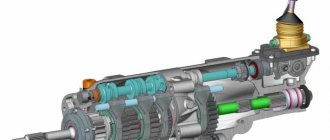
A transfer case (transfer case) is a component of an all-wheel drive vehicle that increases engine torque and distributes it between the drive axles. This allows you to fully realize the capabilities of all-wheel drive on asphalt, slippery surfaces and off-road. On special equipment, the transfer case can transmit torque to a winch, crane or other equipment. The transfer case also performs the following functions:
- an increase in torque required to overcome the rolling resistance of the drive wheels when driving off-road;
- ensuring vehicle stability in slow motion while achieving maximum torque.
Transfer case device
Transfer case design
The general design of transfer cases has the following layout.
- Main drive shaft.
- Drive shafts for front and rear axles.
- The transmission is chain or gear.
- Center differential and locking mechanism.
- Downshift or synchronizer.
Structurally, the transfer case consists of a two-part housing filled with oil, in which the engine drive shaft is connected through a chain (or gear) transmission to a center differential and a locking device, connected to two drive shafts of the front and rear axles.
Video about how the transfer case works
Why do you need a transfer case on SUVs?
How the gearbox works on a VAZ 2107
The transfer case of a UAZ and any other SUV is needed to provide the vehicle with the ability to effectively drive off-road, rough terrain and on poor country roads and dirt roads.
With the help of the RK, the driver can reduce wheel torque when overcoming particularly difficult sections. Such actions can significantly reduce the level of slippage even in the most difficult conditions, including when stuck in a wetland.
The UAZ transfer case is a functional product, the value of which is clear to almost all car owners. This item:
- increases cross-country ability;
- improves vehicle handling;
- increases maneuverability;
- makes the car universal, capable of performing well on any trip.
Typically, an SUV drives on the rear axle (it is the drive axle), and no torque is transmitted from the engine to the front. However, if the driver has to overcome a difficult section, he can make both axles driven.
The design of the UAZ transfer case is such that it can only be used when driving on difficult roads; you won’t be able to drive on asphalt on two bridges if you don’t want to pay for the repair of the transfer case.
Types of transfer cases
Among the mass of modifications, we can distinguish the main types of transfer cases:
1. According to the location of the drive shafts of the drive axles
- with coaxial shafts (the drive shaft from the gearbox is coaxial with the rear axle drive shaft). This type is widespread due to its simple design.
- with misaligned shafts (the gearbox drive shaft is not aligned with the rear axle drive shaft). This type is characterized by high efficiency, compact dimensions, and from the point of view of acoustic parameters (not the least important parameters) it looks much more attractive than its counterparts.
2. By driving axles
- with a drive axle drive blocking mechanism. This type allows you to use the maximum traction force of the car without slipping the wheels. But this type has some disadvantages - an increase in fuel consumption by the car, increased tire wear and an increase in load on transmission elements.
- with differential drive. This type of gearbox is distinguished by the presence of a center differential, which makes it possible to rotate the drive shafts at different speeds. The downside is a decrease in the vehicle's cross-country ability. To increase traction characteristics, center differentials are manufactured with a forced locking element.
3. Based on the number of gears, there are one, two and three-speed gearboxes. Transfer cases with two-stage transmission are more popular.
Types of handouts
According to the type of application, there are 4 types of manual transmission:
- RKP with coaxial shafts - the system is widely applicable, as it allows the use of interchangeable main gear;
- with a misaligned driven shaft - it is distinguished by reliability, lack of leakage, due to this manual transmission it is compact;
- with drive locking - excellent for off-road use, however, on the highway there will be increased tire wear due to slipping of one side of the wheels when cornering; to avoid this, the front axle is disabled;
- transfer case with differential - allows the wheels to rotate at different speeds, ensuring safe driving on an asphalt road in 4WD mode.
Center differential
This unit allows you to distribute the interaxle torque and allows the drive shafts to rotate at different angular speeds. This is especially important when cornering as the wheels travel different distances and therefore must rotate at different speeds. If the transfer case is not equipped with such a unit, the wheels can only be rotated at different speeds by disabling one axle.
