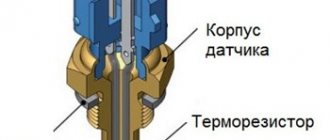
The coolant temperature sensor (CTS) is essentially a thermistor or thermal resistance. Depending on the temperature of the environment in which it is immersed, the resistance in the circuit changes up or down. The process of checking the coolant temperature sensor is quite simple; this can be done in several ways. However, you should understand the main aspects of its operation, and to identify a defect, know the common causes and signs of breakdowns. Most often, a multimeter is used for checking. Below we present the most popular options for diagnosing the sensor.
Operating principle of the sensor
Let's briefly look at how a thermistor sensor works, this will help to correctly diagnose it. The sensor consists of two output contacts and a measuring head in which the thermistor is located. The contacts are connected via wires to the electronic control unit (ECU). The head is immersed in the liquid being measured. Since DTOZh has a negative temperature coefficient, as the coolant temperature increases, the resistance value on the thermistor decreases, and as the temperature decreases, the resistance increases. The control unit reads the information and, based on it, gives a specific command, and the thermostat opens or closes the flow of antifreeze through the radiator.
Based on the readings of the antifreeze temperature sensor, the ECU, when starting the engine, sets the required number of idle air control (IAC) steps, ignition timing and injector injection time, thereby adjusting the fuel supply. The sensor is supplied with a constant voltage of 5 V from the ECU through a resistor having a constant resistance value, which is located in the control controller. That is, the control unit responds to changes in voltage at the sensor.
Symptoms of malfunction
But what to do if the sensor has already broken down, but due to various circumstances it will not be possible to repair it in the near future? By the way, such situations are not uncommon, because at this moment the driver may be on the road, moving along a route of many kilometers.
Of course, you can travel without such controllers, but without losing your vigilance. In this case, you have to focus on the symptoms of the malfunction. Among the main signs of this breakdown it is worth highlighting:
- loss of functionality of engine heating indicators;
- random start or failure to turn on the cooling fan, even if the working fluid begins to boil, heating up to 100 degrees Celsius;
- the appearance of antifreeze leakage.
It is important to remember that boiling and leaking are reasons to put the car on hold as quickly as possible until the problem is completely eliminated.
The motorist should also be alert to such potentially dangerous manifestations as difficulty starting the engine after idle time followed by its shutdown caused by damage to the thermoelement, as well as interruptions in engine operation when idling, an additional reason for which may be faulty spark plugs.
In addition, you should not trust the dashboard if the boiling of antifreeze becomes obvious and it is best in this case to rely on your own hearing.
Main signs and characteristics of DTOZh malfunctions
The failure of the coolant temperature sensor can be judged by several signs. However, it is worth understanding that the typical manifestations listed below may also be the cause of other car engine defects. Therefore, to be sure, you need to conduct an additional check.
The main signs indicating a sensor malfunction:
- The Check Engine light came on on the dashboard. If you see this icon, scan the error code; it may indicate other problems.
- Fuel consumption has increased. Due to the fact that the electronic unit receives incorrect data from the sensor, it cannot correctly read it and determine the required command. Namely, how much fuel is needed to form a fuel mixture and maintain the optimal engine temperature.
- Unstable engine operation. This includes failures at idle, difficulties when starting the engine (more often in winter) or a complete stop at low speeds.
- The car stalls when the engine is warm. As soon as the antifreeze temperature reaches a certain point, the engine stops spontaneously. Regardless of what liquid was used in the system (good antifreeze or plain water).
- Unstable fan operation. There are several manifestations - sometimes it does not work at all, and in other cases it does not switch to emergency mode. Here it is important to additionally check the thermistor for serviceability.
- The car does not start easily when the engine is cold.
More often, such sensors are made with a non-separable housing, so if they are defective, they are replaced with new ones. This applies to cars of any manufacturer, both domestic and foreign.
