 6-7 bar by a booster pump. He's either gear
chatted and built into the fuel injection pump housing, or electric - in the fuel intake module or in the line.
Nozzle
The injector serves to supply fuel into the engine cylinder under high pressure in a finely atomized form.
A typical injector includes a body 5 with a spray nozzle 3, a guide pin 4 and a union nut 2, a spray needle 1 with a rod b, a spring 7 with a support washer, an adjusting screw 9 and a bushing 8, a cap nut 10 and a fuel inlet fitting 12 with a strainer 11 The sprayer and the needle must be very precisely adjusted to each other. In the upper part of the atomizer there is one annular and several (most often three) vertical fuel channels, and in the lower part there are central inlet and outlet channels with spray holes. The diameter of these holes is 0.2...0.4 mm. The needle closes the exit channel with its lower conical end. The sprayer is tightly attached to the nozzle body using a union nut. The fuel channel of the housing is connected to the annular channel of the atomizer through its vertical channels. The correct position of the sprayer relative to the body is ensured by a guide pin.
Rice. Nozzle: 1 — spray needle; 2 - union nut; 3 - sprayer; 4 - guide pin; 5 — nozzle body; 6 — rod; 7 - spring; 8 — bushing; 9 — adjusting screw; 10 - cap nut; 11 - mesh filter; 12 — fuel inlet fitting
Fuel supplied to the nozzle through the fuel inlet fitting passes through a strainer and enters its annular cavity through the fuel channels of the housing in the upper part of the nozzle. Upon reaching the required pressure in this cavity, which acts, among other things, on the conical belt of the needle, it rises upward, overcoming the resistance of the spring. At this time, the outlet channel opens, and fuel flows through it and the spray holes into the combustion chamber of the engine cylinder.
After the pumping section of the injection pump stops supplying fuel and the pressure drops, the needle sits back in its seat, stopping fuel injection. The fuel that has leaked through the leaks enters the upper part of the nozzle and through the holes in screw 9 and nut 10 through a special pipeline is drained into tank 7 to collect fuel.
Injector repair kit.
Already in the mode of cranking the crankshaft with the starter, the injection pump creates a starting pressure of 350-400 bar. At minimum idle speed - up to 500-600 bar, and at maximum load - up to 1300-1500 bar. There are pumps with pressure up to 2000 bar. Its value is set by a regulator located on the fuel injection pump housing or on the ramp and subordinate to the electronic engine control unit. When issuing commands, the ECU relies on signals from the rail pressure sensor.
Fuel is supplied through high-pressure pipes to the injectors, which open under the influence of an electrical signal. There are two design options - electromagnetic or with a piezoelectric element. The first one was not particularly fast at first, which forced the designers to look for an alternative. In a piezo injector, voltage is applied to a piezo crystal, which instantly expands. The spool compresses the spring, the injector needle opens the way for fuel - and it is injected into the combustion chamber. However, designers continue to improve electromagnetic devices - both options work successfully on modern engines.
Features of diesel fuel
Most of the requirements for the diesel engine power system are put forward taking into account the fact that diesel fuel has a number of specific features. This type of fuel is a mixture of kerosene and gas oil diesel fractions. Diesel fuel is obtained after gasoline is distilled from oil.
Diesel fuel has a number of properties, the main one of which is considered to be the self-ignition index, which is estimated by the cetane number. The types of diesel fuel available for sale have a cetane number of 45–50. For modern diesel units, the best fuel is fuel with a high cetane number.
The power supply system of a diesel internal combustion engine ensures the supply of well-purified diesel fuel to the cylinders, the injection pump compresses the fuel to high pressure, and the nozzle supplies it sprayed into small particles into the combustion chamber. Atomized diesel fuel is mixed with hot (700–900 °C) air, which is heated to such a temperature from high compression in the cylinders (3–5 MPa) and self-ignites.
Please note that the working mixture in a diesel engine is not ignited by a separate device, but ignites independently from contact with heated air under pressure. This feature greatly distinguishes diesel internal combustion engines from their gasoline counterparts.
Diesel fuel also has a higher density compared to gasoline and also has better lubricity. An equally important characteristic is the viscosity, pour point and purity of diesel fuel. The pour point allows the fuel to be divided into three basic types of fuel: summer diesel fuel, winter diesel fuel and Arctic diesel fuel.
WE DIAGNOSE
There is a minimum of equipment without which it is unreasonable to start working. Diagnostics of electronic systems begins with reading fault codes, checking sensors and actuators. There are no special diesel scanners, there are universal ones, that is, for a wide range of cars, or dealer ones - for a specific brand. To study the signal from the device under test, you need an oscilloscope. But it is expensive; it is more profitable to buy a scanner with an additional oscilloscope function.