Center differentials can be symmetrical or asymmetrical. The first works in such a way that the torque is distributed equally to both axles, the second divides it in a certain proportion.
Center differential locking mechanism
In order for the car to fully realize its off-road capabilities, the center differential is equipped with a locking mechanism, the purpose of which is to force the wheels of both axles to rotate at the same speed. Blocking can occur either forcefully or manually, depending on the type of mechanism. The following types of locks are currently used:
- self-locking differential Torsen;
- friction multi-plate clutch;
- viscous coupling (viscous coupling).
The transfer case of crossovers is equipped with the first two mechanisms due to the disadvantages described below.
Viscous coupling
The viscous coupling is built on the basis of a special fluid, which is located between numerous transfer plates that rotate relative to each other with small gaps. The plates are connected to the output shafts, and when the difference between the rotations of the plates becomes very large (one of the axes is slipping), the liquid sharply increases its viscosity and binds (rigidly glues) the plates together, blocking the differential.
But it cannot remain in this state for a long time because the liquid overheats and loses its properties.
Differential Thorsen
This differential is created on the basis of worm gears and its main ability is to quickly and accurately redistribute torque between the axles. A very good mechanical design based on worm gears, but its main drawback is unreliability, that is, in critical situations it is prone to rapid destruction.
Multi-plate clutch
This is a more reliable mechanism, which all modern crossovers are switching to.
Its device is a set of disks that rub against each other depending on the force that presses on them. And the greater the force, the stronger they block the differential.
The clamp is controlled by a computer based on readings from sensors and the position of the selector.
It should be said that the two previous systems did not require driver participation and worked independently.
The multi-plate clutch also begins to overheat during prolonged slipping, and in order to preserve the mechanism, the electronics turns off its operation, and the car becomes single-wheel drive. This is a wise decision for “delicate” SUVs, which are sometimes unknowingly tested for off-road use, preserving them from damage.
Another important factor in crossovers is the absence of a low range in the transmission.
As for SUVs, it is worth noting the highest reliability of their transmission when driving off-road. The locking in them is carried out rigidly, without the possibility of smoothly changing the torque between the axles.
Yes, this has a bad effect on control at high speeds, but you can skid as much as you like without fear of overheating.
In addition, in the transfer case of such cars there is a range of multipliers for engaging a lower gear. There may be one or two reduced modes.
Thanks to this, SUVs can climb very steep mountains or drive through mud without fear of not having enough engine traction.
Also, a lower gear makes it possible to move at very low speeds (1-2 km/h), which gives the driver time to more accurately choose the trajectory without stopping the car.
To summarize, you can see that the transfer case is a very useful unit. And if you don’t abuse it in vain, but take into account the purpose of the vehicle, its service life will be very long.
Drive type and the influence of the transfer case on it
The operating features of the transfer case affect the type of all-wheel drive, of which there are only three:
- Constant full.
- All-wheel drive, manually activated.
- Automatic drive.
An example of permanent all-wheel drive is a transfer case with a conventional differential equipped with a lock (common name - Full Time). In cars with such a system, the transfer case provides constant rotation transmission along two axes.
A manually connected drive is called Part Time. In a car with such a drive system, the transfer case in normal driving mode supplies rotation to only one axis, while the second is activated when necessary. In such units, a differential is not used, but instead, clutches are installed - mechanical, electromagnetic, which connect/disconnect the second axle.
A system that uses both bridges in automatic mode is OnDemand. It is used on passenger cars, and in this case the transfer case is aimed at increasing cross-country ability and improving handling. The control is carried out by electronics interacting with the ABS. In such transfer cases there is no differential, but instead an electrically driven clutch is installed. In the OnDemand system, the transfer case by default only applies rotation to one axle. But when certain driving conditions arise, the electronics engage the clutch drive and the second axle is connected.
Classification
In general, there are many designs of handouts, which is why their classification is used. It divides all existing types of transfer cases according to the following criteria:
- Power distribution method;
- Number of gears;
- Type of control mechanism;
- Shaft location.
