Trouble code P0123 indicates a problem with the throttle/pedal position sensor. When the engine control module (ECM) detects that the rated output voltage of the throttle position sensor exceeds the manufacturer's specification, it generates trouble code P0123.
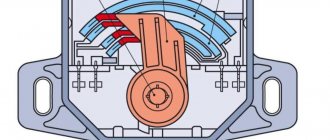
The throttle position sensor (TPS) is another name for a potentiometer. It is located on the throttle body while the pedal position sensor is connected to the accelerator pedal.
The throttle position sensor monitors the movement of the accelerator pedal and determines how much power the engine requires. Code P0123 is triggered when the TPS voltage value is outside the specified range.
What does it mean?
This diagnostic trouble code (DTC) is a generic transmission code, which means it applies to OBD-II equipped vehicles. Although general, specific repair steps may vary depending on the make/model.
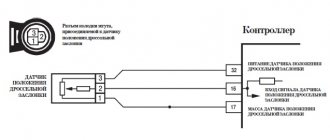
The TPS (Throttle Position Sensor) is a potentiometer mounted on the throttle body. It determines the throttle angle. When the throttle body moves, the TPS sends a signal to the PCM (powertrain control module), which is the main computer that controls the vehicle. Typically a three wire sensor: 5V reference from PCM to TPS, ground from PCM to TPS, and signal return from TPS to PCM.
The TPS sends throttle position information back to the PCM via this signal wire. When the throttle is closed, the signal is about 45 volts. At WOT (Wide Open Throttle), the TPS signal voltage approaches the full 5 volts. When the PCM sees voltage above the normal upper limit, P0123 is set.
VAZ fault code P0123
VAZ fault code P0123, a high signal level of the throttle position sensor, is entered into the controller’s memory if, with the engine running, the sensor signal voltage is higher than 4.8 V. In this case, after 8 seconds, if a permanent malfunction occurs, the “Check Engine” lamp lights up. This means that if, when the ignition is turned on, the voltage at the sensor is in the range of 0.3 - 0.7. B, then the controller uses this value as corresponding to a closed throttle.
All subsequent changes are based on the initial value. During the test, if the value goes beyond this range, it is necessary to check the throttle valve drive for serviceability and the drive cable for jamming. If they are in good working order, it is necessary to check the voltage between ground and terminal “C” on the connector removed from the sensor with the ignition on. It should be around 5V. A voltage of less than 1V indicates a break in the 25GO wire or poor contact in the sensor connector. A voltage above 10V indicates a short on the 25GO wires to the power supply or a controller malfunction. If the voltage is normal, it is necessary to check the integrity of the sensor ground circuit. To do this, connect the probe to the positive of the battery and terminal “B” of the sensor block. If the lamp does not light, then there is a break in wire 63, 53 ZP or the controller is faulty. Otherwise the sensor is faulty.
Source
Possible solutions
A good starting point is always to check the technical service bulletins (TSB) for your specific vehicle. Your problem may be a known problem with a known fix released by the manufacturer and could save you time and money during diagnosis.