The torque from the differential side gears to the drive wheels is transmitted by shafts called axle shafts. In addition to torque, axle shafts can be loaded with bending moments from forces acting on the drive wheel. Such forces are the reaction of the road F from the vertical load falling on wheel 1 (Fig. a), the traction force P (or the braking force during braking), the lateral force T that occurs when turning and skidding. Depending on the installation method, the axle shafts can be completely or partially unloaded from bending moments arising under the action of the listed forces at distances c and z, respectively.
The fully unloaded axle shaft 4 (Fig. b) is installed with its inner end on splines in the differential side gear, the housing of which rests on bearings, and is connected to the wheel hub with the outer end using a flange. The hub 5 with the wheel is mounted on two bearings 2 on the bridge beam 3. With this installation, the axle shaft transmits only torque, and all bending moments are perceived through the bearings by the bridge beam, which facilitates the operating conditions of the axle shaft. Fully balanced axle shafts are used on transport wheeled vehicles of medium and heavy load capacity.
Rice. Axle shaft installation diagram
In the drive of the steered drive wheels to the constant velocity joint 19, torque is supplied from the differential by the inner axle shaft 6. The outer axle shaft 23 has a flange, from which the torque is transmitted to the wheel hub 2. The wheel hub is mounted on a steering axle 22 using two tapered roller bearings 1, which transmit all bending moments from the above forces to the axle. The axle with its body 4 is mounted on pins 21 with bearings 5, rigidly mounted on the tips of the bridge beam 7. Axle shafts 6 and 23 are loaded only with torque.
If the axle shaft with its outer end directly rests on bearings 2 (see a) installed in the bridge beam, then it receives bending moments from all the forces listed above and, in addition, transmits torque to the drive wheel. Axle shafts of this type are called semi-balanced. They are usually used only on passenger cars. On all-wheel drive wheeled vehicles, fully balanced axle shafts are used almost exclusively.
On high-speed tracked vehicles, the turning mechanisms used to control movement are included in the transmission, since torque is transmitted through them from the engine to the drive wheels.
Many drivers ask the question: “What is a car axle shaft?” This is a shaft that transmits rotation from the car engine to its drive wheels. The more commonly used name for the axle shaft is the drive shaft.
- What is a car axle shaft used for and where is it located?
- The design and principle of operation of the axle shaft in a car
- Types of axle shafts Semi-weighted
- Unloaded
We recommend: How to check and replace the camshaft sensor in a car?
Interesting ! The undisputed leader in the production of spare parts for cars, especially drive shafts, is the German company GKN(LOBRO).
What is a car axle shaft used for and where is it located?
Let's look at what the axle shaft is for and where it is located. The axle shaft or drive axle shaft provides moving contact between the engine and the drive wheels, transmits forces, maintains the ability to turn the wheels, and allows the suspension to move smoothly with minimal vibration.
The main purpose of a car's axle shafts is to absorb the force of gravity that falls on the wheel due to traction and braking forces. It accounts for bending moments and the consequences of lateral forces during skids.
The axle shaft design has two hinges that ensure uniform transmission of force in any position of the suspension and steering parts. This significantly dampens vibration of the steering column and prevents the car from moving jerkily.
Important! If the drive shaft breaks, the vehicle may become partially or completely uncontrollable.
The design and principle of operation of the axle shaft in a car
The design of the axle shaft is such that the effect of power transmission will be maximum at any position of the wheels. This design consists of three parts:
- external constant velocity joint (CV joint);
- shaft;
- internal CV joint.
A shaft is, roughly speaking, a piece of pipe of a certain length to which adapters for installing CV joints are welded. To prevent these elements from scrolling, they are equipped with special slots. At the end of the adapter, the shaft is secured with a retaining ring, otherwise the shaft may jump out of the CV joint when moving.
In passenger cars, the front drive wheel is driven by external and internal constant velocity joints connected by an axle shaft.
The use of two hinges in the drive is caused by the independent suspension of the front wheels.
Internal hinges are responsible for the movement of the wheels during vertical suspension strokes
, and
external ones - for turning the wheels relative to the vertical axis
, which is necessary when changing direction.
Types of axle shafts
Depending on the device, the types of car axle shafts are divided into fully unloaded axle shafts or partially unloaded axles, depending on the bending moments affecting it.
