If the expression “the main thing is to stop on time” in everyday communication concerns moral principles, then in the context of motor transport this expression can affect the material aspect of the life and health of the motorist.
There are no secondary units in the car, but the braking system should be a priority in car maintenance and repair. In the operation scheme of hydraulic brakes, the main ones are both the main and the working brake cylinders. Let's look at the operating principle, design, diagnostics, repair and replacement of this unit using the example of a common VAZ car.
Classification of car brake systems
Modern cars are equipped with three or four types of brake systems:
The main and most effective braking system of a car is a working one. It is used throughout the movement to regulate speed and come to a complete stop. Its device is quite simple. It is activated by pressing the brake pedal with the driver's right foot. This procedure ensures simultaneous reduction of engine speed, by removing the foot from the accelerator pedal, and braking.
The parking brake system, as the name suggests, is designed to keep the vehicle stationary during long periods of parking. In practice, experienced drivers leave the car in first or reverse gear. However, on large slopes this may not be enough. » alt=»»> The manual parking brake is also used when starting off on uneven sections of the road, when the right foot should be on the gas pedal and the left foot presses the clutch. By smoothly releasing the brake lever with your hand, simultaneously engaging the clutch and adding gas, you can prevent the car from arbitrarily rolling downhill.
The auxiliary braking system is installed on heavy-duty vehicles, for example, on domestic KamAZ, MAZ, KrAZ vehicles. It is designed to reduce the load on the main working system during prolonged braking - when driving in the mountains or on hilly terrain.
System design and principle of operation
The main thing in the braking system of any car is the brake mechanisms and their drives. The hydraulic brake drive used on passenger cars consists of:
- pedals in the cabin;
- working brake cylinders of front and rear wheels;
- vacuum booster;
- pipeline (brake pipes);
- master brake cylinder with reservoir.
The principle of operation is as follows: the driver presses the brake pedal, driving the piston of the brake master cylinder. The piston squeezes fluid into the pipelines to the brake mechanisms, which in one way or another create resistance to the rotation of the wheels, and thus braking occurs.
When the brake pedal is released, the piston returns via a return spring, and the fluid flows back into the master cylinder - the wheels are released.
On domestic rear-wheel drive cars, the brake system design provides for a separate supply of fluid from the master cylinder to the front and rear wheels.
On foreign cars and front-wheel drive VAZs, the pipeline circuit diagram “left front – right rear” and “right front – left rear” is used.
Why is GTZ needed?
The GTZ converts the energy of pressing the brake pedal into the energy of compression of the brake fluid. And the force is transmitted very quickly through the system.
Its task is to provide braking force in at least one of the circuits of the braking system. If one part of the system fails, another circuit always remains operational. This allows the car to brake, although not as effectively.
In modern cars, the GTZ works in tandem with the ABS system - the latter regulates the braking force on the wheels by controlling the pressure through the main brake cylinder.
Types of brake mechanisms used in cars
The vast majority of cars are equipped with friction-type brake mechanisms that operate on the principle of friction forces. They are installed directly in the wheel and are structurally divided into:
There was a tradition of installing drum mechanisms on the rear wheels and disc mechanisms on the front. Today, depending on the model, the same types can be installed on all four wheels - either drums or discs.
Design and operation of the drum brake mechanism
The drum-type system device (drum mechanism) consists of two shoes, a brake cylinder and a tension spring located on a shield inside the brake drum. Friction linings are riveted or glued onto the pads.
Replacing a faulty brake cylinder
The replacement scheme in the VAZ family is almost the same for cylinders of both circuits with minor differences.
Initially, you need to prepare the necessary keys and plugs suitable for the size of the pipes. After removing the wheel and unscrewing the pipes, we put plugs on them to prevent fluid leakage. Having unscrewed the corresponding nuts, we dismantle the old cylinder and put a new one in its place, reassembling it in the reverse order. If, after replacement, wheel assembly is hindered by pads that are too far apart, you can file the ends of the pads, just don’t overdo it, as this may affect the operation of the handbrake.
