Many different gaskets and rubber bushings are installed on automobile mechanisms for normal functioning or as a connecting element. But such elements wear out quite quickly due to increased intensity. As a result, play appears in them, which makes traveling by car unsafe. In addition, worn bushings can lead to more serious problems.
This also applies to bushings installed on the stabilizer. If you begin to notice noise in the car's suspension while driving, this may mean that the stabilizer bushings need to be replaced. Moreover, this applies to replacing the front and rear bushings. This will be discussed in more detail in this article.
Stabilizer design features
In the field of mechanical engineering, the stabilizer appeared along with the first cars whose maximum speed exceeded 20 km/h. Due to the large rolls that occur when turning, there was a need to install this component. The main purpose of the stabilizer is to protect the vehicle from rollover, since during a turn the load on the outer wheels increases, and on the inside, on the contrary, decreases. This causes the car to rock. The stabilizer makes it more stable on the road, preventing it from turning over.
On a note! All car suspensions are equipped with a stabilizer, not only in the front, but also in the rear. A stabilizer is not needed only if a torsion beam is installed at the rear of the car: the functions of the stabilizer will be assigned to the suspension itself.
The design of the stabilizer of many cars is a U-shaped metal rod made of spring steel. To secure the device to the body, special clamps and bushings are used to allow the stabilizer to rotate. To make the car more stable and increase the elasticity of the stabilizer, bushings are used - all impacts from various suspension elements fall on them.
Suspension diagnostics at a service center
The cost of such diagnostics varies from five hundred to a thousand rubles. Diagnostics allows you to identify suspension defects. Since this part of the car is most susceptible to wear and tear, diagnostics must be carried out promptly and in a timely manner.
You can determine that it is time to check the suspension for serviceability by an uncharacteristic knocking sound and an increase in the braking distance of the car. The vehicle's stability on the road also weakens over time. Diagnostics in service centers are carried out using high-precision equipment (play meter, lateral care tester) and provide maximum information content. After diagnosis, you will receive a special diagnostic card with the results of the work.
What are bushings and why are they needed?
The main task of bushings is to reduce the noise of the suspension when driving and attach the stabilizer to the car body. As a rule, they are made from two materials: polyurethane and rubber. The parts have high elasticity and strength, which is why there are no squeaks or knocks when the height of any of the wheels changes. In addition, it is impossible to rigidly attach the stabilizer to the body, since the distance from the attachment point to the edge of the stabilizer changes when bending.
Bushings can be made from different materials
Often, a faulty bushing can be indicated by various sounds that occur when driving and making sharp turns - squeaks, knocks, and so on. This phenomenon is associated with the loss of elasticity of the bushing, as a result of which it becomes very rigid. Dust or sand may also accumulate under this part.
Modern car suspension
Design and operation of the suspension
The main task of the suspension is to provide an elastic connection between the body and the wheels. Thus, the suspension softens the shocks and jumps that occur when the car moves on an uneven road or its absence. The smooth ride of a car directly depends on the suspension.
The suspension serves as a kind of shock absorber, absorbing the energy that occurs when hitting bumps or falling into holes and ruts. However, it does not guarantee complete smoothness of movement and wears out greatly with frequent movement over uneven surfaces.
Pendants are divided into the following types:
- McPherson;
- double lever;
- multi-link;
- adaptive;
- "De Dion"
- rear dependent;
- rear semi-independent;
- pickups and SUVs;
- trucks.
McPherson type suspension
The McPherson type suspension is one of the oldest. It was developed by the talented engineer Earl McPherson in 1960. Consists of a stabilizer bar, a lever and a block. A serious disadvantage of the suspension is the change in the wheel camber angle, but it is very popular due to its availability and reliability.
Double wishbone suspension
The double wishbone suspension is one of the most advanced designs. This is a suspension with two arms of different lengths (the upper one is short and the lower one is long). This design allows the car to maintain stability on the road and ensures the durability of the tires. Each wheel accepts its own obstacle independently and does not transfer the load to the other wheels.
Multi-link suspension
The multi-link suspension was developed not so long ago and is an even more advanced design. It is a set of many levers, silent blocks and hinges. All these components are designed to absorb shocks and strong shocks while driving. The noise level from the wheels in the cabin is also reduced. The suspension has separate lateral and longitudinal adjustments. The wheels are independent of each other. The design is ideal for all-wheel drive vehicles.
The cost of a multi-link suspension remained quite high for some time, but now even golf car drivers can afford it.
Adaptive suspension
The adaptive suspension is very interesting from a design point of view. For a long time it was primitive and weighed a lot, but now it has been greatly modernized. Thanks to this, it allows maximum body roll and wave swing at high speed and allows you to automatically adapt to any type of road surface. The adaptive suspension includes: adjustable anti-roll bars, active shock absorber struts, a chassis control unit and electronic sensors that record road irregularities and other parameters.
