A car, in essence, is wheels that carry the driver and passengers; there is a steering wheel to control these wheels, an engine to drive it, and a brake to stop it, which is the main element in terms of safety. There is a service brake system and an auxiliary one, which is the parking brake. It is also known as a handbrake or simply a handbrake. With modern cars, the word manual is already becoming an anachronism, since leading automakers are converting the handbrake drive to electronic.
The parking brake is designed, as the name implies, to keep the car stationary while parking (stopping), especially if the roadway or parking surface has a slope. However, this brake is also used as an emergency brake system if the main one fails. Let's try to understand the design of the parking brake system. let's find out how it works.
What are the types of brakes?
The parking brake differs according to the type of drive; the main types are:
- mechanical drive (the most common);
- hydraulic (the most rare;
- electromechanical EPB (button instead of lever).
The prevalence of the mechanical version is due to its simplicity of design and high reliability. To activate the parking brake, simply pull the lever upward (towards you). At this moment, the cables are tense, the mechanisms block the wheels, which leads to a stop or reduction in speed. In new cars with rich equipment, the third option is increasingly used; hydraulic is not very common and is liked mainly by fans of extreme driving.
There is also a conditional division into inclusion methods:
- There is a pedal (aka foot);
- There is a lever one (with a lever).
As a rule, the pedal “handbrake” is used on cars equipped with an automatic transmission. Installed as a third pedal instead of the missing clutch pedal.
Braking mechanisms also vary and are as follows:
- drum brake;
- cam;
- screw;
- transmission (aka central).
In the first case, the cables, when stretched, act on the pads, which in turn are pressed tightly against the drum, thus braking occurs. The central parking brake does not block the wheels, but the driveshaft. In addition, there is an electric drive with a disc mechanism that is driven by an electric motor.
Let's take off with the handbrake
So, you stopped on an overpass and put the car on the handbrake. How can you move away without hitting the car behind you?
Over the past 40 years or more, commercial vehicle braking has been accomplished by drum brakes in a variety of designs and traditional forms of mechanical, hydraulic and pneumatic actuation. Modern air drum brakes today have reached the peak of their development and sophistication and have met the demands of current braking applications.
Requirements for braking performance around the world are becoming increasingly stringent, resulting in existing commercial vehicles absorbing more energy when braking and reducing stopping distances. Several factors contribute to this.
You need to start driving as usual, however, when releasing the parking brake, it is recommended to do the following manipulations.
Press the lock button while the handbrake is in the up position.
As soon as you feel that the car can start moving, you need to quickly lower the handbrake down.
The car should move forward without rolling back.
The average speed of vehicles increases. It is known that even with a small increase in average speed it leads to a large increase in braking force, since kinetic energy is a function of the square of the speed. Increasing demand and expectations from commercial vehicle drivers who want more car-like braking performance, especially in the case of stability, modulation and high performance, areas where drum brakes are compromised depending on your design constraints.
The most important thing here is to correctly determine the moment to release the handbrake.
Signs of this are a decrease in the crankshaft speed, a change in the tone of the engine noise, and the appearance of new vibrations. We strongly advise you to learn this not in traffic jams or on the highways, but outside the city, where no one will accommodate you, or rather you will not allow anyone...
We have concluded that heavy commercial vehicles will inevitably have to move from drum brake technology to new disc brake technology in the not too distant future. The main advantages of disc brakes are: They do not lose effectiveness when immersed in water.
Nowadays, drum brakes are still used on low-end vehicles due to their lower cost over disc brakes. Increased braking distance. Increased brake pedal travel. Noise or vibration when braking.
Good luck learning to drive and starting with the handbrake.
The article uses an image from the website www.volga-gaz.nnov.ru
Today we can say with great confidence that the car plays a huge role in our lives. The status of the owner is often judged by how presentable and well-groomed a car is. Therefore, true car enthusiasts pay enough attention to the care of their car. They take care of both the external and internal condition of their favorite car. Rarely do any individual devices grab our attention. But in every car there is one small system that plays a very important role, this part is the parking brake.
Reduced brake fluid level. The benefits of this new system include its ability to respond to wet or dry surfaces, braking stability, lower assembly weight and long disc life. Technicians predict a promising future for ceramic brakes, as they can be installed into a current system by replacing rotors and brake pads, without having to change pistons, servo or other brake hardware components.
