Power steering (hereinafter referred to as power steering) in a car is a system designed to reduce the effort applied to the steering during a maneuver. Initially, agricultural and cargo vehicles were equipped with such systems.
Since the early 70s, power steering began to be installed on passenger cars. Not the least role in this was played by the fact that women increasingly acted as drivers.
In addition to providing comfort when driving a car, power steering allows you to:
- reduce the diameter (dimensions) of the steering wheel;
- change the gear ratio of the steering shaft-rack system, providing greater maneuverability during a turn;
- automate the vehicle's control system.
Considering that steering is the second factor in traffic safety after the braking system, high demands are placed on reliability, information content, and other power steering parameters. Special attention should be paid to the operation and maintenance of this system.
How does a power steering steering rack work?
The power steering is connected to the steering rack housing, so it is activated only when the engine is running and power steering fluid is being pumped. The power steering pulley is driven by a belt drive, in turn, a hydraulic pump inside the rack creates pressure and acts on the wheel rods at the request of the driver. An important role in the operation of power steering is played by the built-in computer, which calculates forces and pressure.
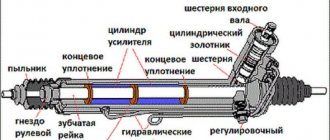
- The torsion bar, in conjunction with electrical systems, distributes pressure depending on the rotation of the steering wheel;
- The spool valve is a source of pressure, capable of increasing the pressure in the rack depending on the need;
- A special container is used to collect oil when the engine is turned off. As soon as the steering wheel begins to rotate, oil is injected through the spool valve, exactly where pressure needs to be created. After the steering wheel stops rotating, the power steering pump stops pumping oil, causing it to return to the container.
The power steering must be constantly maintained, its condition monitored, faults corrected in a timely manner and the power steering fluid changed in accordance with the requirements of the car manufacturer. The quality and timeliness of system maintenance can be considered a fundamental factor in the issue of long-term and trouble-free operation
You should pay attention to the viscosity of the oil, it should not be too viscous, as this can cause excessive pressure in the rack and lead to unpleasant consequences
Types of steering racks
- Regular, without amplifiers. It was used back in the 70s - 80s of the last century on 90% of cars. Here, all the effort to turn the steering wheel lies with the driver, there are no amplifiers, and therefore it is not always easy to turn the steering wheel.
- Steering rack with power steering or power steering. In essence, this is the same ordinary rack, only a special pump and a closed circuit with oil seals (where a special fluid is pumped) are added to it, which helps to turn the steering wheel. That is, the driver does not need to exert much effort to turn the steering wheel. This is especially valuable on heavy vehicles (trucks, buses and SUVs).
- Steering rack with EUR or electric power steering. This is a dry type of amplifier, no oil is used here, and the operating principle is completely different. Next to the shaft there is an electric motor with a gear (powered by the on-board network), which helps turn the steering wheel. The ECU gives him orders, he sees where the wheels are deviating and orders the electric motor to help turn.
Steering rack structure and 6 signs of malfunction
If exaggerated, the types are divided as follows: - conventional mechanics with 100% use of muscle power, rack with hydraulic booster and electric booster.
Types and principle of operation of steering racks
1. Mechanical steering racks
The movement of the mechanism of mechanical steering racks is carried out due to the force with which a person turns the steering wheel. And this makes the car less maneuverable. Moreover, while driving, shocks are transferred from the suspension to the steering wheel. Therefore, to drive a car with a mechanical steering rack, the driver makes significant efforts.
2. Steering racks with power steering
The hydraulic power steering includes a pump, distributor, slave cylinder, oil tank, and connecting hoses.
When the engine is started, the pump sucks lubricant from the tank and pumps it into the spool valve. This mechanism allows oil to be dosed into the working cylinder to the left or right of the piston (depending on where the steering wheel is turned). Oil pressure moves the piston and rack, causing the wheels to turn. The person driving the car needs to make a small effort to turn the steering wheel, even when the car is not moving.
The distributor is controlled by a torsion bar; it is a springy iron rod mounted on the steering shaft and connected to a spool valve. If the steering wheel is in neutral, the distributor spool closes the supply channels, so the lubricant flows back into the tank. If the steering wheel rotates, the torsion bar twists and turns the inside of the spool valve. This leads to the opening of the metering channels of the distributor, and the lubricant enters the working cylinder.
As the angle of rotation of the steering wheel increases, the torsion bar becomes more twisted. As a result, the throughput of the distributor channels increases, as well as the force applied to the steering rack.
If the steering wheel is turned to the extreme left or right, the safety valves are activated. With their help, oil pressure is relieved to prevent failure of the power steering.
Remember that if you have a car with such a mechanism, in order to prevent damage, do not leave the wheels turned out, regularly check the oil level in the tank, and change it if necessary.
3. Steering racks with EUR
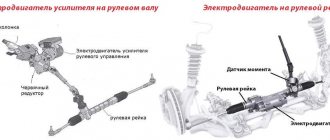
If your car has electric power steering, driving the car will be easy. This mechanism is compact, so fuel consumption will be reduced, especially when compared with a hydraulic booster. In the latter case, the pump operates continuously if the engine is running, the electric drive is turned on only when the driver turns.
