AFS (Active Front Steering) is an active steering system, which is essentially an improved classic steering system. The main purpose of AFS is the correct distribution of force between all components of the steering system, and the main goal is to improve the efficiency of driving at various speeds. The driver, if the car has active steering, receives increased comfort and confidence in driving. Let's consider the principle of operation, the AFS device, as well as its differences from the classic steering system.
What is active steering
Active steering is essentially a modified version of conventional steering. The presence of this system on board the car helps to improve dynamic characteristics, better control of the car, and also improves comfort. The AFS (Active Steering) system was first installed in 2003 on top-end BMW models.
In more detail, active steering can change the ratio between the steering wheel and the steering mechanism, depending on the speed of travel. In addition, the system can independently adjust the angle of rotation of the front wheels when entering a turn or braking on a slippery road. In addition, the active steering system can steer the rear wheels, thereby increasing the vehicle's maneuverability.
Where is the
The location of the electric power steering depends on how it is connected to the steering system. There are several ways:
- On the steering shaft using a worm gear;
- On the rail. Transmission is carried out through a gear;
- Parallel to the rail. Through a belt drive, the force from the electric motor is transmitted to the ball screw nut, which rotates the rack screw in the desired direction.
In the first case, depending on the layout of the vehicle components, the electric power steering may be located directly on the steering column or in the engine compartment, closer to the steering rack. Let us consider in detail all the ways to connect an electric amplifier.
How the system works
Active Steering is activated when the engine is started. The system works by changing the steering gear ratio depending on the speed and driving conditions.
When performing maneuvers at low speed, the electric motor turns on in accordance with the signal from the steering angle sensor. The electric motor transmits rotation through a worm pair to the epicyclic gear of the planetary gearbox. Rotating the gear in a certain direction at maximum speed provides the smallest steering gear ratio, which reaches a value of 1:10. At the same time, the steering wheel becomes sharp, the number of rotations of the steering wheel from lock to lock is reduced, thereby achieving high driving comfort.
As the driving speed increases, turning is accompanied by a decrease in the rotation speed of the electric motor, and the steering gear ratio increases accordingly. At speeds of 180-200 km/h, the gear ratio reaches the optimal value of 1:18. At the same time, the electric motor stops rotating, and the force from the steering wheel is transmitted directly to the steering mechanism.
With a further increase in speed, the electric motor turns on again, while rotating in the opposite direction. The steering gear ratio can reach 1:20. At this gear ratio, the steering has the least sharpness, the number of rotations of the steering wheel from lock to lock increases, thereby ensuring safe maneuvering at high speeds.
If, when cornering, the car is oversteering (loss of traction of the rear wheels with the road), the AFS system, based on signals from the DSC system sensors, independently corrects the angle of rotation of the front wheels. As a result, the vehicle's directional stability is maintained. In the event that the active steering system cannot fully ensure vehicle stability, the dynamic stabilization system is activated.
Likewise, Active Steering stabilizes the vehicle when braking on slippery surfaces, thereby increasing the effectiveness of the ABS anti-lock braking system and reducing braking distances.
Active Steering is always on and cannot be switched off.
Active steering device
The design of the active steering system is not the simplest and at the same time combines several other safety systems. Nevertheless, experts identify the main parts that are responsible for turning the wheels and stabilizing them; other mechanisms are considered auxiliary, including steering the rear wheels. Among the main mechanisms are the steering rack, sensors, control unit, the steering wheel itself and steering rods. Now let’s take a closer look at what function each of the parts performs.
The entire activation process of the active steering mechanism begins with the input sensors. Regardless of the car model, they are designed to measure different parameters. For example, steering angle sensors, electric motor position, total rotation angle sensors, as well as vehicle dynamic stabilization sensors. Although, recently they have stopped using the total rotation sensor, taking information from other sensors of the car.
Having received the necessary information from the sensors, it enters the electronic control unit (ECU). We can say that this is the heart of the entire system and thanks to it, all active steering mechanisms are controlled. The task of the ECU is not difficult: to receive signals, process them and transmit them to actuators. Most of all, the electronic active steering wheel unit interacts with the electric power steering, the engine management system and the vehicle dynamic stabilization system.
After processing the information, the signals are sent to the steering rack, or rather the steering rack electric motor. Due to this, the system can independently decide how much to turn the rack in one direction or another. The electric motor itself rotates the ring gear, as a result of which the gear ratio of the mechanisms changes. As for the steering wheel and tie rods, they perform the same functions as in normal driving.
