Defects that appeared after replacing the clutch
What does it mean to replace the clutch? This action means changing the driven or driven clutch disc; often both parts are changed at once. In this case, the release bearing must also be replaced. After such an operation, side defects are suddenly revealed that were not there before the repair.
If we think logically, then there are few reasons for the appearance of new malfunctions. Typically this is:
- Unqualified repairs;
- Defect of new spare parts;
- Erroneous diagnostics, as a result of which not all or the wrong parts were replaced, and previously hidden problems manifested themselves in full.
In general, the issue of the appearance of new unpleasant signs is very difficult and is individual in each specific case, but these signs have common characteristic features.
There can be many sources of noise. What could be the cause of clutch noise?
Extreme wear of the torsional vibration damper
1. Extreme wear of the torsional vibration damper - this severe wear of this clutch element usually occurs as a result of frequent driving at low speeds, extremely irregular engine operation (usually due to some kind of malfunction) or severe wear of the joints in the drive system.
A worn torsion damper causes many components to become overloaded and the driver may be able to hear the noise level.
Separation of the torsional vibration damper cover
2. Torsional Damper Cover Separation - This can be caused by a number of common mechanical problems, including the clutch bell and crankshaft housing flange being off-center or a missing guide bearing. When the torsional vibration damper casings come off, the weakened springs rub against adjacent elements, which is accompanied by a characteristic ringing sound. This type of fault usually also results in problems with the clutch disengaging.
Damage to the clutch slave cylinder
3. Damage to the clutch slave cylinder - due to excessive wear on the clutch, grooves can begin to form on the inner ring of the clutch slave cylinder, which leads to the formation of the so-called relative movement. These movements cause the clutch to heat up and make noise. This type of failure also results in loss of lubrication and therefore a significant reduction in bearing life.
Wrong hub profile
4. Incorrect hub profile - The causes of this phenomenon can be seen in several different mechanical faults, but the most important is the loss of communication between the engine and the transmission. At an early stage, this type of fault leads to noise and clutch disengagement problems.
Broken shock absorber springs
5. Broken shock absorber springs is another problem that can have many causes and will ultimately lead to loss of communication between the engine and transmission. As in the previous case, in its early stages there are problems with noise and clutch disengagement.
If after replacing the clutch the car jerks
For example, before the repair, the car did not pick up speed well, it was slipping, and the clutch pedal was activated at the very top. All the signs of a worn driven disc were present. After replacing the disk, the car began to jerk. What could happen after the repairs were carried out?
- The issue may be a defective part. This is not so rare when it comes to non-original spare parts. In Russian-made cars (VAZ, GAZ, AZLK, IZH), defects also occur in factory parts. That is, the driven disk is simply curved. On the clutch basket (drive disc), the pressure petals may be at different levels, then the release occurs unevenly and the car jerks.
- The car may jerk due to clutch adjustment. More precisely, it was not performed after replacing the disk. The linings of the new part are much thicker; in this case, the clutch pedal “takes at the very end”. When starting off, the car moves jerkily, and the gear shifts into gear with a crunch.
- The car jerks due to the replacement of not all the parts that needed it. In particular, the cause of jerking is the worn surface of the flywheel under the driven disk. If the flywheel has not been replaced, there may be jerking when driving, and the car may also slip.
Signs of clutch problems
Often drivers, especially new car owners, when problems arise with the clutch, realize that the car has begun to behave differently, but continue to drive without making any attempts to find out what the reason is. As a result, this leads to serious damage and the car completely fails. Knowing the main symptoms of a clutch malfunction, you can take timely measures - carry out repairs yourself or contact service center technicians or service stations.
Below are the main symptoms of clutch malfunctions and which unit is responsible for this or that atypical behavior.
Incomplete clutch release
Among motorists - “the car is driving.” In other words, when the clutch lever is pressed, the driven disc is partially disconnected from the motor wire shaft. This leads to the fact that the car begins to twitch at the beginning of the movement at the moment of changing gear, even though the pedal is depressed smoothly, as usual.
What causes this problem to occur:
- Small pedal free play. It may be different for each car; you should look for information in the technical data sheet.
- The drive is poorly adjusted. On mechanical and hydraulic drives, the defect is eliminated in different ways.
- Clutch disc deformation. This happens more often when the axial runout value is greater than 0.5 mm. Under such circumstances, the friction lining of the disk bends and presses it against the flywheel of the internal combustion engine.
- Clutch disc wedge in shaft grooves. A common reason is parking the car for long periods of time, especially outdoors.
That is, it is not so easy to determine exactly what led to the clutch failure, because one defect may be the result of damage to one or more elements.
If after adjustment the defect has not been eliminated, the only option is to replace the clutch with a kit. Always change the clutch as a set (disc, basket, release) since saving on spare parts usually leads to repeated disassembly, loss of time and money.