How electric power steering works: During a maneuver, the torsion bar transmits force from the steering wheel to the steering mechanism. The torque sensor signals the amount of force to the ECU (electronic control unit), and it also receives data from the crankshaft, steering angle and speed (ABS) sensors. Once the information is processed, a control signal is created that starts the electric motor located on the steering rack.
Driving a car with electric power steering has its own characteristics:
- when the maneuver is performed at low speed, the electric motor receives a signal to create the greatest torque, so the driver is comfortable driving the car;
- if the car turns at high speed, the electric motor produces a small torque, so the steering wheel “fills up”;
- as soon as the car changes lanes, the electronic control unit issues a command for the wheels to return to the middle position;
- when driving, the ECU monitors how much the wheels deviate from the average position due to differences in tire pressure or their uneven wear, side wind and other factors, and then signals to the electric motor which trajectory of the car will be correct;
- Since one gear rotates when you turn the steering wheel, even if the electric drive breaks down, you can drive the car.
We recommend
“The steering rack is broken: causes and further actions” Read more
Modern cars are increasingly installing electric power steering, which in its characteristics is much superior to power steering.
History of the creation of power steering
VAZ 2110 steering rack repair
The first representatives of four-wheeled vehicles had primitive steering. The swivel wheels were mounted on one beam, which was attached to the body only in the central part on a hinge - according to the principle of horse-drawn transport.
Such a mechanism did not allow self-propelled carts to be maneuverable, and the turning radius was so huge that the car could turn around completely somewhere in the square. In addition, power steering was not required to make turns.
Over time, adjustments were made to the steering system in order to minimize the turning angle of the car. To make the task easier for the driver (each time the invention made turning the steering wheel tighter), various options were developed, ranging from increasing the diameter of the steering wheel itself to introducing different types of gears into the system.
As a result of many years of trial and error, engineers concluded that the steering rack design is the golden mean between simplicity, accessibility and increased torque coming from the steering wheel. In addition, such a device is compatible with power steering.
Drive unit
The drive in the steering design is used to transmit the movement of the rack or bipod to the steered wheels. Moreover, the task of this component is to change the position of the wheels at different angles. This is due to the fact that the wheels move along different radii when turning. Therefore, when changing the trajectory of movement, the wheel on the inside must turn at a larger angle than the outside.
The design of the drive depends on the mechanism used. So, if a car uses a “rack and pinion”, then the drive consists of only two rods connected to the steering knuckle (the role of which is played by the shock absorber strut) via a ball end.
These rods can be attached to the rail in two ways. Less common is their rigid fixation with a bolted connection (in some cases the connection is made through a silent block). For such a connection, a longitudinal window is made in the mechanism body.
A more common method of connecting rods is a rigid but movable connection to the ends of the rail. To ensure such a connection, a ball tip is made at the end of both rods. By means of a nut, this ball is pressed against the rail. When the latter moves, the rod changes its position, which ensures the existing connection.
In drives that use a worm-roller mechanism, the design is much more complex and consists of a whole system of levers and rods, called a steering linkage. So, for example, on the VAZ-2101 the drive consists of two side rods, one middle rod, a pendulum arm and steering knuckles with levers. At the same time, to ensure the possibility of changing the angle of the wheel position, the steering knuckle is attached to the suspension arms using two ball joints (upper and lower).
A large number of component elements, as well as connections between them, makes this type of drive more susceptible to wear and backlash. This fact is another reason for abandoning the worm gear in favor of a rack and pinion mechanism.
DIY steering rack repair
Lada Granta steering rack repair
The steering rack must be restored in a timely manner, otherwise the entire assembly will have to be completely replaced. During the repair, we will clean the parts from dirt, replace worn parts with new or restored ones, and check the functionality of the unit.
So, we compared our capabilities with the strength and upcoming labor costs and came to the conclusion that we would repair the steering gear ourselves. We will need the following spare parts and tools:
- repair kit for gearbox (costs about 2100-2800 rubles, contains rubber seals and fluoroplastic bushings with rings);
- anthers with clamps (price about 630 rubles);
- set of wrenches;
- special devices for disassembling and assembling the unit.
To remove the gearbox we take the following steps:
- we place stands under the front part of the car, remove the wheels;
- use a special puller to press the steering tips out of the steering knuckle axles;
- dismantle the heat shield of the steering gear;
- if the car has a hydraulic booster, then unscrew the oil supply and return hoses and place a container under them to drain the fluid;
- if the car has electric power steering, then remove the steering shaft position indicator or disconnect the connector;
- unscrew the bolts that attach the steering gear to the engine shield or subframe;
- loosen the coupling bolt of the universal joint between the unit being repaired and the steering shaft;
- release the spline connection by pulling the gearbox in the direction of the steering shaft;
- remove the gearbox through the wheel arch.
If the subframe interferes, then unscrew only the rear bolts and the motor mount, then move the subframe down. Then we release the steering gear. That is, in certain cars, complete removal of the subframe is not required.