Classic power steering
Additional friction worsens the self-return of the steering wheel and feedback from the road, making the steering wheel weak and uninformative. But the engineers partly neutralized these points. They increased the castor on modern cars (the longitudinal inclination of the axis of the front struts) and worked their magic on the hydraulic part of the amplifier: they changed the geometry and characteristics of the spool valves. Fortunately, only mechanics rule the roost here. However, a person who has driven a passenger car with a steering gear will still feel a clear difference.
When operating such amplifiers, the hydraulic part causes the most trouble, for example: leaks of oil seals and external lines; wear of the power steering pump. However, the lion's share of problems is associated with inadequate intervention. When simply replacing steering rods, servicemen are too lazy to install the boots correctly, using ordinary plastic ties instead of standard metal clamps. As a result, moisture gets into the rail, causing corrosion. In advanced cases, repair will no longer be possible and the unit will have to be replaced once assembled. We wrote about this in detail in the material about the main faults and repairs of steering racks. In general, today the classic power steering causes the least amount of trouble and requires reasonable repair costs compared to other variations of amplifiers.
EGUR - electro-hydraulic booster
Electric power steering is just a variation of the classic hydraulic booster circuit with the same driving sensations and problems in general. The only difference is that instead of a mechanical pump, an electric one is used. Otherwise, it is the same hydraulic rack and circuits. However, when you try to dig deeper, a lot of hidden differences emerge, some good and some not so good.
Such a system has a separate control module. The trouble is that it is combined into a single assembly with a pump electric motor and its hydraulic part. On many older machines, the tightness of such a sandwich is broken and moisture or even oil itself gets into the electronics. This happens unnoticed, and when it comes to obvious problems in the operation of the amplifier, it is already too late to try to repair something. You will have to change expensive elements.
On the other hand, such a scheme with its own control unit, unlike the classic power steering, has an important advantage - a kind of “fool protection”. If for some reason there is a large oil leak from the system, it will turn off the pump itself, preventing its sudden death due to dry operation. As is the case with a classic hydraulic booster, any blood loss does not result in wear and tear of the elements in the rack itself.
Electric power steering (EPS) built into the steering column
With the advent of pure electric amplifiers, a parasitic moment of inertia was added to friction losses in steering mechanisms. Instead of hydraulics and a pump, electric motors came, built into the rack itself or standing outside it. Thanks to their rotation in one direction or another, assistance is provided when turning the steering wheel. However, the rotor of any electric motor has its own mass and, therefore, a moment of inertia. Therefore, it is impossible to instantly stop it and change the direction of rotation. Electronics need time to adapt. This moment is expressed in temporary additional resistance on the steering wheel when a person abruptly changes the direction of its rotation while driving.
In addition, most amplifier circuits with an electric motor are also equipped with a worm gearbox. In particular, this applies to systems where the EUR is built into the steering column. Because of this, friction losses further increase. As a result, the information content of the steering wheel drops even more than in the case of a hydraulic booster. It is impossible to configure the electronics in such a way as to significantly eliminate such a drawback. Therefore, a person who switches from a car with power steering to an electric steering system will immediately feel the difference and will probably be disappointed.
In the circuit with amplifier elements in the steering column, we have a conventional mechanical rack. The simplicity of its design is much preferable to a complex and technologically advanced hydraulic system. However, this medal also has a flip side. In the event of internal corrosion, a conventional rack will remain silent until the last moment, until the shafts rot catastrophically and there is nothing left to repair. The hydraulic unit will very quickly begin to leak due to wear of the seals, and restoration will cost a fortune.
In defense of this type of EUR, we can add that the electronic part in the steering column fails extremely rarely. And in terms of resource, the system as a whole is comparable to its conventional hydraulic counterpart.
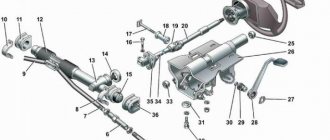
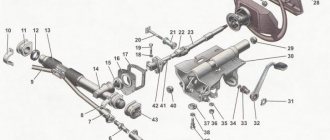
Car active steering diagram
Taking into account the complex design of the active steering mechanism, as well as understanding what certain parts are responsible for, we should consider the laughter of the mechanism.
The photo shows a diagram of the car's active steering
- steering angle sensor;
- steering wheel shaft;
- shaft gear;
- steering wheel torque sensor;
- electronic control unit;
- electric motor;
- rack;
- amplifier gear.
We can say that these are the main parts of the active steering system. In addition to the listed elements, the mechanism also includes a reservoir for working fluid, an emergency lock, connecting hoses, a gearbox and a system valve.
Power steering or electric power steering: advantages and disadvantages of power steering
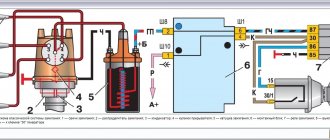
The AFS system design combines a planetary gearbox and a control system.
