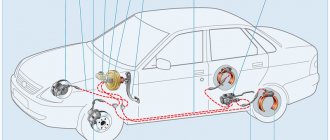
How to properly bleed the brakes
Before starting work, you should make sure that you have the necessary materials and tools that should be on hand:
- brake fluid;
- wrench “8” (socket or open-end) to loosen the fittings;
- elastic hose suitable for a tight fitting on the fitting;
- a suitable container for receiving used brake fluid;
- slotted screwdriver;
- wheel chocks;
- lift, inspection pit or overpass.
A partner, sitting in the cabin, will press the brake on command.
Sequencing
Hang the car on a lift or secure it with wheel chocks on a viewing hole or overpass. Wheel bleeding procedure:
- Rear right wheel.
- Front left wheel.
- Rear left wheel.
- Front right wheel.
The algorithm of actions performed is the same for all four wheels.
Leveling procedure
Bleeding the Kalina brake system will require you to first take the following preparatory steps:
- Open the electrical circuit of the low brake fluid level indicator sensor in the expansion tank.
- Unscrew the cap and remove it together with the float, freeing the neck to quickly replenish the volume of fluid in the braking system during adjustment.
- Make sure that the level is above the MIN mark, top up if necessary.
- Check that the pressure regulator valve is set correctly (otherwise it will not be possible to bleed the rear wheels).
Self-bleeding brakes
In the future, you cannot do without an assistant who, sitting in the driver’s seat, will operate the brake pedal according to the commands of a partner located under the bottom of the car. The procedure for pumping wheels on Kalina is as follows:
- The protective cap is removed from the fitting and its tip is covered with an elastic tube. The mating part of the tube is placed in a suitable container.
- Using a ring wrench “8” with a slot, the swivel nut of the fitting is covered.
- The person in the cabin, upon command, presses the brake pedal all the way with successive movements and holds it close to the floor.
- A partner under the car unscrews the fitting counterclockwise and, after waiting for the brake fluid to stop leaking, closes it again.
The last two steps are repeated until air bubbles stop appearing in the liquid. Having put the safety cap on the screwed fitting, they begin to work with the next wheel according to the scheme.
Fluid control
Constantly monitoring the level of brake fluid in the expansion tank above the minimum mark will help eliminate the occurrence of air locks in the system.
Why does the brake pedal fail?
One of the elements of the described hydraulic system is a special composition circulating through tubes and other cavities. The main feature of brake fluid is that it cannot be compressed. As a result, the force from pressing the pedal is transferred “unchanged” to the pads, which stop the rotation of the wheel. “Sinking” indicates that the line has become larger in volume or has depressurized. The main causes of the problem are discussed below.
Low quality brake fluid
The composition circulating in the system is quite aggressive. Gradually, bad brake fluid begins to corrode rubber and even metal parts, hoses, and tubes through which it moves. The walls of the latter become thinner to such an extent that they swell when pressure is created. Because of this:
- an excess volume is created into which the brake fluid goes;
- when you add it, the pressure is restored, but the tubes may not be able to withstand it: microcracks form through which the liquid gradually leaves and air enters instead (when the pedal moves in the opposite direction, it is literally sucked in). In the worst situation, the hoses may burst.
Air in the brake system
Its entry into the line is a consequence of depressurization of components and parts of the brake system. A plug may also form due to the fact that the fluid level in the tank has dropped below the existing MIN mark. Another reason is improper bleeding of the brakes when replacing the circulating compound. The danger with air in the system is that, unlike liquid, it is compressed. As a result, the force applied to the pedal goes to waste - in the literal sense of the word.
Master cylinder malfunction
Its main problem is most often related to depressurization. This occurs due to deformation and rupture of seals - cuffs. Their destruction is caused by poor-quality brake fluid or natural aging of the elements. The main brake cylinder becomes leaky even if scratches or wear appear on its walls.