To disassemble and reassemble the steering gearbox, it is necessary to ensure cleanliness of the room. Otherwise, particles of sand or dust will penetrate inside, which will cause rapid wear of surfaces and seals:
- We mark the position of the gear rod or measure its protrusion from the body on both sides. This will help at a certain stage to correctly assemble the unit.
- We also indicate the position of the adjusting nut.
- We fix the mechanism in a bench vice, without clamping it too tightly, since the body made of a fragile aluminum alloy can bend or break. If there is no vice, then we will disassemble the rail on a clean sheet of dense material.
- We remove the clamps and tighten the steering rod boots.
- We firmly fix the gearbox housing and use an open-end wrench to unscrew the steering rods.
- We unscrew the locknut and the adjusting device nut, while noting the number of turns. This is necessary to return the pressure sleeve to its natural position during the assembly process.
- We take out the clamping sleeve and washers from the mounting socket.
- Use a special wrench to unscrew the housing or nut of the drive shaft and remove the shaft from the housing.
- We take out the gear rod of the gearbox.
- We remove the sealing cuffs, bushings and fluoroplastic rings from the steering gear housing.
We look at the condition of the housing, gear shaft and other spare parts. The shaft surface must be free of defects. Any defect in the teeth and the area of the rod in contact with the bushings, oil seals and rings, including burrs, risks and rust, can cause rapid deterioration of the seals and leakage of the steering gear.
The oblique teeth of the drive shaft gear should not be covered with cracks, burrs, chips or signs of deep wear. If you install a shaft with such defects, then when moving it will jam the steering rack.
We examine the pressure bushing for smoothness, absence of scoring and punching. If a part is damaged, you will have to buy it again if it is not included in the repair kit.
After troubleshooting the parts, we begin repairs:
Steering racks: design features, causes of breakdowns and repair nuances
The steering rack is one of the oldest and most common steering mechanisms. The key to success is the simplicity and reliability of the system. Nevertheless, rack breakdowns are not at all uncommon, since all components are subject to aging and wear. How fast do they come, what can break, is it so difficult to repair? Let's try to understand all the issues.
The design of the rack and pinion steering mechanism is probably one of the simplest. What could be simpler than an ordinary worm-rack pair in a steering linkage? Moreover, with the spread of independent front wheel suspensions, such a scheme quickly paved its way to popularity.
In addition to the simplicity of the mechanism, there are many more reasons for success. For example, a very low friction design, making control easier without power assistance and more precise with power assistance. It was possible to implement a variable gear ratio system, which improved controllability. And the amplifier is integrated into this design simply and logically, while simultaneously working as a steering damper.
Is this not enough? There may be even more advantages. There are no high-precision elements in the rack; there is virtually no need for lubrication if the working pairs are successfully selected. Let's add to this the small size and convenience of the rack-and-pinion steering arrangement, the rich possibilities for creating injury-proof elements of the steering column and, finally, the low cost of the design and minimal risks of “biting” due to the fault of the mechanics. In general, the bright future of this design was predetermined.
Components / Articles
Half a century ahead of Infiniti: the French DIRAVI steering system
But, despite the simplicity of the design, the number of possible breakdowns turned out to be quite large. The majority of problems are associated with the appearance of gaps in the mechanism, which means knocking, play and shock in the steering. Less commonly, “biting” occurs due to the destruction of gear pairs or damage to oil seals and bushings. A typical problem with power steering racks is leaks of working fluid. Malfunctions of the spool valve mechanism are less common. And many rack malfunctions are associated with dirt getting inside - through damaged boots or a hydraulic line.
Almost all breakdowns can be repaired. However, there are also those that do not allow you to completely get rid of operational problems, especially in the case of racks with a built-in electric amplifier.
The most common problem is related to rack knocking . This usually indicates that the gap in the connection of the worm pair has increased or that the side bushings of the rack rod have failed. Sometimes the cause is a violation of the fastenings of the rail itself. In addition, runout often causes leakage of rod seals in the presence of power steering.
Checking the cause is quite simple: if the rack fastening is in order, then you can measure the runout of the rack in the bushings when applying force - just remove the rack boot (in most cases the problem is observed visually). If the runout is imperceptible, you need to check the gap of the working pair. This operation can also be done without disassembling the mechanism. You just need to try to rotate the rack shaft around its axis (if it is round, triangular shafts cannot be checked this way). If the shaft rotates slightly, it means that the gap in the working pair has changed due to a violation of the geometry of the surfaces or the operation of the clamping mechanism. Most designs have a block that regulates the pressing force or clearance in the worm pair due to spring tension.
The reasons for changes in mechanical clearances may be different. Firstly, this is the natural wear of the bushings, working pair, stop and crankcase. The mechanisms are quite durable, but several hundred thousand kilometers and increased loads can damage everything. Shock loads also often cause problems. For example, when falling into potholes or in an accident. And also a very common cause is banal corrosion due to moisture getting into the steering rack.
