A driveshaft is a unit that directly transmits torque (rotation energy) to the wheels. Beginners sometimes confuse the concepts of “propeller shaft” and “universal drive”. To prevent this from happening, it is important to learn the following things:
- The cardan shaft has two support points; there are no intermediate supports.
- A driveline drive may have multiple supports and includes multiple driveshafts.
Cardan shafts are easy to find in passenger vehicles (all-wheel drive and rear-wheel drive cars), light trucks, buses, dump trucks, trucks, truck cranes, loaders, tractors, ATVs. But driveshafts are unpopular among front-wheel drive cars. It is difficult to achieve synchronous rotation of the shafts. An exception is vehicles with a HF with a CV joint.
Cardan shaft device
The main elements of the most popular modification of the device:
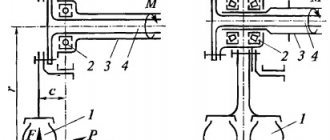
- Central shaft (cardan tube, axle). Hollow metal pipe. Solid drawn part. A structural element onto which other parts are attached.
- Cross. Important for implementing the function of controlling variable tilt angles and, accordingly, rotating elements. The correct range of variable tilt angles is from 0 to 20 degrees. This is important so that the shaft does not interrupt rotation. High-quality crosspieces are made of alloy steel by hot stamping.
- Welded fork. Connecting element between the intermediate and main shaft. Plays the role of a compensator for the height distance between the shafts. The value of a welded fork is especially easy to appreciate off-road. When selecting a fork for a HF (for example, in case of replacement), it is important to take into account the size of the cross, the mounting diameter of the pipe, the maximum hinge angle and the type of fastening.
- Hinge fork flange (cardan flange). The fork flange is mounted in the area where the shaft is attached to the bridge. It consists of a flange (flat disk) and two horns in which holes are made for the crosspiece for bolts. The fork is attached to a mating flange on the drive axles or gearbox. The most promising are fork flanges with 4 splined “heels” in the bolt installation areas and splines on the mating flanges. Such solutions are a guarantee of high-quality connection of nodes. When choosing a flange when replacing a part, it is important to take into account the diameter of the holes and their number, and the diameter of the flange itself.
- Spline connection. Responsible for the transformation of working length during movement. One spline connection point is fixed on the gearbox, the other on the gearbox. When the vehicle is forced to overcome bumps and holes, the interval between the support points increases, and thanks to the spline connection the cardan “stretches”.
Both forks, the cross and the spline joint form the so-called hinge unit. Its main task is to transmit torque with a changing angle.
Exception! On some SUVs, instead of a crosspiece, you can find cardans with CV joints. In this case, there is no spline connection.
The device of the KV series includes an elastic coupling. It helps smooth out torque fluctuations and compensate for axial and angular deviations.
Bearings
If we are talking not only about the cardan shaft, but also the cardan transmission as a whole, when considering the device, we must not forget about the bearings.
To maintain the propeller shaft in a technically correct position, a suspended metal bearing with a metal cage and a rubber cushion is installed on it. It is the suspended bearing that takes on the load (axial, radial) and ensures rotation and rolling. This is one of the most loaded elements of the transmission, and therefore requires regular maintenance.
The intermediate bearing performs the function of supporting the main shaft, providing it with the ability to rotate in the required direction. Bearings in the form of a ring made of elastomer have the best damping properties.
Operating principle of HF
The principle of operation of the cardan transmission is the ability to transport torque when the position of the “cardan” in space changes. This principle is implemented through two mechanisms:
- Sliding fork of the cardan shaft;
- Cross joint.
A sliding fork is necessary to slightly increase the length of the mechanism when driving on uneven roads. Due to the long spline connection, the supply of torque does not stop when the suspension, together with the rear axle, moves up or down.
The hinge, in turn, ensures rotation of the wheels when the bending angle of the CV changes. It is believed that the mechanism is capable of working productively at angles of no more than 20°. Then its active wear begins.
What is the function of the driveshaft?
HF is capable of performing two important functions.
- Basic. Transmission of torque from the gearbox or transfer case of the car to the rear wheels. The cardan allows you to gently transfer torque from the transmission to the wheels, dampen vibration off-road, and ensure smooth driving.
- Additional. Plays the role of a link between the steering column and the rack. That is, it is already part of the steering mechanism. HF helps improve steering feel.
Thanks to the HF vehicle, good acceleration is ensured even on uneven roads. KV is actually an optimizer of effective unloading of the front wheels and a tool for reducing the risk of slipping.
