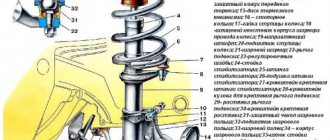
The front suspension is independent with telescopic hydraulic shock absorbers and coil springs.
The front suspension consists of stamped lower wishbones and an anti-roll bar mounted on the front suspension subframe.
The front suspension subframe is stamped-welded, box-section, secured in the front part with two bolts to the side members of the engine compartment, in the rear part with two bolts to the power elements of the front panel.
Front suspension: 1 – front suspension arm; 2 – subframe; 3 – bolts securing the suspension arm to the subframe; 4 – anti-roll bar; 5 – bracket for fastening the stabilizer bar; 6 – shock absorber strut and shock absorber spring; 7 – steering knuckle; 8 – bolt securing the stabilizer bar; 9 – coupling bolt connecting the steering knuckle and the ball joint pin; 10 – ball joint; 11- rear silent block of the lever (front silent block is not visible);
General view of the MacPherson front suspension assembly: 1 – suspension subframe; 2 – right and left front suspension arms; 3 – steering knuckle with hub and bearing; 4 – shock absorber; 5 – anti-roll bar
Subframe: 1 – places where the subframe is attached to the front part of the body; 2 – places for attaching the front suspension arm to the subframe; 3 – rear mounting points for the subframe and anti-roll bar; 4 – bracket for fastening the rubber suspension cushion of the exhaust system; 5 – bracket for securing the rear support of the power unit.
Front suspension lever: 1 – lever; 2 – ball joint; 3 – ball joint boot; 4 – silent blocks of the suspension arm (front and rear)
Anti-roll bar: 1 – nut; 2 – lower rubber bushing; 3 – rubber-metal bushing; 4 – plastic washer; 5 – upper rubber bushing; 6 – screw; 7 – anti-roll bar; 8 – rod fastening bracket; 9 – stabilizer rubber cushion
Front suspension shock absorber : 1 – shock absorber strut; 2 – shock absorber spring; 3 – compression buffer with boot; 4 – nut for attaching the shock absorber to the body; 5 – support washer; 6 – nut for fastening the upper support; 7 – upper shock absorber support; 8 – upper support bearing; 9 – upper thrust spring cup
About modern car suspensions
The suspension connects the body to the wheels, absorbs the forces acting on a moving car, and dampens vibrations. Suspension settings directly affect the car's handling.
The suspension design is divided into four groups of parts. Conventionally, because in various schemes some elements can perform the functions of two groups, and sometimes even three.
The first group is elastic parts that absorb the effects of forces transmitted from contact with the road surface (springs, springs, torsion bars or hydraulic pneumatic elements). The second group is guide rods that transmit lateral and longitudinal forces and their moments, as well as connecting the body with other suspension elements, transmission and wheels. The third group is elements that dampen vibrations (shock absorbers or shock absorber struts). The fourth is the suspension fastening elements.
There are also dependent, independent and semi-independent suspensions.
Actually, the car inherited the first versions of the suspension design from the cart. The oldest of them is the spring; it was used by the Romans back in the first century BC. It is still widely used today on commercial vehicles and SUVs. In the production of modern springs, advanced materials are used, for example, instead of metal it can be reinforced plastic.
On front-wheel drive vehicles, McPherson struts are most often used in the front suspension design. This is actually a shock absorber and spring assembly. It is attached from below to the steering knuckle, from above to the roof splash guard. This scheme also includes one or two wishbones. The main advantages of the McPherson suspension are compactness and ease of installation, which is important both for manufacturability and ease of repair. On some cars, McPherson struts are also used in the rear suspension.
Checking the chassis and transmission
We check the condition of the chassis and transmission every 15 thousand kilometers. The parts of the chassis (wheels, suspension arms, anti-roll bar, front suspension subframe, rear suspension beam, shock absorbers and suspension springs) and transmission (front wheel drive shafts) must be free of deformations, cracks and other mechanical damage affecting the shape and strength of parts. Alternately hanging the front and rear wheels (while the car must be securely fixed on stands), we check the condition of the wheel hub bearings.
Use only factory-made stands. The wheel should rotate evenly by hand, without jamming or knocking.
Holding the wheel in a vertical plane, we alternately sharply pull the upper part of the wheel toward ourselves, and the lower part away from us, and vice versa. We make sure there is no play (knock). If there is a knock on the front wheel, ask an assistant to press the brake pedal. If the knocking noise disappears, then the wheel bearing is faulty, and if the knocking noise remains, then the ball joint is most likely worn out. The hub bearings of the front and rear wheels are not adjustable and must be replaced if there is play. To check the serviceability of the ball joint, insert a mounting blade between the steering knuckle eye (which includes the ball joint pin) and the suspension arm.