When runout occurs, the side bushings are simply replaced. If there are no visible signs of wear on the rack rod, then this is a very effective measure. Often, such repairs do not even require removing the rack from the car; you just need to unscrew the steering rod and remove the boot. If there are visible scratches or corrosion, the rod is repaired by regrinding to the repair size. At the same time, they are replaced with repair bushings and oil seals. The bushings themselves are not necessarily rigid. Often the bushing is an elastic structure in which there is no clearance, but it allows you to slightly change the height for normal operation of the worm pair.
Designs with a rigid aluminum or brass bushing, typical of Japanese and Korean cars, are more likely to cause knocking in the steering precisely because of the material used.
If after replacing the rod bushings there is still play and clearance in the working pair, it is worth checking the wear of the clamping block and its shaft in the rack housing. Tightening the rack is possible within small limits, but if the working pair is worn out a lot, this will no longer help, and the rack will become difficult to move in the bushings.
When the crack itself and its shaft wear out, it is replaced with a repair one, and the shaft is ground. In any case, if tightening does not help, the rack must be checked for wear on the working pair. Sometimes the teeth in the center of the stem are too worn and require replacement. Otherwise, it is enough to replace the rack shaft with a repair one, grind the rack rod or use repair shaft bushings. But such work is quite expensive, and in this case it is most often recommended to replace the rack with a new one or a factory-restored one.
Components / Articles
All-wheel drive systems: what they are and what problems to expect from each of them
Racks with built-in power steering also have a whole class of faults associated with oil seal leaks and hydraulic leaks. Leaks through the rack rod seals occur when the seals themselves and the rod wear out. The reasons are usually rod corrosion, oil contamination, overheating of the power steering fluid, pressure surges above the nominal value and general aging of the seal material. Any rod beating worsens the operating conditions of the seals and increases the likelihood of leaks. Corrosion damage to the rod surface is also a common cause.
The repair is the same as for wear of the rod bushings. The rod is ground to repair size, and the bushings and seals are changed at the same time.
Shaft seal leakage is also very common. It ages first at elevated amplifier fluid temperatures. It is heated by the pump, and this zone has the worst cooling conditions. Sometimes corrosion of the shaft itself occurs. This usually results in a "slow" leak, as opposed to the "fast" leaks associated with stem seal leaks.
Malfunctions of the spool mechanism in most cases are associated with wear of the crankcase by Teflon seal rings, which results in a flow of working fluid. This leads to disruptions in the operation of the hydraulics - usually the amplifier stops working completely or partially. The repair consists of either replacing the crankcase, or installing a repair sleeve followed by boring.
A rare malfunction is a violation of the rigidity of the torsion shaft. Over time, it weakens, and power steering assistance becomes more intrusive, and the reactive action on the steering wheel worsens.
The Servotronic system from ZF is also distinguished by the installation of an additional valve on the spool mechanism that regulates the pressure on the rack. The electronics or the valve itself may fail. Otherwise there is nothing to break there.
Wear of the rack working cylinder housing in most cases leads to its replacement. The fact is that the separating piston of the rack rod during operation of the machine wears out mainly the “near-zero” zone. Over time, this causes a force “step” to form between straight-line driving and cornering force. Power steering assistance in the “zero” position disappears, and there is a feeling of “biting” when turning the steering wheel. At the initial stage, sometimes replacing the rod seal helps, but in most cases you will need to replace the rack housing, which is done very rarely. Most often, replacement of the entire housing or the rack assembly is required.
The ZF rack used in the BMW Active Steering system stands out from other designs. In this case, it itself has a completely traditional design and a set of faults. But the working shaft of the rack is more complicated: the drive to the rack is differential. The moment is transmitted to it from the steering shaft and from the drive electric motor. Based on sensor signals, the motor “helps” or “prevents” rotating the shaft, thereby increasing or decreasing the resulting steering ratio.
If the electric motor malfunctions, in order to ensure the operation of the steering, its drive is completely blocked by an additional emergency lock. This ensures the safety of the structure in case of electrical problems. In addition to the introduction of additional sensors and an electric motor, which are prone to failures, the system wears out intensively the cylindrical differential gears and the worm gear from the electric motor to its housing. Over time, play in a small transmission increases, thereby worsening the “steering feel” of such a mechanism. The differential block is replaced as an assembly if there is any play, and the remaining components are repaired in the same way as classic designs.
Electric power steering comes in two types. Some are located on the steering column and transmit force directly through the working pair of the rack. The latter have a direct drive, and only a torsion bar and steering wheel position sensors are located on the steering shaft or rack.
The first version of the ESD design has nothing to do with the racks themselves, except that it is worth noting that the load on the working pair of racks in such a mechanism is very high and the resource of the rack itself is noticeably reduced. But the problems of electric power steering with direct drive can be considered in more detail.
The first place among malfunctions is held by breakdowns of torque sensors. For example, on very common ESD designs used by VW, the cause of failure is the breakdown of the flexible sensor cable. Repair consists of cutting off the broken part and soldering it to the sensor contacts.
Various malfunctions with the motor, its bearings or electrical wiring, as well as the power module do occur, but are still very rare. Mostly individual models are noted, for example EPS from Honda.
