- Short circuit in the electrical circuit
- Permissible current limit exceeded
- Insufficient level of connection to the block
- Part wear
- The current supply in the circuit is disrupted
- Choosing the wrong or cheap fuse
- Visual inspection
- Using a multimeter
- Repair work
- Replacement procedure
- If a problem occurs on the road
Every electrical circuit in a modern car has special protection against short circuits and serious overloads. To troubleshoot the problem, it is first important to determine why the fuse blew. If the driver delays solving the problem, then failure to perform a simple procedure may result in serious consequences in the future, requiring expensive material costs. In some cases, even a fire may occur.
General information about car fuses
The simplest and most economical means of maintaining the functionality of electrical appliances is the use of low-fusible inserts located in separate blocks. They are considered the most effective in ensuring safety during operation, require a minimum of financial investments and are easy to operate.
Ensuring a long service life for the fuse is possible in the following situations:
periodically inspect the most dangerous and worn areas in the on-board wiring in order to find the fault as quickly as possible;
prevent short circuits from occurring;
try to avoid overloads for a long time, including the electrical components of the car;
the load capacity of the battery and generator should not exceed the specified value;
keep moving parts in good working order.
By following the above rules, the car owner has the opportunity to reduce the risk of fuse failure.
Purpose and functionality
The main function of a fuse is to effectively protect electrical equipment from mechanical damage. If a dangerous situation occurs, the consumer is disconnected from the power source through self-destruction, that is, combustion if the current exceeds the permissible rating.
What types exist
There are several types of fuses used in cars and they differ in the method of switching off consumption:
fusible link;
electromechanical relay;
electrical device (transistor, thyristor).
A relay or electrical appliance is sometimes equipped with automatic restoration of electrical power after the technical fault has been eliminated.
It is customary to distinguish several types of protective devices:
Cylindrical.
Knife (different formats: mini, maxi, standard).
Thermal or electromagnetic protection, where the power supply is restored manually.
Tape. Used for high rated circuits.
Localization
Despite the fact that the fuses are equipped with high-quality protection, they are located in an easily accessible place. Grouping of elements occurs depending on their purpose. Next to the battery under the hood are elements of the starting system, lighting and starting system.
The multimedia unit, air conditioning system, and interior lighting are most often located on the left side of the dashboard, or under the side panel.
How to check the fuse in a car for serviceability
- Types of Electrical Fuses
- Checking using a diagram
- Visual inspection
- Checking with a multimeter
- Checking with a tester
- Important information when checking
The automotive industry has undergone great changes, with more electrical components being introduced into cars and processes being automated. The failure of one component can lead to the failure of another. To prevent such a situation, automotive fuses are installed, the function of which is to protect the electrical circuit from short circuits. If a situation arises in which increased voltage is applied to the circuit, the protective element burns out and interrupts the circuit. If such a situation arises, it is necessary to find the blown fuse to restore the function for which it was responsible.
Why does a fuse blow: main reasons
Insurers collecting statistical data have found that about 90% of the total number of fires are due to technical problems with on-board wiring using low-quality fuses.
There are several reasons why fuses burn in a car:
a short circuit has occurred as a result of excessive load;
short circuit in the wiring as a result of a violation of the insulating layer and a short circuit in the housing;
increased voltage level in the on-board network;
the wrong denomination is used;
unsatisfactory connection with the contacts of the block;
physical and chemical wear.
Short circuit in the electrical circuit
This reason why a fuse could blow is the most common. A situation arises when the resistance rapidly drops, and the current increases several times. Typically this occurs in the following situations:
violation of the insulating layer in some places of the wiring as a result of excessive heating;
moisture has entered unprotected areas under voltage;
the components have mechanical damage;
Wrong load connected.
Permissible current limit exceeded
When the current increases and exceeds the permissible limit, it is distinguished from a short circuit by the nature of its occurrence and the duration of the effect. If a fuse is blown, this may happen for the following reasons:
a load is connected that exceeds the permissible value several times;
the consumer works in difficult conditions (when pulling a car out of the mud with an electric winch).
Insufficient level of connection to the block
Another equally common reason why a fuse may blow. Unreliable contact can lead to the formation of sparks in a given place, overheating of the material or fusible insert. In practice, low-quality parts are used, where the thickness of the legs is less than the established norm or the group of contacts has lost its springy properties.
Part wear
This process is often explained by the occurrence of oxidative processes and atmospheric exposure. Corrosion gradually appears, which negatively affects the metal. As a result, contacts begin to break down, which will lead to interruption of power supply to consumers.