We recommend: Timing belt VAZ 2109
Semi-unloaded
The semi-balanced axle shaft is installed mainly on passenger cars. In this type of design, the bearing is located between the axle shaft itself and its casing; the axle shaft is attached directly to the wheel hub.
This leads to the appearance of bending moments on the axle shaft. In cars with front-wheel drive, the axle shaft has a different structure.
Did you know? In 1929, front-wheel drive was first used on a car.
Unloaded
The balanced axle shaft is used mainly on trucks and buses. Such a part will be freely installed inside the bridge, and the wheel hub will rest on the bridge beam with two bearings.
The entire force of the bending moment in such a device is taken by the bearings, and the axle shaft only transmits torque.
Main causes of axle shaft failure
The axle shafts bear heavy loads when the vehicle moves over uneven ground and potholes, as well as along broken roads. The cause of failure may be wear of bearings and seals. The oil heats up as it moves and washes out the bearing lubricant through defects in the seals. Another reason could be a defective retaining ring. If they jam, the axle shaft may break.
Attention! If your car leaves a trail of oil stains, the first thing to do is inspect the oil seal.
On cars with front-wheel drive, CV joint boots tear, which also affects the hinges. With a long service life, the axle shaft may become loose and break the splines. Breaks of the axle shafts themselves occur in the middle or at the fastening points. Problems can arise suddenly and accidentally, if you remember the condition of the roads. But they can also be natural in case of careless attitude towards the car, with low quality of repairs and replacement parts.
Subscribe to our feeds on social networks such as Facebook, Vkontakte, Instagram, Pinterest, Yandex Zen, Twitter and Telegram: all the most interesting automotive events collected in one place.
Vehicle axle structure
The overall design includes 3 main elements:
- outer CV joint;
- drive shaft;
- internal CV joint;
In fact, the axle shaft is a shaft of one length or another (depending on the characteristics of the vehicle). Adapters for installing CV joints are attached (welded) to the shaft.
In order to prevent twisting, the connections are splined. At the end of the adapter, the shaft is secured with a retaining ring, which prevents the shaft from accidentally coming out of the CV joint.
To put it simply, front-wheel drive passenger cars have inner and outer CV joints, which are connected to each other by an axle shaft. The need to install two hinges is dictated by the features of the independent suspension.
The inner CV joint is responsible for moving the wheel during vertical movement of the suspension, while the outer one is responsible for turning the wheel.
If we talk about the types of axle shafts of a car, axle shafts according to types and types are divided into:
- partially unloaded
- completely unloaded
This division occurs depending on the influence of the bending moment on the semi-axis. A semi-balanced axle shaft is usually installed on passenger cars. In this design, the bearing is located between the axle shaft and the casing, and the axle shaft itself is attached to the wheel hub. As a result, the axle shaft is subjected to a bending moment.
The unloaded axle shaft is installed on trucks, buses, etc. In this case, the axle shaft stands inside the bridge, and the wheel hub rests on the bridge beam with two bearings.
This design means that the bending moment is borne by the bearings, and the only task of the axle shaft is to transmit torque. It turns out that such an axle shaft does not experience additional loads compared to a half-loaded one.
Axle shaft (drive shaft)
Main types of axle shafts
Depending on the design, the axle shaft can be fully or partially unloaded from the bending moments acting on it.
An unloaded axle shaft is more typical for heavy-duty vehicles, including buses. In the drawing, such an axle shaft will look like a part freely installed inside the bridge, and the wheel hub will rest on the bridge beam using two bearings.
The semi-loaded axle shaft is installed in the vast majority of cases on passenger cars and light trucks. The design of this type of axle shaft is different in that it has a bearing between the axle shaft itself and its casing, and the axle shaft is attached directly to the wheel hub.
On front-wheel drive vehicles, axle shafts of a slightly different design are installed to transmit torque from the gearbox to the wheels. Such a drive shaft consists of an axle, internal and external CV joints.
Drive shaft design of a front-wheel drive vehicle.
Causes of axle shaft failure
During the operation of the vehicle, the axle shaft constantly operates under quite serious loads, including:
- bending moment, which appears due to the effect of gravity on the car;
- tangential reaction that occurs when the vehicle starts to move and brakes;
- lateral force due to car skidding;
- lateral loads arising from the influence of strong cross winds.
Axle shafts experience almost extreme loads when the vehicle moves on dirt roads, as well as on broken highways.
