This device, which is popularly called a “sorcerer,” is one of the important elements in the braking system of any car. The main function of the brake force regulator is to prevent the car from skidding. In more modern domestic and foreign car models, the traditional mechanical regulator no longer exists. Electronic assistants took its place. In particular, the functions of the “sorcerer” are performed by the EBD system. But in basic configurations, manufacturers save on everything, so sometimes mechanical regulators are found even in new foreign cars. Let's look at what this element is, why it is needed in a car, and how to configure it.
Functions and purpose
The brake force regulator is used to automatically change the fluid pressure in the rear brake cylinders of a vehicle. In this case, adjustment is carried out according to the loads acting on the machine when the speed decreases. Such regulators are used in systems with pneumatic or hydraulic drive. It is necessary to change the cylinder pressure in order to prevent the rear wheels from completely locking. If they are blocked, the car will skid and the driver may lose control.
In some car models, in order to maintain controllability and stability, similar mechanisms-regulators are additionally used on the brake drives of the front wheels.
In addition, a brake force regulator is used to improve the efficiency of stopping an empty vehicle. When a car is not loaded, its grip on the road will be different from that of a loaded car. Therefore, it is very important to be sure to change the braking force on different axles. In passenger cars, static devices are used as regulators. Automatic solutions are installed in trucks.
In cars created for sports, another type of “sorcerer” is used. This is a screw regulator. What it is? It is located in the cabin, and with its help you can adjust the balance of the braking system directly during the race. Settings depend on the weather, track conditions, and tire conditions.
Adjusting the braking forces of Lada Vesta
The operating principle of the system that regulates and distributes brake fluid pressure on Lada Vesta cars is fundamentally different from previous models, and there is no “witchcraft” in it. The Lada Vesta brake pressure regulator is directly connected to the ABS system and is electronically regulated depending on the speed of each wheel.
The ABS control unit transmits signals from speed sensors and analyzes the situation. The system “understands” any skidding and allows you to distribute the braking force with maximum efficiency. The pressure is controlled by the valves in the ABS hydraulic block, and there is no need for any magic. In addition, the electronics itself detects all malfunctions and reports them to the driver using a special lamp on the dashboard.
How does the mechanism work?
It should be noted that the brake force regulator is not installed on cars with ABS, although the “sorcerer” is the ancestor of this system. It also helps protect the wheels from locking during braking.
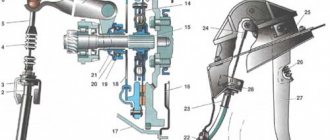
In passenger cars, the “sorcerer” has a fairly simple device. It consists of three elements - the body, pistons, and valves.
The device body is internally divided into two cavities. The first cavity of the regulator is connected to the master cylinder (MC). The second is connected to the rear brake mechanisms. When emergency braking is necessary, the front of the car will tilt. With the help of pistons and valves, due to this tilt, the access of the working fluid to the brake cylinder will be blocked.
Thus, the VAZ brake force regulator automatically controls and distributes forces on the wheels of the rear axle. The car does not skid in the event of an emergency press on the pedal.
"Chevrolet Niva"
In the normal position of the regulator, as the vehicle's weight increases, its braking distance decreases - this affects the more complete use of the traction weight by the rear wheels.
The best braking is at full load, when the regulator minimally limits the pressure in the rear brakes.
But at partial load this is fraught with skidding. The high center of gravity and short wheelbase of the Shnivy contribute to a significant redistribution of mass during braking, therefore, at partial load, the contribution of the rear axle to braking is small.
Where is the regulator located?
The “sorcerer” can be found on a passenger car mainly in the rear of the body. It can be located either on the left or on the right on the bottom.
The regulator is connected to the rear axle or beam by means of a rod and a special torsion lever. It is this lever that acts on the piston inside the regulator. The incoming part of the brake force regulator is connected to the GTZ, and the output part is connected to the working brake cylinders of the rear mechanisms.
Brake pressure regulator, or how the sorcerer works on VAZ cars
A brake force regulator, or sorcerer in common parlance, is a mechanical device designed to relieve excess pressure in the rear drum brakes.
On VAZ-2109, VAZ-2108, VAZ-2114 and other front-wheel drive models produced in Togliatti, it was installed in the rear left part of the body, under the bottom, in front of the rear suspension beam. The brake pressure regulator on the VAZ-2107 model and other “classics” is located on the right in the direction of travel of the car.
New vehicles equipped with ABS and EBD do not use the sorcerer.