After any manipulations with the brake system, it must be bled according to the diagram.
Comparative characteristics
Drum brakes are simpler and cheaper to manufacture. They have a property called the mechanical self-reinforcement effect. That is, with prolonged pressure on the pedal with your foot, the braking effect increases many times over. This occurs due to the fact that the lower parts of the pads are connected to each other, and the friction of the front pad on the drum increases the pressure of the rear pad on it.
However, the disc brake mechanism is smaller and lighter. Temperature resistance is higher, they cool faster and better due to the provided window openings. And replacing worn disc pads is much easier than replacing drum pads, which is important if you carry out the repairs yourself.
Working principle of the parking brake
It is a purely mechanical device. It is activated by raising the handbrake lever to a vertical position until the latch clicks. In this case, tension occurs on two metal cables running under the bottom of the car, which tightly press the brake pads of the rear wheels to the drums.
To release the car from the parking brake, press the locking button with your finger and lower the lever down to its original position.
Car brake system care
As one of the most important components, the car's braking system requires constant attention and care. Here, literally any malfunction can lead to unpredictable consequences on the road.
Some diagnoses can be made based on the behavior of the brake pedal. Thus, an increased stroke or a “soft” pedal most likely indicates that air has entered the hydraulic drive system as a result of a brake fluid leak. Therefore, it is necessary to periodically monitor the liquid level in the tank.
Its increased consumption may be a consequence of damage to hydraulic hoses and tubes, as well as ordinary evaporation over time. This causes air to enter the system and cause brake failure.
Parts that have become unusable must be replaced, and the system will have to be pumped by bleeding air from each working cylinder on the wheels and adding fluid. The process is long and tedious. » alt=»»> If the car pulls to the side when braking, it indicates a possible failure of one of the working cylinders or excessive wear of the linings on a particular wheel. If the brake mechanisms are dirty, a characteristic noise may occur when you press the pedal.
All these malfunctions can be easily fixed independently or by contacting a service center. And to minimize the troubles described above, take care of your brakes and use engine braking more often, especially on steep and long descents. Prolonged activation of the main working system leads to overheating of parts and causes various breakdowns.
One of the main systems that ensures safety when driving a car is the braking system. The most widespread are brake mechanisms that use the frictional force of different materials. Such mechanisms are installed on all cars, including VAZs belonging to the “Classic” family.
As an example of a classic VAZ, model 2107 will be used. The brake system of the VAZ-2107 includes working and parking systems. The task of the working component is to reduce the speed of movement of the car until it is completely immobilized.
It consists of two components: the first is the brake mechanisms, which act on the wheels, which is why their rotation decreases. The second component is the drive, through which the driver operates the mechanisms.
The parking component ensures that the wheels of one of the car's axles are locked, in the case of the VAZ-2107 - the rear axles, while the car is immobilized. The use of this brake prevents spontaneous movement of the car. This system uses a separate drive that acts on the rear axle mechanisms.
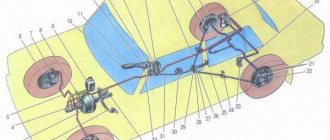
In more detail, what the brake system of the VAZ-2107 looks like is shown in the diagram:
Now let's take a closer look at the design of the VAZ-2107 brake system. First, let's go through the working component. Its drive is hydraulic and includes:
- Control pedal;
- Vacuum booster;
- Main cylinder;
- Tank for working fluid;
- High pressure pipelines;
- Rear axle bellows pressure regulator;
The use of liquid as a working element of the drive is due to a number of positive qualities: a complex system of levers for the drive is not required, the wiring of pipelines to the mechanisms is facilitated, the transmission of force from the driver’s foot is enhanced several times due to the vacuum booster.
The working mechanisms on the VAZ-2107 are of two types: disc brakes are installed at the front, using calipers; drum-type mechanisms are used on the rear axle, which also includes a parking mechanism.
