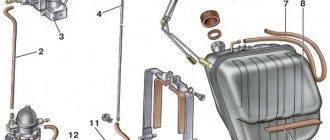
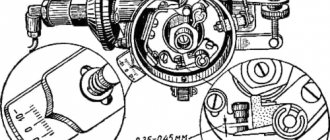
The high pressure fuel pump (HPFP) is one of the most specific and complex components of a modern diesel engine. These units are used not only in diesel engines, but also in injection-type power units, where the fuel supply is organized directly into the cylinders without intermediate stages.
The fuel pump is not only complex in design, but also an expensive engine element. This is due to the peculiarities of production and the need to use high-precision equipment. The well-coordinated and high-quality operation of the fuel injection pump determines how efficiently the engine functions. This is explained by the fact that the fuel pump is responsible not only for pumping the fuel mixture, but also for dosing portions and supplying them to the nozzles at the right moment in the operating cycle.
High pressure fuel pump design
The injection pump is a key element of the fuel supply system in a diesel engine. The main function is to timely transfer a portion of the fuel mixture to the combustion chamber. When diesel fuel is used as fuel, ignition directly depends on the pressure level. A standard piston system cannot be used; it is not capable of providing a working pressure of 150 MPa or more. To create conditions for ignition of the fuel mixture, the design of diesel power units includes a fuel injection pump.
After manufacturers began to produce industrial versions of Common Rail fuel supply systems with electronic control of nozzles, the functions of the fuel pump were noticeably reduced and were limited to only control over the level of discharge pressure.
Types of injection pump
There are several types of diesel fuel systems with different design features. This in turn affects the fuel injection pump device. So, on diesel engines the following pumps can be used:
- in-line;
- distribution;
- main lines.
Diesel engine injection systems
Despite the differences in design, they all use the same main working unit - a plunger pair. It is this that provides the pressure.
Design Features
Regardless of the model of the diesel power unit, the fuel pump is located in the engine compartment near the engine. For most engines from foreign manufacturers, the pipelines of the fuel supply systems between the injectors and the injection pump are made of metal, which significantly reduces the number of available places for installation. The design of the fuel pump includes two main elements - a small diameter cylinder and a piston, which in combination with the cylinder forms a plunger pair. These components are made only from high-quality steel that can withstand high pressure loads. It is important to maintain maximum precision in production, because the efficiency of the plunger pair largely depends on the minimum gap between the parts. In technical language this is called precision mating.
The nozzle acts as an intermediate element connecting the pump with the cylinders. The lower part is located in the combustion chamber. The exact moment of ignition of the fuel mixture depends on the advance angle and is controlled by the vehicle's electronic control systems.
Pressure check
Finally, the pressure in the pressure line is checked, which is an indirect check of the condition of the plunger pair. For this purpose, you will need a pressure gauge rated for pressures up to 350 bar, a connecting hose for connecting to the pump and an adapter that includes a bleed valve.
The TAD-01A pressure gauge or the older KI-4802 pressure gauge is suitable as a measuring device. If the adapter is not available for sale, you will have to make it yourself.
Of course, it is necessary to take into account the dimensions of the connecting thread and where you plan to screw the connecting hose. To measure, the device is connected to the central hole of the distribution block or to one of the pressure fittings.
After connecting the pressure gauge to the injection pump, rotate the pump shaft using the starter and record the reading of the dial indicator. If the device shows more than 250 atmospheres, this is normal (the pressure will be higher when the engine is running).
Types of high pressure fuel pumps
Manufacturers of diesel power units use several types of injection pumps:
Row
This type of design is popular for its long service life and unsurpassed reliability. Lubrication is carried out with engine oil, which allows you to fill even diesel fuel of not the highest quality. In-line injection pumps are installed on engines with separate combustion chambers and are equipped with plunger pairs corresponding to the number of cylinders. The pump pistons are driven by a cam shaft, which is connected to the engine crankshaft. Springs are responsible for permanently pressing the plunger pair against the cam. The injection pump operates on the following principle: when the cam shaft rotates, the piston begins to move, which leads to the blocking of the inlet and outlet channels of the fuel mixture. This automatically increases the pressure to the chamber, opens the discharge valve, causing a portion of fuel to be directed to the nozzle for atomization and ignition.