Also a feature of the ZF/Bosch/MSG designs of the first to third generations is the presence of a second gear drive in the rack. The electric motor has its own gear train, optimized to transmit more torque. Thus, the rack has a second cracker and a second worm pair, which slightly complicates diagnostics when backlash occurs and places higher demands on the quality of work performed.
Newer designs feature a recirculating ball helical drive, direct drive or belt drive from an electric motor. Such a mechanism is less prone to the accumulation of backlash and the appearance of knocks, but it is very sensitive to contamination and loss of rod lubrication. So you need to monitor the condition of the anthers much more carefully. If the rod is dirty or the transmission bearings are damaged, the mechanism begins to howl during operation, and in advanced cases it may even jam. Repair of rod threads after cavities appear is rarely performed; usually in this case the rod must be replaced.
A rigid drive on a screw drive is prone to knocking and also has a high load on the electric motor. In order to somewhat soften the operation of the unit, some designs use an elastic toothed belt drive. It significantly reduces the load on the node, increasing its resource. But, in turn, it may require replacement after 3–5 years of operation, depending on conditions and load.
Types and options
As mentioned earlier, the key elements of the steering rack have not changed for many decades. Only minor adjustments are made to the mechanism, but the principle remains the same.
The only thing that distinguishes all units of this type is the amplifier drive. There are three modifications in total. Let's look at the features of each of them.
Mechanical steering rack
This modification is classic. All cars were equipped with it until hydraulic and electric amplifiers were created. A mechanical steering rack is the simplest type of device. Thanks to the small teeth and larger steering wheel in comparison, the driver does not have to exert much effort to turn the car.
There are steering racks with different gear ratios. In the center of the bar there is a gear train with a smaller amplitude, and at the ends this figure increases. This makes it even easier for the driver to turn the steering wheel when starting out or when cornering at high speed. And in parking lots, when the wheels need to be turned all the way, the driver does not need to turn the steering wheel many times.
Device
All vehicles have a control system. It consists of a lot of different spare parts. The device is constantly being improved. Certain parts are introduced, and some are removed. To make it easier for the driver to control the vehicle, the steering mechanism is equipped with a hydraulic booster.
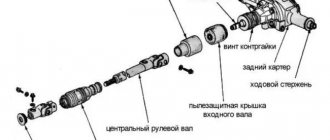
The mechanism itself consists of the following elements:
- Rods, as well as tips. They are attached to the moving rack mechanisms. They are responsible for which direction the wheels turn.
- Gear type bar and gears. Allows you to transfer rotation from the steering wheel to the rods.
- Frame. Made from aluminum. It contains the main parts of the rail itself.
- Spring system. The purpose of the springs is to help the gear fit tightly to the rack. When the spring is in good condition, the free play of the steering wheel is minimal.
- Bearings. Designed to make rack maneuvers easier.
- Limiting elements. They determine the maximum steering angle.
Troubleshooting steering rack
Steering rack malfunctions are quite common, since this unit and the entire steering system on domestic roads are subject to increased loads. You can detect a broken rack yourself, based on a number of signs:
If these symptoms of rack failure appear, it is recommended not to delay dismantling the steering gear for inspection and troubleshooting in order to minimize repair costs.
- it has become harder to turn the steering wheel, or it periodically bites (difficult rotation is observed only periodically in certain positions of the steering wheel);
- there is a knock from the front suspension, which clearly “irradiates” into the steering wheel;
- The power steering pump is noisy;
- play in the steering wheel, which means there is play in the rack;
- oil leakage from the steering rack, which is often accompanied by a noticeable increase in the steering force and noise arising during this action.
The manifestation of such signs indicates that the steering rack device
somewhere is broken and this mechanism requires diagnostics and further repair.
What is rack and pinion steering - in simple words
Rack and pinion steering , or rack and pinion steering as it is also called, is an incredibly common front-wheel steering system on modern passenger cars. Even if you are not an automotive technology guru, you have most likely heard of such a mechanism. But how does it work? Let us explain the principle of operation for beginners, as they say, on the fingers.
Most likely, your car has rack and pinion steering. This incredibly popular engineering choice is due to the progressive operation of the system as a whole (ideal for modern dynamic, fast and powerful cars), good feedback to the front wheels (you understand exactly at what angle the wheels are turned and how quickly they turn) and the ability to install controls for vehicles with front independent suspension.
Basic malfunctions of power steering racks, their elimination and repair
During operation, the power steering rack system requires constant inspection, maintenance and repair (if necessary). The most common system malfunctions include:
1. Flow
Oil seal leaks are most often caused by corrosion when water gets on the shaft, which, as rust appears on it, destroys the working surface of the oil seal. Such a malfunction is possible when the boot is destroyed due to mechanical stress or natural wear.
The repair consists of restoring the integrity of the shaft and removing traces of corrosion (usually the shaft is ground). After this, a new oil seal with the appropriate mounting dimensions is installed.
Leakage of hydraulic hoses is caused by high pressure in the system (100 atmospheres or more), wear of the hoses, especially at the junction of the rubber and metal elements of the high-pressure hoses. Usually the hose needs to be replaced, but there are workshops that repress the connections.
2. Knock
It may occur for reasons:
- breakage or abrasion of the central tooth of the rack;
- wear of the support sleeve;
- malfunction of the clamping block.