Now in more detail about the elements of this system. So, the pedal that the driver presses is located on the same axis as the clutch control pedal. To ensure that it can be returned to its original position, it is spring-loaded.
Checking the brake master cylinder
The design of the brake master cylinder involves the use of rubber sealing parts, which periodically fail and become the main problem during testing. Therefore, if the brake system has problems described above, it is necessary to check its operation. And you need to start with the GTZ. The check is performed in the following sequence:
- It is necessary to check for drips on the body, as well as for cracks on it.
- Next, you need to check the tightness and condition of the cylinder sealing elements. For any amount of repair work carried out, it is necessary to replace all rubber seals that are included in the repair kit for the main brake cylinder.
If the check shows changes in the operation of the gas turbine engine, then without waiting for it to completely fail, we recommend repairing it by replacing some elements from the repair kit. Please note that it can only be used to fix minor problems (for example, brake fluid leaks).
If the cylinder mirror is damaged , that is, scratches, cavities or other damage appears on it, then it becomes unrepairable. The only way out in this case is to completely replace it.
Source
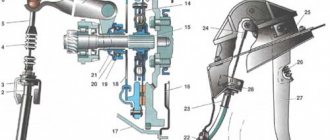
Vacuum brake booster
A rod connected to the amplifier is connected to the pedal. The design of the VAZ-2107 vacuum brake booster is quite interesting; it is shown in the figure:
The amplifier is a sealed container, internally divided into 2 chambers by means of a membrane. The chamber located closer to the pedal is called atmospheric, and the chamber separated from it by a membrane is called vacuum. The diaphragm itself is connected to the piston rod of the master cylinder.
The vacuum chamber is connected by a pipe to the intake manifold of the engine, where the vacuum comes from. The design also includes a follower valve controlled by the pedal rod, which does all the work.
When the pedal is released, this valve connects the chamber cavities through a channel, providing identical pressure. When the pedal is applied, the valve closes the channel connecting the chambers and opens the channel connecting the atmospheric chamber with the atmosphere. Since a vacuum is maintained in the second chamber, atmospheric pressure begins to put pressure on the membrane. Since it is connected to the piston rod of the master cylinder, due to the movement of the piston, fluid is displaced from the cylinder into the pipelines.
Selection and purchase of GTZ
It is best to select a GTZ based on the car’s VIN code, although you can get by with the make, model and type of engine. The part does not have different options to choose from, so the only option to choose from is the manufacturer. Choose reliable brands, because the operation of the GTZ is critical to your safety. The website partreview.ru has good reviews for products from the brands TRW, ATE and LPR.
As mentioned above, sometimes you can get by by replacing parts of the GTZ repair kit. But if the housing itself or components not from the repair kit are worn out or damaged, the entire master brake cylinder is replaced.
Related terms
- ABS (Anti-lock braking system)
- Vacuum brake booster
Caliper device
Let's move on. The front axle mechanisms are disk ones, consisting of calipers with the main brake elements - pads, and brake discs.
A caliper is a body with cylinders made in it for the pistons. This model has two of them, one for each block. The support structure is shown in the figure.
The caliper pistons have the form of a glass, which is placed in their cylinders, but they can move along it. To prevent fluid leakage, the pistons are equipped with o-rings.
Pads are small metal plates onto which linings made of friction material are glued.
The brake disc is made of metal for better adhesion to the surface of the pads; its side surfaces are well processed so that there are no protrusions or shells on them.
The VAZ 2107 brakes work like this: the fluid moves into the caliper cylinders, where it begins to push out the pistons. They come out of the cylinders, pressing the pads against the disc.
Drum and disc actuators
The main work during braking lies with the actuators, because they are the ones who slow down the rotation of the wheel.
Their work is based on the force of friction, which is why all brake mechanisms on cars are of the friction type.
Two types of such mechanisms have become widespread on cars - drum and disk.
Each of them has its own design features, advantages and disadvantages.
It is noteworthy that combining them is quite acceptable. So, in many cars, all mechanisms can be either only drum (usually on trucks) or only disc (many passenger cars).