Operating principle
When the driver presses the pedal sharply, the car will definitely “peck” at the front of the body. This will cause the rear end to rise slightly. At this moment, the “sorcerer” is starting to work.
If the rear pair of wheels brakes together with the front ones, then in this case the likelihood of the car skidding increases significantly. If the wheels on the rear axle stop later than the front ones, then in this case the risks that the car will skid are minimal.
When the braking process is carried out, the distance between the bottom and the rear axle of the car increases. Due to this, the piston of the VAZ-2110 brake force regulator is released. As a result, the line with the liquid inside is blocked. The wheels will not be blocked, but will continue to rotate.
How to check the regulator?
This device is called a “sorcerer” for a reason. Although many beginners do not really know how it works. Let's see how to check the operation of the regulator to see if it is working properly.
The test will require at least two people - one to drive the car and the other to monitor the car. During the test, the driver will have to accelerate the empty car on a flat area to a speed of approximately 60 kilometers per hour. Then you should perform sharp braking. Next, at the moment, the observer must control how the rear wheels work. It is important to note whether they lock or rotate when you press the brake pedal.
If the rear wheels lock immediately or they continue to rotate and do not react in any way to pressing the pedal, then the brake force regulator 2110 is faulty.
There is no room for optimism in brake operation
Many cars continue to drive with a completely soured regulator, because their owners do not understand the full role of this simple device and are not even aware of its existence. It turns out that the operation of the rear brakes depends on the position of the regulator piston in which it soured and lost mobility. The car will either greatly lose in braking efficiency; in fact, only the front axle works, or, on the contrary, it constantly throws the rear during hard braking due to the beginning of a skid. This can happen with impunity only until the first emergency braking from high speed. After which the driver will not even have time to understand anything, so quickly he will find himself flying forward into the oncoming lane with the trunk.
The operation of the regulator must be checked at each maintenance according to the instructions. The piston must be mobile and the clearance must be within the normal range. And the stand indicators correspond to the passport data. The only thing that saves you from these procedures is the fact that the “sorcerer” has not been used in modern cars for a long time, and its role is assigned to an electronic system, designed and tested in completely different ways. But when buying an older car, you should remember the presence of such a device.
What happens if you drive without a regulator?
If the check shows that the “sorcerer” does not work, then the car owner has two options. The first and most correct is to purchase and install a new regulator. The second option is to remove the “sorcerer” from the system. Let's look at the dangers of operating a car without this device. Some owners even intentionally remove the regulator to reduce braking distance.
However, experts do not recommend removing the mechanism - this path is wrong. Without an adjuster, both the front and rear brakes will apply at the same time. The risk of a possible accident increases - the driver moving behind may not have time to react correctly to the braking process.
The presence of a working brake force regulator on the 2114 VAZ is very important. It is prohibited to remove it from the system - this is indicated in the traffic regulations. If the mechanism is not working properly, you can try to adjust it.
How to adjust the VAZ distributor?
To ensure that the workload on the front and rear brake drives is distributed as correctly as possible, adjustments should be made periodically. Its principle is as follows. There is a gap between the end of the piston and the plate. It can range from two to three millimeters. However, the difficulty is that the gap size is imprecise. It is determined empirically. To make more precise adjustments of the brake force regulator, move the regulator along its bracket.
The clearance parameters should be selected depending on how the rear wheels behave in each case. If skidding of the rear axle wheels is not observed when braking, then the gap can be reduced. If the rear brakes engage earlier than the front brakes, then the gap should be increased.
"Chevrolet Niva"
"Chevrolet-Niva" "Chevrolet-Niva"
The third state - we reduce the influence of the regulator by increasing the gap from the original one by 8 mm, that is, we set it to 24 mm. When there are two people in the car, the braking distance remains virtually unchanged - 34.3 m. However, now the rear wheels are blocked. But at full load the braking is very effective, the deceleration is easy to control and the result is a record: only 30.8 m!
- In the normal position of the regulator, as the vehicle's weight increases, its braking distance decreases - this affects the more complete use of the traction weight by the rear wheels.
- The best braking is at full load, when the regulator minimally limits the pressure in the rear brakes.
- However, at partial load this can lead to skidding. The high center of gravity and short wheelbase of the Shnivy contribute to a significant redistribution of mass during braking, therefore, at partial load, the contribution of the rear axle to braking is small.
Service
This part cannot be repaired. But in order for it to work properly, it needs to be maintained. This is usually done before making adjustments. The unit is installed in an unfavorable location - during operation it gets exposed to water, snow, dirt, and reagents from the road. All this makes the job worse. Gradually, water and snow become causes of corrosion.