Types of cardan shafts
Cardan shafts and cardan transmissions can be classified according to a number of criteria:
- By type of cardan transmission: open and closed HF. An open cardan is a separate element of the vehicle, a closed one is integrated into another unit. A common option for closed CVs is their inclusion in the drive axle housing.
- By design: rigid cardan, ball cardan and cam-type cardan of equal angular velocities. The transmission of rotational torques from the fork with rigid cardans is uneven. Therefore, the decision is also unpopular. It can only be found in some passenger cars. In commercial vehicles, you can more often find ball driveshafts (the most popular option) and cam-type driveshafts. A huge plus of ball cardans is the dividing grooves, which ensure the optimal position of the balls in the plane. Functional, practical.
- According to the material. The base material of all HFs is metal. The most popular option nowadays is steel. Cast iron and aluminum HFs are somewhat less common.
- According to the ability to perform compensation. Solutions that allow for compensation of significant axial movements between the centers of cardans are considered universal. If this is not possible, then we have simple HF.
- According to kinematic properties. Asynchronous and synchronous. Asynchronous designs are popular solutions with a spider and a fork (found on rear-wheel drive vehicles). Synchronous – solutions with CV joints (found on front-wheel drive vehicles, some models of all-wheel drive vehicles). Asynchronous transmission is noisier than synchronous transmission, but at the same time cheaper to produce and easier to maintain.
- By the number of supports. Most vehicles have three-leg driveshafts with a single bearing that acts as a connector between the main and intermediate shafts. Two-legged structures are somewhat less common (they are mainly mounted on trucks and a number of all-wheel drive vehicles). And even less often you can find three-legged structures. This solution is usually inherent in Chrysler and Lexus.
- By the number of sections. Single-section (in fact, it is a pipe, at the end of which there are crosses and tips) and multi-section.
Conclusion
A cardan shaft is a seemingly simple product with which problems often arise. Despite the high durability of such shafts, they require periodic inspection and maintenance. Due to its long service life, a car enthusiast can even purchase a used one. driveshaft, however, a new product must be checked very carefully. There are also new cardans on sale - they are produced both at domestic and foreign factories. Despite the fact that original cardans are the most reliable, many consider their cost to be inadequate. You can buy a non-original cardan shaft, but it is difficult to give any recommendations on manufacturers - the quality of products from almost all companies working on the aftermarket cardan shafts is approximately the same.
Checking the condition of the cardan shaft
Even if the car is operated in non-extreme conditions (driving on city roads), checking the condition of the driveshaft is necessary every 5 thousand kilometers.
When driving on dirt roads, checking is recommended even more often: every 3 thousand km. Special equipment has its own requirements. It all depends on what objects it is used on. When checking, the greatest attention is paid to the crosspiece, which can begin to roll and jam, as well as the outboard bearing. The appearance of backlashes after a certain mileage is a completely natural phenomenon. The spline connection is also very vulnerable. First of all, because it is a moving mechanism that constantly encounters dynamic loads.
It is recommended to check the parts in the following order:
- Connecting elements (nuts, washers) of bearings, couplings, flange forks. It is important that not only all connections are in place, but also the tightening torques meet the requirements of the operating conditions.
- Couplings at the moment of shaft torsion. The presence of cracks, let alone ruptures, on the couplings is unacceptable. If there is such a problem, the part needs to be replaced urgently.
- Spline connection at the moment of shaft rotation. Here it is important to understand whether there are any backlashes. In order for the assessment of the spline condition to be as reliable as possible, it is advisable to rotate in both directions.
- Hinges. A simple visual inspection is not enough here. You need to place a screwdriver between the forks and pump thoroughly. The unpleasant moment is, again, finding a gap. In this case, you will have to install a new cross.
- Bearings. How the verification is carried out is of fundamental importance. Skills are important. In order not to miss the backlash, you need to hold the HF with one hand, and with the other you pull it in different directions.
But if there is a suspicion of HF imbalance, you cannot do without diagnosing the unit on a balancing stand. You can’t do without such a check especially if you feel constant vibrations while driving, and an unpleasant grinding noise regularly occurs when changing gears.
Useful tips
Remember that you should never ignore any signs of a cardan malfunction. If you do not heed this advice, you may experience the following consequences:
- If the cardan breaks, the vehicle body itself is damaged. Additionally, the cardan can damage the pipeline that runs along the bottom of the car.