A broken axle shaft leads to a complete or partial loss of vehicle control, so proper, thorough and timely care is of great importance.
During operation of the drive axle, it is necessary to periodically check the condition of the bearings located on the axle shafts. Their long-lasting performance can be achieved by providing complete protection against the penetration of dirt and liquids.
Axle shaft failures
The main problem that most often has to be fixed is crunchy bearings.
It should be noted that the axle shaft in most car models is considered a very reliable part that rarely fails. This is especially true for cars operating in the urban cycle. But still there are problems with them.
Quite often, the cause of early failure of axle shaft bearings is transmission oil leakage due to wear of the axle shaft seal. When the machine moves, the oil heats up, washing away the lubricant of the bearings, which increases the force of internal friction and destroys them.
In general, bearings are the most common cause of axle shaft failure. In addition to being filled with transmission oil, they break due to defects in the locking rings, and sometimes become jammed due to foreign objects.
DETAILS: Design of a vacuum brake booster for a car
A torn CV joint boot leads to failure of both the angular velocity joint and the drive shaft as a whole.
Due to prolonged use, the axle shaft can become loose at the mounting points, even leading to the splines breaking. It is extremely rare, but breakdowns of the axle shafts themselves with separation into two parts also occur. Most often they break in the middle, at the spline or near the bearing.
On cars with front-wheel drive, CV joint boots often tear, which subsequently has a detrimental effect on the joints.
Problems can be caused by accident, prolonged or excessively careless operation of the car, unprofessional repair work, or poor quality of the parts themselves. Repair is most often carried out by replacing the axle shaft, bearings or other elements of the mechanism.
https://m.etlib.ru
legkoe-delo.ru
The principle of operation of axle shafts on a car
Although the drive shaft, often referred to as the axle shaft, is not part of the driveline, it is part of the vehicle's transmission and is an important part of it.
Today we will look at what tasks the PV performs, what axle shafts are, and how they function.
Let's also consider why these transmission components fail and how to increase their service life.
Operating principle
The gases produced by fuel combustion expand and press on the pistons, which drive the engine's crankshaft. Through the flywheel and clutch, rotation is transmitted to the gears of the gearbox. To move the drive wheels, the design includes two axle shafts with constant velocity joints attached to the ends. The inner CV joints are inserted into the transmission, and the outer CV joints are attached to the front wheel hubs.
Due to the use of CV joints, the torque is stable regardless of the angle at which the wheels are turned. This design allows the vehicle to move when turning and maneuvering.
Purpose
Actually, why “half shaft”? The axle of a car, front or rear, is called a conventional line connecting a pair of wheels. The driven wheels can be connected by a rigid coupling (dependent suspension), which is highly reliable. But you can’t install such a design on drive wheels. Therefore, two segments are used, each of which runs from the differential to the wheel and moves independently of the other. Axle shaft is the most common and most accurate name. In fact, the axle shaft is one of the elements of the transmission.
The function of the drive shaft (half shaft) is to transmit torque from the main gear and differential to the drive wheel while maintaining the speed and smoothness of its rotation when turning and hitting bumps. For this purpose, hinges are installed on the axle shaft, transmitting torque at different angles. The shaft itself and two CV joints (constant velocity joints) on it are a complete set of axle shafts.
Symptoms of a problem
It is important to understand that the axle shafts (especially in the case of passenger cars) bear quite large loads. Moreover, such loads increase significantly if the car is operated in off-road conditions, the driver often makes sharp turns at high speed while driving, practices sharp starts with the wheels turned out, etc.
Also, problems with semi-pistons often result from wear of seals, bearings, and damage to retaining rings. In some cases, problems cause the axle shaft to break. In this case, fractures occur in the middle of the drive shaft or at the attachment points.
Taking into account the above, it is recommended to constantly monitor the condition of the CV joint boots, check the joints for play, etc., since spline joints may become unusable during long-term operation.
If repairs and replacement of worn-out elements are carried out, it is necessary to purchase parts and spare parts of proper quality. The fact is that the use of non-original cheap substitutes can lead not only to the rapid failure of such a spare part, but also cause an accident.
Axle shaft failures
https://m.etlib.ru
legkoe-delo.ru
First of all, external CV joints fail due to the greatest load on the structure in the wheel hubs and the maximum rotation angles of the external part of the drive. Internal hinges are more durable, but over time, wear forms on the contacting parts of the CV joints, which subsequently leads to part failure.