Signs of failure of the coolant sensor
A number of signs will indicate the need to check the coolant temperature sensor. However, it is worth noting that the situations listed below may be signs of other breakdowns in the car’s engine, therefore, to obtain an accurate result, it is necessary to perform additional diagnostics. So, signs of a faulty coolant temperature sensor include:
- Activation of the warning lamp on the Check Engine panel. However, it can also be activated during other failures, so it is necessary to perform an additional scan of the error code.
- Increased fuel consumption . This is due to the fact that incorrect information is supplied to the electronic control unit, and accordingly, it is also unable to determine exactly how much fuel is needed not only to create an optimal air-fuel mixture, but also to maintain the engine temperature in the normal (non-emergency) range.
- Unstable motor operation . In particular, its unstable operation at idle, difficulty starting (especially in the cold season), spontaneous stopping at low speeds.
- The engine stalls when hot . That is, it may suddenly stall when the critical coolant temperature is reached. Moreover, this does not depend on what kind of coolant was poured into the system (in particular, factory-made antifreeze or ordinary water).
- Problems with the cooling fan on the radiator . This can manifest itself in different ways. In some cases, the fan does not turn on at all, in others it does not turn on in emergency modes, in others it does not turn off even when the engine cools down. When the coolant temperature sensor is disconnected, the electronic control unit perceives this as an open circuit in the sensor and forcibly turns on the fan. In any case, to obtain an accurate picture, it is necessary to perform additional diagnostics of the sensor and/or thermostat.
Due to the fact that this sensor has a fairly simple device and most often a non-separable housing, if it fails it must be replaced. This applies to almost all machines on which this device is installed.
Where to find the sensor on the car
To check the sensor you need to know where it is located. Naturally, its location will differ in different brands and models of cars. However, there are several signs by which you can determine where it is installed.
Most often, the coolant temperature sensor is located on the outlet pipe of the cylinder head. Its design includes a thread with which it is mounted in the appropriate place. An important requirement is direct contact of the sensor head directly with the coolant. This provides the most accurate sensor readings.
It should also be taken into account that some car models have two coolant temperature sensors at once. In such cases, the first one takes and transmits readings of the antifreeze temperature at the engine outlet, and the second one at the radiator outlet. This provides more accurate information about the condition of the engines and cooling systems.
All information about the number and location of sensors can be found in the car’s registration certificate.
Niva Chevrolet
For installation, you can use DTOZH 2112-3851010 Kaluga (23.3828). It is difficult to visually determine the location of the device, because it is covered by other parts.
After removing them, you can see that the device is located in the upper part of the thermostat in the hole in the front pipe of the water jacket (the one that goes into the cylinder block). After unscrewing it (snap on 19), antifreeze does not flow.
The check is carried out according to the same schemes as discussed above. In this case, you need to have before your eyes a table with the parameters of temperature and resistance of the DTOZH.
Table 3.
| Temperature, 0C | Resistance, Ohm |
| +100 | 177 |
| +90 | 241 |
| +80 | 332 |
| +70 | 467 |
| +60 | 667 |
| +50 | 973 |
| +45 | 1188 |
| +40 | 1459 |
| +35 | 1802 |
| +30 | 2238 |
| +25 | 2796 |
| +20 | 3520 |
| +15 | 4450 |
| +10 | 5670 |
| +5 | 7280 |
| 0 | 9420 |
| -4 | 12300 |
| -10 | 16180 |
| -15 | 21450 |
| -20 | 28680 |
| -30 | 52700 |
| -40 | 100700 |
Also on the Chevrolet Niva, in the area of the 4th spark plug, there is a DUTOZH (coolant temperature indicating sensor), which displays data on the instrument panel; it does not transmit information to the ECU and does not affect the operation of the engine.
But it can provide incorrect data to the instrument panel and mislead the driver.
You can unscrew it without draining the coolant, but before doing this, relieve the pressure in the system by unscrewing the cap of the expansion tank.
It is also checked by comparing the temperature with the readings of the multimeter.
See table below.