But there is also a combination of them - disc mechanisms are installed on the front wheels, and drum mechanisms are installed on the rear wheels.
Disc type brake mechanism.
Nowadays, such a mechanism is increasingly used, due to a number of advantages over the drum type.
Structurally, it consists of several elements:
- Disk;
- Pads;
- Caliper.
The disc acts as one of the friction parts of the mechanism and is used to create friction during braking. It is fixed to the hub and rotates at the same speed as the wheel.
Pads are the second friction component. By pressing them against the disk, friction is created between these elements, which reduces the speed of rotation of the disk, and with it the wheel.
To increase the friction force, the pads have special friction linings.
The caliper design includes a drive working cylinder. It is this component that ensures the clamping of the pads.
There are different designs - both single-piston (the most common) and two-piston.
The design of this mechanism looks like this: a caliper with pistons is fixed above the disk, while the working pistons (one or two) are located perpendicular to the side surfaces of this disk.
Pads are placed between the caliper and the two lateral (working) surfaces of the disc. When the brakes are released, there is a gap between the friction components, so the pads do not interfere with the rotation of the disc.
Now a little about how mechanisms with single-piston and two-piston calipers work.
In the first case, the caliper can move along the guides, which allows you to simultaneously press both pads.
It works like this: when the pressure in the working cylinder increases, the piston comes out and begins to press the pad. This creates a reverse force that moves the caliper along the guides.
Shifting, he begins to press the second block with his body. As a result, the pressing force of the pads on both sides of the disc is equalized.
In a two-piston caliper, its movement is not provided, since each pad is pressed by its own piston.
Design and operation of the drum brake mechanism.
The design of the drum actuator differs from the disk one, and radically.
Its device includes:
- Drum;
- Pads;
- Double piston working cylinder;
- Shield;
- Tension springs.
As in the case of a disk mechanism, a drum mechanism has two friction components, between which friction occurs during braking. Here their role is played by a drum and two blocks made in the shape of a crescent.
The drum is a movable element; it is located on an axis and rotates along with the wheel. The stationary element is the shield with the working cylinder (top) and pad support (bottom) attached to it.
The pads (with friction linings) are placed so that their tops rest against the cylinder pistons and support.
They are held in this position by tension springs (top and bottom) and clamps. All elements located on the shield are placed inside the drum, that is, they are covered by it.
It all works very simply: when you press the pedal, the pistons come out of the cylinder and, overcoming the force of the springs, spread the pads.
This movement causes the pads to begin to press against the inner surface of the (working) drum, which slows down its rotation.
When the pedal is released, the springs return the pads to their original position.
Comparative characteristics.
As already noted, each of the types of mechanisms used has its own advantages and disadvantages.
The positive qualities of disk mechanisms include:
- High efficiency;
- Less response time;
- Due to the open design, ventilation is ensured (the mechanism is better cooled and wear products are removed);
- Quick removal of moisture;
- Easy to disassemble for maintenance and repair.
But at the same time, such mechanisms wear out faster, so their maintenance, with the replacement of consumables, must be carried out more often.
The open design also has its downsides.
Firstly, more foreign particles get between the pad and the disc, which increases the wear rate.
Secondly, it is much easier for moisture to get onto the working elements. Moreover, if the disk is very hot, there is a high probability of warping.
Also, such mechanisms are difficult to use as elements of a parking system.
As for drum mechanisms, their advantages include:
- Long service life without the need to replace consumables;
- The working elements are protected from foreign particles (they are closed);
- High drum resistance to sudden temperature changes;
- Possibility of use as a parking brake element (this is why such mechanisms are often used on the rear wheels).
But such brakes are less effective, there is a possibility of their failure when overheated, and they have a more complex design, which makes repairs more difficult.
In addition, destruction of the springs or the pads themselves can lead to jamming of the mechanism.