This occurs due to the appearance of foreign particles in the line. They can get inside if the system is carelessly and inaccurately filled. Sometimes “extra” elements are wear and tear products if the car has been in use for a long time.
Repairing a brake cylinder is a difficult task. If you do not have the relevant experience and do not have special tools or devices, it is better to take the part to a workshop or buy a new one.
Problems with the vacuum booster
If it is faulty, then most often this can be determined by the characteristic hissing sound that occurs when you press the brake pedal. This situation may indicate depressurization of the vacuum pump. The reason may lie in a ruptured diaphragm, seals, or a broken equalizing valve. To solve the problem, purchase a repair kit and replace all rubber parts. Air can also enter the vacuum booster due to cracks in the underwater pipes: tighten the clamps on them or, if damaged, replace them (in a carburetor car, such a hose fits at the bottom of it).
Incorrect clearances
We are talking about the presence of a gap between the main brake cylinder (its rod) and the pedal. The latter in this case fails and remains in this position. If the clearance is correct, the pedal will initially move smoothly, but at a certain period of travel it will become stiff. If the distance to the GTZ rod is large, resistance to pressing will be felt only at the very end of the stroke.
Unprofessional repair
The reason when the brake pedal fails may lie in the caliper, the fastenings of which are not tightened well enough. Then its vertical axis will be shifted in relation to the brake disc and the pads will not be able to get used to function properly. Also, any unprofessional actions (poor tightening, lack of spring washers where needed, etc.) when repairing or bleeding the brake system will lead to its ineffective operation.
Corrosion
The metal that makes up some of the brake system elements can simply rust. In such cases, the pedal goes down and freezes there, from where it has to be “picked out” with a pry bar or other improvised tool. Corrosion usually succumbs to traction, which just needs to be sanded off.
Brake pad wear
In this situation, an increased gap appears between the disc and the pads. As a result, the pressure created in the system is not enough to brake the wheel. The solution is obvious: replacing the pads.
Payment via PayPal
After selecting payment via PayPal, the PayPal payment system will launch, where you need to select the payment method: bank card or PayPal account.
If you already have a PayPal account, then you need to log into it and make a payment.
If you do not have a PayPal account and you want to pay using a bank card via PayPal, you need to click on the “Create an Account” button - shown with an arrow in the picture.
PayPal will then prompt you to select your country and provide your credit card information.
After specifying the information required to make the payment, you must click on the “Pay Now” button.
Repair
For repairs, you need a garage, the ability to hang the car, a set of tools, knowledge and skills in troubleshooting typical faults in the brake system of Kalina and other cars. If you have all this, you can repair it yourself, but if not, it’s better to contact a car service center, where they will do a high-quality restoration for little money. If the car is under warranty, it is especially not worth repairing it yourself.
Source
To perform the work, you will need a special wrench for the brake pipe fittings.
1. We prepare the car for work.
2. We clean the connections of the brake hose tips and pipes from dirt and corrosion. We treat the tube fittings with penetrating lubricant.
Warning!
When performing the following operation, make sure that when unscrewing the fitting, the tube does not rotate with it. If the tube is “sour” in the fitting, replace it.
3. While holding the upper end of the hose from turning with a 15 mm open-end wrench, use a special wrench to loosen the tightness of the tube fitting.
4. We finally unscrew the fitting with a 10 mm open-end wrench.
5. To prevent brake fluid leakage, place a protective cap on the end of the brake pipe for the working cylinder bleeder fitting.
6. We remove the upper tip of the brake hose from the hole in the body bracket.
7. In the same way, unscrew the tube from the lower tip of the brake hose and release it, leading it out of the hole in the bracket mounted on the rear axle beam.