- If constant vibrations are observed, this will negatively affect the rigidity of the suspension and body mounts. All threaded connections and fastenings of interior panels will also begin to loosen. The car will literally begin to fall apart while driving.
- All parts directly connected to the driveshaft will wear out faster and more intensely. This will significantly shorten their service life and require early replacement and expensive repairs.
It is unlikely that any car owner will consciously want to face such troubles.
But in many ways they can be avoided if you follow a few simple rules. All these recommendations are aimed at increasing the service life of the driveshaft.
If you are interested in preserving the HF resource, then you need to:
- try to minimize vehicle operation in rough terrain;
- do not accelerate sharply;
- move away smoothly;
- do not skid the car for a long time;
- do not skimp on quality spare parts;
- carry out diagnostic measures;
- If complex faults occur, contact qualified technicians.
The driveshaft is in many ways an important element of a vehicle, which, although considered an intermediate link, plays a key role in the operation of rear-wheel drive and all-wheel drive vehicles.
The unit does not have an extremely complex structure, and its operating principle is clear to many. This allows you to independently solve problems that arise, detect faults in a timely manner and maintain the HF in working order for a long period of time, simply by following a few simple rules.
Drive shaft maintenance
The traditional maintenance scheme is based on three operations:
- Checking the condition of the shaft (see above).
- Replacing faulty parts (precisely replacement, restoration in the presence of backlashes and cracks is an illiterate solution to the problem).
- Spline joint lubrication. When selecting a lubricant, pay attention to the welding load (responsible for extreme pressure properties). Expensive products are oriented towards welding loads up to 3920 Newtons. For HF splines on heavy freight vehicles, their use is only encouraged. For passenger cars, lubricant for low-load splines is sufficient. Overpaying for the product is not advisable here.
On some cars, the bearings of the KV crosspieces also need to be lubricated. But there are not very many vehicles that require such a procedure. These are HF vehicles with a grease fitting. An example of a HF with a grease nipple is shown in the figure below.
Asynchronous
The asynchronous circuit is used in many cars with rear-wheel drive or all-wheel drive. Feature - during the movement, unequal angular velocities are formed. This is due to the connection of the two forks using a cross at a right angle. The secondary shaft lags behind the main shaft 2 times and overtakes the main one 2 times.
To compensate, additional universal joints of unequal speeds are installed. They are mounted at the ends of the shaft. With this scheme, the angle between the pipes can be changed by up to 20°. Disadvantage: due to the complexity, frequent maintenance and repairs are required.
Malfunctions of cardan shafts
The problem can occur both with the entire device, and only with its individual components and parts:
- Broken welded fork. It occurs due to the initial incorrect installation of the crosspiece, damage to the mounting holes for this part, and destruction of the fork.
- Flange-fork failure. Occurs due to wear, chipping, cracking or damage to the fastening bolts.
- Bearing failure. More often - due to natural wear, installation errors, constant contact of the bearing with dust, and a driving style based on constant hard gear shifting.
- Deformation, bending of the HF. Based on the inspection, the technician makes a decision whether the problem can be solved by purely mechanical restoration or whether a number of elements need to be replaced.
- Vibration of the driveshaft. Most often, this is a “response” to incorrect alignment of parts, an increase in gaps between parts when operating a vehicle in difficult operating conditions, or incorrect repairs (unprofessionally performed welding work).
- The cardan begins to “ring.” The reasons may be different. If the support is damaged, the best option is to replace the cardan; if the protective boot is loose, it is enough to carry out repairs by welding. The simplest option: there is a problem with the spline cover - just replace it with a new one.
What can break? how should the failure occur?
It would seem that the driveshaft is an extremely simple element in which very little can break. In practice, the list of possible failures is surprisingly long:
- The rubber of the shaft support is broken - there is nothing to repair, it needs to be replaced. And as soon as possible.
- A worn driveshaft support is the most common consequence of severe wear in the drive system and is a consequence of very high mileage on the vehicle.
Read news about the new Niva
- Chevrolet Niva idle speed sensor
- Koreans will switch to domestic Humvees |
- Gasoline for Chevrolet Niva - what kind to pour and what is the consumption? Using the example of a trip of 600 km
- Volkswagen Tiguan I: chassis, gearboxes, engines - KOLESA.ru - automobile magazine
- Engine VAZ 21213 Niva | Niva engine tuning and repair
- Bleeding Chevrolet Niva brakes: step-by-step instructions
- VAZ 21213 transfer case device, diagram, alignment, removal of transfer case
- How to prepare a Niva for off-road use