By pressing the lever away from the steering knuckle with a mounting blade, we monitor the movement of the ball joint housing relative to the steering knuckle eye. If there is play in the connection, replace the ball joint.
When to change the shock absorber on Largus?
According to the Lada Largus maintenance regulations, all shock absorbers must be checked at every scheduled inspection. They change, as usual, depending on the condition. Obvious signs for replacement are the same as on other cars - loss of stability, poor road holding, body sagging, leaking shock absorber struts, etc. The average mileage on original shock absorbers can be up to 60 thousand km. But you should not rely on this figure, since it greatly depends on many factors, including operating conditions and driving style.
Functional load of Lada Largus suspensions
- Comfort during movement is achieved through the interaction of mechanisms focused on smoothness, muffling unevenness and eliminating unwanted vibrations.
- Handling is characterized by an adequate response to all steering commands from the driver. Moreover, accuracy and convenience of maneuvers become important aspects when increasing or switching speed.
- The suspensions of the Lada Largus contain actively moving parts, so the safety of the entire vehicle largely depends on them.
Front suspension
One of the main tasks of this element of the chassis is to ensure smooth movement. When the front wheel encounters an uneven road, the body continues its movement along the previously traversed trajectory, “damping” all vibrations.
Its design is much more complex than the rear variation, since it provides the ability to change the position of the front wheels, thereby providing effective control of movement in all directions. This is justified by a number of design features that are subject to additional loads.
It is worth noting that the front part of the Lada Largus, like any other car, is heavier than the rear, because the weighty units of the power and chassis are concentrated there. Undoubtedly, this causes a large load, which contributes to its rapid wear. Thus, the condition of the front suspension is directly related to the safety of driving the car.
Rear suspension
As a rule, the rear suspension of the Lada Largus is much simpler than the front: the wheels of the same name are not required to change the angle of rotation, and their orientation is focused only on vertical movement. But, despite this, the condition of this unit is also related to the safety of movement and the corresponding level of comfort.
Analogs of rear shock absorbers
As for analogues of largus. We do not have exact data (sizes). Therefore, we will not mislead you. But, we authoritatively declare that on the spare parts market you can choose the necessary goods from global manufacturers and products from Russian companies. Here are some of them:
- The products of the manufacturer Monroe are of interest. You can order directly and save money.
- Sachs products are considered softer.
- Among the domestic manufacturers, one can single out the Russian one, which produces several lines. The “Comfort” kit has won the greatest popularity among Largus owners. They have an acceptable price/quality ratio. Many people like the kit, although they complain about excessive rigidity. The best absorption of road surface irregularities occurs at a speed of 50 km/h.
Malfunctions and ways to eliminate them
During its operation, the suspension can cause not only all sorts of sounds in the form of knocks and squeaks, but also direct problems with the steering. If this part behaves suspiciously, it should be immediately fully diagnosed.
Noise and knocking while driving
The main reasons for the suspension failure of the Lada Largus are related to uneven roads. For example, a knocking sound in the front suspension of a Lada Largus begins after the car falls into a hole or hits a bump.
In addition, the inexperience of the car owner is not the last circumstance that leads to repair of the chassis. Having noticed a pothole belatedly, the brake pedal is pressed, which only increases the load several times and aggravates the situation.
The problem may be faulty shock absorbers, worn ball joints, loose fastening bolts, or lack of lubrication. If worn parts need to be replaced, this should be done immediately. When a malfunction of the suspension is associated with the fixing force or lack of lubricant, tightening them and appropriate lubrication will correct the situation.
If there is noise or knocking in the rear suspension, in addition to rubber seals and torque rods, attention should be paid to the condition of the exhaust pipe. A detailed analysis of the entire mechanism allows you to accurately determine the cause of the breakdown and eliminate it in a timely manner.
Departure of a vehicle from straight-line motion
Most often this is due to different tire pressures, incorrect wheel alignment or incorrect bearing clearance. These problems are resolved by checking and adjusting the characteristics to suit normal operation.
In some cases, even disassembling the suspension using specialized equipment is required. For example, if the front suspension arm of a Lada Largus is severely deformed, then the entire axle will need to be replaced.
It is worth noting that tire defects may not be immediately noticeable, so you should swap the wheels of the front of the car. If the direction of care changes, then the problem is in the condition of the rubber. When the loss of strength of one of the springs is to blame, it will immediately compress, affecting the visual tilt of the car body.
Vertical oscillation of the front wheels
This situation most often develops during braking or accelerating to maximum speed. The passenger car begins to tilt, and under the influence of road unevenness it makes oscillatory movements. This is justified by a possible imbalance of the wheels, settling of the suspension springs or failure of the shock absorbers.