The current supply in the circuit is disrupted
The current in the circuit is calculated in advance, not exceeding the established values when the equipment is running. However, mechanical faults in contacts and damage to the insulating layer can change the final load value and also affect the current distribution. When these violations appear, the current strength begins to increase.
Choosing the wrong or cheap fuse
Sometimes inexperienced drivers mistakenly purchase unsuitable fuses, the rating of which is lower than required. In this case, even with operating voltage, the current flowing significantly increases the limiting value of the parts used. As a result, the insert will soon burn out.
Examination
First of all, the electrical circuit “rings” to the housing. In this case, the battery terminals are disconnected. It must be remembered that the second wire from the engine goes to the housing; it must have zero contact resistance. The supply conductor is checked for short circuit.
If the wiring is intact, proceed to checking the voltage of the electrical circuit assembly. Measuring points are determined according to the diagram in the car manual. Also, the power at the battery terminals must be at least 12 V when the engine is off. When operating, a value above 13.6 V is measured.
With a multimeter you can measure resistance, contact integrity, and check voltage. The presence of oxides or mechanical damage is determined visually.
Carrying out self-diagnosis
From time to time, the driver is faced with the need to replace failed fuses. First of all, a similar situation arises with racing cars and SUVs. When driving like this, electrical equipment begins to operate at the maximum permissible level, which increases the level of wear. Over time, fusible links begin to deteriorate. The suitability of the structure for repair can be assessed visually, making sure of its integrity. To do this, a multimeter is most often used to make sure there is patency.
When replacing, it is important to follow the most important rule - purchase a new fuse with the same current rating. Or the deviation should not exceed 30%.
Visual inspection
All components of the structure are specially made from durable materials. Then sputtering and breakage can be determined without the use of additional tools. It is also recommended to pay attention to ensure that the fusible insert maintains the integrity of the structure. Then you need to find traces of melting of the plastic case. Also, a malfunction can be proven by traces of a spark or thermal effects on the contacts.
Using a multimeter
It is important to understand that this device does not guarantee 100% results. However, compared to a normal visual inspection, a multimeter gives the most accurate readings with resistance value. If the fuse is working, then the voltage at its ends will not be recorded.
To determine the integrity of the fuse, you can use not a tester, but an ordinary light bulb or probe. If the fuse is broken, the light will come on.
Is the fuse blown or not: how to find out without a tester
With knife-type designs, this trick does not always work. Firstly, not all “preds” are packaged in a transparent plastic case. There are a lot of cars that have elements with an opaque body installed. And not only for this reason.
Sometimes it is impossible to determine by eye whether a section of fusible metal is torn or not. We are talking about a situation where the fuse is visually intact, but in reality it turns out that it has burned out. What can be determined for sure by eye is that the plastic housing of the safety element has melted. And this situation should be alarming. The issue could be either a fuse or an overload in the circuit.
What actions should be taken in case of problems
Even if the fuse is blown, you should not immediately buy a new replacement device or try to turn it on. First, it is recommended to check the condition of the wiring and connected devices, as well as the presence of defects, signs of burning, and melting. When, after replacement, it burns out again, resume troubleshooting.
Repair work
In the process of detecting a malfunction of a unit that causes a fuse to blow, it is recommended to disconnect it from the on-board network and, if possible, send it to an electrician for repair or replace it. It is not worth repairing the fuses themselves, as this can lead to serious consequences, including a fire in the car. It is better to categorically refuse to use independent fuses, which can pose a serious danger.
Replacement procedure
When replacing a fuse, the likelihood of error increases due to the same size of parts, differing only in color. Product labeling is not always visible. Therefore, when changing low-current fuses, you should be careful not to install a more powerful option.
If a problem occurs on the road
When setting off on the road, you should prepare a supply of fuses that caused complaints when the car was operating. To speed up the replacement of parts on the road, draw up in advance a diagram of the location in the mounting block, the purpose and indicate the denomination on the card.
Mounting block relay in the engine compartment
Convoy
Name
Consumers
Cooling fan high speed relay (for vehicle with air conditioning)
Cooling fan motor
Air conditioning compressor electromagnetic clutch
Low speed cooling fan relay (for vehicle with air conditioning) or cooling fan relay (for vehicle without air conditioning)
Cooling fan electric motor (for a car with air conditioning - through a resistor)
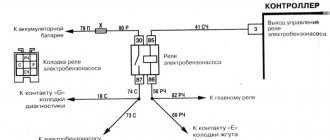
Fuel pump and ignition coil relay
Fuel pump and ignition coil
Engine control system main relay
Oxygen concentration sensors (heating circuit); speed sensor; fuel injectors; adsorber purge solenoid valve; relay windings K1, K3, K2; Engine control ECU
Fog light relay
Fog lamps
Heater Fan Relay
Heater fan motor
In order to replace fuses or relays, you need to disconnect the negative terminal from the battery.