In a light vehicle, the braking system is the most important component from a safety point of view. Understanding its functioning makes it easier to maintain such a system and can facilitate action in the event of failure. When the brake pedal is applied, the booster increases the force and applies more pressure to the wheel cylinders, in some cases the booster works with the combustion chamber of the engine, if the engine stops, the booster also does not have a brake system, so simply apply more force to the pedal to perform the braking.
In the proposed material we will talk about the varieties, its structure and principle of operation.
To make our information more accessible to you, let’s first learn what a parking brake is. Then we will analyze its goals, functions, and also provide a short instruction on its use.
The parking type of brake, also known as manual, is an element that is designed to fix the car in a stationary state (wheel locking). It is mostly used on uneven surfaces and parking lots.
The brake alloy used must be of the highest quality possible to ensure a high boiling point and not absorb water from the steam created by the high temperatures to which the system is subjected. This alloy must be replaced every 000 every year or every time the brake system is maintained in air-to-air contact. Never use prolonged contact with air.
In an emergency situation where the complete braking system fails, it is possible to brake the vehicle using the parking brake, but there is a danger that the wheels may skid on the pavement because they lock suddenly. Any sound when braking requires servicing, as there are sensors on the pads that make a sound when they are close to wear.
On some vehicles, the parking brake acts on the transmission rather than the wheels. Transmission brakes come in both disc and drum types, with drum brakes being more widely used than disc brakes.
The parking brake system is an indispensable mechanism in your car. Her mission is quite simple, but at the same time noble. This mechanism will protect your car from both awkward situations by blocking (the car driving off the side of the road onto a deserted road in your absence) and from serious accidents (the car driving onto the roadway). The consequences can be different, so experts recommend using the handbrake.
How does the handbrake work?
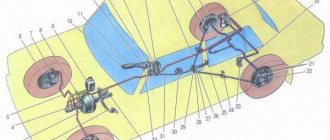
The parking brake design consists of three components:
- Actually, the brake mechanism that interacts with the wheels or engine;
- The drive mechanism that operates the brake mechanism (lever, button, pedal);
- Cables or hydraulic lines.
The handbrake system, as a rule, uses one or three cables; the three-cable version is the most popular and reliable. The system has two rear cables, one front. In this case, two rear cables go to the brake mechanism, the front one interacts with the lever.
The cables are fastened or connected to the handbrake elements using special adjustable ends. In turn, the cables have adjusting nuts with which you can change the length of the cable itself. The system also has a return spring, which returns the mechanism to its original position after the handbrake is released. The return spring is installed either on the brake mechanism itself, on the equalizer, or on a cable connected to the lever.
Functions and purpose of the hand brake
General view of the handbrake
The main purpose of the parking brake (or handbrake) is to hold the car in place during long-term parking. It is also used in case of failure of the main brake system during emergency or emergency braking. In the latter case, the handbrake is used as a braking device.
The handbrake is also used when making sharp turns on sports cars.
The parking brake consists of a brake drive (usually mechanical) and brake mechanisms.
Disc brake
Cars that have disc brakes all around have a hand brake with minor differences. The following varieties are distinguished:
- screw brake;
- cam;
- drum brake.
The first option is used in single-piston brake systems. The piston is controlled by a special screw screwed into it. It rotates, driven by a cable and a lever. The piston moves along the thread, pushing the pads against the brake disc.
The cam mechanism is simpler; it uses a pusher that acts on the piston. The cam has a rigid connection with the lever (also a cable connection). The pusher along with the piston moves when the cam rotates. The drum mechanism is used in multi-piston systems.
Spring energy accumulators [ edit | edit code]
On trucks and buses with a pneumatic brake drive (for example, on KAMAZ vehicles), spring energy accumulators are installed in the brake chambers, braking the vehicle not only in operating mode, but also when parked or in the event of an accident (reduction of pressure, failure of the air compressor, breakage of the brake hose). To park, the driver reduces the pressure in the pneumatic system, the straightening springs reliably press the brake pads to the drum. They release the brakes, increasing the air pressure. When towing an emergency vehicle (on a rigid hitch), it is necessary to unscrew the bolts in the energy accumulators, compressing the springs. [7]
How to use it correctly
Immediately after getting into the car, you need to check the position of the handbrake lever. You should also check it before any start; you cannot drive with a handbrake, as this leads to engine overload and rapid wear of the brake system elements (discs, pads).
As for putting the handbrake on the car in the winter, experts do not recommend doing this, as this can lead to the wheels locking and the impossibility of movement. Melted snow and dirt stuck to the wheels at night can freeze, causing the pads to freeze to the discs or drum. If you use force, you can damage the system; you need to warm the wheels with steam, boiling water or carefully with a blowtorch.