In this case, the anti-roll bar may simply not work during acceleration and braking. Here you should check the condition of all parts and, if they are worn, replace them by securely tightening the fixing bolts.
Such vertical vibrations are unacceptable, since the chassis and steering perceive them as natural dynamic loads, which ultimately leads to loss of controllability.
Replacing shock absorbing struts
It is necessary to change the Lada Largus shock absorber when a factory defect is detected or when a certain mileage has been covered. Unscheduled work is carried out in the presence of obvious defects or leakage of technical fluid. And also, in case of loss of their performance.
Carrying out technical work is preceded by diagnostics, and the tightening of the bolts securing the shock absorbers to the levers is also checked.
Removing shock absorber struts
Let's find out the algorithm for dismantling actions:
- The vehicle must be placed on a lift. It is possible to carry out dismantling activities in the inspection pit. In this case, you need to put the car in first gear and put stops under the front wheels.
- If the car is designed for 5 passengers, as is the case with the R90 model, you need to move the lining of the rear wheel arches to the side. Having opened the luggage compartment door, we remove the rear seats of the third row, if we are talking about a station wagon.
- Remove the trim from the rear arches and remove the lower mounting bolts. Remove the trim frame.
- Remove the rubber cap from the shock absorber.
- Next, you can see the nut that holds the rod. She is also being filmed.
- Then the rubber cushion is removed.
- The fastening bolts are removed.
- The shock absorber is removed.
- The compression buffer and protection cover are removed from the rod.
- They must subsequently be separated.
- The protective cap is dismantled.
- If there are worn out and/or damaged parts, remove them.
After this, the shock absorber is placed vertically. The rod lowers and extends until it stops. In this case, there should be no extraneous noise, knocking or failure.
If the above points occur, the shock-absorbing structure changes. It is also dismantled if deformation of the rod is detected and/or the integrity of the threaded connection is compromised
When checking, pay attention to the degree of compression of the spring
Similar to the procedure described, the second shock-absorbing device is dismantled and replaced.
It remains to consider the issue of installing a new kit, which is what we will do.
Shock absorber installation
Installation of the rear shock-absorbing structure is carried out in reverse order.
So, as we have already said, installation is carried out in the reverse order:
- You need to install a new nut that secures the shock absorber rod.
- It is advisable to change the shock absorber mounting bolt connecting it to the rear suspension.
- The following is placed on the rod: a washer, a hinge bushing, and a lower cushion.
- We install the shock absorber in the rear wheel arch of the car.
- We connect it to the lever of the rear suspension structure.
- The rod fits into the mounting hole of the wheel arch.
- The upper hinge pad, control washer and new fastening nut are put on the rod. The tightening torque of the nut is 14 Nm (1.4 kgf.m).
Don't forget to put the plugs where the new elements are attached to the rear wheel arches.
The above operations in the specified sequence are acceptable for working with the second shock-absorbing structure.
We put the wheels in place. We fasten the arch trim, storage compartment, fastening parts and brackets for the side and rear armrests.
We lower the car to the ground. And only now we tighten the bolts securing the shock absorbers to the arms of the rear suspension structure.
The tightening torque of the bolts is 105 Nm (10.5 kgf.m. We work with a replaceable head No. 21.
Choosing stabilizer struts for Lada Largus
Since the suspension on Largus remains unchanged from Logan, the range of spare parts in stores is very wide.
On sale you can find both original spare parts produced by AVTOVAZ OJSC and original repair kits for Renault Logan (Sandero). The standard stabilizer link comes complete with rubber dampers, bushing, washers and nut. In the tuning rack, rubber is replaced with polyurethane. It is harder and provides minimal play in this connection. The use of polyurethane slightly increases the sensitivity of the car on the road, makes it more collected, and the steering wheel more accurate. The disadvantages will be a slight decrease in comfort, stiff suspension, and increased load on other components in the suspension. Installation of tuning parts will be justified for the powerful 16-valve version.
Factory part number – 8200277960 (or 6001547138) manufacturers Renault, AvtoVAZ.
Non-original parts may have their own markings and article numbers. Approximate prices for January 2022:
- JSC AVTOVAZ, original – 500-570 rubles;
- BalZap, duplicate – 280 rubles;
- FR, duplicate – 260 rubles;
- Forward, duplicate – 276 rubles;
- TORK, duplicate (article TRK0069) – 115 rubles;
- Trialli, duplicate (article SP0101) – 305 rubles.
Advice ! It is recommended to purchase racks from well-known brands, for example Lemforder (catalog number 3124301), or original Renault, Lada. The service life of a cheap substitute can be only a few thousand kilometers. There were cases when parts did not fit without modification.