Causes of malfunction of the coolant temperature sensor
The design of the sensor is extremely simple, and accordingly, its breakdowns occur very rarely. The most common causes are wear and tear or mechanical damage. For example, the appearance of corrosion may be caused by the fact that ordinary water was used in the cooling system instead of antifreeze.
The most common causes of DTO failure:
- Damaged hull. It is expressed in different ways, but more often it is a noticeable leakage of coolant from the thread of the sensor or its housing. It is also possible that the thermistor itself or its contacts may be damaged, which will cause it to produce an incorrect signal.
- Oxidized contacts. When exposed to high humidity or simply because the sensor is old, oxidation can appear on its contacts, which prevents the passage of electrical current through them (or significantly increases the resistance of the circuit).
- Damaged group of contacts (chips). More often caused by mechanical damage to the wires at the base of the connector.
- Broken contact inside the coolant temperature sensor. May be caused by aging, strong impact or vibration. Leads to broken contacts. In such cases, repair is impossible, since the sensors are manufactured with a sealed housing and therefore must be replaced.
- The wire insulation is damaged. Refers to the power conductors going from the ECU to the sensor. Occurs from mechanical stress, old age, due to the use of low-quality insulating materials, etc. It is especially important for vehicles operated in high humidity environments.
In many cases, to restore normal operation of a temperature sensor, it is enough to remove unwanted deposits, traces of corrosion and possible oxidation from its body, threads and contacts. If this does not help, it is easier to replace it with a new one.
The cost of the sensor is low, and installation will not be difficult for even a novice car enthusiast.
Recommendations for care and maintenance of sensors
- Strictly adhere to vehicle maintenance schedules;
- Buy parts with original catalog numbers. The exact data is indicated in the instruction manual for your technical device;
- Carry out preventative maintenance, install consumables and spare parts at certified service stations. Relevant while the car is under factory warranty. There are frequent cases of warranty cancellation due to third-party intervention.
- When the first signs of engine malfunction appear, contact a service station.
Checking the serviceability of the DTOZH
The antifreeze temperature sensor is checked in two main ways: without removing it from the car or by removing it from its seat. The second method is also divided into two diagnostic options: with and without a thermometer.
If the sensor is not stuck to the thread, then it is quite easy to remove it with an open-end wrench of a suitable size. It is important to disconnect the contact connector before unscrewing. The next step is to check whether power is coming from the ECU to the sensor.
It’s quite easy to do this with a universal tester (multimeter):
- disconnect the connector from the sensor;
- switch the multimeter measurement mode to “20 V constant voltage”;
- attach the probes to the terminal contacts coming from the ECU.
Under normal conditions, the voltage should be 5 V. If this condition is met, then you can proceed to further testing of the sensor.
If you don’t have a multimeter on hand, the serviceability of the ECU and the wiring to it can be checked by simply removing the connector from the coolant temperature sensor while the engine is running, the radiator fan will automatically turn on. This will happen because the control unit will see an open circuit and go into emergency mode. If this does not happen, then either the ECU or the cooling fan is faulty.
Check without removing from the car
The most convenient way, because there is no need to dismantle and then install. The check is performed using a tester, by measuring readings on the sensor contacts.
To provide access to the contacts, you will need to disconnect the terminal block from the sensor. When performing work on a hot engine, be careful, because you can not only burn yourself, but also melt the case or probes of the multimeter.
The tester is then moved to the resistance measurement position and connected to the sensor output contacts. It is worth noting that for a cold engine the reading will be high, and for a hot engine it will be significantly lower.
For a general understanding of what values the sensor produces at different temperatures, as an example, below is the data for the VAZ-2110. The readings of other passenger cars will not be much different.
Sensor readings depending on temperature changes
| Liquid temperature, °C | Conductor resistance, Ohm | Liquid temperature, °C | Conductor resistance, Ohm |
| 5 | 7 280 | 45 | 1 188 |
| 10 | 5 670 | 50 | 973 |
| 15 | 4 450 | 60 | 667 |
| 20 | 3 520 | 70 | 467 |
| 25 | 2 796 | 80 | 332 |
| 30 | 2 238 | 90 | 241 |
| 40 | 1 459 | 100 | 177 |
It is worth noting that the sensor rarely breaks down; situations occur when it produces incorrect information. Therefore, you should compare the temperature readings on the dashboard with the data received from the coolant temperature sensor in accordance with the table. If the data differs, then it makes sense to remove the sensor and carry out further diagnostics.