"De Dion"
“De Dion” is named after its French creator. The main function of such a suspension is to reduce the load on the rear axle of the car by separating the final drive housing. In this case, the crankcase rests on the body. This design allows you to make the suspension dependent or independent. But there are also disadvantages. With a sharp start, the car body can put a lot of pressure on the rear axle.
Rear dependent suspension
The rear dependent suspension is a real classic option, as it was used on many old VAZ cars. The suspension is based on cylindrical coil springs, which are elastic elements. The rear axle beam “hangs” on springs and is fixed to the body by means of four longitudinal arms. The reactive crossbar acts as a roll absorber and has a positive effect on handling. But don’t expect comfort and smoothness from this suspension, since the rear axle weighs a lot.
This is interesting: Anti-gravel in a can: advantages of coating, application features + 4 best brands
Semi-independent rear suspension
Semi-independent rear suspension is most often used in vehicles with all-wheel drive. Its main elements are two longitudinal arms attached in the center to the cross member. This suspension weighs little and does not require any special maintenance or major repairs. But such a suspension can no longer be installed on rear-wheel drive cars.
Other types of pendants
Pickup trucks and SUVs have different suspensions. There are completely dependent and completely independent varieties of such suspension. Dependent suspensions are used less frequently, since the rigid connection of the wheels to each other leads to large loads, reduced controllability and other troubles when driving off-road. Much more popular is the spring system, which is more soft.
The suspension of trucks is most often dependent with transverse or longitudinal springs and hydraulic shock absorbers. This design simplifies the process of producing and repairing trucks.
Signs of bushing wear
The design parameters of the bushing are a little similar to the parameters of a ball joint, only the bushing has one unpleasant feature - it wears out, as a result of which the part becomes faulty. It should also be noted that driving a car with damaged suspension elements is unsafe, so if you have identified a fault with the stabilizer bushing, try to replace it as soon as possible. Determining the unsuitability of the bushing for the driver will not be difficult, because when driving it will become difficult to control the vehicle.
How to bleed shock absorbers
Detailed information with step-by-step instructions can be found here. You may also be interested in an article about increasing vehicle clearance.
In most cases, wear of the stabilizer bushing is accompanied by characteristic sounds in the suspension area, which increase as the vehicle accelerates. Overcoming road irregularities (bumps, holes, pebbles on the road) makes drivers shudder from the resulting shocks in the lower part of the car. An attentive driver will immediately notice extraneous noises and minor deterioration in the car’s handling, and will also begin to find out the cause of this problem.
This is what a worn bushing looks like
To prevent the bushings and suspension from reaching such a state, it is recommended to carry out regular inspections of all structural elements. In this case, it is necessary to conduct a close diagnosis of the bushing.
How to choose new bushings
Before you begin replacement, you need to purchase a set of new parts. And here a natural question arises among motorists about which option to give preference to.
In fact, 2 materials are used to produce bushings. These are rubber and polyurethane. But which of them is better and which is suitable for repairing the stabilizer is an open question. All bushings have their own characteristics.
- Rubber. For the production of such parts, rubber of increased strength and high wear resistance is used. Sufficiently elastic.
- Polyurethane. The level of rigidity is higher compared to rubber, but this guarantees a longer service life. In terms of their characteristics, they are in no way inferior to rubber analogues, but in practice they are changed less often.
If you ask motorists which bushings for the stabilizer in the car suspension system are better, polyurethane will be the leader. And rubber is gradually fading into the background. Moreover, even in situations where rubber parts are provided from the factory. They prefer to replace them with polyurethane ones.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of stabilizer bushings consists of two steps:
- visual assessment;
- providing mechanical impact.
It is necessary to park the car on an overpass or pit to check the rubber bands. Some people use a lift for this purpose, but this can be dangerous. The fact is that diagnosing bushings involves strong tugging of the stabilizer, as a result of which the car sways and may fall. The same applies to jacks, from which the car will come off much faster than from a lift. This can lead to the most dire consequences, since the weight of the car is very large, and this entire metal structure can crush the mechanic.
Diagnostics of stabilizer bushings
The purpose of a visual assessment is to inspect the rubber bands for tears and cracks. If even one crack is found on one part, then the entire set needs to be replaced. Mechanical action requires brute force - grab the stabilizer next to the bushing that connects the part to the body, and pull it hard in all directions. During the process, knocking or squeaking noises may occur. This means the bushings need to be replaced. During the mechanical impact, do not be afraid to damage the stabilizer or the bushings themselves - they are designed for heavy loads, so your attempts to check the serviceability of the parts will not cause them any harm.
Anti-roll bar: why is it needed, how is it designed and what cars do not have it
An anti-roll bar is an important part of a car's suspension that helps reduce vehicle body roll during fast cornering or over bumps. This is a curved metal rod - essentially a torsion spring, which connects the wheels on the same axis with the help of short levers - stabilizer struts.