8. Remove the hose from the car.
1. Install the hose in reverse order.
2. We remove air from the brake hydraulic drive and check the connections of the brake hose and pipes for leaks.
Source
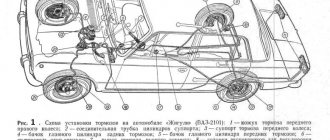
The brake system of the Lada Kalina car
The hydraulic brake system of a VAZ 1118 car consists of a pedal lever, a hydraulic master cylinder, a vacuum brake booster 1118, a hydraulic reservoir, a pressure regulator, a regulator drive lever, pipelines, flexible reinforced rubber hoses, tees, and fastening clamps. At the same time, the brakes on this VAZ model can be equipped with an anti-lock braking system, but it was not installed in the first series of Kalina production. Today, almost the entire line of cars comes with an ABS system.
Vacuum booster on a VAZ 2170 2171 2172 Lada Priora: 1 - tip mounting flange; 2 — rod; 3 — diaphragm return spring; 4 — sealing ring of the master cylinder flange; 5 - main cylinder; 6 — amplifier pin; 7 — amplifier housing; 8 - diaphragm; 9 — amplifier housing cover; 10 - piston; 11 — protective cover of the valve body; 12 — pusher; 13 — pusher return spring; 14 — valve spring; 15 - valve; 16 — rod buffer; 17 — valve body; A - vacuum chamber; B - atmospheric chamber; C, D - channels
Features of the front wheel braking system
The front wheels of the VAZ 1118 are equipped with a ventilated disc system with a piston floating caliper. It includes a wheel cylinder and a caliper, which are tightened together with special screws. The cylinder itself is attached to the guide pins with two bolts installed in the guide block (holes). The pads are pressed against the guide grooves by springs. Inside the cylinder there is a piston with a sealing ring having a rectangular cross-section. The elasticity of the ring provides an optimal gap between the disc and the brake pads, which ensures high-quality functioning of the system.
Front wheel brake mechanism on a VAZ 2170 2171 2172 Lada Priora: 1 - brake disc; 2 — pad guide; 3 - caliper; 4 — protective casing; 5 - working cylinder; 6 — brake hose; 7 — air release valve; 8 - guide pin; 9 — protective cover of the guide pin; 10 — brake pads
Features of the rear wheel braking system
The brake system of the Lada Kalina, the design of which significantly increases its safety, is distinguished by its thoughtfulness and high reliability. The rear wheels of Kalina are of the drum type, with a two-piston wheel-type cylinder, as well as automatic adjustment of the clearance space between the drum and the block. A drum brake consists of the drum itself, shoes, hydraulic cylinder, tension springs, protective disc, retainer and shoe spacer.
Rear wheel brake mechanism on a VAZ 2170 2171 2172 Lada Priora: 1 - rear brake pad; 2 — parking brake drive lever; 3 — lower tension spring of the pads; 4 — brake mechanism shield; 5 — parking brake cable; 6 — front brake pad; 7 — guide spring; 8 — expansion bar; 9 - working cylinder; 10 — upper tension spring of the pads; 11 — finger of the parking brake drive lever
Function of the braking system
It is important to note that only the smooth functioning of all elements of the device ensures safety and reliable deceleration of the vehicle.
The brake system of the Lada Kalina operates as follows: when you press the brake pedal, the piston, moving in the cylinder, displaces fluid through the main outlet valve into the brake hydraulic system hose. The fluid moves through pipelines to the main wheel mechanisms, which helps move the pads to the discs in the front wheels, and the rear ones to the drums. When contact occurs, braking begins, and the angle of change of the pedal lever affects the speed of deceleration of the car.
Parking brake and its device
In addition to the main brake system, mention should be made of the parking brake, which has a standard mechanical configuration and consists of an adjusting rod, a lever, two cables, an equalizer, spacer bars, and pad drive levers. The parking brake system of the VAZ Kalina is driven by the brake mechanism of the rear pads, which ensure reliable fixation of the car from accidental movement.
It is important to remember that a properly configured brake should ensure vehicle immobility on a slope of up to 23% when empty, and up to 19% with a full load.