Rear axle brake mechanism
The brake system of the VAZ-2107 rear axle has a different device. All its elements are hidden inside the brake drum:
The working brake cylinder of the VAZ 2107 has the following device: there is a body, also known as a cylinder, with two pistons placed in it. When exposed to fluid pressure, they come out of the cylinder.
The pads are metal, made in the shape of crescents, with friction clutches glued to their upper edge. The pads installed on the hub form a ring.
In the lower part, the pads are installed in the seats made under them, and in the upper part - in the grooves made in the pistons. To prevent the pads from moving apart spontaneously, they are tightened with springs. The parking brake mechanism is also located there.
On top of all this there is a drum mounted on the hub shaft. When braking, the fluid pushes the pistons, and since the pads fit into their grooves, this movement of the pistons is accompanied by the divergence of the pads. At the same time, they are pressed towards the drum and the rotation slows down.
Possible faults
During operation, the master brake cylinder, like all vehicle mechanisms, becomes unusable, which entails repair or replacement of parts. The main reason may be uneven distribution of brake fluid inside the structure. Diagnosis of malfunctions is carried out first using an external inspection: checking for defects and brake fluid leaks. Then they check the functionality of the unit: with normal pressure on the rod, there should be no jamming or sagging.
Parking system
Although it engages the mechanism of the rear axle wheels, it is in no way connected with the working mechanism. It uses a cable as a drive connected to the handbrake located inside the car.
Under the car, this cable is divided into two parts, going into the rear axle mechanisms. Inside, the ends of the cable are connected to the drive lever, which in turn is connected to a spacer bar. The drive lever is connected to one of the pads.
When the handbrake is engaged, the cable pulls the lever, and since it rests against the bar, the pads are released. The toothed sector of the handbrake fixes the position of the lever when the pads are spread apart.
Pressure regulator
It is installed in the rear wheel drive and not only distributes fluid to the mechanisms, it also prevents possible skidding due to different forces on the mechanisms. This is done by limiting the supply of pressure to the mechanisms, depending on the position of the car body relative to the bridge.
The regulator is driven by a rod, one end of which is fixed to the rear axle, while it itself is fixed to the body. As the load on the rear axle increases, the body changes position relative to the axle; as a result, the rod puts pressure on the regulator piston, which adjusts the pressure supplied to the mechanisms.
The principle of operation of the VAZ-2107 brake system
If it is necessary to reduce speed, the driver presses the pedal. Its force is transmitted to the amplifier valve, which opens the required channel to supply atmospheric pressure to the membrane. The membrane is connected to a rod connected to the piston of the main cylinder. This rod displaces fluid into the pipelines leading to the operating mechanisms. Since the liquid is not compressed, all force is completely transferred to the mechanisms.
The liquid presses on the pistons of the working cylinders, and as they move out, they unclench (on drum bellows) or press the pads (on disk bellows) to the disk or drum connected to the wheel hubs. Due to the friction of the pads on the discs (drums), the rotation slows down.
Pneumatically driven
The last type of drive used in vehicles, pneumatic, has found greater use in trucks.
This type of work is identical to hydraulic, but compressed air acts as the working element.
The brief design of the system is as follows: there are the same drum brake mechanisms with a cam shaft. But this shaft is connected to a membrane-type working brake chamber.
Air supply lines connect to this chamber. Air pressure is provided by a compressor and under pressure it is stored in receivers.
The mechanism is controlled by a brake valve.
Principle of operation.
- The driver uses the pedal to open the air supply lines using the brake valve.
- Compressed air enters membrane-type working chambers.
- The diaphragm is connected by a rod to the cam shaft rotation mechanism.
- Compressed air presses on the membrane, which deflects and pushes the rod, which acts on the mechanism and the shaft rotates, releasing the pads.
Types of maintenance work
Despite the fact that the system is not so complicated structurally, it requires periodic maintenance, including:
- Checking the fluid level in the system;
- Checking the degree of wear of friction clutches, pads, discs, drums;
- Bleeding the system to remove air;
- Checking the condition of the handbrake cables;
- Adjustment of cable tension;
- Adjusting the rear brake adjuster;
Before each trip, you must always check how much brake fluid is in the VAZ-2107 system. An insufficient amount of it can lead to the fact that the efficiency of the system can be significantly reduced due to air getting inside the pipelines. In addition, a decrease in level may indicate damage to pipelines and fluid leakage.