Checking DTOZH with a thermometer
For such diagnostics, it is necessary to remove the sensor from its seat. As mentioned above, this can be done using a suitable wrench. At the same time, you can clean the sensor itself, remove plaque from the threads on the pipe and lubricate it, inspect the contacts for oxidation and, if necessary, remove them.
Then put water into an electric kettle or another container, but in this case you will have to use a boiler. In addition, to measure you need to take a multimeter and move its switch to the position for measuring conductor resistance.
The sensor head is lowered into the water, and the tester probes are connected to its contacts. A thermometer is also placed in the container with the sensor; for ease of measurement, an electronic one is preferable, but a mercury one is also possible.
Then, gradually increasing the temperature of the liquid, compare the readings of the sensor and the electronic thermometer in accordance with the table. For greater accuracy, it is better to record readings every 5 degrees. As a result, you will receive data that can be entered into a table. They can subsequently be compared with the information provided in the technical documentation for a specific car model. As a last resort, you can compare it with the table above.
During testing, small deviations from the values are allowed. Small errors may depend on various conditions and on the sensor itself. Often, even coolant temperature sensors of the same model have slight differences in readings under the same measurement conditions.
Checking without a thermometer
This method is not very different from the previous one, only here a thermometer is not used and readings are taken only once.
To check the sensor, immerse it in a container of water and bring it to a boil. Then connect the multimeter probes to the output contacts and see what it shows.
If the DTOZH is fully operational, then its resistance should be 177 Ohms. However, errors should be taken into account. In addition, the multimeter probes also have their own resistance, and the water temperature may be slightly below 100 degrees, and accordingly the resistance will be slightly higher.
Kalina
The official version of the DTOZH for the VAZ 2112 is 2112-3851010. But you can use analogues, for example, ERA (33026), Luzar (LS 0112), Fenox (TSN 2211207).
The location of the sensor on a car with an 8- and 16-valve engine is near the thermostat. In this case, the device is slightly closed by the filter housing.
In this case, on the Lada Kalina 1 you will have to remove the air filter to access the temperature meter.
To unscrew, use a 19 key. There is no need to drain the antifreeze.
Check, as in the previous case, after removing the device with the key to “19”.
For temperature and resistance readings, see Table 3.
Checking the presence of operating voltage is carried out with a multimeter with the ignition on without removing the sensor between the block terminal “B” and ground (there are two terminals on the blocks “A” and “B”), standard readings are within 4.8-5.2 V.
How to check the DTOZH using the example of a VAZ 2110
In general, the coolant temperature sensor on different VAZs is checked using the same methods and in the same sequence as described in the previous sections. Most often, sensors with article numbers 23.3828 and 405213, or its analogues – 423.3828, are installed on Ladas 2110, 2112, Priora, Kalina and others.
To carry out the test, you need to know what its resistance is at different temperatures:
- 15 °C - from 4,033 to 4,838 Ohms;
- 128 °C - from 76.7 to 85.1 Ohm;
— output voltage at 15 °C – from 92.1 to 93.3% of that supplied from the ECU;
— output voltage at 128 °C – from 18.1 to 19.7%.
Before dismantling the DTOZh for subsequent inspection or replacement with a new one from the cooling system, it is necessary to drain the antifreeze a little. This is done on a cooled engine to avoid injury and damage to engine parts or tools.
The sensor is unscrewed with a 19 mm wrench. To do this, unscrew it and remove it together with the sealing ring.
Measurements are carried out in steps of 10 °C from the boiling point to room temperature. The resistance values are recorded and finally checked against the table.
Gazelle (engines ZMZ 406, 405, 409)
Installation location - on the power unit in the area of the thermostat or on the body of the latter.
