Since the advent of the first automatic transmission, gearboxes of this type have provided serious competition to manual transmissions. At the same time, for a long time, automatic transmission was installed on cars of the middle class and premium segment, but later the unit became widespread.
Due to its enormous popularity, as well as the constant tightening of regulations and standards regarding fuel efficiency and environmental friendliness, manufacturers are constantly improving automatic transmissions, offering innovative solutions, etc.
As a result, today we can distinguish at least three main types of “automatic machines”, which differ greatly from each other in design and operating principles, but each of them is called an automatic transmission. Next we will talk about what types of automatic transmissions there are, as well as what features this or that unit has.
Types of automatic transmission
Automatic transmissions of modern cars can be divided into several types, differing in the control system and control over the operation of the automatic gearbox. The first type of transmission is controlled by a hydraulic device, and the second by an electronic distributor.
Types of automatic transmission
The internals of both transmissions are identical, but there are a few layout differences that each automatic transmission has.
We will briefly consider all 3 types of automatic transmissions in more detail in order to understand their differences between each other and the principle of operation.
Types of automatic transmission - briefly about the main thing.
Hydraulic automatic transmission - classic automatic transmission
The hydraulic type of automatic transmission is the simplest automatic transmission. Such a box eliminates direct connection between the engine and wheels. The torque in it is transmitted by two turbines and working fluid. Due to the improvement of the mechanism, a specialized electronic device appeared in such a box, which was also able to add operating modes such as “winter”, “sport”, and economical driving.
One of the main disadvantages, in comparison with manual transmission, is slightly higher fuel consumption and acceleration time.
Robotic automatic transmission
MTA popularly sounds like a DSG robot, structurally most similar to a manual transmission, but from a control point of view, it is a typical automatic transmission, which, as a result of evolution, not only reduces fuel consumption, but also a number of other advantages, naturally with its own nuances.
CVT transmission
Although considered an automatic transmission, a CVT and an automatic transmission are fundamentally different both in design and operating principle. There are no steps in such a gearbox since there is no fixed gear ratio. Drivers who are accustomed to listening to the engine of their car cannot monitor its operation, because the torque in the variator box changes smoothly and the engine tone does not change.
Comparison of 4-speed and 5-speed gearboxes
If you want to make a thorough comparison of the two options, you should consider maintenance costs and ride comfort (speed and ride comfort). As mentioned earlier, if price is a key factor, then choose a 4-speed manual.
For those who value travel comfort more, a 5-speed automatic transmission was specially created. The final decision always remains with the driver, but today it is extremely difficult to find a 4-speed manual. Be sure that it is better and more comfortable to find additional funds to guarantee maximum comfort while traveling than to use more budget models! The purchase of a 5-speed gearbox is more likely to pay off in fuel consumption, since on average, a 5-speed gearbox has a fuel consumption that is 10-20% lower than a 4-speed gearbox.
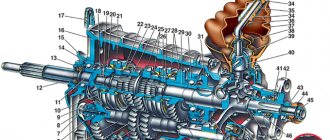
Automatic transmission components
- torque converter
, which replaces the clutch, and does not require participation and control by the driver. - a planetary gear set
is installed in the automatic transmission . This part helps change the attitude in the automatic transmission when shifting the transmission. - front and rear clutch
, as well as a brake band, thanks to which gears are directly changed. - the last and most important part is the control device
, which is a unit consisting of a transmission pan, a pump and a valve box that performs control functions. This component transmits movement data through signs that transmit a signal to the automatic transmission itself.
Design and operation of an automatic transmission.
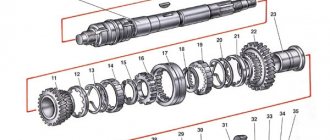
Of all the main components, we will pay the most attention to the torque converter of the box.
The torque converter includes:
- centrifugal pump;
- stator;
- centripetal turbine;
- pump wheel;
- turbine wheel;
The stator is a guide device that is located between these parts. The pump wheel is connected to the engine crankshaft, and the turbine wheel is connected to the gearbox shaft. The reactor has 2 functions. It can rotate or be locked by the overrunning clutch.
The main task of the torque converter is to dampen strong shocks that are transmitted by the transmission to the engine and in the opposite direction. This device increases the service life of these parts. Using liquid oil, torque is transmitted from the engine to the automatic transmission.
In order for the automatic transmission to work for a long time and properly, it is necessary to regularly undergo diagnostics at a service station.
Pay attention to the following details:
- gears must be changed in 1 second, maximum time - 1.5 seconds;
- notification of switching is carried out by light jolts;
- Gear shifting should be silent.
Robotic transmissions
Robotic transmissions are a hybrid version of a manual transmission and an automatic transmission.
In their design, robotic boxes are incredibly similar to mechanics, but the operation and control of switching is carried out completely automatically.
This type of gearbox made it possible to solve the problems associated with the excessive fuel costs of automatic machines.
Loss of dynamics was also reduced, but during operation one unpleasant pattern became clear: the faster the acceleration, the more clearly the transitions from one stage to another are felt.
This phenomenon could be compared to the twitching of poorly functioning automatic transmissions.
Automakers could not tolerate the existing problem.
Improvements did not take long to arrive. The German concern Volkswagen has produced a robotic transmission with two clutches.
It was called "DSG". Drivers have probably heard this abbreviation. The box received a pair of clutch discs that control different gears. One was in charge of the even steps, the second was in charge of the odd ones.
Thanks to this, changing gears became almost imperceptible.