Anti-roll bar with bushings and clamps for mounting to the body and Meyle stabilizer bar. Source: Mayle
The stabilizer increases the lateral stiffness of the suspension and its roll resistance in corners, regardless of the spring stiffness in the vertical direction. Canadian engineer Stephen Coleman received a patent for an anti-roll bar in 1919.
The main purpose of the anti-roll bar is to force the unloaded side of the vehicle to lower or rise to the same height as the loaded side to reduce the lateral lean of the vehicle when cornering.
Thanks also to the anti-roll bar, the car has moderate roll even in extreme driving conditions. Source: Drive2, dinerooo
In a fast arc, due to the dynamic distribution of mass, the car body is pressed against the outer wheels, creating a roll, and the anti-roll bar creates a force that, as it were, pushes the wheels on the opposite side. As a result, the entire car is pressed against the road surface during a fast turn because all the wheels are closer to the body.
How does the anti-roll bar work?
The anti-roll bar is a torsion spring, or, more simply, a curved metal bar that resists body roll. It is usually made of a cylindrical steel rod, which is connected to the body at two points, and the ends are attached to the suspension elements on each side through a flexible hinge - a stabilizer link.
Wear of stabilizer bushings is one of the common causes of suspension malfunctions. They are made from rubber, which can quickly lose its properties due to time or aggressive environments such as reagents. Source: Mayle
If the left and right wheels move synchronously, the stabilizer rotates completely inside the bushings at the points of attachment to the body. And in the case when they move relative to each other, that is, only one wheel is loaded, the rod is subject to twisting. The anti-roll bar end link, in turn, connects to a location next to the wheel or axle, allowing forces to be transferred from a heavily loaded axle to the opposite side.
Thus, the force applied to the loaded wheel is first transmitted to the stabilizer strut, then to the stabilizer itself, and then through the second strut to the opposite wheel. Due to its rigidity, the stabilizer resists torsion, and this in turn depends on the thickness of the stabilizer and the length of the lever arms - that is, the length of the curved “tails” on both sides of the rod. The shorter this lever, the stiffer the stabilizer and the more the body resists roll.
What else does the work of the stabilizer affect?
However, the roll is counteracted not only by the anti-roll bar, but also by the suspension springs. But there is an important point here - if too stiff springs are installed, the car will lose its smooth ride, and thanks to the stabilizer, engineers are able to find a compromise between handling and comfort.
Sports cars tend to have very stiff anti-roll bars, so they often "lift" the front inner wheel - while still maintaining maximum grip on the outer one. Source: Drive2, Andi777
An interesting point: if you change the stiffness of the anti-roll bars, you can influence the car's steering. Understeer and oversteer behavior can be eliminated by changing the proportion of overall roll stiffness generated by the front and rear axles.
For example, increasing front axle stiffness will increase the proportion of total load transfer to which the front axle responds and decrease the proportion to which the rear axle responds. In other words, the front wheels will “hold” to the road more tightly than the rear wheels, which means the car will wobble less when turning.
Are stabilizers always needed?
Without a stabilizer, the articulation of the suspension on each side increases significantly - this worsens the stability of the car at high speed, but increases off-road maneuverability. For this reason, many SUVs do without stabilizers - for example, it is not in the rear suspension of the new Mercedes-Benz G500. But its “big brother” G63 has it: stability is a priority there over off-road capabilities.
Instead of a stabilizer bar, the younger Mercedes-Benz G-Class has a Panhard rod. It prevents the axle from moving in the dependent wheel suspension in the transverse direction. Source: Mercedes-Benz
Can the stabilizer fail?
You might think that a curved metal rod could last forever. This is partly true, and stabilizer struts, which have moving parts and rubber elements, fail much more often. The stabilizer itself can also break, but, as a rule, not literally. It can wear out at the points of attachment to the body: in these places it becomes thinner. There will be general discomfort when driving, as well as knocking noises when driving over uneven surfaces.
For example, in some models of Volkswagen cars, due to aging, the adjusting washers on the stabilizer may break, and the stabilizer bushings may lose their lateral stability.
A typical example of a time-worn anti-roll bar. Source: Drive2, user Energosila
Why not install stabilizers as thick as possible?
It should be remembered that the use of a stabilizer bar has some side effects. In fact, because of it, even the independent suspension becomes dependent to some extent. Therefore, when one wheel shakes on a large bump, the impact energy is transferred to the opposite wheel through the stabilizer. If the road consists entirely of potholes and bumps, the car may begin to sway violently from side to side, and the stiffer the stabilizer, the more shaking and uncomfortable the car will become.
Manufacturers of spare parts eat their bread for a reason and always find the perfect balance of handling and smoothness. In the Meyle range you can find anti-roll bars that are suitable for your vehicle and can guarantee ideal vehicle behavior in all conditions. And sophisticated enthusiasts who know exactly what their needs are will find parts to customize their cars in Meyle's catalogues.