Principle of operation
The main criterion is that all elements of the Lada Kalina braking system must function clearly, which guarantees the safety and reliable braking of the vehicle.
The operating principle of the Lada brake system is as follows. After pressing the brake pedal, the piston begins to move in the cylinder. Fluid from the main exhaust valve enters the Kalina brake system through hydromechanical hoses. The fluid is then directed towards the main wheel mechanism through pipelines, creating the necessary conditions for the movement of the pads to the front wheel disks and to the rear drums. Contact occurs and braking occurs.
Repair work: debugging the brake system
If the following problems are detected, it is recommended to immediately contact a car service to eliminate them.
- Presence of air in the system. You can solve the problem not only with service, but also yourself. To do this, you need to bleed the brakes.
- Brake fluid leaking. This situation indicates a malfunction of pipelines and rubber hoses.
- Increasing pedal stroke. The problem that has arisen indicates a problem with the vacuum booster. It is recommended to replace the hose and check its attachment points.
- Reduced braking efficiency. In this case, the reason may be oily brake linings, jammed cylinder pistons, compromised gasket integrity, or defective adjustment by the regulator.
- Squeaking or vibration when braking. Perhaps the tension spring is weakened, the linings are out of order, or the rubbing linings are oily.
Return to contents
Downloading a book
After successfully completing the payment (by any method) and returning to the KrutilVertel store from the payment system website, you will be taken to the successful payment page:
The book you purchased will be in your personal account, from where you can always download it.
Please note that after making the payment, you need to return back from the payment system website to the KrutilVertel website. If for some reason you did not return back to the site and closed the payment system tab with a message about the successful completion of the payment, please let us know - we will send you a letter indicating access to download the book
If for some reason you did not return back to the site and closed the payment system tab with a message about the successful completion of the payment, please let us know - we will send you a letter indicating access to download the book.
Features of front and rear wheel brakes
The front wheel brake mechanism is made in the form of ventilated discs with a single-piston floating clamp. This clamp includes the caliper and wheel cylinder, which are tightened with screws. The cylinder is attached directly to the guide pins using two bolts.
The bolts are placed in the passages of the guide blocks, pressed by the guide spring grooves. A piston with a sealing ring of rectangular cross-section is placed inside the cylinder. This ring provides the most rational distance between the disc and the brake pads. This organization of Kalina's braking system contributes to its efficient functioning.
Replacing the brake drum
The rear brakes are drum type. They consist of a two-piston hydraulic wheel cylinder, a drum, shoes, tension springs, a protective disk, shoe spacers and an automatic distance regulator from the drum to the shoes.
In addition to the head system, the developers equipped the Lada with a mechanical parking brake, which is driven by the brake mechanisms of the rear wheels.
The parking brake system includes:
- adjusting rod;
- lever arm;
- two cables;
- equalizer;
- spacer bars;
- pad drive levers.
Causes and solution to the problem
When the driver understands how the brake system works, he can deal with its malfunction. If the brake pedal fails, it is necessary to carry out diagnostics as soon as possible and identify the cause. First of all, it is recommended to check the level of brake fluid, which is stored in a special reservoir.
This tank has two manufacturer's marks . One displays the minimum permissible liquid level, and the second the maximum. Although this substance is incompressible, its amount can still decrease over time. This is due to the fact that brake pads can gradually wear out during operation. Because of this, the working cylinder needs to travel a longer distance to act on the wheel, and this requires more fluid.
Thus, air begins to leak into the free space of the tank, and, as a result, airing occurs. The brake pedal begins to sink and stops working as it should.
There is another reason why airing can occur. In this case, the fluid level may be completely normal. This is due to situations where the driver brakes too often at high speeds or drives at low speeds with the pedal constantly pressed. For example, this happens during a systematic descent from a steep slope. This problem is also facilitated by high air temperature, which heats the liquid even more.
This problem can be solved with the help of brake discs that are equipped with a cooling system. Specialized brake fluid designed to work in high temperature conditions can also help.