Tightening the rack in case of wear of the central tooth does not give any result. There may be less play, but since the other teeth are less worn (increased wear on the central tooth is due to the fact that the steering wheel spends more time in the middle position), the steering wheel may not return from its extreme positions due to pinching.
Video about the service life of the power steering rack:
The support bushings are severely damaged when driving on uneven road surfaces. Most rack and pinion mechanisms of foreign cars are not designed for Russian roads.
3. Tight steering wheel
If the steering wheel turns with force only in one direction, most likely the o-ring in the distributor body is leaking fluid under pressure. This may be the result of dirt or dust getting into the system, which causes grooves over time. The fluid does not enter the hydraulic cylinder, but goes directly into the expansion tank. Repair can be carried out by grinding the working area and replacing the O-ring.
If the steering wheel turns tightly in both directions, there may be several reasons:
- faulty piston Teflon ring;
- grooves in two chambers of the distributor;
- worn pump operating pair;
- torsion bar failure.
To diagnose a specific malfunction, disassembling the mechanism and diagnosing the components is required. In most cases, you will need the help of a specialist.
Diagnostics and repair
Driver comfort and road safety depend on the serviceability of the device. The simple design of the rack with hydraulic booster allows you to perform repair and diagnostic work at home. To detect breakdowns and replace parts, special equipment and devices are required.
Power steering rack malfunctions: symptoms
To protect yourself on the roads, it is necessary to regularly carefully check the technical condition of the control mechanism. Serious breakdowns manifest themselves clearly and do not require special detection devices. Just watch out for the following signs:
- Difficulty turning the steering wheel or not returning to the center position after a turn. This happens as a result of deformation of the rack, crankcase or shaft.
- A knocking sound when driving over uneven surfaces and potholes, which decreases when the wheels are set to their extreme position. The reason is wear of the steering column universal joints, rod joints, and wear of the teeth of the central rack gear.
- Increased sensitivity - a discrepancy between the angle of rotation of the wheels and the steering wheel, or a situation where the car “throws to the sides” at the slightest movement of the hands. This happens as a result of malfunctions in the power steering hydraulic system.
- A decrease in the fluid level in the tank, the appearance of smudges and oil stains on the boots. Leakage occurs as a result of shaft corrosion and wear of rubber seals.
Any manifestation of a breakdown requires immediate intervention. Failure of the steering system is one of the most dangerous problems, which even the failure of the brake system cannot compare with. Delays in repairs lead to worsening of the problem. Failure to correct minor problems in a timely manner will cause financial losses and, in the worst case, an accident.
Types of steering racks
There are three types of mechanisms installed on passenger cars. They differ in the presence or absence of auxiliary devices that facilitate control.
Mechanical steering rack
The simplest version of the device in which the steering wheels are turned due to the efforts of the driver. To reduce the load on the hands and at the same time make it easier to control on the track, cars are equipped with racks, in which the variable number increases with increasing angle of rotation of the wheels. This makes parking maneuvers easier and provides sharp steering at speed.
Hydraulic steering rack
The driver's influence is supplemented by a hydraulic booster. This allows you to create easy and at the same time “sharp” control.
Power steering softens the loads that arise when driving over uneven surfaces. The only drawback of such a device is the deterioration of “sensitivity”. It is compensated in two ways:
- install an electric hydraulic booster with feedback;
- change the suspension design.
Electric steering rack
In these devices, the driver's influence on the steering wheel is enhanced by the engine. It is powered from the on-board electrical network. Depending on the location, there are three types of units in which the motor is mounted on the steering shaft, column and in the rack housing. The last option is the most reliable.
The design with an electric motor on the shaft is dangerous because if it breaks down, it practically stops working.
Today, most production cars of the budget and middle class are equipped with a power steering rack.
Types of power steering
Initially, power steering was installed on passenger vehicles, made according to a scheme similar to the amplifiers installed on heavy vehicles. They have a significant drawback: as the speed of the vehicle increases, a smaller steering angle and applied force are required to carry out a safe maneuver. At high speeds, the road-steering feedback is significantly reduced, and the driver stops “feeling” the road. In slippery conditions, the vehicle may lose control.
To eliminate this problem, a variable ratio rack was developed.
This rack is installed on the VAZ 2110. It has a large gear ratio at small steering angles. This usually corresponds to high speeds and low turning angles where little force is required. The gear ratio decreases towards the “edges”, that is, at large maneuvering angles, which are possible at low speeds. The use of this design did not eliminate all controllability problems.
Video - types of steering racks, how power steering and power steering differ:
Manufacturers have developed electric power steering
, adding an electrovalve with an electronic control system to the standard circuit. The electric power steering system combines the information content of the steering wheel and comfortable driving conditions to the maximum extent.
In some car models, the power steering pump is driven by an electric motor. In such cases, the hydraulic booster works even when the engine is not running.
Electric power steering is increasingly being installed in modern cars.
. Their significant drawback is their complete dependence on the serviceability and reliability of the electronics. If any of the electronic components, drives, or even a fuse fails, the efficiency of the electric power steering becomes zero and controllability deteriorates sharply.