The planetary gearbox is used to change the speed of rotation of the steering shaft. It is installed on the steering shaft. The planetary gearbox includes a sun gear, a planetary gear unit and a ring (epicyclic) gear. At the input, the steering shaft is connected to the sun gear, at the output - to the satellite block.
The epicyclic gear is rotatable. When the gear is stationary, the gear ratio of the planetary gearbox is equal to one and the steering shaft transmits rotation directly. Rotation of the epicyclic gear in one direction or the other allows you to increase or decrease the gear ratio of the planetary gear, thereby achieving a change in the gear ratio of the steering mechanism. The rotation of the gear is ensured by an electric motor connected to its outer side via a worm gear.
A control system has been created to implement the functions of the active steering system. The electronic control system includes input sensors, an electronic control unit and actuators.
Input sensors are designed to measure system operating parameters and convert them into electrical signals. The AFS system in its work uses sensors for the position of the electric motor, the total angle of rotation, the angle of rotation of the steering wheel, and sensors for the dynamic stabilization system (vehicle rotation speed around the vertical axis and vertical acceleration). The total steering angle sensor may not be installed; in this case, the angle is calculated virtually based on the signals from other sensors.
The electronic control unit receives signals from sensors, processes them and, in accordance with the established algorithm, generates control actions on actuators. The electronic control unit has a connection and interacts with other vehicle systems: Servotronic, DSC dynamic stabilization, engine control, vehicle access.
The electric motor acts as the actuator of the AFS system. It ensures the rotation of the epicyclic gear of the planetary gearbox. The electric motor is equipped with an emergency electromagnetic lock that blocks the worm gear. In the initial position, the transmission is blocked. When current is supplied to the electric motor, the electromagnet is activated, and the latch, overcoming the force of the spring, releases the rotor of the electric motor. If a malfunction occurs in the AFS system, the supply of current to the electric motor is stopped and the latch blocks the worm gear.
The occurrence of malfunctions in the system is accompanied by the activation of a warning light on the instrument panel. A self-diagnosis message appears on the information display.
Active rack - don't listen to diagnosticians - logbook BMW 5 series 3.0D Black Raccoon 2004 on
- logbook BMW 5 series 3.0D Black Raccoon 2004 on
I'll tell you a long story. which I had been meaning to tell for a long time. The car was purchased at 20% cheaper than the market value due to one drawback - its active drive did not work, it gave an error when the ignition was turned on. Having found out that, as my colleague says, this does not affect the speed, it was decided to buy the car and fix the problem if the finances become available. And 90% is replacing the rack, the price of the issue is just plus or minus that 20% of the cost of the car. However, it was possible to travel with a non-working one, this does not affect anything. A little later, another problem was discovered - a non-working rack was pulling the stabilization control (DSC) off. Friends from the BMW center suggested looking for broken wires - it turns out that the active rack harness does not go from the rack itself to the cabin in a straight line, but passes under the bottom! As a result, the wires rot, they can be damaged in winter, etc. No question, we lifted the car and found that the plastic protection on the right was missing, that’s where the required harness goes. It is in it that two wires are broken. There was hope! The wires were restored, the car was lowered, the errors were cleared. Now the situation has changed - when the ignition was turned on, the error did not appear, and the active drive worked! But after starting to move, it became clear that the steering wheel was crooked by 45 degrees. After 50-100 meters of movement, the active steering error appeared again. After another 15-20 minutes of driving, the DSC error appeared. In principle, everything is logical - the steering wheel is crooked, the car, based on the steering sensor, thinks that I am turning, but in fact I am driving straight. He tries to level it, can’t and gives up :) I went to the dealers, did diagnostics, found an error in the steering position sensor and hydraulic pump sensor. They said that the steering wheel is crooked due to the fact that the teeth in the rack wear out, jump and blah blah blah... in general, save up money for a new one! And at the same time on the steering position sensor and the entire hydraulic pump, because the sensor does not change. In this very place, I realized that I was going to drive with the active steering error until the end of my days. I studied a lot of forums, ours and foreign ones, read repair options and found more one clue: some have cured a problem similar to mine with a simple wheel alignment. Following the wheel alignment, adjustment of the active rack is required. At that time I was still on summer tires and decided to leave the wheel alignment until winter tires were installed. I was really looking forward to it, really looking for tires :) So I bought it and installed it. The very next day I was busy getting the wheel alignment and alignment done. With a trembling hand, I inserted the key and drove off after receiving the car, and lo and behold, the errors disappeared! Active stirring works, stabilization does not turn off. You can't even imagine how happy I was!