To simplify the replacement of parts using a standard tool, the Meyle stabilizer links are secured with a 16 mm washer. Source: Mayle
Particularly durable Meyle spare parts are labeled HD - such parts are intended for use in countries with poor quality roads and harsh climates. Source: Mayle
To make repairs even more convenient, MEYLE offers the MEYLE HD repair kit, which includes the stabilizer assembly and stabilizer links to make the installation process as simple as possible. Ideally matched components enable quick and easy replacement of faulty parts. For additional ease of installation, the stabilizer is supplied ready for installation, complete with supports and, in most cases, fasteners.
By fine-tuning individual parameters, it was possible to achieve a significant increase in the service life of parts. For example, the use of a larger and more durable 22 mm diameter ball head has reduced the specific surface pressure at the same load levels, which in turn minimizes wear on the part. By relying on MEYLE's advanced development technology, professional service companies can confidently offer an extended four-year warranty that covers not only MEYLE HD repair kits, but all products in the MEYLE HD range.
Source
What will you need for replacement?
You won't need many tools to do this job, but you will still need to prepare them ahead of time.
To replace stabilizer bushings you need:
- jack;
- ruler or caliper;
- special extension for the key;
- ratchet wrench;
- ring wrenches, one for 13, and the other for 10;
- extended socket heads or regular ones (14,13).
It is worth noting that this is only a basic set of tools; in fact, others may be needed. This is due to the need to unscrew the fastening nuts when removing the stabilizer. This is the whole problem, because with a regular wrench you will not be able to unscrew the fastening nuts (during operation they become stuck to the part). In this case, many resort to emergency measures - using a hacksaw or grinder. In the process of loosening the nuts, the stabilizer links may be damaged, so replacing the rubber bands alone will not do.
Let's sum it up
As you can see, the rear stabilizer bushing or the front stabilizer bushing is a simple element both in terms of design and replacement
At the same time, the bushing of the stabilizer link and the bushing of the stabilizer itself are different, so it is important not to confuse these elements when selecting the necessary spare parts
The vehicle suspension is one of the most important parts, subject to heavy loads and taking on all the impacts of a rough road. Thanks to its operation, the driver can feel comfortable and not be afraid that while driving the situation may get out of control. However, due to heavy loads, especially when driving on bad roads, which is not uncommon in the Russian Federation, its parts often fail. The most common problem is broken stabilizer bushings. Let's take a closer look at why this happens and how the stabilizer bushings are replaced.
Replacing front bushings
This procedure can be performed in two ways: jack up one side of the car or two. The second method is considered more labor-intensive, but many motorists prefer it. In addition, with both sides of the machine raised, installation and removal of the bushings will be much easier. The main thing is safety precautions and following the step-by-step instructions given below.
Step 1: First, buy replacement parts. You can take the original or an analogue - it depends on your preferences and financial capabilities. Although even if you choose the original, you will have to pay no more than 400 rubles for the parts.
Try not to save money when choosing new bushings
Step 2. Having installed the wheel chocks, jack up the car. Then unscrew the bushing bracket mounting bolt. To do this, you will need a 12mm wrench. If the bolt does not turn, then treat it with WD-40 or, as this product is popularly called, “Vedeshka”. After 5-10 minutes, the fastening element can be easily unscrewed.
If the bolt is very rusty, then you will have to use a grinder
Step 3. After the fastening bolts are unscrewed, bend the retaining bracket slightly upward. It is very difficult to do this with bare hands, so use a screwdriver and slightly pry the outer part of the bracket with it.
Bend the fixing bracket
Step 4: Carefully remove the bushing. There is no need to use any tools for this; the bushing can be easily removed as is. After removal, inspect the part for damage, signs of wear, or cracks.
Removing the stabilizer bushing
Step 5: Place the new bushing in place and lower the retaining bracket onto it. Before doing this, it is advisable to treat the surface of the bushing with a small amount of graphite lubricant so that the bracket is installed on the rubber band without problems. After this, tighten the mounting bolt, being careful not to strip the thread. Otherwise, you will have a few more worries.
Place the bushing in its place
Brand tour
When choosing between an analogue and an original, you can give preference to the first only when you are completely confident in the correctness of the brand and are aware that the manufacturer has a good reputation. On average, original bushings last up to 30,000 kilometers . Durable bushings can be found under the following brand names:
- Japan Parts (Italy);
- Yamato (Japan);
- RBI (Taiwan);
- Lemforder (Germany);
- CTR (South Korea);
- Sidem (Belgium);
- Zekkert (Germany).
On average, good non-original bushings last about 23,000 kilometers . The products of the last two companies are especially pleasing - despite the low price and little popularity among car enthusiasts, Sidem and Zekkert can be a very pleasant surprise.
Replacing rear bushings
The rear stabilizer is secured using two bushings made of rubber. As a rule, during the operation of the car, these parts lose their strength and elasticity, as a result of which they are no longer able to perform their main functions. As a result, the rear suspension begins to knock when driving. If you hear characteristic sounds, it means you need to replace the rear bushings. Just like when replacing front bushings, you need to jack up the car. It is advisable to lift two sides at once - right and left. Now get to work.