Power steering device
Main components of power steering
Power steering is installed on any type. For passenger cars, the rack and pinion mechanism is most widespread. In this case, the power steering scheme is as follows:
- tank for working fluid;
- oil pump;
- spool valve;
- hydraulic cylinder;
- connecting hoses.
Power steering reservoir
Power steering reservoir
A filter element and a dipstick are installed in the tank or reservoir for the working fluid to monitor the oil level. Oil lubricates the rubbing pairs of mechanisms and transmits force from the pump to the hydraulic cylinder. A mesh in the tank serves as a filter from dirt and metal shavings that arise during operation.
The liquid level inside the tank can be checked visually if the tank is made of translucent plastic. If the plastic is opaque or a metal reservoir is used, the fluid level is checked using a dipstick.
In some cars, the fluid level can only be checked after briefly running the engine or by turning the steering wheel several times in different directions while the car is idling.
Special notches are made on the probes or reservoirs, both for a “cold” engine and for a “hot” one that has already been running for some time. Also, the required liquid level can be determined using o and “Min”.
Power steering pump
Power steering vane pump
necessary to ensure that the required pressure is maintained in the system and oil circulation occurs. The pump is installed on the engine cylinder block and is driven from the crankshaft pulley using a drive belt.
Structurally, the pump can be of different types. The most common are vane pumps, which are characterized by high efficiency and wear resistance. The device is made in a metal case with a rotor with blades rotating inside it.
During rotation, the blades capture the working fluid and, under pressure, supply it to the distributor and then to the hydraulic cylinder.
The pump is driven by a crankshaft pulley, so its performance and pressure depend on the engine speed. To maintain the required pressure in the power steering, a special valve is used. The pressure that the pump creates in the system can reach up to 100-150 bar.
Depending on the type of control, oil pumps are divided into adjustable and unregulated:
- adjustable pumps maintain constant pressure by changing the productive part of the pump;
- Constant pressure in unregulated pumps is maintained by a pressure reducing valve.
The pressure reducing valve is a pneumatic or hydraulic throttle that operates automatically and controls the level of oil pressure.
Power steering distributor
Schematic device of the distributor
The power steering distributor is installed on the steering shaft or on elements. Its purpose is to direct the flow of working fluid into the corresponding cavity of the hydraulic cylinder or back into the tank.
The main elements of the distributor are the torsion bar, the rotary spool and the distributor shaft. A torsion bar is a thin springy metal rod that twists under the influence of torque. The spool and distributor shaft are two cylindrical parts with fluid channels inserted into each other. The spool is connected to the steering gear, and the distributor shaft is connected to the propeller shaft, that is, to the steering wheel. The torsion bar is fixed at one end to the distributor shaft, its other end is installed in the rotary spool.
The distributor can be axial, in which the spool moves translationally, or rotary, in which the spool rotates.
Hydraulic cylinder and connecting hoses
The hydraulic cylinder is built into the rack and consists of a piston and a rod that moves the rack under the influence of fluid pressure.
Fluid circulation diagram in the hydraulic booster
High pressure connecting hoses ensure oil circulation between the distributor, hydraulic cylinder and pump. Oil flows from the tank to the pump and from the distributor back to the tank through low pressure hoses.
Adjusting the device
Adjustment of the steering mechanism is used to compensate for gaps in the worm-roller and pinion-rack mechanisms. During operation, play may appear in these mechanisms, which can lead to rapid wear of the elements. The steering mechanism must be adjusted only in accordance with the manufacturer’s recommendations and at specialized service stations. Excessive “clamping” of the mechanism can lead to it jamming when turning the steering wheel to extreme positions, which can lead to loss of control of the car with corresponding consequences.
Operating principle
In fact, the principle of operation is not as complicated as it initially seems. Additional force helps to turn the steering wheel to the side. The bottom line is that gears are placed on the steering column, as well as specialized racks equipped with rods.
Over time, they began to use a hydraulic mechanism. Essentially, it works exactly like a mechanical one. The only difference is that the force is supplemented with the help of a special oil-based fluid. As a result, the driver can operate the car simply and easily. A slight rotation of the steering wheel will be enough to enter the sharpest turn.
The hydraulic steering mechanism is quite interesting. To fully understand what it is, you should look at it in more detail.
The hydraulic booster also makes driving safer. The quality of asphalt on domestic roads is not the best. Every now and then the driver will fall into various kinds of holes and potholes. The presence of such a knot allows you to not feel them so much. And it’s much easier to hold the steering wheel when vibrations are transmitted to it. If you compare it with a mechanical rack, then everything is much worse here. There are known cases when a motorist's steering wheel was torn out of his hands.
Lately, many have criticized hydraulics. They do this because the steering wheel is not sensitive enough, according to some drivers. It is difficult to say whether this is true or not, because each person feels the road and the car differently. Be that as it may, when there is power steering in the car, driving becomes much easier. It’s just that many have already forgotten how difficult it was to park without it. Sometimes I had to turn the steering wheel so much that I didn’t have the strength to continue driving. This problem was especially pressing on VAZ family cars produced in the late eighties and early nineties of the last century.