General maintenance activities include cleaning the “sorcerer” from rust, removing the old rubber boot and installing a new one, replacing the lubricant, and cleaning all elements of the regulator from contamination. The old grease is first removed from under the boot.
Malfunctions
To determine the cause of the failure, a visual inspection of the mechanism is sufficient, so we climb under the car and take a look.
The most common cause of sorcerer failure is piston jamming.
This is due to its location on the bottom of the car. Strangely, all the road dirt, winter reagents and other “poop” collect on it. We test the piston head for movement. If, when you press it, the rod does not go inward and does not move at all, it is jammed. The first sign of a wedge may be a torn or collapsed boot. If it is damaged, then all the “shit” from the road will get into the regulator body, it will refuse to work.
Regulator controls are missing.
It’s rare, but it happens that a lever falls out, brackets and other parts of the structure break, or simply rot. If something is missing, it will be clearly visible, so the “shaman” does not “shamanize.”
In the case of a visual inspection, nothing criminal was found, everything works - you just need to configure it.
Adjusting the “sorcerer” on “Logan”
Finding a brake force regulator on a Logan is not a problem. It is located on the bottom between the front and rear axles. Many people claim that only professionals can properly adjust the operation of the distributor on this car, but this is not at all true. The initial adjustment is carried out by the manufacturer - a special installation is used, and the nut is pulled with a strictly defined torque. Only fixing the loose thread on the nut is allowed.
To self-adjust, you need to clean the “sorcerer” and replace the lubricant in it. Then make half a turn with the adjusting nut. Then you can go for the test. If the rear pair of wheels does not brake, then tighten the nut again.
If the vehicle being tested does not have ABS, then even if you tighten the nut all the way, you may not achieve the result. Sometimes replacing the sorcerer can help, but this does not always save the situation. The fact is that in 9 out of 10 Logans without ABS, the regulator does not work at all. The reasons are a weak spring. And the owner again has two options - he can change the springs to stiffer ones or install a rubber gasket to increase the pressure on the “sorcerer” mechanism.
Replacing the regulator with a tee
Car enthusiasts sometimes replace the standard “sorcerer” with a tee. Among the reasons are the initial malfunction of the unit, souring and failure, and various other problems. The tee allows you to simultaneously block and evenly distribute the braking force between all wheels.
Among the disadvantages are dangerous braking (especially in winter on ice) and the risk of skidding. Benefits include a sharp and responsive brake pedal.
Car manufacturers do not recommend excluding “sorcerer” from the car’s braking system. Moreover, the price of a brake force regulator for VAZ models ranges from one and a half thousand rubles. This is a low cost, considering that safety depends on the “sorcerer”.
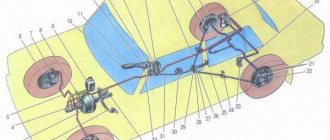
Parking brake system
When changing the position of the lever of the manually controlled brake valve 16, the working pressure of the compressed air in the spring energy accumulator of the pneumatic cylinder 19 . In this state, the force on the wheel brake mechanisms is applied due to the elastic forces of the springs of the pneumatic cylinders. At the same time, the air pressure in the line is released in the area from the manually operated 16 17 . When the road train is parked, the trailer is held by applying pressure to the control line. Since the Council Directives of the European Economic Community (ECEC) include the requirement that a goods road train (truck and trailer) can only be held in place by the vehicle's braking system, the pressure in the trailer braking system can be relieved by moving the manually operated brake valve lever to "Control position". This allows you to check whether the parking brake system of the road train meets the requirements of KKEO.
General view of the Hyundai Porter brake system
Hyundai Porter light commercial vehicles (as well as its “related” H-100 and Kia Bongo) use a number of technical solutions typical for passenger cars. This also applies to the truck’s braking system: the Porter has a dual-circuit braking system with a hydraulic drive and a vacuum booster, with front disc and rear drum brakes. The car also uses a component called a distributor valve (brake force regulator, popularly known as a “sorcerer”).
The Hyundai Porter brake system contains the following main parts: a brake pedal assembled into one unit with a master cylinder and a vacuum brake booster, a reservoir for storing brake fluid, front disc brakes, rear drum brakes, a brake force regulator, a supply piping system brake fluid to the brake mechanisms. Each component plays its role in the system.