which I had been meaning to tell for a long time. The car was purchased at 20% cheaper than the market value due to one drawback - its active drive did not work, it gave an error when the ignition was turned on. Having found out that, as my colleague says, this does not affect the speed, it was decided to buy the car and fix the problem if the finances become available. And 90% is replacing the rack, the price of the issue is just plus or minus that 20% of the cost of the car. However, it was possible to travel with a non-working one, this does not affect anything. A little later, another problem was discovered - a non-working rack was pulling the stabilization control (DSC) off. Friends from the BMW center suggested looking for broken wires - it turns out that the active rack harness does not go from the rack itself to the cabin in a straight line, but passes under the bottom! As a result, the wires rot, they can be damaged in winter, etc. No question, we lifted the car and found that the plastic protection on the right was missing, that’s where the required harness goes. It is in it that two wires are broken. There was hope! The wires were restored, the car was lowered, the errors were cleared. Now the situation has changed - when the ignition was turned on, the error did not appear, and the active drive worked! But after starting to move, it became clear that the steering wheel was crooked by 45 degrees. After 50-100 meters of movement, the active steering error appeared again. After another 15-20 minutes of driving, the DSC error appeared. In principle, everything is logical - the steering wheel is crooked, the car, based on the steering sensor, thinks that I am turning, but in fact I am driving straight. He tries to level it, can’t and gives up :) I went to the dealers, did diagnostics, found an error in the steering position sensor and hydraulic pump sensor. They said that the steering wheel is crooked due to the fact that the teeth in the rack wear out, jump and blah blah blah... in general, save up money for a new one! And at the same time on the steering position sensor and the entire hydraulic pump, because the sensor does not change. In this very place, I realized that I was going to drive with the active steering error until the end of my days. I studied a lot of forums, ours and foreign ones, read repair options and found more one clue: some have cured a problem similar to mine with a simple wheel alignment. Following the wheel alignment, adjustment of the active rack is required. At that time I was still on summer tires and decided to leave the wheel alignment until winter tires were installed. I was really looking forward to it, really looking for tires :) So I bought it and installed it. The very next day I was busy getting the wheel alignment and alignment done. With a trembling hand, I inserted the key and drove off after receiving the car, and lo and behold, the errors disappeared! Active stirring works, stabilization does not turn off. You can't even imagine how happy I was!
So my car began to cost 2-3k euros more 
Total treatment costs: Advice to look at the harness under the bottom - free Restoration of wires - 500 rubles Resetting errors - free Diagnosis off-dealer and replacement diagnosis for only ~100 thousand rubles. — 1500 rub.
Wheel alignment + adjustment — 1800 rub.
Instead of 100-150k it turned out to be 3800 
Price: 3,800 ₽ Mileage: 210,000 km
www.drive2.ru
Cost of repairs and parts for AFS
Today, the AFS system can be found not only on BMW cars. Most premium cars are equipped with this mechanism or offered as an option. For example, on Lexus cars the active steering system can be found most often.
As practice and reviews from car owners show, car body position sensors most often fail. No wonder, since the roads leave much to be desired and frequent body roll is simply inevitable. On average, the cost of replacing a sensor is about 150-175 dollars per 1 piece. Depending on the car model, there are at least 4 of them and more often they fail in pairs. The sensor itself will cost about $100-120, so 50% of the cost is the repair itself. The AFS electronic control unit will cost about 10,000 rubles. Repairing the steering rack will cost the most, on average about $1000.
Some car owners manage to replace the sensors themselves. We can say that this is the simplest thing in this mechanism and does not require special skills or tools. In addition, there are many tips and similar situations that are described in detail.
The active steering system, although a complex mechanism, without it, modern cars would not be as comfortable, and safety would be much lower. If it is possible to order the AFS system as an option, paying extra for it, then this will not be superfluous, and the difference in control will be noticeable from the first kilometers.
Bottom line
Some power steering imperfections have been eliminated in models with electric power steering: efficiency has increased, it has become possible to set the necessary parameters, and the drive belt has been replaced with an electric motor. But the future still lies with electromechanical power steering. This is a worldwide trend because their benefits are obvious.
- Next Mud tires for Niva and other SUVs: how to choose the right one
- Back Popular compact SUVs: choosing the best SUV for Russia
- News / Ratings
Oct 3, 2019
- Oct 3, 2019
- Oct 2, 2019
- 1 Oct, 2019
- BMW Crossovers / News
Sep 30, 2019
- Sep 30, 2019
- April 13, 2019
- March 12, 2019
- Feb 17, 2019
- News/Reference information
Jun 22, 2019
- April 11, 2019
Active car steering: what is the highlight of the BMW brand?