It is recommended to regularly service the vehicle and check the condition of the entire system. This way you can protect yourself from unpleasant situations on the road that can lead to serious consequences.
Malfunction after replacing pads
Quite often, drivers are faced with a situation where new brake discs, pads or drums have just been installed, and the problem of a failing pedal appears immediately. The first thing to note is that after such events, during the first days, the braking system may not work entirely correctly. This is a normal procedure that occurs quite often. In this regard, after replacing brake system elements, it is recommended to use the car as carefully as possible.
This problem is due to the fact that the brake pads and discs cannot work properly right away. They need some time during which they need to get used to properly. This procedure must be completely completed within 200-400 kilometers. If this does not happen, then most likely the problem is in the details themselves.
During the first time after replacing the pads, when you press the pedal, the car may not respond immediately, twitch and vibrate.
It is recommended to prepare for this in advance and not accelerate to high speeds to avoid consequences.
Vacuum booster
The last popular reason for problems with a car's brake system is problems with the vacuum booster. However, in this case, the pedal does not fall, but is pressed quite tightly, which greatly affects the effectiveness of the brake.
The vacuum booster is another element of most brake mechanisms, which are designed to make pressing the pedal more comfortable. This happens more easily and requires much less effort from the driver. However, the VU diaphragm may become unusable, which will cause difficulties in the operation of the entire system.
This problem can only occur when the engine is running. When the car is turned off, the pedal will be pressed normally. This feature allows for easy initial diagnosis. If the engine does not work and the pedal works correctly, but problems begin when the engine is running, then this is due to the diaphragm. To find a solution, you need to contact the service center.
Payment via PayPal
After selecting payment via PayPal, the PayPal payment system will launch, where you need to select the payment method: bank card or PayPal account.
If you already have a PayPal account, then you need to log into it and make a payment.
If you do not have a PayPal account and you want to pay using a bank card via PayPal, you need to click on the “Create an Account” button - shown with an arrow in the picture.
PayPal will then prompt you to select your country and provide your credit card information.
After specifying the information required to make the payment, you must click on the “Pay Now” button.
How does the Kalina brake system work?
Braking is carried out by transferring force from the vacuum brake booster through two circuits to the brake cylinders with simultaneous automatic adjustment depending on the load on the rear wheels. The front-wheel drive is equipped with disc brakes, and the rear-wheel drive is equipped with drum brakes.
Brake system "Kalina" - diagram
The braking system of this machine is formed by the following components:
- brake pedal;
- vacuum booster;
- brake master cylinder block with expansion tank;
- two separate circuits for transmitting force hydraulically to the brake pads;
- pressure regulator in the circuit to set the braking mode of the rear wheels.
Pressure on the brake pedal is amplified by the system and transmitted to the wheels. The circuits operate on a cross principle - one circuit is responsible for braking the left rear and right front wheels, the other - the right rear and left front.
In this way, the duplication function is implemented in the event of a sudden failure or malfunction of one of the circuits. The remaining working circuit is capable of providing braking to the vehicle.
For a more even distribution of forces, the rear wheels are equipped with an automatic pressure control device depending on the load on the rear axle. As the load increases, the force applied to the brake pads increases proportionally. The operation of the regulator is controlled by a special lever that sets the gap, after overcoming which the system for redistributing the braking force between the front and rear pairs of wheels is activated.
Brake system equipment
- Brake pedal. This is a hanging type part. There is a spring return mechanism. Just above the pedal part, the developers placed a brake signal switch.
- Vacuum reinforcement is a part of the diaphragm structure. It is designed to reduce the force exerted by the driver when pressing the brake pedal. It operates due to the difference in pressure in vacuum and atmospheric tanks.
- Fluid pressure regulator. Installed in systems without anti-lock wheels. Serves as a limiter for the flow of fluid towards the rear brakes when the vehicle is partially loaded. This element prevents the wheels from locking and prevents the rear of the vehicle from skidding.