In cars equipped with an automatic transmission, the parking brake should also be used, despite the presence of a “parking” mode in the transmission. This will reduce the load on the shaft locking mechanism and will also ensure that the car is firmly held in place; sometimes in a limited area you can accidentally run into a neighboring car.
Instead of an epilogue
In conclusion, I would like to remind you that the parking brake is one of the guarantees of vehicle safety, so monitoring its technical condition is extremely important.
It’s not difficult to check if everything is in order - tighten the handbrake and, engaging first gear, try to move away. Ideally, the car should stall, but if movement still begins, it’s time to contact a service center for preventive maintenance.
That's all, thank you for studying cars with me, friends!
Tags Brake system
Conclusion
Despite its simple design, the parking brake does not fail very often. A competent car enthusiast should know how this brake works and what malfunctions are typical for it. In the event of a malfunction, repairs can be carried out even by a non-specialist - all you need are tools, spare parts, a little time and, optionally, cleaning products. Fortunately, all this can be found in a wide range even in small stores. We strongly advise against ignoring handbrake malfunctions, because this brake not only allows you to safely park your car on a slope, but is also responsible for emergency braking.
A little about the functions of the handbrake
The main function of a handbrake is to hold the vehicle in one place for a long time. Second function : providing braking in case of an accident or emergency braking. In fact, the handbrake is also a braking device at the same time. It can not only save the driver and his passengers in an emergency, but also simply helps to park the vehicle normally.
In sports cars, the handbrake can also be used to make particularly sharp turns. On such vehicles, the brake lever is not located in the same way as in urban vehicles. By the way, on some trucks and even SUVs the handbrake may look quite ordinary, but in reality it interacts not with the wheels, but with the car transmission. Here the subtleties are in the details. Let's look at some points.
Do not leave the machine only in “P” mode
When parking a car with an automatic transmission, it must also be secured with the handbrake. The fact is that on a slope the standard machine shaft mounts experience too much stress. For example, the machine presses on a small latch with a force that is equal to the product of the mass and the sine of the angle of inclination. For a car weighing 1200 kg on a 23% slope, the rolling force reaches 269 kg. Such a force sooner or later breaks the shaft clamps. After a few years, metal fatigue will occur, and the box will have to be taken in for repairs. Therefore, it is better to relieve the tension from the box using the handbrake.
Cable drive design
The handbrake device of this type, installed on the vast majority of passenger cars, is simple and provides for autonomous activation, independent of the main system. How standard service brakes function:
- The driver pressing the pedal in the cabin sets the piston of the main hydraulic cylinder in motion.
- Under the influence of the piston, pressure is created in tubes with incompressible fluid laid to all wheels.
- Transmitted to the working cylinder of the wheel, fluid pressure pushes the pistons of the drum or disc brake. In the first case, the pads are moved apart and the force of friction stops the rotation of the drum. In the second, they tightly compress the spinning disk.
For parking braking, the handbrake uses standard elements - pads, but moves them apart with its own mechanical drive, consisting of the following parts:
- the above-mentioned lever in the cabin, equipped with a locking mechanism in different positions and a push-button unlocking device;
- the main cable connected to the lever and ending with a mounting bracket or an arcuate guide;
- secondary cables connected to the main one and connected to the brake levers of the rear wheels;
- cable adjustment mechanisms (spacers, nuts and springs), suspension brackets to the underbody;
- spacers between the pads.
Note. The main cable is connected to the rear drum mechanisms in two ways: with one cable hooked in the middle to a guide, or with two separate drives.
The rod system is usually hidden under the bottom in the recess of the central tunnel. Cable drives are equipped with protective covers that prevent corrosion. How does a mechanical handbrake work:
- The driver lifts a handle in the cabin, which automatically locks into the selected position.
- The traction moves the main cable forward, and it carries the secondary drives along with it through a mounting bracket.
- A lever inside the drum mechanism rotates and pushes the upper ends of the shoes apart. The automatic regulation function is taken over by the spacer bar.
- When the driver removes the car from the handbrake, the springs inside the drums tilt the lever back and the pads move. At the same time, the spring pulls the cable drive back to its original position.
The parking brake described above locks the drum wheels mounted on the rear axle. On cars equipped with brake discs, the same principle works: a cable pulls a lever, which causes the pads to compress. The only difference is the location and shape of the lever - on disc brakes it is placed outside, behind the hub.