Advice! To understand the symptoms of a malfunction, you can compare the crunch of a failed CV joint with the sharp sound that a manual transmission makes when you try to engage reverse gear while the car is still rolling forward.
For external CV joints, this symptom appears when driving with the wheels turned to their extreme positions. If there is a malfunction, the internal joints crunch when coasting in a straight line, when starting from a stop, and also when driving under load (for example, uphill).
The cracking sound of the internal joints is especially pronounced with large suspension strokes (straight-line driving over potholes or off-road).
Also, if the CV joint is faulty, jerks during rotation of the drive wheels are characteristic, which are clearly visible to an observer from the outside when driving slowly on a level surface.
To confirm the malfunction, you can check for play in the internal CV joint: if the drive has free play, urgent replacement is required.
The rapid failure of internal and external CV joints is due to one of the following reasons (or a combination of them):
- particles of dirt, dust or water getting into the hinge mechanism through damage to the protective covers (anthers),
- insufficient amount of lubricant in the CV joint mechanism;
- poor workmanship of parts or metal defects;
- harsh driving style on broken roads (starts with slipping, sharp turns of the steering wheel to extreme positions at high speed, etc.).
Causes of failure
Most often, hinges break in axle shafts: CV joints fail due to damage to the boots and the ingress of water and dirt. However, the CV joint can be replaced without changing the entire axle shaft.
It is much more unpleasant when the shaft itself breaks. There may be several reasons: corrosion (on some models rubber balancers are installed, under which the metal deteriorates even faster than in open areas), overloads when driving off-road, sudden loads (falling into a hole, hitting an obstacle). The axle shaft is a reliable design, but there is a certain load limit for which it is designed, and it is better not to exceed this limit.
And finally, axle shafts fail simply from time to time: even the best metal gradually loses its properties, rusts, and the splines wear out. In order not to get stuck somewhere on the road at one “wonderful” moment, at each maintenance a visual diagnosis of the condition of the CV joints and other suspension parts is carried out. First of all, for pockets of corrosion, play, bearing performance, and leaks from under the boots.
Axle shafts are not repaired: the faulty part (usually hinges, less often the shaft itself) is simply replaced with a new one.
For information on how to choose an axle shaft, read our Buyer's Guide.
Recommendations for replacing internal CV joints
The automatic transmission system also contains a number of bearings, which can cause the entire gearbox to fail. For example, such vital elements for a car include the outboard intermediate bearing of the drive shaft. Of course, if one bearing breaks, it won’t lead to anything serious, but still, driving with a strong roar from under the hood is not very pleasant.
DETAILS: Four effective methods for cleaning injectors in garage conditions
Another detail that is worth paying attention to is the hinge kit; the drive shaft cannot do without this structural element. It is this that ensures the uniform transmission of traction forces that fall on the drive wheels.
Most often, drive shaft joints fail due to a leaky boot. The malfunction of this part is immediately visible; you will feel how unevenly the weight of the car is distributed on the wheels while driving. Of course, first of all you need to check the tire pressure, and then deal with the automatic transmission.
The constant velocity joint is a bowl-shaped housing with an axle shaft (trunnion), into which a cage and a cage with bearings are inserted. Special grooves are applied on the outer surface of the holder and the inner side of the body. When in motion, the inner race transmits force to the CV joint housing, causing it to rotate.
The dimensions of the parts are different: the internal CV joints are made more massive compared to the external ones.
There are two types of hinges: regular (with ball bearings that move along the dividing grooves) and tripoidal, in which three rollers with hemispherical surfaces rotate on needle bearings. According to their design, hinges can be dismountable or non-dismountable.
For the manufacture of CV joints, high-strength alloys are used, which theoretically guarantee a long service life of the unit and the absence of malfunctions.
As a rule, to replace a part it is necessary to remove the front wheel, unscrew the fasteners of the suspension elements and remove the corresponding drive shaft assembly with constant velocity joints. Also, this operation requires first draining the transmission oil from the gearbox to at least 1/3 of its total volume.
Next, the protective boots and the CV joints themselves are removed from the dismantled axle shaft.
In some cases, it is necessary to knock the hinges off the shaft with a hammer, and sometimes to remove parts of a collapsed CV joint from the axle shaft, it is necessary to use a milling cutter or grinder.