- Brake fluid height sensor. Indicates a drop in liquid height below the minimum value. It is located in a plastic tank, attached through the upper passages of the cylinder using rubber bushings. After the brake fluid level drops below the permissible level, the sensor transmits a signal to the light on the instrument panel.
- Brake signal switches. Their operation is as follows: after pressing the pedal, the electrical contacts close.
- Main brake cylinder. Attached with two studs to the vacuum booster. A reservoir for brake fluid is attached to the base of the brake cylinder.
- Pipelines.
- Regulatory drive lever.
- Elastic reinforced rubber hoses.
- Tees.
- Fastening clamps.
Problems when paying with bank cards
Sometimes difficulties may arise when paying with Visa/MasterCard bank cards. The most common of them:
- There is a restriction on the card for paying for online purchases
- A plastic card is not intended for making payments online.
- The plastic card is not activated for making payments online.
- There are not enough funds on the plastic card.
In order to solve these problems, you need to call or write to the technical support of the bank where you are served. Bank specialists will help you resolve them and make payments.
That's basically it. The entire process of paying for a book in PDF format on car repair on our website takes 1-2 minutes.
If you still have any questions, you can ask them using the feedback form, or write us an email at
General checks
Brake Line Connections
Check the condition of the service brake system and parking brake components.
Brake Line Connections
Leakage of brake fluid in connections and hydraulic drive is not allowed.
Parking brake tensioner locknut
The full travel of the parking brake lever should be 2-4 teeth of the sector ratchet device, adjust if necessary:
Move the parking brake lever to its lowest position, loosen the locknut of the tensioning device and, by tightening the adjusting nut, tighten the cable so that the stroke of the lever along the sector ratchet device is 2-4 teeth (clicks).
Checks while driving
Check the effectiveness of the service and parking brakes.
Check the operation of the vacuum brake booster. With the engine not running, press the brake pedal 5-6 times, holding the pedal pressed, and start the engine. If the amplifier is working properly, the pedal should “move forward” after starting the engine. If the pedal does not “go forward”, it is necessary to check the attachment of the tip, the condition and fastening of the vacuum booster vacuum hose, and if necessary, tighten the tip and hose clamp.
Service
Maintenance consists of inspecting all components and replacing them in case of wear. All service looks like this:
- checking the brake pedal travel;
- checking and possible adjustment of the parking brake (Kalina has a handbrake from “nine”, so it must be tightened often);
- inspection of all tubes and hoses;
- inspection of the condition of brake discs, drums and pads;
- checking the brake fluid level and replacing it approximately every 40 thousand kilometers.
Problems when paying with bank cards
Sometimes difficulties may arise when paying with Visa/MasterCard bank cards. The most common of them:
- There is a restriction on the card for paying for online purchases
- A plastic card is not intended for making payments online.
- The plastic card is not activated for making payments online.
- There are not enough funds on the plastic card.
In order to solve these problems, you need to call or write to the technical support of the bank where you are served. Bank specialists will help you resolve them and make payments.
That's basically it. The entire process of paying for a book in PDF format on car repair on our website takes 1-2 minutes.
If you still have any questions, you can ask them using the feedback form, or write us an email at
Differences in the brake system of the Lada Kalina Sport
Kalina Sport is an improved version of the Lada Speed. Kalina characteristics of this model are significantly braking. The Kalina Sport system has also undergone changes during modernization of the car. The rear wheel brakes were replaced with disc brakes. On Kalina Lada Sport, an anti-lock braking system is installed exclusively on the wheels. This eliminates the possibility of the car skidding.
The use of high-quality spare parts affects many factors. It is recommended to use original factory spare parts. It is better to carry out adjustment and repair work at specialized technical points. brake maintenance is a guarantee of the safety of all road users
Attention to the brake system will ensure its longevity. The operation of the entire machine depends on this.