Fuel pressure is checked with pressure gauges. Low - mechanical, with a scale of up to 10 bar, and high - with a special device with adapters and a range of at least 2000 bar. And to measure the amount of fuel drained from the injectors, you need your own set.
The troubleshooting algorithm depends on the nature of the failure. If the engine does not start (electronic locks and forgotten secrets do not count), we check the integrity of the timing drive. If the starter rotates the crankshaft with force, this is not bad for the owner, but if without resistance, the repairmen will be happy: the work ahead will be expensive. After all, diesel engines are “plug-in” - when the timing drive is destroyed, the pistons bend the valves, and then whatever happens.
Diesel fuel vapor pressure, flash point and vapor explosion potential
Saturated vapor pressure determines the volatility of oil and petroleum products, which affects the conditions of their use. Saturated vapor pressure increases with increasing temperature. The formation of saturated vapors leads to the fact that the pressure on the free surface cannot be lower than the saturated vapor pressure. As with all petroleum products, in diesel fuel the vapor pressure (the equilibrium stable concentration of vapor above the surface of the liquid) depends on temperature, it increases with increasing temperature and is compared with atmospheric pressure at the beginning of boiling.
The flash point (not to be confused with the auto-ignition temperature) is the temperature at which the pressure (concentration) of liquid vapor is so high that it ignites in the presence of a provoking source. This concentration is between the lower and upper explosive limits. It can be said that the flash point in the presence of a provoking source is a value that relates the pressure and concentration of saturated vapors located within the LEL and VKPR.
Diesel fuel vapors are only dangerous at temperatures above 55°C. Diesel fuel ignites only when the vapors are evaporated and heated; an explosion of diesel fuel vapors in an open space is practically excluded from the presence of fire. Diesel fuel vapors are practically safe at ambient temperatures, i.e. their concentration is always below the lower concentration limit.
During operations with petroleum products, it is easy to trace the occurrence of situations in which the transformation of vapors of a high non-explosive concentration into a low explosive concentration occurs. There are instruments for determining the saturated vapor pressure of diesel fuel. Determination of saturated vapor pressure occurs at a temperature of 380°C and at a ratio of the volume occupied by the fuel sample to the volume occupied by fuel vapor equal to 1:4.
Stand for testing injectors and high pressure pumps.
If the timing drive is in order, we proceed to checking the fuel supply. The electric booster pump comes into operation with the turn of the key. When this pump wears out or is damaged, the power it consumes changes; the ECU records this as a malfunction and records its code in the system memory. But you shouldn’t rely completely on electronics, so we connect the pressure gauge to the low pressure line. (For ease of control, the mechanical booster pump has a fitting.) If the pressure here is normal, we move on to the injection pump.
Let's check the fuel pressure in the rail while cranking the crankshaft with the starter. This part of the system is equipped with a fuel pressure sensor, so we will use its services. We connect the scanner to the diagnostic connector and find the desired parameter. If it is below normal, we look for where the fault is hidden. The culprits may be injectors, solenoid valves (regulators) and the fuel injection pump itself.
Diagram of the common rail diesel power system:
What is compression in a diesel engine
Compression is an indicator of the pressure in the cylinder that is created by the piston at the maximum highest (dead) point of the stroke. In technical literature, it is customary to use the abbreviation TDC (highest dead center). The value is measured in kg/cm² and depends on two main factors:
- Violation of the tightness of the combustion chamber: air leaks, pressure in the system drops. Worn valves, cylinder-piston units, or incorrect adjustment of the gas distribution mechanism leads to a decrease in compression.
- Condition of the crankshaft and its rotation speed: loss of stable speed leads to heat losses when air is compressed by the piston. The compression ratio becomes lower than normal, which directly affects the energy that is generated as a result of the formation of working gases during the combustion of the fuel mixture in the cylinders.
Rapid wear of CPG mechanisms (cylinder-piston group) depends on the quality of lubricants, the intensity of loads during operation, the number of cold starts at sub-zero air temperatures and hours of operation at maximum speed. Incorrect adjustment of the valve system contributes to the formation of carbon deposits on the walls of the combustion chamber, cylinder liners, and coking of the piston and oil scraper rings. As a result of insufficient pressure, the fuel mixture does not burn completely and mixes with oil residues, leaving burning products and soot on the CPG units. The first sign of wear in this case is a smoky exhaust and a drop in engine power.