Step 1. Get new rubber bands first. In this case, they come complete with a special lubricant, which extends the service life of the parts and facilitates the replacement process.
Stabilizer bushings with lubricant
Step 2. Clean the surface of the stabilizer and fastening element from dust. To do this, use coarse sandpaper or a stiff brush. Then spray some WD-40 on the bolt to make it come out easier.
Spray the wedge onto the fastening bolt
Step 3. Unscrew the mounting bolt by 14, and then lightly press the bracket with pliers so that you can then remove the part. As you can see, the processes for replacing the front and rear hubs are not much different from each other, with the possible exception of the screw being removed.
Removing the bushing bracket
Step 4. Lubricate the stabilizer with the liquid from the kit, after which you can install a new bushing. Do not mix up the sides of the part; install it with the same side as before. Otherwise, you risk significantly reducing the life of a completely new part.
Lubricate the stabilizer and bushing before installation
Step 5. Carefully install the stabilizer bracket into place and secure it with the bolt. In this case, you need to be careful not to damage the fastener or the bracket itself. Now lower the back of the car and drive it to check your work.
Reinstall the bushing. Gently tighten the mounting bolt.
Sequence of work
- The car is securely fixed when jacked up.
- The wheels are unscrewed and removed. There is an engine protection shield in the right wheel arch. Its fastenings are unscrewed and the shield is removed.
- Most of the fasteners under the bottom are pretty acidic, so to speed up the process of replacing stabilizer bushings, they need to be thoroughly treated with a WD 40 solution, which removes corrosion.
- Using an open-end wrench, we fix the finger on the left post. It is slightly hidden from direct access, so you need to find the grooves almost by touch.
- We throw a spanner, preferably a ratchet, onto the nut that secures the shock absorber. Unscrew both fasteners.
- Having freed the stabilizer struts from their fastenings, we disconnect them from the shock absorber strut.
- We install a jack under the left rear part of the subframe. With its help, the subframe is fixed so that when the fasteners are removed, it does not suddenly jump off the studs. A metal plate of considerable size must be placed under the supporting head of the jack so as not to deform the subframe.
- Smoothly lower the jack a few centimeters from the body. Thanks to this, the subframe also lowers slightly, opening access to the bushings.
- A pipe is inserted into the resulting gap, and the subframe is further pressed down. A stopper is inserted into the resulting gap. A 27mm head is suitable; when installing it between the body and the subframe washer, it is better to use pliers. This will save your hand from injury if the pipe slips off the subframe washer.
- We generously water the bracket fastenings with WD-40. We unscrew the bolts gradually, without pressing too much.
- Remove the freed bracket from the bushing, and then remove the bushing itself.
- We install the bushing from the new kit. The cut on the part should be directed strictly back. We position the new part exactly in the place of the old one.
- Install a clamp over the bushing. Lightly tighten the fasteners with your fingers, and then tighten them with a wrench, tightening all the bolts one by one and evenly.
- The stopper, for which the key head was used, is removed. The subframe is lifted by hand and screwed to the body.
- All of these steps are performed in the same way with respect to the second clamp.
- Once the bushings are in place, both posts are screwed into place.
When performing the above work, you should be careful and pay attention to safety precautions. In general, such work can be done with your own hands.
Naturally, the design of different car brands differs significantly, so the replacement instructions are rather of a general recommendation nature. For more detailed information, a series of videos on carrying out this type of repair for various brands of cars is presented. Video on replacing stabilizer bushings on a Ford Explorer:
Video Chevrolet Aveo 3 - split bushings used in this model make the repair process quick and easy.
Nissan X-Trail Video:
Video explaining workflows for Renault Logan:
Benefits of timely replacement
Every driver can cope with replacing bushings on his car, because this process is not a very complicated repair. You can do everything yourself, but if you don’t have the time or desire, then it is advisable to seek help from specialists. This will protect the stabilizer bar links from premature wear.
Driving on poor-quality road surfaces will fade into the background if you have previously installed new bushings. And in general, installed new bushings mean the absence of difficulties and problems when moving, as well as comfort and safety.
avtoexperts.ru
Before dealing with the topic of what a stabilizer bushing is, it wouldn’t hurt to refresh your memory about the stabilizers themselves, what are they for? The main task of this part is to keep the car as parallel to the road as possible. Despite various risks, for example, turns, braking, which cause both lateral and longitudinal rolls. The stabilizer must cope with them.
In the photo: stabilizer bushings for Honda Civic 5D
Structurally, the stabilizer is a conventional rod, the task of which is to connect the subframe with the wheel mount. When it comes to the front suspension, it makes more sense to say that the attachment occurs with the suspension arm, since MacPherson struts are often installed at the front.