For owners of cars on which CV joints of a collapsible design are installed, there is an alternative, faster option: It is necessary to open the clamps and move the boot of the inner CV joint onto the axle shaft. The bolts on the inner hinge are then screwed together, resulting in the structure being held in place by the flange fit.
By turning the front wheels to their extreme positions, you can achieve a situation in which the drive falls out of the gearbox on its own. After this, all that remains is to replace the inner CV joint, add lubricant, install a new boot and assemble the structure.
Knowing the characteristic symptoms of failure of internal CV joints and understanding the potential causes of this malfunction will allow you to detect the breakdown in time and take measures to ensure safe operation of the vehicle.
Safety first
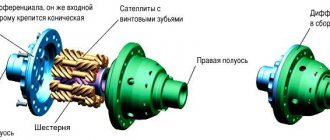
The differential is designed to ensure safe, comfortable maneuvering on the highway. The disadvantages described above apply to driving in extreme conditions, as well as on rough terrain. Therefore, if your vehicle is equipped with a manual locking drive, it should only be used in appropriate road conditions. And highway cars, which are difficult to “persuad” to drive slower than 100 km/h, are generally impossible and even dangerous to operate without a differential. This is a simple, but infinitely important mechanism in the transmission.
Purpose and types of axle shafts | Transmission
The torque from the differential side gears to the drive wheels is transmitted by shafts called axle shafts. In addition to torque, axle shafts can be loaded with bending moments from forces acting on the drive wheel. Such forces are the reaction of the road F from the vertical load falling on wheel 1 (Fig.
a), traction force P (or braking force during braking), lateral force T, which occurs when turning and skidding. Depending on the installation method, the axle shafts can be completely or partially unloaded from bending moments arising under the action of the listed forces at distances c and z, respectively.
The fully unloaded axle shaft 4 (Fig. b) is installed with its inner end on splines in the differential side gear, the housing of which rests on bearings, and is connected to the wheel hub with the outer end using a flange. The hub 5 with the wheel is mounted on two bearings 2 on the bridge beam 3.
With this installation, the axle shaft transmits only torque, and all bending moments are absorbed through the bearings by the bridge beam, which facilitates the operating conditions of the axle shaft. Fully balanced axle shafts are used on transport wheeled vehicles of medium and heavy load capacity.
Rice. Axle shaft installation diagram
In the drive of the steered drive wheels to the constant velocity joint 19, torque is supplied from the differential by the inner axle shaft 6. The outer axle shaft 23 has a flange, from which the torque is transmitted to the wheel hub 2. The wheel hub is mounted on a steering axle 22 using two tapered roller bearings 1, which transmit all bending moments from the above forces to the axle.
If the axle shaft with its outer end directly rests on bearings 2 (see a) installed in the bridge beam, then it receives bending moments from all the forces listed above and, in addition, transmits torque to the drive wheel. Axle shafts of this type are called semi-balanced.
DETAILS: Lada Granta and Kalina - replacing rear wheel brake pads - Za Rulem magazine
On high-speed tracked vehicles, the turning mechanisms used to control movement are included in the transmission, since torque is transmitted through them from the engine to the drive wheels.
ustroistvo-avtomobilya.ru
Design
The drive shaft is a part consisting of an axle and two CV joints, namely an internal and an external one. An internal one is located on the differential side; it transmits a small rotation angle. The outer one is located on the side of the wheel hub; it requires more space for movement. As a result, the axle shaft is involved in transmitting rotation regardless of the vibrations of the wheel or the angle when turning.
The structure of the axle shaft provides for the replacement or dismantling of the CV joint, in other words, the central shaft must be used more than once. Since the axle shaft is a reliable and rarely breaks part of the mechanism. In most cases, it becomes necessary to purchase hinges . Splined cavities and a special groove for the locking ring are designed for fastening the hinges.
The axle shaft experiences various directional loads during vehicle operation:
- Rolling force , restrains resistance when the wheel swings;
- Diametrical load when the car picks up speed or brakes;
- Expansion and contraction during maneuvers.