The hydraulic booster is often compared to an electric drive. Does this make sense? To understand, you need to understand what it is. An electric drive can be installed on the column at the factory, or can be mounted as an additional option. Its design is quite interesting, and therefore many people want it installed in their car. We must admit that the mechanism is good, but has a lot of shortcomings. This often leads to traffic accidents.
The first Lada Priora were equipped with this type of power steering. There were frequent failures and failures in the system. As a result, the engineers decided that it would be more correct to install a hydraulic booster, which completely justified itself. To this day, the steering wheel on such machines works due to the fact that it is assisted by the oil fluid circulating in the system.
In order for the hydraulic booster to work properly, it must be properly monitored. First of all, you need to regularly check the fluid level. If it does not hold and falls, then you need to check the seals. Possibly leaking into them. If it is difficult to turn the steering wheel, you need to perform a full diagnosis of the unit.
Car steering design
A car's steering system consists of three components:
- Columns.
- Mechanism.
- Drive.
Due to the interaction of these components with each other, the driver’s actions are transmitted to the wheels of the steered axle, which ensures their rotation.
Additionally, the design of the car includes an auxiliary mechanism - power steering, which partially compensates for the driver’s effort, thereby simplifying the control of the car.
Column
The steering column is a shaft through which the driver’s force is transmitted to the mechanism. One end of this shaft is inserted into the cabin, and a steering wheel is mounted on it (with a spline connection), through which the driver carries out actions to change the direction of movement (rotates it).
In modern cars, the steering shaft is composite - consisting of several parts connected to each other by cardan joints. Advantages of this design:
- Possibility of adjustment. A composite device allows the driver to adjust a comfortable steering wheel position for himself (change the reach and angle of the column);
- Increased security. The composite design is injury-proof - due to the universal joints, when the car hits an obstacle frontally, the column “breaks” and does not go out into the cabin towards the driver;
The steering column shaft is hollow, which allows you to run wiring inside it to power the elements - the horn button, the airbag squib, the steering wheel heating system.
A number of vehicle equipment controls are installed on the column:
- turn signal switch;
- lever for setting the headlight operating mode (low, high beam);
- switch for windshield wipers and washer systems for windshield and rear windows;
- gearshift switches (in cars equipped with automatic transmission, manual transmission, variator);
- control keys for the multimedia system, cruise control (directly on the steering wheel);
- egnition lock;
The location of these elements on the steering column provides convenient access to them for the driver.
Mechanism
Worm type steering mechanism
The steering mechanism is key in the system. This unit increases the force applied by the driver to the steering wheel and transfers it to the drive.
There are two types of steering mechanism most commonly used: worm and rack and pinion.
In a worm steering mechanism, the main elements are the worm and the roller. In passenger cars, a rack-and-pinion type mechanism has become widespread. In a unit of this design, the rotational movement of the gear is converted into the reciprocating movement of a rack with a gear sector. The gear and rack are the key elements of the mechanism. These components are placed in a housing mounted in the engine compartment on the engine shield or subframe.
The helical gear is rigidly mounted on the other end of the steering column shaft, so applying pressure to the steering wheel causes the gear to rotate.
Thanks to the teeth, the gear has constant mesh with the gear sector on the rack. The rack itself is a rod, so rotation of the gear leads to a displacement of the rack along the longitudinal axis (for example, when the steering wheel rotates to the left, the rack moves to the right). The steering rack is connected to the steering drive, which acts on the wheels.
Due to this design of the mechanism, force is transmitted (and its increase due to a given gear ratio) from the steering wheel to the drive.
Article on the topic:
- Power steering: design and principle of operation
- What is a damper in a car and why is it needed?
- How to adjust wheel alignment with your own hands?
Drive unit
The steering drive includes a system of rods connecting the rack to the steering knuckles of the wheels. The rods are rigidly attached to the rack, but they are connected to the steering knuckles through steering ball joints.
Depending on the design of the suspension, the role of the steering knuckle can be a shock absorber strut (MacPherson suspension) or a wheel hub (in wishbone suspensions).
In a MacPherson suspension, the ability of the strut to rotate around an axis is provided by a support bearing and a ball joint. In lever suspensions, the rotation of the hub is carried out through the use of two ball joints (upper and lower). Although supports and support bearings are components of the suspension, the operation of the steering also depends on them.
Features of the unit and design
Cars use a kinematic method of changing the direction of movement, implying that turning occurs by changing the position of the steered wheels. Usually the front axle is steered, although there are also cars with a so-called steering system. The peculiarity of working in such cars is that the wheels of the rear axle also turn when changing direction, albeit at a smaller angle. But so far this system has not received widespread use.
In addition to the kinematic method, the technique also uses the power method. Its peculiarity is that to make a turn, the wheels on one side slow down, while on the other side they continue to move at the same speed. And although this method of changing direction has not become widespread in passenger cars, it is still used on them, but in a slightly different capacity - as a directional stability system.
This car assembly consists of three main elements:
- steering column;
- steering gear;
- drive (system of rods and levers);
Steering unit
Each component has its own task.