The elements of the mechanism should be checked every few months, this is especially true for the pads, since they wear out quite intensively. If necessary, worn elements are replaced.
If air gets inside the drive of the working system, pumping is performed, as a result of which the air is expelled from the system.
Loosening the tension of the parking brake cables can lead to its failure, so you need to periodically monitor it and, if necessary, restore the tension.
Servicing brake discs and pads
Wear and replacement of discs
Brake disc wear is directly related to the driver's driving style. The degree of wear is determined not only by mileage, but also by driving on bad roads. Also, the degree of wear of brake discs is affected by their quality.
The minimum allowable thickness of a brake disc depends on the make and model of the vehicle.
The average value of the minimum permissible thickness of the front brake disc is 22-25 mm, rear – 7-10 mm. It depends on the weight and power of the car.
The main factors indicating that the front or rear brake discs need to be replaced are:
- disc beating when braking;
- mechanical damage;
- increase in braking distance;
- decrease in the level of working fluid.
Wear and replacement of pads
Brake pad wear primarily depends on the quality of the friction material. Driving style also plays an important role. The more intense the braking, the greater the wear.
The front pads wear out faster than the rear ones due to the fact that they experience the main load during braking. When replacing pads, it is better to change them at the same time on both wheels, be it rear or front.
Pads installed on one axle can also wear unevenly. This depends on the health of the working cylinders. If the latter are faulty, then they compress the pads unevenly. A difference in the thickness of the linings of 1.5-2 mm may indicate uneven wear of the pads.
There are several ways to determine whether your brake pads need to be replaced:
- Visual, based on checking the thickness of the friction lining. Wear is indicated by a lining thickness of 2-3 mm.
- Mechanical, in which the pads are equipped with special metal plates. As the linings wear out, the latter begin to come into contact with the brake discs, which causes disc brakes to squeak. The reason for squeaking brakes is abrasion of the lining up to 2-2.5 mm.
- Electronic, which uses pads with a wear sensor. As soon as the friction lining wears down to the sensor, its core comes into contact with the brake disc, the electrical circuit is closed and the indicator on the dashboard lights up.
Features of the braking system
One of the features of the VAZ-2107 brake circuit is the presence of a dual-circuit system. The essence of a dual-circuit system is that the working drive is divided into two parts, each of which supplies fluid to only two mechanisms, while the circuits do not interact with each other.
The presence of two circuits ensures the operability of the brakes of at least two wheels in the event of depressurization of one of the circuits. That is, even if the pipelines of one circuit are punctured, the second will remain fully operational, which will ensure the functioning of the brakes.
In the VAZ-2107, the circuits are divided in such a way that the drive of the front axle mechanisms is separated from the drive of the rear mechanisms. This allows you not only to maintain the functionality of the system when one of the circuits fails, but also to pump each circuit separately. That is, if one of the circuits is airy, then it needs to be pumped, but it is not necessary to service the second one.
This is only general information about how the VAZ-2107 brake system works, and does not include all the details on its maintenance and repair. In general, the brakes of this car work quite well, although some elements of it cause complaints from car owners.
Which brake brake should I choose?
The modern market is full of different types of rear brake cylinders, so when buying this element, it is not easy to make a choice. Numerous reviews on the Internet will help us with this. Having studied the content on this topic, we came to the following conclusion: By and large, all brake cylinders in the same price category have the same quality, but the rear brake cylinder from ATE turned out to be the highest quality and most desirable. Our Basalt, which is one of the best domestic manufacturers of these products, does not lag behind.
It’s only recently that I started making quality products. The Belarusian company fenox, whose products are, to put it mildly, “unreliable,” even wanted to buy it, but they couldn’t buy it. The products also perform well.