Stabilizer bushing - yellow
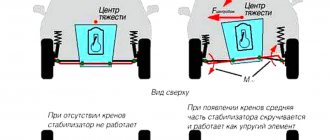
At the slightest roll, the ends of the stabilizers begin to move, thereby reducing the roll. The movement occurs along the bushings, which will be discussed. The purpose of the latter is to allow the stabilizer to twist in different directions. That is why they secure it with bushings. Over time, the bushings wear out, causing play to occur, which will lead to improper operation of the entire mechanism. The so-called “freedom of the part” increases, then, by and large, the presence of a stabilizer plays no role. Because, similarly to its absence, roll increases due to large strokes and rotation, controllability is lost and this is felt mostly in turns.
Suspension diagram
Kinds
There are several types of bushings:
• Rubber bushings.
• Polyurethane. Similar to the previous ones, except for the production material.
Rubber left, right polyurethane stabilizer bushing
Recently, motorists have given preference to polyurethane bushings due to their high performance characteristics. As a rule, they “walk” longer. But this is also individual, depending on how you drive.
Also, you should not lose sight of the nuance that almost every model has its own size and configuration of bushings, which is why special attention needs to be paid to the selection and selection for a specific model. This issue is most acute for foreign cars.
What resource?
This question is quite individual; as such, no manufacturer can give exact “mileages”. It all depends on the specific operating conditions; keep in mind that bad roads, driving style, all of this affects the “life” of the bushing, and the stabilizer mechanism as a whole.
By the way, bushings are considered the most problematic area in the suspension on the Lada Vesta. A creaking noise begins almost immediately from the factory, and a knocking sound is often added to it while driving over bumps. The problem is that they use low-quality material for manufacturing, which is why the resource of the original bushings on Vesta is very small. It’s all very simple to treat; you need to select analogues from other models. For example, it is known that bushings from Toyota Corollas, Avensis and KIA Rio fit perfectly and do not cause problems for West owners.
Stabilizer bushings for Lada Vesta from Kia Rio. Bushing article - Hyundai/Kia 54812-1G100, bracket - 54814-1G000
Judging by the reviews of drivers, bushings from German brands, which are often installed on “Germans” from the factory, performed well. For example, original parts can often last more than 150,000 km. At the same time, when it comes to analogues from China, the resource is reduced several times.
In general, it is generally accepted among motorists that the average “mileage” for a rubber bushing is 70,000 km; more advanced polyurethane bushings “run” 100,000 km. Some manufacturers even recommend carrying out a scheduled replacement after 30,000 km in order to avoid “surprises”. But, as already mentioned, everything is individual, you need to take into account all the operating features.
It is also worth clarifying this nuance; the life of the bushings is greatly influenced by the state of the thrust (stab) itself . For example, if there is a hole in the place where the bushing is attached, then the part will definitely not last the stated period and will not fully cope with the task. As a rule, after replacing the original bushings, owners observe a small amount of metal wear, somewhere around 1.5 mm. With each replacement of the bushings, the output will only increase, so in case of severe wear, it is wiser to replace the entire part so that, in general, the operation of this mechanism will be useful.
Signs of trouble
The following signs may indicate that something is wrong with the suspension. And one of the places that is worth checking is the stabilizer. So:
• Steering wheel wobble appears.
• There is a slight play when turning the steering wheel.
• The car began to “yaw” when moving.
• When turning, distinct clicks are heard from the wheels.
• The car drives in one direction.
• Vibration is felt.
How to replace?
The issue of replacement for some cars is purely individual, because depending on the model, the fastenings may differ. For example, to replace the bushings on the Mazda 6 and 5 at the front, you will also have to remove the steering rods to get to the brackets securing the rod itself. But, in general, you can draw up a small work plan. So:
• Lift the car on a lift or drive it into a pit for convenience.
• Before unscrewing the bolts, we recommend treating them with a special agent so that they can be easily unscrewed, for example, WD-40.
Replacing stabilizer bushings using the example of Volkswagen Polo sedan
Keep in mind that the bolts may not budge even after this. Then the “grinder” comes into play. But first take care to remove the fuel hoses from the “dangerous” area. Cut off the "ears" of the staples to "free" the bar.
• After unscrewing the brackets (clamps), we move the stabilizer itself away from the subframe to make it easier to remove the bushing. Use a crowbar.
• Pull off the old bushing.
Photo — Drive2.ru
• We put on a new part.
Replaced the bushing
• Next, return the clamp to its place.
Please note that in most cases, the clamp fits extremely poorly on the new bushing, so try to position it as evenly as possible and minimize friction (use lubricant).
• We tighten the clamp with a bolt. By the way, we recommend that you pre-treat the bolt and nut with lubricant so that in the future there will be no problems with unscrewing it.
By the way, this is an important nuance during replacement. You need to change both bushings at once, that is, do not leave the old part on the right side, but, for example, install a new one on the left side. There should be new bushings on both sides.
Features of the problem for popular models
Statistics show that owners of such car models as Renault Megane, Skoda Rapid, Volkswagen Polo, Lada Vesta (and other representatives of the domestic automobile industry) are faced with problems associated with stabilizer bushings. Let's look at the features of specific car models, as well as recommendations for replacement.