In modern engines, dosing the volume of the fuel mixture is carried out by an electronic mechanism. In older analogues, this was ensured by turning the piston inside the cylinder at a certain angle. A gear connected to the accelerator pedal and connected to a rack is responsible for turning. When the pressure on the pedal changes, the clutch with weights provides the desired advance angle and adjusts the injection intensity.
Distribution
The design ensures stable and smooth operation. This type of fuel pump is smaller in size than an in-line one. Depending on the principle of action, it is divided into two subtypes:
- Rotary or plunger injection pump.
- Pump with cams of end, external or internal placement.
The key element of the design is a plunger pair that serves all combustion chambers at once. The pistons make a number of revolutions proportional to the number of cylinders in a diesel engine. This explains the high level of load on components and accelerated wear of some parts.
Trunk
It is used in diesel power units with the Common Rail system and is popular for the most efficient control of ignition processes. Proper control of the operating cycle is ensured by supplying fuel not directly to the combustion chamber, but to a special frame that acts as a preliminary accumulator. Thanks to this technological solution, it was possible to separate the process of injection of the fuel mixture and the formation of excess operating pressure. The performance of this type of pump is controlled by electronic engine control systems.
You can read more about the adjustment here.
or call back 7 (921) 932-25-54
Common Rail injection pump
A slightly different type of high pressure pump is used in the Common Rail fuel system. The design of the injection pump is affected by the operating features of the system itself.
Single-plunger Common Rail injection pump
In this system, the injection is controlled and controlled by the computer, so the dosage and timing of fuel injection are not part of the pump's task. It has only one function - to pump fuel into the ramp (battery).
Therefore, the design of the injection pump is greatly simplified. In fact, the pump consists only of a shaft, plunger pairs (from 1 to 3) and valves - inlet and discharge. There are no regulators here as they are unnecessary.
Double plunger high pressure pump
Everything is simple here - the shaft rotates from the drive and the plungers constantly pump fuel into the ramp. This is all that is required from the injection pump.
Operating principle of the fuel pump
The operation of the injection pump is based on a piston and a discharge valve. After the camshaft receives the necessary impulse from the crankshaft, it runs up against the clutch and increases the pressure in the fuel portion located above the piston. At the same time, the inlet line is closed. After the pressure level in the system reaches the required level, the discharge valve opens and admits the fuel mixture into the injector. During the reverse cycle and the piston moves downwards, the remaining fuel is removed through the screw channel. The cavity in the piston at a certain point in the cycle is located at the same level as the exhaust tract, after which the process is repeated.
The operating modes of the fuel pump are controlled by electronic units. High-precision equipment receives information in real time from temperature sensors and shaft rotation controllers, which is the basis for generating command signals. The ECU memory contains several optimal operating algorithms, with which the information received from the sensors is compared. Based on it, the electronic unit sets the best fuel mixture supply cycle and advance angle. In some engine models, the fuel injection pump design includes components that complement the electronic control system.
Classification
Several criteria are used to classify fuel injection pump.
Based on the principle of operation, a distinction is made between direct-acting fuel pumps and systems that provide battery injection. The first type is also divided into two types - with mechanical and pneumatic drive. It ensures the simultaneous implementation of pressure build-up and injection processes, and is therefore simpler and much more often used in practice. The second type - a fuel pump with a hydraulic accumulator - separates the pumping of the fuel-air mixture and its injection into the injectors. First, the fuel is collected in a special storage facility, which is called a battery, and then transferred for combustion. As a result, the efficiency of the engine increases, but at the same time the design of the fuel injection pump becomes noticeably more complicated. The last argument was the main reason why pumps with hydraulic accumulators are not among the popular ones.
The second classifying feature is the design features of the pump. In accordance with them, it is customary to distinguish three types of injection pumps:
- In-line. The simplest and most reliable design, which provides for the presence of several niches or sections, each of which is designed to supply fuel to one engine injector. In this case, the plunger pairs are placed in a row, which gives the unit its name. Today, this type of injection pump is used exclusively on trucks, which is explained by its reliability and low level of fuel quality requirements. However, due to the large dimensions and low efficiency compared to alternative options, installation on passenger cars was discontinued in 2000.
- Distribution. This type of pump assumes the presence of one or two plungers, the number of which is determined by the engine size. Due to the design features, this turns out to be quite enough to service cylinders, the number of which varies from 4 to 12. As a result, a reduction in the weight and size of the injection pump is achieved, which allows its use on passenger car engines. The main disadvantage is the comparative fragility of distribution-type pumps.