To remove it, it is necessary to partially drain the coolant from the engine, disconnect the spring clamp of the harness block and discard the block from the sensor.
Next, using a key set to “19” you need to loosen the broach and unscrew the device.
When choosing a device, you need to focus on the engine and ECU.
406 engine and ECU Mikas 7.1, 5.4, SOATE, VS5.6
In such cases, a DTOZH is used, operating at a voltage of 5 to 12 Volts through a resistance of 9.1 kOhm.
Several types of devices are suitable for replacement: Kaluga 19.3828, Luzar LS 0306, Rikor 40.5226 or Autotrade 42.3828.
When checking, you will also need water with a boiler and variable temperature, as well as a multimeter.
To work, you need to assemble a circuit and apply 1 to 1.5 mA to it. In this case, it is necessary to measure not resistance, but voltage.
When checking, the following parameters must be present:
- -60 0С - 2.13 V;
- -40 0C - 2.33 V;
- -20 0C - 2.53 V;
- 0 0C - 2.73 V;
- +40 0С - 3.13 V;
- +80 0С - 3.53 V;
- 105 0C - 3.83 V;
- 125 0C - 3.98 V.
When the engine is running, the voltage will be 5 V.
Engine 405, 409, UMZ 4216E3, 4213 control unit Mikas 11 / 10.3, VS8, SOATE
DTOZH with catalog numbers 234.3828, 40.5215 or 421.3828 are used here.
Unlike the method discussed above, here it is necessary to measure resistance.
In this case, the dependence should be as follows:
- 128 0C - 80.8 Ohm;
- 100 0С - 177 Ohm;
- 80 0С - 332 Ohm;
- 60 0С - 667 Ohm;
- 40 0С - 1459 Ohm;
- 20 0С - 3520 Ohm;
- 0 0С - 9420 Ohm;
- -20 0С - 28680 Ohm;
- -40 0С - 100707 Ohm.
In case of significant deviations from these parameters, the device must be replaced.
Operating principle and triggering requirements
So, the main element of the DVV is the contact group inside the node. When the desired temperature is reached, the sensor contacts begin to expand and at a certain moment close. After this, the signal goes to the ECU, which, in turn, gives a command to the fan.
What should the switch-on temperature be? You must remember that DVVs are available with different temperature limits.
Most often, switching on occurs when 92 degrees Celsius is reached, and switching off occurs at 87. Sensors are also sold with other temperature ratings, but for the VAZ-2110 the 92/87 option is most suitable - so give preference to it.
How to dismantle
Many drivers are confused where the temperature sensor is located in the system, which provides information to the ECU, and where the instrument cluster is. In Kalina, the first controller is embedded in the thermostat, which is located on the coolant outlet pipe from the engine. The transmitting sensor is located nearby; you can find it using a thin wire.
All work on removing and installing parts is carried out with the engine turned off and the negative terminal of the battery disconnected. Dismantling order step by step:
- Loosen the screw securing the air hose coupling to the air filter housing. This will allow you to get to the instrument sensor. If necessary, remove the air filter housing for good access to the sensors.
- Remove the screen or engine cover, using force, remove the cover from the latches.
- Drain the coolant from the radiator. On Kalina, antifreeze or antifreeze is used. To do this, the fluid needs to be cooled, but experienced drivers replace it without draining the antifreeze. In this case, all replacement work will need to be carried out quickly and accurately. Therefore, if the sensor is changed for the first time, it is better to drain the coolant so that an air lock does not form in the system.
- Disconnect the wire block.
- Using a socket head or a 19 mm wrench, unscrew the sensor from its seat. If the coolant is not drained, antifreeze will flow out of the hole. Therefore, experienced drivers who are too lazy to drain it immediately clamp the hole with their finger and insert a new one.
Installation of the elements is carried out in the reverse order - the sensor is inserted into the hole, screwed in, connected to the wire block, and antifreeze is poured. The functionality of the system is checked after connecting the battery.