Table. Description of the problem for some models
| Model | Description of the problem |
| Lada Vesta | Often, it is the structure of the suspension of a given car that is the main cause of problems with bushings. Vesta is famous for its large travel of stabilizer struts, which can cause unpleasant sounds when moving. Many car owners lower the seating position of their car to solve this problem. You can also use a special silicone-based lubricant. |
| Volkswagen Polo | There is one proven method for eliminating squeaks - install a small piece of an old timing belt between the stabilizer bushing and the car body. The replacement of bushings itself is no different from that indicated in the instructions above. |
| Skoda Rapid | As practice shows, the best way to get rid of squeaks is to install original VAG rubber bands. Also, many motorists use repair bushings that differ from the usual sizes (repair bushings are 1 mm smaller). As an alternative, you can install rubber bands from other models of this manufacturer, for example, from the Skoda Fabia. |
| Renault Megane | The process of replacing the bushing is no different from other models, but before installing a new rubber band, it and the seat must be treated with a lubricant, which will not harm the parts later. You can use shampoo or soap for this purpose. Depending on the modification, Renault Megane can be equipped with reinforced or conventional suspension, therefore, the dimensions of the bushings and the stabilizer itself may differ. Please keep this in mind when purchasing replacement parts. |
| Mercedes Sprinter | Before purchasing bushings, you must first measure the diameter of the stabilizer, since their dimensions may vary depending on the modification. To do this, use a caliper. Many experts recommend buying special rubber bands for your car, equipped with anthers to protect against dust and water. To treat the surface of parts, it is necessary to use silicone-based products that will not corrode the rubber. Such products include “MOLYKOTE PG-54”, “Litol-24” and others. |
Service life and prices
Typically, stabilizer bushings are replaced every 30,000 km. They may fail earlier during active use of the vehicle. You need to carefully monitor their condition in order to notice wear in time and extend the service of the entire car suspension.
Cost of parts for Kia
To change the stabilizer rubber bands on a Kia, it is recommended to remove the crankcase protection. Then the process will go faster and easier. One spare part costs 50-200 rubles, depending on the car model.
Cost of parts for Toyota
For premium car models, even small spare parts are expensive. For example, for Corolla, Avensis, Rav4 bushings cost 250-400 rubles. For other models the price is 50-150 rubles.
WATCH THE VIDEO
Price of spare parts for Renault
Renault models have reinforced and conventional suspension. The bushings for them have different diameters, this must be taken into account when purchasing. The average cost of auto parts is 100-200 rubles.
WATCH THE VIDEO
Price of spare parts for Nissan
The cost of parts for Nissan depends on the model and the city where you live. Buying auto parts online can help you cut costs and save time. The average cost of bushings is 100-300 rubles.
Which bushings are suitable for Ford, diameter and part numbers
The article number of spare parts for Ford is 4671720. They cost 200-400 rubles. The diameter of the bushings must match the diameter of the stabilizer. It is different for all manufacturers. Common sizes are from 18 to 25 mm.
Need for replacement
Stabilizer bushings are among the parts that are subject to the greatest dynamic loads. They require regular replacement, depending on the maintenance regulations adopted by various car manufacturers and models. The maximum mileage before replacing the rear and front bushings is usually from 15,000 to 30,000 km. Considering the state of our roads, it is recommended to replace them based on wear and tear.
Untimely replacement can lead to the formation of a roll in the car's stabilizer, and this, in turn, increases the risk of the car tipping over at speed. The complete set must be replaced, regardless of the difference in external signs of wear. The cost of such a repair service at a service station is often overpriced, given the ease of replacement for most car models, so it is advisable to replace the front and rear bushings yourself.
What are the risks of buying a low-quality bushing?
Obviously, a bushing made without technology or using low-quality materials will fail early. It simply won’t withstand the loads and will begin to crack and wear out. A mediocre bushing begins to creak immediately after installation in the car. Here are the causes of squeaks:
- The bushing material hardened in the cold and ceased to be elastic. Rubber suffers from frost ;
- The element is badly worn and will soon fail;
- This is an unpleasant design feature of the car. For example, in the Lada Vesta the suspension creaks menacingly all the time. The problem can be fixed in a car repair shop: lubricate the bushings (the element will still creak on a wet road) or shorten the suspension travel, thereby lowering the car;
- Low quality material was used to make the bushings.
In any case, you should not ignore the creaking of stabilizer bushings. It is better to go to a service station and consult with a specialist. The use of silicone lubricants for bushings is undesirable - the lubricant immediately begins to collect dirt and debris, and really helps in solving the squeaking problem only for a while.
Diagnostics
Knocking of the stabilizers is a guaranteed sign of the need to immediately replace the bushings. In addition, squeaks may appear, especially when it gets colder, when the rubber loses its elasticity.