- Trunk. This type of injection pump provides a Common Rail fuel supply system, which has become one of the most popular in recent years. The main feature is the accumulation of fuel before entering the injectors in a special ramp. The main advantage of main fuel injection pumps is a high pressure level (over 180 MPa), due to which more efficient combustion of fuel is achieved, ensuring an increase in efficiency while reducing fuel consumption.
Signs and causes of fuel pump malfunctions
As mentioned earlier, the injection pump is one of the most complex and expensive components of a diesel engine. In most cases, the cause of malfunctions is the use of low-quality fuel and oil. If foreign particles, dust and dirt, or combustion products get into the injectors or plunger pair, the latter very quickly fail. The following signs indicate this:
- Difficulty starting the engine.
- Increased fuel consumption for no apparent reason.
- Dips in the power of the power unit.
- Smokiness.
- Extraneous sounds and noises when starting the engine.
Another cause of breakdowns is the natural wear of the plunger pair, which leads to an increase in micron gaps, carbon deposits getting into them and failures in the system.
As practice shows, the reasons for interruptions in the supply of fuel to the combustion chambers can be:
- Critical wear of valve teeth or rack.
- Mechanical defects and damage to the bushing.
- Piston abrasion.
- Reducing the throughput of fuel atomizers.
You can read more about the malfunctions in the article.
Basic faults
Although injection pumps differ in their design, there are several important rules that the car owner must follow in order for the pump to serve its allotted time:
- Most pumps are sensitive to fuel quality, so it is necessary to comply with the requirements set by the manufacturer for a specific pump;
- Due to the complexity of the design and the loads placed on the mechanisms, high-pressure pumps require regular maintenance;
- All rotating and rubbing parts must be well lubricated, so it is extremely important to follow the manufacturer's recommendations for choosing lubricants.
If these rules are not followed, the device will quickly become unusable, which will require replacement or expensive repairs.
The following factors indicate a malfunction of the injection pump (if other systems are working properly, faults in which may have similar manifestations):
- Black smoke in the exhaust and, as a result, more toxic emissions into the environment;
- Increased fuel consumption (due to fuel leaks);
- Decrease in engine power;
- While the engine is running, noises from the pump are heard;
- Difficulty starting the engine;
- The timing belt often slips;
- Unstable engine speed.
The most common malfunction in such elements of the fuel system is failure of the plunger pair. Most often this happens due to low-quality fuel - plaque accumulates on surfaces, impeding the movement of parts. Also, the cause of mechanism failure is water, which often condenses in the fuel tank. For this reason, it is not recommended to leave the car with an empty tank overnight.
Features of diagnostics and repair of injection pumps
Due to the complexity of the fuel pump design, diagnostics can only be performed on specialized stands. The procedure is quite complex and requires careful attention to the process on the part of mechanics. Even technically, it is impossible to perform it in a garage service environment - only at specialized service stations for servicing diesel engines. If there are interruptions in the operation of the fuel system, we recommend that you immediately contact our service center and sign up for diagnostics. A timely procedure makes it possible to identify pressure stability, uniform supply of the fuel mixture, residual life of parts and their degree of wear, and other factors affecting the operation of the fuel injection pump. Thanks to a systematic approach, you can save on the purchase of components.
Often the cause of malfunctions is not the wear of the fuel pump elements, but problems with the electronic unit or sensors that transmit incorrect information. The generation of incorrect control signals leads to failures in the fuel supply. Only a specialist can determine the exact cause and perform high-quality repairs, and attempts to replace parts yourself can lead to global malfunctions of the engine as a whole.
High-precision diagnostic equipment, repair stands, original spare parts from manufacturers, qualified personnel - all this allows us to carry out comprehensive repairs within 1 business day!
History of development and improvement
Robert Bosch is considered to be the developer of the injection pump.
The active use of this type of fuel pump in passenger cars began in the second half of the 30s of the last century. Originally, the high pressure fuel pump was intended exclusively for diesel engines. However, currently, fuel injection pumps are also used for gasoline units equipped with an injection system that provides indirect fuel injection into the cylinders. The constant increase in requirements in terms of labor protection and compliance with environmental standards explains another important area for improving fuel injection pumps. In modern conditions, mechanical fuel pumps have been replaced by devices equipped with electronic control of fuel supply. The second version of the fuel injection system is much more economical and minimizes the amount of harmful emissions into the atmosphere.