A malfunction of the phase sensor , which is also called a camshaft position sensor, leads to the engine starting to operate in pair-parallel fuel supply mode. That is, each injector fires twice as often. Because of this, fuel consumption increases, exhaust toxicity increases, and problems with self-diagnosis arise. A malfunction of the sensor does not cause more serious problems, but if it fails, replacement is not delayed.
What is a camshaft sensor
The camshaft (1 or 2) is located in the engine cylinder head. It is equipped with off-center lugs to control the intake and exhaust valves.
To know which cylinder is on stroke, the vehicle's computer monitors the rotational position of the camshaft in relation to the crankshaft.
The main function of this sensor is to correctly establish the position of the first cylinder. To do this, the sensor works together with the camshaft by sending signals to the computer (ECU), which uses these signals to synchronize while the device reads the grooves and tips of the camshaft gears, it can determine the position of the valves. Accordingly, the correct synchronization of the fuel injector sequence occurs. These signals are needed to correctly detect when the number one cylinder is at top dead center, and also uses the signals from these two sensors to generate the ignition spark. On certain engines with variable timing, the sensor is also used to check the camshaft drive.
Suspected problems with the sensor:
- the computer (ECU) is operating in emergency mode;
- The check engine light comes on;
- difficulty starting the car;
- the vehicle engine begins to stall;
If the vehicle is scanned, it should show a fault code.
On which cars is this problem most common?
The problem with code P0343 can occur on different machines, but there are always statistics on which brands this error occurs more often. Here is a list of some of them:
- Audi (Audi a4, Audi TT)
- BMW
- Cadillac (Cadillac SRX)
- Chery (Chery Amulet, Jagi, M11, Tiggo)
- Chevrolet (Chevrolet Avalanche, Aveo, Lacetti, Traverse)
- Chrysler
- Citroen (Citroen C4)
- Dodge (Dodge Ram)
- Ford
- Geely (Geely MK)
- Hyundai (Hyundai Accent)
- Kia (Kia Rio, Sportage)
- Lexus
- Mercedes
- Opel (Opel Corsa)
- Peugeot (Peugeot 308)
- Skoda (Skoda Octavia)
- Toyota (Toyota Camry)
- Volkswagen (VW Beatle, Jetta, Passat, Tiguan)
- VAZ 2110, 2111, 2112, 2114, 2115
- Volga Chrysler, 31105
- Gazelle Chrysler, 405
- Lada Vesta, Granta, Kalina, Largus, Niva, Priora
- UAZ Patriot
With fault code P0343, you can sometimes encounter other errors. The most common are: P0030, P0036, P0124, P0332, P0335, P0336, P0340, P0341, P0342, P0345, P0346, P0347, P0348, P0349, P0365, P0366, P0367, P0368, P0369, P039 0, P0391, P0392, P0393 , P0394, P0606, P2122, P2138.
Working principle of the camshaft position sensor
Its operation occurs according to the Hall principle. This principle of operation of the sensor means that when the ring gear rotates, the Hall element in the sensor head changes. These changes are sent to the control unit, where they are evaluated to determine the required information.
It is extremely important to carefully check the phase sensor. Checking the position sensor does not take much time and can be done independently.
Why is DPRV needed?
For the internal combustion engine to operate, a crankshaft sensor is sufficient; for good operation, a camshaft sensor is needed. Without DPRV, fuel is injected into the cylinders in pairs. The working mixture is supplied to 2 simultaneously open nozzles.
In this case, one cylinder is in the compression stroke and, after fuel is supplied, begins to work, and the second cylinder simply throws fuel into the atmosphere. Environmentalists have drawn attention to this problem.
In addition, there was a need for economical consumption of fuel in transport. Installing a camshaft sensor allowed only one injector to be opened. In this case, the mixture does not flow into other cylinders.
Symptoms of a Malfunctioning Camshaft Sensor
If the sensor is faulty, the computer does not know when to fire the injectors and may not activate them. Poor readings will also result in ignition timing misalignment, which will affect the vehicle's fuel economy. This sensor is used simultaneously with the crankshaft position sensor. This is necessary to control the ignition timing. Failures of this sensor occur quite often, which can be explained by heat and oil leakage. This is due to its location.
Camshaft position sensor failure is most often caused by oil leaks. In such cases, there is only one solution - repair or replacement. When replacing, check the alignment of the timing belt to ensure that fluids do not enter the area position sensor mounting bracket. In some cases, the software is updated during installation.
The correct engine oil must be used. Accordingly, the camshaft will remain perfectly lubricated, as this is very important for the correct operation of the engine.