To determine the need for replacement, it may be necessary to remove the crankcase protection. To check the source of vibration, place your hands on the stabilizer link and directly on the mounting bracket. The partner must press firmly on the hood of the car several times. If vibrations are felt on the brackets, which are transmitted to the rack, it is necessary to install a new set, even if no play was noticed when inspecting the seats on the stabilizer.
If the hole inside the bushing has taken the shape of an ellipse, cracks are visible on the surface, and the material has hardened, immediate replacement is necessary. Continued operation of the vehicle will significantly reduce the service life of the stabilizer struts.
How not to buy a fake
The sale of counterfeit bushings and elements of the suspension and braking system in general is by no means uncommon. Moreover, they can offer you a fake both in the market and on the Internet or in a small, little-known store on the outskirts of the city. Here's how to avoid buying a fake:
- Go to the store with a smartphone, tablet or computer with Internet access. Be prepared to search for the bushing by code, look at photos and study reviews from car enthusiasts . Now you will understand why this is necessary;
- Pay attention to the placement of the inscriptions and the font. On fake bushings, the inscriptions are located completely differently than on the original ones. The difference in fonts can only be noticed upon careful examination;
- Examine the section of the bushing. On fakes it is sloppy and seems to have been made with an ordinary knife, not according to marks, but by eye;
- Examine the bushing for external damage, presence of coating, and packaging. Firstly, the original bushings are often coated with paraffin. The fakes are always clean. Secondly, based on the information on the packaging, you can check what is inside. If you come across an image of branded packaging , then compare the fonts, inscriptions, and check the sleeve code;
- Remember that the original cannot be cheap. All original spare parts have their own red price, which very rarely falls below (exception: during the holidays). Using the Internet, study the average market prices for bushings on manufacturers’ websites and in well-known online stores. If the bushing you find is very cheap, then it is probably fake.
Even if you bought a bushing and realized that a fake was installed only a few days later, there is no need to sound the alarm. As practice shows, even a fake of average quality can last a year , or at most two years . In the worst case, it will begin to creak and play will appear in it after just three days. In this case, the money was truly wasted.
Advantages and disadvantages of SPU
Given the obvious simplicity of the design of the mechanism we are interested in (you only need a reliable support for its fastening, high-quality rubber bushings, rods, bones), it easily copes with the tasks assigned to it. But here it is worth saying that SPU reduces the travel of the independent suspension and “takes away” some other important properties from it. For this reason, the installation of a stabilizer bar is not carried out on off-road vehicles.
When driving such all-terrain vehicles equipped with off-road tires on bad roads, the wheel loses contact with the road and hangs up. And this negative phenomenon is caused precisely by the use of SPU. It is clear that car designers are not going to abandon the use of stabilizers in these cases either. Several options have now been developed to improve the design of SPUs intended for off-road vehicles.
For example, she created a modern system consisting of hydraulic cylinders that act as struts, a lateral acceleration sensor, a hydraulic pump and a special control unit. This system, which does not require rubber bushings, has proven itself to be an effective replacement for traditional SPU.
Also, Western automakers began to actively install adaptive suspensions on their cars. These mechanisms make it possible to completely abandon the control system, guaranteeing ideal behavior of the vehicle (without rolls) in any driving conditions (when accelerating, turning, hard braking, and so on).
Replacement and repair of SPU - when is it required and how is it done?
Repair of the stabilizer must be carried out immediately in cases where its elements are clearly deformed. If you see that the bar has bent slightly, it is recommended to carefully align it. But in case of significant deformations, the solution is to immediately replace it.
In addition, repair or replacement of the SPU is carried out when the mechanism cushions lose elasticity (severe wear) and their fit to the rack is poor. In order to repair or install new pillows, you need to perform the following steps: unscrew the mounting bolts from the bracket that holds the pillows; Slide a screwdriver under the bracket, carefully pry it up and remove it.
After this, you can remove the pillow (the right one should be moved outside the machine for dismantling, the left one should be moved towards the center) and repair it or install a new one. Removing and replacing SPU racks also does not require too much time. The process is carried out using keys “14” according to the following scheme:
- unscrew the nut on the rod that holds the fastening bolt;
- take out the bushing (upper);
- move the strut bolt from the suspension arm (direction down), after which two more bushings are dismantled - a rubber bushing and a special spacer bushing.
Using the same principle, the second rack is removed, replaced or repaired, and then installed in the reverse order. If you need to dismantle the bar, after removing the racks you will need to remove the cushion brackets (we described this operation earlier), after which the bar can easily leave its location.
The suspension of any car is always the first to take the blow from road irregularities. Depending on the design and settings, suspension units are designed to most effectively absorb shock loads from uneven road surfaces, as well as to ensure vehicle controllability and stability at high speeds when cornering, as well as during sudden changes in the trajectory of movement (“snake”, avoiding obstacles ). And not only comfort, but also the safety of the driver and passengers depends on how efficient the suspension is. Each of the suspension elements performs its role. Trunnions and levers support the wheel in a given plane, ensuring unhindered rotation in two planes (when turning).