During startup and activation of the starter, the crankshaft in a diesel unit rotates at a speed of 200-300 rpm: the higher the torque, the higher the compression. If the pressure in the combustion chamber is below 16 atmospheres, then starting the diesel engine in the usual way with the key becomes impossible. Heat loss causes a decrease in the compression ratio and disruption of the valve timing adjustment.
Important! Prolonged operation of a diesel unit with incorrect operation of the gas distribution mechanism leads to failure of the entire cylinder block. Up to the jamming of the pistons without the possibility of restoration and major repairs.
WE REPAIR
Restoring the pump's functionality can only be done by a specialized workshop with qualified personnel and diagnostic equipment. The cost of repairs is from 7 thousand rubles, then it depends on the complexity. In case of some damage, it is wiser to buy a new injection pump. The usual price, about 30 thousand rubles, will shock the tight-fisted diesel operator, which is why repaired or restored products are in use.
A CR diesel with high mileage is often impossible to start due to a malfunction of at least one of the injectors. Fuel leakage through its valve does not allow the pressure in the rail to rise to starting values. There is a special diagnostic kit to check the pressure at start-up. It includes a control pressure gauge, a pressure sensor, connection tubes, plugs instead of actuators and backflow measuring containers.
How to start an engine with insufficient compression
At low compression rates, the diesel unit does not start by turning the starter normally. If the start is made at sub-zero temperatures on a cold engine, then more force is required for normal crankshaft rotation speed, since the oil becomes more viscous in cold weather. To heat the cardan, use a regular blowtorch, which is installed below and heats the engine systems with hot air.
You can also artificially increase compression for a one-time cold start by creating an oil film in the cylinders. To do this, turn out the glow plugs or injectors and pour motor oil using a syringe directly into the combustion chamber, with a volume of no more than 50 ml. Repeat the entire procedure on each cylinder separately. Afterwards, rotate the crankshaft so that a uniform oil film forms on the walls, which will ensure the creation of a tight seal during start-up. Using this method, you need to monitor the distribution of oil in the cylinder; before starting the engine, the piston must make several strokes with the starter to avoid hydrocline.
Source
A cutaway view of a high-pressure fuel injection pump with a plunger section shut-off valve.
It is reasonable to replace worn out injectors as a set. The price range is very wide: depending on the model and manufacturer, they cost from 8 thousand to 25 thousand rubles. a piece. The characteristics of each new injector must be recorded in the memory of the engine control unit, because no two injectors have the same performance. Different ones not only have a bad effect on the uniformity of engine operation and its dynamic loads, but also worsen the characteristics of the car. Although each ECU has dynamic adaptation (constant adjustment of the cyclic fuel supply for smooth engine operation), you need to remember that it cannot replace the coding if, for example, you forgot to write it down.
The problem of difficult starting of a diesel engine is one of the most common. And the owner is sometimes dissatisfied, for example, with reduced engine power or exhaust smoke. These problems are the most complex, because they require an assessment of the accuracy of measuring air flow or supercharging operation, the efficiency of recirculation, the exhaust gas system, including the diesel particulate filter (DPF) and the converter. However, these technologies are now well mastered by diagnostic masters.
Source
Turbodiesel power supply diagram
To increase the power of a diesel engine, a turbine is installed. The design of the diesel engine fuel system does not change if the engine is turbocharged. The scheme and option for supplying fuel to the engine changes from the scheme of the atmospheric engine.
A turbocharged engine is obtained by installing a turbocharger. In a diesel engine, the turbine runs on exhaust gases. First, the turbocharger compresses the air, cools it and supplies it to the working combustion chamber of the cylinders of the diesel power unit. The air is pumped under a pressure of 0.15-0.2 MPa (Mega Pascal).
Turbocharging classification by pressure:
- up to 0.15 MPa;
- 0.2 MPa - medium power turbocharger;
- > 0.2 MPa.
In both gasoline and diesel engines, the turbine serves to supply additional air to the combustion chambers. The more air, the more and better the fuel burns. Engine power with a turbine increases by 30%.
The disadvantage of turbocharged engines is that such units operate in more difficult conditions: the temperature rises; parts, especially the cylinder-piston group (CPG), the crank mechanism (CPM), and the gas distribution mechanism (GRM), experience more pressure and the turbine itself usually needs to be changed after 100,000 km.
Operating principle of a Common Rail diesel engine (CRDi)
The fuel systems of most modern engines use advanced technology known as CRDi or Common Rail Direct Injection.
The common rail direct injection system has one rail (fuel rail) that contains diesel fuel under high pressure.
It acts as a common fuel reservoir for all injectors. In the CRDi system, the fuel rail constantly accumulates and supplies fuel to the injectors of the solenoid valves, at the required pressure.