Brake pedal, master cylinder and brake booster. This assembly is installed under the dashboard in the truck cab on a common bracket with the clutch pedal. The system is designed in such a way that the force from the brake pedal is transmitted to the vacuum booster, and from it to the main brake cylinder. The vacuum for the operation of the amplifier is taken from the diesel intake manifold and is supplied through a special tube. Brake fluid is transferred from the reservoir to the cylinder by two flexible hoses, and from the master cylinder to the wheel brake cylinders by two metal tubes.
Brake fluid reservoir. It is installed in the engine compartment using two bolts. The tank has a filler neck, fittings for connecting to the working fluid supply pipes to the main cylinder and a working fluid level sensor with a connector.
Front brake mechanisms. Disc type, have a standard design. A steel brake disc is installed on the wheel hub, which in the front part fits into a caliper (it is mounted on a brake shield fixed motionless on the wheel hub) with two pads. A special feature of the Hyundai Porter front brakes is the presence of two cylinders located in the caliper (and, accordingly, two pistons) that provide drive to the brake pads. The caliper has a fitting for connecting the brake pipe (brake fluid is supplied through it) and a fitting for bleeding the brake system. The car uses massive ventilated brake discs.
Rear brake mechanisms. Classic drum brake pads with internal brake pads. The semicircular pads, together with the brake cylinder (which has two pistons), the parking brake actuator and other parts, are mounted on the brake shield and covered with a cast-iron brake drum, which is mounted on the hub using five studs. These studs also serve to mount the rear wheel disc.
The brake force regulator should be described in more detail.
How to install a tee instead of a sorcerer
In the case of the VAZ 2106-07, you can simply remove the regulator; the tee is already installed in the system; the main line from the GTZ is simply connected to it.
- Using a special “10” wrench, unscrew the brake pipe fittings from the mechanism.
- Unscrew the tube coming from the brake adjuster from the rear brake hose.
Disconnect the sorcerer tube from the rear brake hose
- Disconnect the control lever from the axle and body. We take out the regulator assembly with the rod and throw it away.
- Carefully bend the brake pipe from the master cylinder to reduce its length. It should not dangle under the bottom of the car. We connect it to the brake hose of the rear brakes.
bend the brake pipe from the master cylinder to the rear brake hose
Now all the force from the main one goes through the tee to both rear brake cylinders. Therefore, deceleration will occur on both wheels simultaneously with the front ones.
Purpose of the brake system distributor valve
Externally, the braking process seems quite simple - the pads are pressed against the disc or drum, and due to the frictional forces that arise, the kinetic energy of the moving vehicle turns into heat, resulting in a decrease in speed or a stop. However, there are several pitfalls here, which are especially painful on rear-wheel drive vehicles.
For example, when braking, the wheels can completely lock (especially in the absence of ABS), which at certain speeds, even on a dry, flat road, can lead to slipping and skidding. Most often this situation occurs on the rear axle. Therefore, sudden braking poses a particular danger and today designers strive to minimize the likelihood of complete wheel locking.
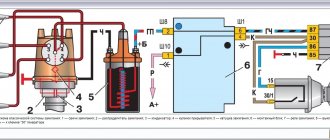
Valve design and operating principle
Structurally, the brake force regulator consists of a valve, which is mounted on the frame using a bracket, and a lever, which is attached to the rear axle beam. The position of the lever is set by spring tension. The valve is designed in such a way that the degree of its opening also changes the flow of brake fluid coming from the master cylinder to the rear wheel circuit.
The valve works simply. Without loading, the car frame is raised as much as possible above the rear axle and the valve is partially closed - in this case, pressing the brake pedal does not cause the wheels to quickly lock. When the car is loaded, the frame lowers, the position of the lever changes and the valve opens completely - in this case, more fluid flows to the rear brakes and they work more efficiently. All this happens when overcoming the nervousness of roads, slopes, etc.
Thus, the brake force regulator automatically adjusts the braking force on the rear axle brakes under different loads and changes in operating conditions.
Examination
Necessary:
- Raise the rear axle of the car with a jack.
- Remove the wheel rims.
- Take off .
- Inspect the brake cylinders for leaks.
- Also check their operation, the cylinders should extend to the required distance for braking.
- After releasing the pedals, they should not jam. If this flaw is detected, the cylinders must be replaced.
- Check the condition of the springs; they should not have any spiral bends. They must also have a flat surface.
- Inspect the quality of the pads themselves. There should be no delamination on them, the thickness should be at least 2/3 of the standard.
- Also inspect the spacer bar; it should not have any defects, since a damaged bar can interfere with the operation of the pads.
