A car battery is an autonomous power source used to start the engine and power the internal electrical network. The battery accumulates energy from the generator during operation of the power unit and releases it when necessary.
The basic principle of operation of a car battery is the conversion of chemical and electrical energy.
General information
The main function of the battery is to supply electricity to the spark plugs to start the engine. Also works as a voltage stabilizer and an additional power source for electrical appliances when the engine is turned off.
A battery is an electrochemical device; it does not store electrical energy, but produces it as a result of the reaction of chemical elements. Two dissimilar metals in the form of plates are placed in an acidic environment. When connecting electricity consumers, a potential difference arises between the plates and electric current is generated.
Batteries
The main function of the battery is to supply electricity to the spark plugs to start the engine. It also works as a voltage stabilizer and an additional power source for electrical appliances when the engine is turned off. The amount of electricity the battery produces is limited.
Design Features
Batteries may differ significantly from each other. The design features of the battery include:
- Battery size.
- Composition of metal alloy plates.
- Type of electrolyte.
- Location of electrical terminals on the housing.
The capacity of the battery will depend on the size of the plates and the amount of electrolyte in each bank, so products installed to start diesel engines in trucks can be several times larger in weight and volume than batteries for passenger cars.
The internal electrical resistance of the battery and the resistance of the element to aggressive environments will depend on the type of lead alloy. Also, the composition of the metal will affect the rate of moisture evaporation, therefore, for maintenance-free models, the plates are made of lead alloyed with calcium.
A large number of battery parameters also depend on the type of electrolyte used in battery banks. The liquid solution freezes at low air temperatures, and when it boils, it leads to the evaporation of water, so replacing it with a gel can significantly increase the service life of the products. Gel batteries tolerate deep discharge much better, which allows them to be used not only as starting devices, but also to power electrical power plants.
Batteries may also differ in the location of the terminals on the case. This parameter must be taken into account when selecting a new battery, otherwise you will need to lengthen the positive wire of the car connected to the power source.
Purpose:
• The engine is not running.
Supplies electrical current to lights, radios and other electrical systems. • The engine starts. Electrical current from the battery is supplied to the spark plugs to start the engine.
• The engine is running. The battery acts as a voltage stabilizer when the generator produces more voltage than required. In the event that the generator cannot cope with the load, the battery makes up for the lack of voltage and is used as an alternative power source for electrical appliances.
Difficulty of choice
Choosing a battery is not an easy task. At first glance it may seem that this is a very simple device.
But in reality it turns out that it is full of characteristics that are important. But don't despair
You basically need to decide on the battery size, type, capacity and starting current. In principle, you can find out all these parameters by inspecting your old battery.
Capacitance and inrush current are usually written in large letters in a visible place. For example, 55 Ah 450 Ampere. This is who they are. Above is a table with capacity depending on the vehicle. It can be used to further orientate oneself. The article also provided the sizes of domestic, European and Asian batteries, by which you can understand what type your battery is. Mainly only these batteries are sold on the Russian market.
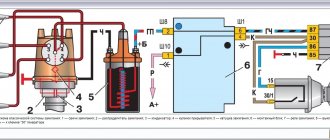
Battery device
1. Case: the container in which all the battery cells are located. Basically, the body is made of heat-resistant and impact-resistant polypropylene. Sometimes the case is made translucent in order to check the electrolyte level without removing the lid and vent caps. 2.Lid: covers the upper part of the body. It has outlets for terminals, ventilation holes for removing gases and servicing batteries - checking the electrolyte and adding water. 3. Plates: current is created by the reaction of the chemical elements of the plates of two types: positive and negative. The metal in the form of a paste is applied to the lattice frame. To produce the voltage of the required value, several grids of different polarities are installed alternately in the battery. The gratings are separated by separators. The positive plates are made of lead dioxide and are dark brown in color. Negative plates are made of pure porous lead, also called sponge lead, and are gray in color. 4. Separators: Thin porous insulators that are placed between the grids of positive and negative plates. Separators do not allow the grids to come into contact, thereby preventing short circuits. Separators are made from polymer-coated paper, foam rubber, fiberglass or foam plastic. 5. Cells or Jars: The plates and separators form a cell, which is a 2.1-volt battery. Cells are also called banks. Typically batteries contain 4 positive and 5 negative plates per cell, but some newer batteries have the same number of plates. A 12 Volt battery has 6 cells connected in series, which produce 6 × 2.1 = 12.6 Volts. 6. Terminals: Metal terminals are located on the housing cover. They are attached to cables that connect the battery via the positive terminal to the vehicle's electrical system and to ground via the negative terminal. 7. Electrolyte: The plates are placed in an electrolyte - a mixture of sulfuric acid and distilled water. A fully charged battery will contain about 36% acid and 64% water. The electrolyte substances chemically react with the active substances of the plates, thereby creating an electric current. During discharge, the amount of sulfuric acid in the solution decreases and the amount of water increases. When charging, the amount of sulfuric acid is restored to its previous level.
Battery parameters
A standard rechargeable battery intended for installation in a passenger car produces a voltage of 12 V – this is the value that most electricity consumers are focused on. Light-duty trucks also use 12-volt batteries, but this is not enough for heavy-duty vehicles - they use 24-volt batteries (to be more precise, two 12-volt batteries connected in series).