Continuous movement of this component causes a lack of lubrication, which significantly reduces its service life. When the oil is completely drained due to the car not being used for many days, the oil pump will take some time to send it to the top of the engine. This situation in certain engine models causes problems with the hydraulic lifters and, as a result, is the cause of more serious problems.
Despite its small size, the camshaft sensor is considered a very valuable magnetic device that collects and sends information about the vehicle's camshaft speed to the engine control unit. Since the signals that are sent to the computer body are interrupted due to camshaft problems, the operating condition of the vehicle is affected.
Basic symptoms may indicate that the camshaft sensors are likely already in need of replacement. Sometimes there are difficulties starting the car. After the car starts moving, you may experience a loss of speed, a decrease in engine power and abnormal acceleration. This is the main sign of a malfunction.
Also, the most common signs indicating suspected camshaft damage are that the car cannot be started and a knocking noise is heard due to a bad gear coupling or worn bushings. In addition, the lack of power can be attributed to poor shaft support. If there is a loud noise in this area of the engine, it is a clear sign that the camshaft is not sticking. This means complete adhesion of the parts, which prevents slipping. Ignoring any of these symptoms will require more time and expense.
When there is an error in the camshaft sensor, it will not work properly. As a result, the onboard computer will not be able to determine the location of the pistons and valves, so it will be impossible to send data about when to ignite the spark or what the pulse should be. There are various causes of malfunction and it is important to familiarize yourself with them.
Phase sensor error (DPRV)
This problem may result in the engine operating in pair-parallel fuel supply mode. The injectors will work more intensely and fuel consumption will increase greatly, as will the toxicity of exhaust gases. Problems with self-diagnosis are also possible. It is highly undesirable to delay replacement.
Converter device
What does it transform? The device uses the Hall effect - conductors with direct current placed in a magnetic field create a potential difference (voltage). This property is used in smartphone compasses.
The sensor reacts to proximity to metal by changing the voltage on the wire. The system is the same as on the crankshaft.
- DPRV has the same design features as the crankshaft sensor. The main part of the device is the coil.
- It receives 12 V voltage through two wires when the ignition is on.
- The third wire is the signal wire, the voltage on it is about 95% of the nominal value.
When the reference point passes the sensor, the potential difference becomes equal to 0.2 - 0.5 V, depending on the make of the car. This signal is sent to the electronic control unit.
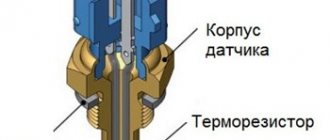
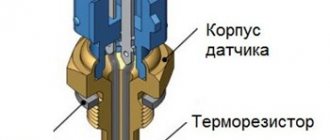
Where is the camshaft position sensor (phase sensor) located?
How the camshaft is positioned depends on various engine characteristics. However, it is not difficult to find. In some modifications it is located below, under the cylinder block. Most often you can see modifications of engines whose camshaft is located in the cylinder head (on top of the internal combustion engine). In the second case, repairing and adjusting the gas distribution mechanism is much simpler than in the first.
Modifications of V-twin engines are equipped with a timing belt. It is located on the camber of the cylinder block, and sometimes with its own gas distribution mechanism. The camshaft itself is fixed in the housing using bearings, which allows it to rotate continuously and gradually. In boxer engines, the design of the internal combustion engine does not allow the installation of a camshaft. However, each side has its own gas distribution mechanism, but its functioning is synchronized.
How to check the camshaft position sensor
So what you need to do:
- You need to start by inspecting the electrical connector and sensor wires. After that, the connector is removed and inspected for traces of rust or dirt. These problems interfere with normal electrical contact.
- It is also important to look for damage to the cables: breaks, poor fixation, and traces of burns from nearby hot parts. The wires should be kept away from the spark plugs or ignition coils. Due to their close location, the sensor signal may be disrupted.
- After these manipulations, you need to use a digital multimeter. This device is required to check the alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC) voltage according to a certain type of crankshaft position sensor.
- For certain sensors, it is also necessary to check the wires using the electrical connector. However, such verification is not possible in all cases. You can also see if you can remove the sensor connector and connect the copper wire to the terminals. Then reinsert the connector so that the two wires pass through the connector body. There is another option - to pierce all the wires with a needle. The main thing is not to short-circuit them during the verification process. If the latter method is used, you will need to cover the pin holes with electrical tape.
Testing the crankshaft sensor can be difficult if the specific design type is unknown. Before such actions, you will need to determine whether the sensor is an inductive sensor or a Hall generator. They are not always easy to identify by appearance. If there are three pins on a connector, no precise statements can be made about the appropriate type. This is where manufacturer specific specifications are helpful. If the design type has not been finalized, the ohmmeter cannot be used for testing. The voltage from the measuring device used to check the resistance can damage the Hall generator!