Unfortunately, if the first series of “robots” could be called cheap, then this definition does not apply to “DSG”.
The main disadvantage of modern robotic boxes is the high price.
Features of automatic transmission operation
- The automatic transmission needs to be warmed up well
before you start driving (this is especially important in winter). - When operating an automatic transmission,
strongly
not recommended
the selector lever in positions P and R while driving . - There is no need to engage neutral gear
when descending a mountain, supposedly
saving fuel
- it still won’t happen, but problems with braking may arise. - Engine braking is not possible in all gearbox modes. This operating point must be studied in detail in the operating manual for a particular vehicle; neglecting this feature can cost expensive repairs.
How to use an automatic transmission
According to auto mechanics at service stations, the main malfunctions of automatic transmissions appear as a result of violation of operating rules and untimely maintenance of the box.
Operating modes
Depending on the type of automatic transmission, there are different automatic transmission modes. Each position of the selector lever or button on it is designed for different driving conditions with its own characteristics.
The main types of automatic transmission modes and their impact on vehicle operation:
- P (parking) - locking the drive wheels and gearbox shaft, used only when parked and warming up;
- N (neutral) - the shaft is not blocked, the car can be towed, equivalent to neutral gear for a manual transmission;
- D (drive) - driving in normal conditions with automatic gear selection;
- L (D2) - low gear for driving in difficult conditions - off-road, steep descents and ascents, speed less than 40 km/h;
- D3 - downshifting for small descents and ascents;
- R (reverse) - reverse movement, activated when the vehicle comes to a complete stop and the brake pedal is pressed;
- O/D - engaging fourth gear when driving at high speed;
- PWR - sport mode, to improve dynamic qualities, gear increases occur at higher engine speeds;
- Normal - for smooth and economical movement;
- Manu - manual gear mode, recommended for use in winter.
How to start a car automatically
The operating features of an automatic transmission require proper starting. To protect the box from incorrect actions and subsequent breakdowns, degrees of protection have been developed.
When starting the car, the selector must be in the “P” (park) or “N” (neutral) position. Only in such positions will the protection system allow the engine start signal to pass through. In other positions of the lever, it will not be possible to turn the key or there will be no changes after turning the key.
To start, it is better to use the parking mode, since the drive wheels of the vehicle will be blocked and this will not allow it to roll away. Neutral mode should only be used for emergency towing.
Automatic - arithmetic
Well, why are you hanging your nose - “six-speed”? Let me cheer you up a little guys. I suggest you calculate what is better in the end for the money.
Look, almost all old automatic transmissions have a consumption of about 12 - 14 liters in the city (of course, someone can even “vomit” and meet 11 liters, but this is rare). Let's take an average figure of about 13 liters.
New automatic transmissions consume 8–9 liters in the city. Let it be approximately 9 liters. Do you know what I mean? The DIFFERENCE is 4 liters (or about that).
If you calculate how much this turns out to be in rubles now (let’s shift it to the average price of 95 gasoline - 40 rubles, 4X40 = 160 rubles) - this is from 100 kilometers.
From a thousand it will be 1,600 rubles, and from 100,000 – 160,000 rubles.
If we consider that the automatic machine will break down at 150,000 km, then it will save 240,000 rubles. And the average cost of repairing a modern automatic transmission is approximately 60 – 100,000 rubles (depending on where you do it). YES, and you can buy a contract for 40 - 50 thousand.
As you can see, everything is very ambiguous. OF COURSE, it’s sad that modern manufacturers deliberately underestimate the service life and remove the possibility of full service - HOW I THINK THIS IS NOT CORRECT!
Now we are watching the video version of the article.
Please vote, which 4- or 6-gear automatic are you for?
I’ll end with this, I think it was interesting, YOURSINCERELY – AUTOBLOGGER.
Similar news
- TIPTRONIK what is it. How to use it? And what does it have to do with manual...
- CVT (variable gearbox): what is it, the principle of…
- Automatic transmission clutches. What are they, how do they work and why do they burn?
Add a comment Cancel reply
Reliability indicators
The presented unit has proven its reliability throughout its entire operation. This representative of the old school, of course, cannot boast of effectiveness at the moment. Its main strength is durability.
These boxes require intervention in their design no earlier than 300 (or maybe more) thousand km. The main problem with such a mechanism is the wear of the locking clutch installed in the torque converter. This malfunction occurs earlier on cars with powerful power units. When the clutch wears out, rapid clogging of the torque converter itself begins, vibrations appear, which causes failure of other parts of the box: oil pump, oil seals, bushings. Such problems are easy to identify; they are manifested by ATF leaks from under the oil seals in the area of the oil transfer pump.
Symptoms of a malfunction of the DP0/DP2 machine
- The box goes into emergency mode. The “gear” symbol blinks in the instrument cluster or “Gearbox Fault” lights up on the display
- The engine revs up willingly, but the car does not accelerate
- Fluid leak from automatic transmission
- Jerking when shifting from first to second gear
- Gears above first are not included.
- The car does not start moving when mode D or R is turned on
Hydraulic unit
To control the gears, shift-type solenoids (A, B) are used. With their help, the necessary combinations are created that help perform all forward gears. There are also 2 additional solenoids for standard applications. They control the ATF pressure and the lockup clutch in the torque converter. These solenoids cannot operate on low-quality oil, so they can quickly fail if it is replaced infrequently. Solenoid #5 is used to control the Overrun clutch pack.
The valve body of this machine practically does not wear out, and in the event of a breakdown, it mainly requires cleaning, nothing more.