Each battery, regardless of type, is characterized by several basic parameters:
- capacity;
- tension;
- cold start current.
These characteristics are usually indicated on the battery label. Let's briefly go through all three of these parameters.
Battery capacity refers to the amount of energy, expressed in amperes, that a fully charged and working battery can supply for 20 hours. So, a 60-amp battery will deliver 3 amperes per hour, a 55-amp battery will deliver 2.75 A.
Reserve capacity is a parameter that is rarely indicated, but is of great practical importance. It is measured in minutes and indicates how long the battery can replace the generator. So, with a total load of 25 A, the reserve capacity should be about 90 minutes, during which the voltage at the terminals will drop to 10.4-10.5 V.
The voltage rating is the total value of the potential difference of all the batteries included in the battery (a car battery usually has 6 of them). For a passenger car this value is 12 volts.
Cold start (cranking) current is the amount of current required to start the power unit at subzero temperatures. Measured under the following conditions:
- temperature: -18ºС;
- operating time: 10 seconds;
- output voltage: 7.5 V.
The higher the cold start current, the easier it will be to start the engine in winter.
Service life and charge-discharge cycles.
Battery life is determined by the number of charge-discharge cycles, not by time. There is no single service life for batteries; manufacturers indicate the service life based on the technical characteristics of this particular battery model. This indicator depends on operating conditions: the deeper the battery is discharged, the fewer cycles it is possible to reproduce.
Characteristics of charge-discharge cycles are given until 60% of the original capacity is retained. For example, the manufacturer lists the number of cycles as 600 at 60% discharge. This means that after 600 ideal charge-discharge cycles (i.e. at a temperature of 20°C), the useful capacity of the battery will be 60% of the initial one. With such a loss of capacity, it is already recommended to replace the battery.
For AGM batteries, the service life is usually 12 years and the maximum number of cycles is 1200 at 20% discharge. There are 100 such cycles per year, about 8 per month.
The service life of lead-acid batteries varies from 300 to 3000 cycles.
It is recommended not to exceed the degree of normal battery discharge by more than 20-30%, and deep - by 70%.
Kinds
For household devices and tools, several types of batteries are offered for sale; they differ in the material used in the banks:
Nickel-cadmium
The rechargeable power source is capable of withstanding several hundred charges and discharges, is resistant to extreme temperatures, and has a high permissible discharge current. Among the advantages are long-term operation and price. At the same time, Ni-Cd has a low capacity and quickly self-discharges. Main areas of application: aviation, electric cars, ships, household appliances.
Nickel-cadmium batteries have a “memory effect” - over time, the useful capacity decreases; to reset, a complete discharge is required, followed by charging with a reduced current. Batteries are sensitive to the quality of the charger used.
Lithium-ion
Lithium-ion batteries.
For a long time, scientists were unable to create a safe battery. Only in 1992 did the first safe samples appear. The Li-Ion battery has a high density, therefore, with similar dimensions, it has 2-4 times greater capacity than its lead-acid counterparts. Another advantage is the charging speed. Using a standard charger, you can completely replenish the capacity in 1-2 hours.
Lithium-ion batteries are in demand in compact, high-tech devices: smartphones, laptops, radio stations. Size, price, and safe operation have made Li-Ion batteries popular with both manufacturers and consumers.
Lithium polymer
The chemical reaction uses a polymer electrolyte instead of a liquid, which takes up significantly less space. The absence of liquid or gel allows the creation of batteries of any shape. The main problem is poor conductivity at room temperature. Therefore, for the normal operation of such batteries, manufacturers add a little gel, increasing current conductivity. This technology is just entering the masses. The current problem is the high cost, which does not allow installing such batteries on inexpensive gadgets.
Signs of a bad battery:
• Premature reduction of electrolyte levels. This means that the plates are sulfated, and during charging, the water in the electrolyte is converted into separate gases of hydrogen and oxygen.
• Excessive corrosion of battery cables or connections. Corrosion is more likely if the battery is sulfated. As the battery charges, acid fumes are forced out of the vents and deposited on the battery cables, sometimes in the compartment underneath the battery.
• The engine is running slower than normal. When battery capacity decreases due to wear or damage, the battery cannot provide the necessary current to start the engine, especially in cold weather.
Battery log and work organization
When using a fleet of electric forklifts, it is advisable to assign its own batteries to each forklift.
To do this, they are numbered: 1a, 1b, 2a, 2b, etc. (batteries with the same number are used on the same loader). After this, a journal is started in which information is reflected daily about each battery, illustrated with an example. Example 1
| Battery number | Installed on a loader | Charged | |||||
| date | Time | Density (average of three elements selected) | Meter readings, machine-hours | date | Time | Density (average of three elements selected) | Meter readings, machine-hours |
| 1a | |||||||
| 1b | |||||||
| 2a | |||||||
| etc. |
Thus, with the help of this measure, you can avoid the use of undercharged batteries, as well as predict and plan the replacement of the battery before it completely fails. In addition, it is advisable to keep another log for each battery, which once a month reflects the information about the battery listed in example 2. This data is the main source of information for the service department, so often maintaining such a log is a prerequisite for warranty service. One or two (in the case of two-shift work) people should be responsible for the entire battery system. Their responsibilities in this area of responsibility should include receiving and issuing batteries, their maintenance and charging, maintaining battery logs, and predicting battery failure.