To access the fuses and relays in the engine compartment, press the three latches
Removing the cover of the mounting block
A faulty fuse is determined by a blown jumper visually or using a tester.
To remove the fuses, you can use tweezers, which are located on the cover of the interior block (Fig. 3).
A new fuse or relay should be installed only after the cause of its operation has been found.
It is necessary to determine why the overload occurred in this circuit.
Fuses of the mounting block in the car interior (Fig. 4)
Designation (A)
Protected circuit elements
windshield wiper; coils of the heated glass of the tailgate; switching block
power supply of the instrument cluster; relay windings K4 of the fuel pump and ignition coils;
power supply to the engine control system ECU from the ignition switch
brake lamps
direction indicator lamps; engine management system diagnostic connector; immobilizer coils; switching block
Left headlight headlight bulbs (low beam); signaling device for low beam headlights in the instrument cluster
Headlight bulbs for the right headlight (low beam)
Left headlight headlight bulbs (high beam); high beam headlight indicator in the instrument cluster
Right headlight headlamp circuit (high beam)
F13 (30) and F14 (30)
Electric window circuits for rear and front doors, respectively
ABS control unit circuit
Driver and front passenger seat heating circuits
Audio signal circuit
Left side headlight lamps; side light bulbs of the left rear light; license plate lamps
Side light bulbs for the right headlight; side light bulbs for the right rear light;
glove compartment lamps; illumination of the instrument cluster and controls on the instrument panel,
consoles and floor tunnel linings; switch box buzzer
Lamps and indicator for turning on the rear fog lamp
Circuit of heating elements of external rear-view mirrors
Airbag control unit circuit
Tailgate glass cleaner, glass washer, reversing lamp
Lamps for interior and trunk lighting; constant power supply to the head unit of sound reproduction; instrument clusters
Hazard switch; direction indicator switch; intermittent operation of the windshield wiper; central locking control; engine management system diagnostic connector; switching block
Central locking chains; switching block
Power circuit of the K7 relay winding for fog lights
Heated tailgate glass relay power circuit
Heater fan relay K8 power circuit
Electric drive circuits for exterior rear view mirrors
Cigarette lighter, power supply to the head unit for sound reproduction from the ignition switch
Heater fan relay coils K8
To access and replace fuses in the vehicle interior, remove the fuse cover, which is located on the left side of the instrument panel.
On the inside of the mounting block cover there are spare fuses (rated for rated currents of 5, 10, 15 and 30 A), a tweezer puller for removing fuses from the block, and a diagram of the location of the fuses.
Overcoming the resistance of the cover latches, remove it
The cover contains spare fuses and tweezers for removing fuses.
Basics
The basis for the operation of mechanisms of this type is the transformation of the so-called electromagnetic microwave field. Such fields are transformed into thermal energy and heat the products that are inside. The operating features of a microwave oven differ from other household appliances in which food is prepared: ovens (both gas- and electric-powered) and stoves.
The ability of a microwave oven to heat only the item inside. Because of this, food heats up very quickly. It is this ability that has gained popularity among buyers and has confidently taken one of the leading positions in the kitchen appliances market. Defrosting or heating food did not require the expenditure of excess energy, since in a matter of minutes electromagnetic waves raised the temperature to the desired level. Thus, the cooking and defrosting processes began to take much less time.
Read also: Equipment for the production of plastic dowels
Posts 6
1 Topic by Mixail 2012-10-24 22:22:12
- mixail
- New member
- Inactive
- Registration: 2012-10-24
- Messages: 1 Thanks: 0
Topic: Resolved: Oversize fuse blows
Why does a car battery explode and how to prevent it?
hello, the VAZ2112 size fuse has blown, it’s pitch dark in the cabin
2 Reply from Admin 2012-10-25 06:13:09
- Admin
- Administrator
- Inactive
- Registration: 2012-02-20
- Messages: 3,257Thanks: 624
Re: Resolved: Dimensional fuse blows
Mixail, at what point does it burn out? Often the cause of this may be problems in the contacts of the rear license plate light.
3 Reply from Admin 2012-11-14 06:24:56
- Admin
- Administrator
- Inactive
- Registration: 2012-02-20
- Messages: 3,257Thanks: 624
Re: Resolved: Dimensional fuse blows
Mixail, is the problem solved?
- From: Arkhangelsk region. Velsk
- Registration: 2012-03-16
- Messages: 472Thanks: 229
- Car: VAZ 21124