Checking the 2-wire inductive camshaft sensor
The camshaft position sensor is not checked by most routine services, but there are warning signs on the car that it will need replacement soon. Due to the fact that it sends data to the camshaft, when the sensor breaks, the engine will have problems and its normal functioning will be disrupted. The indicator lamp should also light up.
How to properly check a two-wire sensor:
- Set the multimeter to "AC volts".
- Turn the ignition key.
- Make sure there is enough power flowing through the circuit. Prepare the multimeter leads. Touch the ground with one of the probes and all the sensor wires with the other. If the wires are not energized, then there are certain faults in the circuit.
- Start the engine.
- Next, you need to attach the meter probe to one of the sensor wires, and place the other probe to the other wire. Then the readings on the glucometer display are checked and the results are compared with the specifications in the instructions for the vehicle. The changing signal should be between 0.3 and 1 volt.
- When there are no signals, this indicates that the sensor cannot be repaired and needs to be replaced.
Checking three-wire DPRV
How to test the DPR sensor:
- You need to install the power wire, ground wire and signal wire, then check the integrity of the wiring going to the sensor.
- The multimeter is switched to DC mode.
- An assistant must turn on the ignition without starting the engine.
- The black probe of the multimeter needs to be connected to “ground” (a metal part of the engine), and the red probe to the dpkv dprv wire.
- A second person must start the engine.
- You need to attach a red probe to the DPRV signal wire, and a dark probe to the ground wire.
If the sensor is faulty, the voltage will be lower than that specified in the repair manual. When no problems are found, the reason may be due to various failures.
How to check the camshaft sensor with a multimeter
How to check DPRV:
- Find ground, power, and signal wires using your vehicle's repair manual.
- Put the device on constant voltage to check the sensor circuit.
- Activate the ignition, the engine must be turned off.
- Use the dark multimeter cable for the ground and the other for the power wire.
- Check the readings of the device and compare them with the readings in the manual.
- The second person must start the vehicle engine.
- Touch the ground wire with the dark cable and the signal wire with the red probe.
- Check the readings and compare them with the information in the vehicle operating manual.
If the voltage reading is lower than it should be in the instructions or if any signal is missing, then there is a serious problem with the sensor. You need to remove it and carefully look at the damage. The reason may be severe physical damage.
Checking the DPRV using an oscilloscope
The phase sensor is checked using an electronic oscilloscope. You need to connect to the sensor and take an oscillogram from it.
What the verification procedure looks like:
- the measuring probe must be connected to the signal wire of the oscilloscope;
- it is required to set the voltage measurement range to 450 V;
- Click on “Start” and remove the signal from the sensor on the display.
Chevrolet Niva error codes: decoding and description of meanings
The popular Russian-made model is very widespread in the CIS countries due to its optimal cost and increased cross-country ability, which is critically important in the conditions of domestic operation. Motorists buy cars for off-road travel and small towns, where the quality of roads leaves much to be desired.
The disadvantages of the car include weak wiring - when the load increases to the design limit, on-board electronic systems often fail, which causes software failures. Chevy Niva error codes appear on the dashboard display or are detected using special equipment, but the common thing is that they all indicate a malfunction of a specific component.
Replacing the camshaft sensor
Camshaft failure or failure is very rare. This is a fairly expensive part, so repairs can be problematic.
So, what does replacing the camshaft position sensor look like:
- Find the sensor.
- Remove the negative battery cable.
- Remove the electrical connector from the sensor by clicking on the tab and sliding it out.
- Remove the sensor mounting screw. You will also need to remove the mounting bolts.
- Remove the sensor from the vehicle.
- Next comes the installation of a working camshaft position sensor.
- You need to insert the sensor straight and align the bolt flange with the mounting hole.
- Then install the sensor mounting screws and tighten them with a wrench or ratchet using a socket wrench of the appropriate size.
- Next you need to reinstall the electrical connector.
- You need to install the negative battery cable.
- The negative terminal is connected to the battery.
Finally, the camshaft sensor, capable of detecting the position of the camshaft at all phases of its rotation cycle - to send this data to the ECU - plays a crucial role in engine control. Indeed, this allows the ECU to know the position of each valve and adjust the amount of fuel injected accordingly in real time. In the event of a malfunction, it will be more difficult to start the engine, sometimes it becomes completely impossible. The engine will suffer from much more misfires and even excessive fuel consumption.