Power distribution
The method of power distribution is one of the main criteria by which transfer cases are divided. It characterizes exactly how rotation is transmitted between axes.
According to this classification, boxes are divided into providing:
- Permanent drive on both axles without the ability to disable any axle;
- Possibility to disable the front or rear axle (it is auxiliary in this transmission configuration);
- "Equal" shutdown. This transfer case allows you to disable any of the axles (allows you to make any type of drive on your car - front, rear, all-wheel drive).
A permanent drive transmission is used in both passenger cars and some SUVs. In the transfer case of such transmissions there is no control mechanism, and all wheels are constantly driven.
Note that in modern designs of transfer cases for all-wheel drive transmissions, a differential is not used; instead, various types of clutches are installed (electromechanical, friction, magnetic). Their peculiarity is that they can provide a varying rotation distribution ratio. These clutches are controlled electronically, allowing the drive system to quickly respond to road conditions and direct more torque to the desired axle.
Transfer cases with one of the axles that can be switched off are the most common layout for crossovers. Its peculiarity is that the driver independently decides when all-wheel drive is needed. In this design, couplings are also often used as a center differential. The control of the box can be either completely mechanical or electrically driven.
Diagram of all-wheel drive types
“Equal” bridge shutdowns are uncommon. This is due to the more complex design of the box itself.
Number of steps
Based on the number of gears, existing types of gearboxes are divided into one-, two- and three-speed. Passenger cars and SUVs typically use a single-speed transmission. This means that the gear ratio of the transfer case is 1, that is, it does not change it and the torque specified by the gearbox is transmitted to the wheels.
On SUVs, a two-stage transfer case is often found. It has two gears, in which the gear ratio is 1 and 2. Often such a box is also called a “transfer case with a divider.” The presence of two gears allows, if necessary, to change the gear ratio on this unit, increasing the traction force on the wheels. But at the same time the car moves twice as slow. In a regular box, this is done simply by the presence of an additional pair of gears.
Three-speed transfer cases are usually not found on vehicles; they are used for special purposes. technology.
Control mechanism
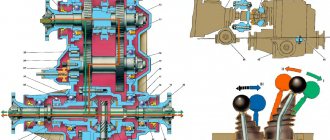
As for the type of control mechanism, it can be manual, semi-automatic and fully automatic. The first option is the most reliable, since the design does not contain any electronics. In such a transfer case, the driver independently, using a system of levers, engages the gears, including the additional axle.
In a semi-automatic mechanism, the additional bridge is activated by an electronically driven control mechanism. That is, turning on and off the additional bridge takes place without driver participation. But such a control system allows the driver to engage all-wheel drive.
Manual and semi-automatic transfer case control mechanism
Automatic control means that the operation of the transfer case is completely controlled by electronics. Based on sensor readings, it determines the moment when all-wheel drive is needed and engages it.
Shaft position
The last criterion by which transfer cases are divided is the position of the shafts. It can be coaxial or non-coaxial. The first option indicates that the driven and front axle drive shaft are located on the same axis. The drive shaft is located parallel to them.
In a non-coaxial design, the drive and driven shafts are located on the same axis, and the front axle shaft is installed in parallel.
Do you need a transfer case?
Like any mechanism, the Republic of Kazakhstan has its advantages and disadvantages.
Let's start, perhaps, with the cons. More precisely, from one but significant disadvantage of the transfer case. The fact is that most of its parts are quite expensive. Therefore, replacing them will not be cheap. And those parts that are sold at reasonable prices are difficult to repair, so they may also require funds from the car owner for the work of a repairman.
Now the pros:
- When the transfer case operates while the car is moving at low speed, torque is transmitted to the axles. This increases the cross-country ability of the SUV.
- It is noteworthy that when the transfer case is operating, large torque cannot be lost. This is achieved thanks to a demultiplier. He is the machine's assistant in reducing the intensity of torsion of the drive shafts.
- Also, the driver of a car equipped with a transfer case has the opportunity to independently determine the gear number.
- When driving in difficult conditions, the RK will become a friend and assistant to the motorist, helping his “iron horse” to effectively overcome landscape obstacles.