This system is completely opposite to the high pressure fuel pump (HPFP), which supplies diesel through independent fuel lines to the injectors, in earlier generation fuel systems.
CRDi technology works in tandem with the engine's Electronic Control Unit (ECU), which receives signals from various sensors. It then calculates the exact amount of fuel and injection timing.
The fuel system has components that are more intelligent in nature and are controlled electronically.
In addition, conventional injectors have been replaced with more advanced electromagnetic injectors. They are opened by a signal from the ECU depending on variables such as engine speed, load, engine temperature, etc.
With common rail direct injection, combustion occurs directly in the main combustion chamber, located in a cavity above the piston head.
Today, manufacturers are using CRDi technology to overcome some of the disadvantages of conventional diesel engines, which were sluggish, noisy and had poor performance.
CRDI is also known by different names, different brands which are given below:
CRDi (Common Rail Direct Injection System) - Hyundai and Kia
DDIS (Diesel Direct Injection System) - Suzuki, Fiat Group
TDI (turbocharged direct injection) -Volkswagen
TCDI (Turbocharged Common-Rail Direct Injection) - Chevrolet
TDCi - Ford, Jaguar, Land Rover Volvo and Mazda
MJE (multi-jet injection), JTDm, CDTi, TiD, TTiD, DDiS and Quadra jet - Fiat groups
i-CTDI and i-DTEC -Honda
Tier3, Tier4, 4D95 and higher HPCR series - Komatsu
Source
Low pressure fuel supply system
One of the main characteristics of a diesel engine is the performance and pressure of both the mechanical part and the fuel equipment itself, which is very capricious and whimsical. To ensure the stability of these indicators and the durability of the equipment parts, we have to modify the fuel supply systems by installing additional accessories (filters, sedimentation tanks, heaters, booster pumps, etc.).
Based on this, the question arises: what exactly and in what sequence needs to be installed in order to obtain an optimal fuel supply system. Let’s not reinvent the wheel, but list in order what a low-pressure fuel system should consist of, from the tank to the fuel equipment (see figure):
Fig. 1 (1 - fuel tank, 2 - diesel fuel heater, 3 - coarse settling filter, 4 - fuel pump, 5 - pre-filter, 6 - fine filter, 7 - pressure-discharge indicator, 8 - transparent fuel line, 9 - engine).
- The fuel preheater
is designed to prevent paraffin from clogging the fuel filter in cold weather. - The coarse settling filter
cleans the fuel from water and large debris. Installed in front of manual and electric pumps, check valves. Prevents their premature wear and failure. - Fuel booster pump
with boost pressure 0.2 – 0.5 kg/cm². Pumps the system before starting, as well as after replacing the fuel filter. Eliminates airing of the system in case of minor leaks in the system. - The pre-filter
traps smaller dirt particles and water that have passed through the coarse filter. Prepares fuel for finer purification. Typically, the better the filtration rating of a filter, the more expensive it is. Thus, installing a pre-filter in the system allows not only to improve the fuel purification system, but also to extend the life of a more expensive fine filter. - Additional fuel heating
is installed when the fuel line is long and the power of one heater is not enough to combat paraffins. - The fine filter
finally cleans the fuel for supply to the fuel equipment (the degree of filtration is selected based on the design of the fuel equipment). - The pressure-discharge indicator
monitors the pressure at the inlet to the fuel equipment, which must be within acceptable limits. - A transparent fuel line
allows you to control the presence and amount of air entering the fuel equipment, which should be as small as possible.
So, now we know what should be on our car and in what sequence, which elements of the fuel supply system we already have installed, and which ones need to be added.
Now we list the main characteristics that you need to pay attention to when choosing additional accessories:
Bandwidth
It should be remembered that the installation of additional accessories, adapters, fittings, and fuel lines should not increase the resistance to the passage of fuel to the fuel equipment. Otherwise, at loads approaching the maximum, the engine will lack fuel with all the ensuing consequences and malfunctions of the fuel equipment.
To ensure that the resistance to the passage of fuel in the system does not increase, it is necessary that the throughput of the installed accessory is not less than the maximum performance of the fuel system where it is installed. As a rule, the throughput of a filter or pump is indicated in its technical characteristics. And the performance of the fuel system is easy to measure yourself.
To do this, simply lower the return hose from the fuel equipment into a measuring container, start the engine and let it run at 3000 rpm for at least 30 seconds. Then you need to recalculate the amount of fuel received in 30 seconds into liters per hour (l/h). The resulting value will be the performance of your fuel system.