Accordingly, the load is directly proportional to the weight of the car. Based on this, three basic types of axle shafts were created. Their difference lies in the method of attaching the axle shaft to the wheel hub. Let's look at them in more detail:
- Fully unloaded - these are axle shafts, with the help of their characteristic fastening method they do not experience lateral and axial loads. Due to this, only the torque is transmitted. In this type, the axle shaft is mounted on the hub. A fully unloaded axle shaft, in most cases, is used on cargo vehicles of any kind or heavy special purpose. technology;
- Semi-loaded ones are the lightest in terms of their design. True, they are subject to all bending forces. They are used mainly on equipment that does not require the ability to carry heavy loads, that is, on passenger cars. The wheel hub is placed on the axle shaft, and the shaft, in turn, is mounted on a bearing;
- Three-quarters unloaded - in such an axle shaft we have only one support bearing, and the wheel hub rests on it. And also it is not subject to bending loads.
Most often, the two axes do not correspond to each other in size. Their main difference is in length, the right one is generally longer than the left one. All this is a consequence of the asymmetrical position of the differential on the axle. We also have two types of mounting to the hub and differential: spline connection or flange connection.
Self-diagnosis methods
On a level surface, the car is placed on the parking brake, the rear wheels are blocked with wheel chocks or auxiliary objects.
Using a jack and two supports, the front of the car is hung so that the drive wheels do not touch the ground.
The engine starts, first gear is engaged (for automatic transmission – mode D). If, when the front wheels rotate slowly, a sharp metallic crack or crunch is periodically heard, then the inner CV joints are faulty. It is in this way that the condition of the internal hinges is determined at service stations by lifting the car on a lift.
Additionally, it is worth inspecting the anthers for damage and lubricant leakage, and also checking for play in the structure. To do this, shake the drive in different directions, preventing the axle shaft from turning.
Warning! A faulty inner CV joint can fall apart or jump out of the transmission at high speeds and cause a serious accident. It is necessary to promptly diagnose and eliminate identified drive defects.
A semi-minor axis is... What is a semi-minor axis?
Not to be confused with the term "Ellipsis".
Ellipse and its focuses
Ellipse (ancient Greek ἔλλειψις - disadvantage, in the sense of lack of eccentricity up to 1) - the geometric locus of points M of the Euclidean plane for which the sum of the distances from two given points F1 and F2 (called foci) is constant, that is
| F1M | | F2M | = 2a.
A circle is a special case of an ellipse. Along with a hyperbola and a parabola, an ellipse is a conic section and a quadric. An ellipse can also be described as the intersection of a plane and a circular cylinder, or as the orthogonal projection of a circle onto a plane.
Related definitions
- The segment AB passing through the foci of the ellipse, the ends of which lie on the ellipse, is called the major axis of this ellipse. The length of the major axis is 2a in the above equation.
- The segment CD perpendicular to the major axis of the ellipse, passing through the central point of the major axis, the ends of which lie on the ellipse, is called the minor axis of the ellipse.
- The intersection point of the major and minor axes of an ellipse is called its center.
- The intersection point of an ellipse with its axes is called its vertices.
- The segments drawn from the center of the ellipse to the vertices on the major and minor axes are called, respectively, the semi-major axis and semi-minor axis of the ellipse, and are designated a and b.
- The distances r1 and r2 from each focus to a given point on the ellipse are called the focal radii at that point.
- The distance is called the focal distance.
- The eccentricity of an ellipse is called the ratio. Eccentricity (also denoted ε) characterizes the elongation of the ellipse as it changes. The closer the eccentricity is to zero, the more the ellipse resembles a circle, and vice versa, the closer the eccentricity is to unity, the more elongated it is.
- The focal parameter is half the length of the chord passing through the focus and perpendicular to the major axis of the ellipse.
- The ratio of the lengths of the minor and major semi-axes is called the ellipse compression ratio or ellipticity: . A value equal to is called compression of the ellipse. For a circle, the compression coefficient is equal to one, the compression is zero. The coefficient and eccentricity of the ellipse are related by the relation
Properties
- Focal property. If F1 and F2 are the foci of the ellipse, then for any point X belonging to the ellipse, the angle between the tangent at this point and the line (F1X) is equal to the angle between this tangent and the line (F2X).
- A straight line drawn through the midpoints of segments cut off by two parallel lines intersecting an ellipse will always pass through the center of the ellipse. This allows you to easily obtain the center of the ellipse, and subsequently the axes, vertices and foci, by constructing using a compass and ruler.
- The evolute of the ellipse is the astroid.
An ellipse can also be described as
Relationships between ellipse elements
Parts of an ellipse (see Related Definitions for description)