But, on the other hand, few people know that today there are several types of amplifiers, each of which has its own characteristics.
What is power steering for? Its task is not only to reduce the driver’s energy consumption when turning the steering wheel. This system makes the car more maneuverable, the impacts of the wheels on uneven roads are not transmitted to the driver’s hands in the same way, and, in the event of a tire puncture, it becomes easier to keep the car on the road.
So, today there are three main types of power steering - electric, electrohydraulic and hydraulic. The first cars had “hydraulics”, and it has not lost its relevance to this day. Over time, electro-hydraulic power steering appeared, and more recently, electric power steering.
Which one is more reliable? Which is better to give preference to? Let's look at each type in more detail.
Comparative characteristics
Disadvantages of electric power steering and advantages of power steering:
- There is sensitivity of the EUR to bad (sloppy, bumpy) roads and moisture (in particular, in bad weather - when there is snow, rain, puddles). In such cases, there is a danger of overheating and shutdown, as well as burnout.
- The power steering better smooths out shocks when the road is uneven and when hitting a curb.
- The EUR does not provide an immediate response if the wheels quickly turn in the other direction. And if you twist the steering wheel sharply, the system may turn off altogether.
- There are more possibilities for self-repair for power steering.
- In the case of electric power steering, the possibility of electronic failure cannot be ruled out (however, this mainly occurs in old and cheap models; another reason is non-compliance with operating rules).
- Production of power steering is less expensive; their price is lower than that of the EUR.
- The EUR is limited for installation on heavy trucks and SUVs (due to lack of power).
Power steering
The power steering consists of several parts - pump, oil, hydraulic cylinder, connecting pipes and distributor. The main element of the system is a hydraulic cylinder, which is activated by a pump. At the same time, the necessary oil pressure is created in the hydraulic system, which exerts its effect on the steering rack piston and makes rotation of the steering wheel easier.
It is worth noting that constant operation of the hydraulic cylinder leads to an increase in vehicle fuel consumption. The weakest link in the entire system is the hydraulic tubes, which are often damaged.
Advantages of power steering:
- The action of the hydraulic booster leads to a decrease in the steering gear ratio, as well as to easier maneuvers;
- The force of impacts transmitted through the steering wheel to the driver’s hands is reduced;
- In unexpected circumstances, it becomes much easier to hold the steering wheel. The steering wheel does not break out of your hands, and controllability remains at a high level;
- Even if the hydraulic booster fails, you can be confident in driving safety;
- The management process is more informative and accurate.
Of the shortcomings, only one can be highlighted - increased fuel consumption.
Electric power steering
This system consists of an electric motor, mechanical transmission and control system. A special feature of the device is the creation of additional force when turning the steering wheel using a special electric drive. Many modern cars have just such an amplifier installed.
The principle of operation is based on the operation of a number of sensors that monitor the position of the steering wheel and the force exerted by the driver of the vehicle. When a certain signal is received from the system, the sensor transmits it to the control unit, where the signal is processed and transmitted to the electric motor placed in the steering wheel rack.
The peculiarity of electric power steering is that it ensures perfect vehicle control when driving at any speed, sharply returning the wheels to the center position or holding them in this place.
Advantages of an electric amplifier:
are compact, fuel saving, easy to set up and adjustable, minimal energy consumption, and the absence of hydraulic lines.
The disadvantages include:
probable failure or shutdown of the system in the event of emergency situations. Such problems are quite likely in the event of serious malfunctions in the operation of the control units, poor contact connections, or a decrease in voltage in the on-board network of the machine. If a malfunction occurs, the corresponding lamp on the dashboard should light up indicating the existing malfunction.
Bottom line
It seems to me that progress is inexorably moving towards electric amplifier options, this is inevitable
If only because all modern systems, such as “steering” and keeping the car in the lane, auto parking, and other autopilots cannot work with the hydraulic version, it simply does not have an electric motor that they can control! Also, the EUR is more economical, less fuel is consumed, which is very important for the environment. Its reliability is the same, that is, both options can last a long time
That is why now many manufacturers, not only European, but also Japanese and Korean, are switching to electric units in passenger cars.
Although two important problems need to be solved, these are control accuracy (it is higher on power steering) and installation on heavy trucks. Now this is practically impossible, because electric motors mounted in a rail are heavy and energy-hungry.
If you now buy an inexpensive car in the city for an ordinary person, and even a small car (you drive at low speeds), then look towards the EUR. If the car is of a higher class, has higher speeds, and you need precision control, then you can consider power steering.
Now we are watching the video version
power steering
EUR