Table 1 - Average performance of the most common fuel systems depending on their design and type.
| Type of fuel equipment | Productivity, l/h | Note |
| In-line injection pumps | 20-40 | Agricultural machinery, trucks, cars before 2000 |
| Single-plunger mechanical fuel injection pumps of distribution type. | 30-50 | All small and medium-duty vehicles up to 2000. |
| Distribution electromechanical injection pumps of distribution type | 40-60 | Passenger and medium-duty vehicles from 2000 to 2010. |
| Common Rail | 40-80 | Medium-tonnage equipment (from 1.5 to 4 liters) |
| Pump injectors | 40-80 | Found on Voltswagen cars |
When choosing an additional filter, you should also remember that as it gets dirty, the throughput of the filter element decreases. Therefore, it is better to choose a filter with a small performance margin. A correctly selected fuel filter should not create resistance in the fuel equipment even if it is 90% dirty. To our surprise, the announced performance of some brands of fuel filters does not correspond to even 60% of the declared one.
Maximum allowable pressure
Fuel pressure in different low pressure systems can vary from 0.45 kg/cm² to 6 kg/cm². On old (up to approximately 2005), as well as on some new designs of fuel systems, fuel priming pumps are located after the fuel filter and are designed for a maximum pressure of up to 1.5 kg/cm². This design is extremely unreliable due to the high probability of airing the fuel system at the slightest air leaks.
In modern cars, designers have corrected this shortcoming of the fuel system by installing a pump in the tank. The pressure in the fuel lines increased from 0.5 kg/cm² to 4–6 kg/cm². Based on this, new fuel system elements (filters, pumps, etc.) were developed to meet these requirements. Therefore, when modifying such a fuel system, you need to pay special attention to the maximum pressure value that the installed accessory can withstand.
The operating pressure of an accessory (filter, pump, etc.) can be found from its technical characteristics. In order to determine the pressure value in the fuel system of your car, you need to connect a pressure gauge to the line in front of the fuel filter, start the engine and take readings at idle and at 2500 rpm. The maximum value will be the pressure in your fuel system.
Filtration degree
Filtration degree
determines the maximum size of mechanical particles that can pass through the filter material.
Table 2 - Recommended filtration degree values for fine filters (final cleaning) depending on the type of fuel system.
| Degree of filtration, microns | Fuel system type |
| 2-5 | Common Rail |
| 5-7 | UIS pump nozzles, UPS pump sections |
| 10-20 | Distribution injection pumps |
| 20-30 | In-line injection pumps |
Table 3 - Recommended filtration degree values for pre-filters (coarse filters) depending on the type of fuel system.
| Degree of filtration, microns | Fuel system type |
| 20-30 | Common Rail, UIS pump injectors, UPS pump sections |
| 50 | Distribution injection pumps |
| 150 | In-line injection pumps |
And at the end of the article, we offer some tips that will help avoid problems with your fuel system:
- Monitor the performance of the fuel supply system components, especially such as fuel heating, contamination and water sensors, and a fuel filter contamination indicator.
- Try to use original spare parts or filters from trusted brands, such as Purflux, Mann, Champion, Stanadyne, Mahle, Knext, Fram, OE. Do not buy cheap filters from unknown manufacturers. Now there are about 30% of filters on the market in which the filter paper does not match the type of fuel equipment, and in some instances the filter paper is not glued at all.
- After replacing the filter element, cut and examine the used element. The condition of the filter media can tell you a lot. Perhaps it's time to wash the tank, or maybe your favorite gas station isn't as good as it used to be, and it's time to look for another one.
- Be selective when choosing a gas station. Always take a receipt after refueling. Do not refuel at suspicious or unbranded gas stations. After all, most of the breakdowns of fuel equipment occur precisely because of poor fuel quality. And if water is poured into your tank instead of fuel, then no filtration systems will help here. Therefore, it is so important to periodically check the water indicator for operation. If, after the next refueling, the indicator gives an emergency signal, then turn off the engine as quickly as possible and sort out the current situation. Drain the water from the filter (in most cases this is sufficient). If this does not help, then most likely water has entered the tank and it requires cleaning. To do this, drain the fuel from the tank, wash and dry it. After this, start the engine as quickly as possible so that the water that gets into the fuel equipment does not start “its rusty business.”
Unfortunately, among car enthusiasts who are beginning to be interested in upgrading their fuel system, there are many who have already experienced all the “delights” of expensive repairs. Therefore, do not repeat the mistakes of others and think about the filtration system in advance, so that it does not happen, as in the popular proverb: “Until the thunder strikes, a man will not cross himself.”
Article from the online store STO "Kovsh"