- Check the brake drums. There should be no burrs or large grooves on them from the operation of the pads.
Attention. It is necessary to check both sides of the vehicle. After the inspection, replace worn or failed parts if necessary.
To carry out regulation it is necessary:
- plate 3 mm thick;
- a set of keys;
- portable lamp with a protective glass cover, with a protective steel mesh.
The process of adjusting the free play of the brake pedal is carried out to ensure the normal functionality of the entire system. If the stroke is reduced, then the rear pads do not fully return to their position. This causes them and the drums to heat up. Uneven acceleration also occurs at the beginning of movement. With increased free play, pressing the pedal causes incomplete expansion.
Questions about maintenance and repair of the Hyundai Porter brake force regulator
We will not touch upon the issues of maintenance and repair of the brake system here - this work is carried out in accordance with the operating instructions and is generally standard for light-duty trucks. However, a few words must be said about the distributor valve.
This unit plays an important role in the operation of the entire braking system, and its malfunction usually immediately affects the efficiency and quality of braking. In particular, a breakdown or simply clogged valve can lead to the following consequences:
• Rear brake failure; • Increased brake pedal resistance when braking efficiency deteriorates; • Incomplete blocking of the rear wheels when the brake pedal is fully depressed; • Leakage of brake fluid from the regulator; • Frequent airing of the rear axle brakes (in this case, air does not appear in the front wheel circuit).
Diagnostics of the regulator is carried out by measuring the brake fluid pressure separately in the front and rear circuits at different positions of the brake pedal. To do this, pressure gauges are connected to the circuits, and when you press the pedal, the pressure in the circuits should change in a certain way. This diagnostic is carried out in a car service center, but in a garage it can be easier to replace the regulator with a new one.
To replace the valve, you need to unscrew three bolts and disconnect the pipelines. The valve is installed in the reverse order, using the adjusting screw to set the working length of the spring (it differs in different valve models, this parameter is specified in the operating instructions), and then the brake system is pumped to squeeze out air bubbles.
You can often hear that the problem can be solved by completely dismantling the regulator, but this is unacceptable, since removing the valve and connecting the rear brake mechanisms directly to the master cylinder is fraught with emergency situations.
With regular maintenance, the use of high-quality brake fluid and timely replacement of a faulty brake force regulator, the braking system of a Hyundai Porter will work reliably and efficiently, ensuring safety in all situations.
On passenger cars with a hydraulic brake drive without an anti-lock braking system (ABS), a pressure regulator is used. Some car owners call it a “sorcerer,” considering it a mysterious and useless device. In fact, this is an important element of the braking system; it makes braking more stable even from high speeds on slippery roads.
Braking is the creation and change of artificial resistance to vehicle movement.
Braking force is the frictional force created at the tire contact patch with the road to slow down the vehicle. It directly depends on the vertical load acting on the wheel and the conditions of adhesion of the tire to the supporting surface.
Locking wheel 1 - stopping its rotation when the car is braking.
Vehicle stability when braking is the ability to maintain a given direction of movement and position on the roadway.
The pressure regulator in the hydraulic brake drive is a device for automatically changing the amount of braking force depending on the force on the pedal (the pressure of the working fluid in the master cylinder), the vehicle load and the intensity of its deceleration.
When braking, the tire tread elements slide relative to the road in the longitudinal direction. The more slippage, the worse the wheel resists lateral forces. When skidding, even a slight lateral force causes it to shift to the side.
Since a brake mechanism (without ABS) of almost any design is capable of blocking a wheel, and it is difficult to completely avoid this 2, the order of skidding is important to maintain vehicle stability.
If the rear wheels lock before the front wheels (Fig. 1, option I), any slightest lateral impact (steering wheel turns, cross slope of the road, gusts of side wind, etc.) can provoke a progressive skidding of the car. It moves by inertia, the rolling front wheels cling to the road, and the stopped rear wheels slide sideways. It turns out that there is a “support” in front, around which the car turns.
When the front wheels are already locked (Fig. 1, option II), but the rear wheels are not yet, the position of the car on the road is stabilized. The “support” at the back holds it in its original position.
Rice. 1. The influence of the order of wheel locking on the stability of the car during braking: CM - the center of mass of the car; Fi is the inertia force during braking; Mi is a turning moment created by force inertia.
When all wheels are simultaneously locked, the car's behavior is better than in the first option, but worse than in the second, although close to it. Such braking is undesirable, since there is no safety reserve 3.