- And, of course, one of the leading advantages is that the operation of the transfer case extends the life of the transmission.
Chain transmission
To redistribute the torque, a chain was created in the transfer case. Thanks to the mutual action of the chain and 2 wheels with teeth, chain transmission occurs. Sometimes there are periods when it is necessary to use a gear drive to replace a chain drive. Comparing these two gears, the gear one is the most reliable.
This is how the distribution box got its name
The box inherited its name due to its close connection with the gearbox. At low vehicle speeds, torque is distributed because the gearbox has both a reduction gear and a range multiplier.
Therefore, vehicles can travel in difficult conditions, without the presence of a road surface. The range-multiplier helps reduce the speed of rotation of the shafts, as a result of which the large torque does not disappear. Thanks to the reduction series, vehicles can have a certain number of gears. In emergency situations, the motorist will have more chances to calculate the required gear ratio. This kind of equipment prolongs the performance of the gearbox, while saving the car owner’s costs.
Transfer case control
Transfer case control
Old SUVs, trucks and special vehicles usually have manual (mechanical) control of the transfer case. To connect or disconnect one of the axles, as well as to engage the differential or low range, a lever is used, usually located in the cabin floor next to the gearshift lever. To turn it on, the car sometimes needs to come to a complete stop.
Newer models have manual electrical control : all operating modes of the transfer case are selected using buttons on the dashboard. If there is a synchronizer in the transfer case, then stopping the car will not be necessary.
Modern cars use automatic transfer case control. When selecting the automatic mode, the on-board computer itself determines the slipping of the axles, after which it redirects the torque. If necessary, turns on the differential lock. The driver can turn off the automation and do all the work on the go independently. There is no control lever.
All types of crossovers and all-terrain station wagons have fully automated transfer case control mechanism. The driver cannot control the mechanism himself, since all decisions are made electronically.
Operating modes
The transfer case can be controlled using a special lever or buttons (rotary device) on the dashboard. On vehicles with all-wheel drive that are not designed for difficult road conditions, the transfer case operates in automatic mode.
Depending on the design features, the transfer case has several operating modes.
- Only the rear axle is active.
- The front and rear axles work. This type of drive is implemented in Niva.
- The front and rear axles work, the differential is locked. This mode provides maximum maneuverability.
- Transfer case with reduction gear. Both axles are working, the differential is locked, and the reduction gear is active.
- The front and rear axles work, the differential locks in automatic mode.
If all-wheel drive is connected, then the following switchable modes can work here:
- 4L – drive on both axles in low gear.
- 4H – torque is supplied to both axles.
- 2H – torque is transmitted to only one (drive) axle.
In this case, it is allowed to switch between 2L and 4H modes while the vehicle is moving only if there is no slipping of the drive wheels. But switching between modes 4L and 4H while driving will not work due to a design feature.
If all-wheel drive is permanent, then there are the following modes:
- 4L LOCK – all-wheel drive, differential lock on, low gear.
- 4H LOCK – four-wheel drive, center differential locking, direct transmission.
- 4H AWD – four-wheel drive, differential lock disabled, direct transmission.
Depending on the design, you can switch the 4H LOCK and 4H AWD modes both while the vehicle is stationary (without wheel slipping) and while driving.
Main malfunctions of transfer cases and their causes
The transfer case is a mechanical device, which, like other mechanisms, can have a certain service life, where some malfunctions occur during operation. There are several factors that influence the lifespan of a relay.
- Design.
- All-wheel drive device.
- Operating mode.
- Maintenance within specified periods.
Commonly encountered major faults include the following.
- Knocking, humming, howling are the consequences of wear of gears and bearings.
- Strong vibration in the transfer case. It can occur especially during movement due to wear of the bearings.
- Leaking or leaking oil. Usually due to a violation of the tightness of the seals or due to other violations of the tightness of the joints in the housing.
- Difficulty in turning on or spontaneous shutdown of the box - wear of the gear teeth or clutch, incorrect adjustment.
- Defect of gears, couplings, clamps. Requires repair, disassembly of the box, replacement of worn parts.
- Stretching of the box chain due to wear.
- When moving, there are jerks, malfunctions in the operation of the gearbox, and strong stretching of the chain.
- Overheating or rapid heating of the clutch with the smell of burning oil, rubber and wear of the servo drive, friction clutch.
- Instability of work occurs under loads and turns.
- The electronic control does not work due to the failure of the electromagnet, there is no power circuit, or the wiring is damaged.
Video on the topic
Sources
- https://AvtoTachki.com/chto-takoe-razdatochnaya-korobka-i-dlya-chego-nuzhna/
- https://VazNeTaz.ru/razdatochnaya-korobka
- https://principraboty.ru/razdatka-razdatochnaya-korobka-chto-yeto-takoe-i-kak-rabotaet-razdatochnaya-korobka/
- https://CarExtra.ru/obzory/razdatochnaya-korobka-ustroystvo-printsip-rabotyi.html
- https://ZnanieAvto.ru/uzly/razdatochnaya-korobka.html
- https://Shinomontazh-Penza.ru/transmissiya/dlya-chego-nuzhna-razdatka.html
- https://auto-ru.ru/razdatochnaya-korobka-chto-eto.html
- https://avtomotoprof.ru/obsluzhivanie-i-uhod-za-avtomobilem/razdatochnaya-korobka/
- https://AvtoNov.com/%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%B7%D0%B4%D0%B0%D1%82%D0%BE%D1%87%D0%BD%D0%B0%D1 %8F-%D0%BA%D0%BE%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B1%D0%BA%D0%B0-%D1%87%D1%82%D0%BE-%D1%8D% D1%82%D0%BE-%D1%82%D0%B0%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%B5/
- https://TechAutoPort.ru/transmissiya/sistemy-polnogo-privoda/razdatochnaya-korobka.html
What can break in the transfer case?
The cost of repairing a transfer case is quite high, so it is important to use your car carefully and undergo regular maintenance. I will list the main malfunctions that occur in the transfer case:
- Bearing wear. This is indicated by noise and vibration during vehicle operation. And after a while, knocking and grinding noises occur, which indicates a significant deterioration of the transfer case.
- Worn shift latches in the mechanism. This will lead to the transfer case starting to turn off on its own.
- Oil leak. It can leak both through the joints in the body and through the oil seals and their seats. Oil leakage occurs due to a leak in the seal.
- The appearance of scoring on gear teeth. This causes problems with gear shifting.
- Noise in bearings. This can be identified by listening to car parts during maintenance. When driving, a constant “howl” with small knocks is heard. The bearings must be replaced with new ones.
- Chain stretching. As a result, the teeth of the gears where the chain is located slip. To identify this, you need to turn the wheels as far as possible to the side and start moving sharply. You should hear a loud cracking noise from the transfer case area. In severe cases, the chain can wipe the crankcase of this unit.
- Wear of the center differential. The satellites of this part are constantly in friction, and if the lubrication is poor or metal particles get into the lubrication system, then after 30-40 km the differential fails. To remove metal chips, use a magnet, which is located at the bottom of the “dispenser”.
- Wear of the viscous coupling. Leads to deterioration in directional stability when cornering, uncertain driving on bad roads, creaking in the transmission, as well as uneven wear of the rubber on the wheels. The viscous coupling should be replaced with a new one or repaired.
- Wear of the all-wheel drive connection mechanism. Some types of transfer cases have electromagnets, the braiding of which is highly responsive to load. Over time, this can lead to breakdown of the electromagnetic clutch connecting the drives.
From this we conclude that the transfer case is a rather complex mechanism that requires regular inspection. The cost of repair work starts from 2000 rubles, and in particular, repair of the actuator will cost over 8000 rubles.
A part such as a “transfer case” can be sold both in finished form and as separate spare parts for it. For Russian cars, transfer cases from YaMZ and ZMZ are often used. And manufacturers of transfer cases for foreign cars: Dana, OEM, Quattro, 4-matic, Eaton, BorgWarner. The price for a “razdatka” starts from 20 thousand rubles.