If there is a noise or whistle after replacing the clutch
Many car owners often complain that after replacement, a noise or whistle appears that was not there before. What could be the reasons for the extraneous sound and why does this happen? » alt=»»>
- The new release bearing turned out to be of poor quality or does not contain enough factory lubricant. A whistling or noise appears when you press the clutch pedal. Many people mistakenly believe that the bearing makes noise when the clutch is disengaged. But this is even illogical, in this state the part does not bear the load, and accordingly the noise (whistle) in this state is minimal.
- The clutch basket has unevenness and roughness at the tips of the pressure petals. Typically, spare parts from Russian manufacturers have such a defect. It should be noted that as the parts are ground in, the whistle that appeared initially disappears. You can temporarily eliminate the noise by lubricating the petals with lithol. But this can be done without disassembly on GAZ cars; on front-wheel drive cars, to perform a similar procedure it is necessary to dismantle the gearbox.
- It is possible that before replacing parts, the car owner did not pay attention to extraneous noises such as whistling, as he was expecting repairs. But after replacing the clutch, extraneous sounds remained, which the owner of the car did not expect. Noises are often caused by the gearbox. If, when the clutch is depressed, the unpleasant sound disappears or noticeably subsides, then most likely this indicates wear on the gearbox input shaft bearing.
- The driven disc linings have roughness. A rustling noise occurs when changing gears. There is no need to worry too much ahead of time - the new parts will get used to it, and the defect will disappear during the operation of the car quite quickly.
- The input shaft bearing in the crankshaft may also make noise. When disassembling the car, you should do an external inspection of the bearing. If it is very dry, it must be lubricated with lithol or other suitable lubricant. It is better to replace a clearly worn part immediately.
Where does noise come from when a car's clutch operates?
Noise, manifested in the form of buzzing sounds of different tones when the clutch is operating (it is turned on, off and when the engine is idling), indicates the occurrence of quite serious problems that require a quick solution.
Clutch design of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars and their modifications
Using the example of the clutch of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars, let’s try to figure out where the noise came from when the clutch was operating and what ways to solve this problem.
Where did the noise come from when the car clutch operates?
Clutch noise when engine is idling
If you listen, from the clutch and gearbox side, while the car engine is idling, you can hear a continuous, distinct noise. When you depress the clutch pedal, the noise disappears or noticeably decreases.
Such signs may indicate a failure of the gearbox input shaft bearing on which the clutch basket and driven disc are “mounted”. The shaft begins to “dangle” together with the broken bearing, making noise, and when the clutch is disengaged, the load on it is reduced and the noise disappears. This malfunction is often accompanied by oil leakage from the gearbox under the input shaft oil seal. In the early stages, the malfunction is practically unnoticeable, but as the bearing deteriorates, it makes itself known.
The release bearing can also make noise and even howl at idle, since its working surface is always pressed against the leaf pressure spring of the basket and rotates with it (the clutch on the VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 is backlash-free). A bearing malfunction may be a consequence of lubricant leaking out of it, after which a play appears and it will begin to make sounds when its moving part rotates. See photo at the beginning of the article.
To determine what exactly is noisy at idle - the releaser or the shaft bearing, we will do the following.
Disconnect the cable from the clutch release fork. We start the engine and leave it idling. Then turn the fork slightly clockwise. The release bearing will come out of contact with the clutch pressure diaphragm spring and the sound should disappear. The howling has disappeared - the release valve is faulty and needs to be replaced. If it does not disappear, you will have to remove the box and replace the input shaft bearing, or replace the oil in it with a better or thicker one.
Checking the serviceability of the clutch release bearing on VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
Noise when disengaging the clutch
If a howling sound is heard from the clutch housing when you press the pedal, then the release bearing has most likely failed. We release the pedal, the noise disappears or decreases. If the bearing jams or is completely jammed, then it will not be possible to press (disengage) the clutch normally. The engine will stall, and it will become almost impossible to “stick” the gear.
Also, when you press the pedal, the clutch may make noise if its drive is not adjusted correctly. It “drives” - the driven disk does not completely move away from the flywheel when turned off, it rubs against it and makes noise. The malfunction can be eliminated by adjusting the drive.
Noise when engaging clutch
When the driver releases the clutch pedal, turning it on, a distinct noise or even rattling, metallic ringing and knocking is heard from the gearbox and clutch.
This indicates wear or breakage of the driven disk (wear, deformation, loosening of its linings, breakage of damper springs) or loosening of the gearbox to the engine.
Notes and additions
— On VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars, the clutch is constantly engaged, that is, the input shaft of the gearbox rotates together with the clutch basket and driven disk. See “Design and principle of operation of the clutch of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars.” When you press the pedal, the release bearing comes into operation, which presses on the pressure spring of the basket, forcing its drive disk to move away from the driven one.
— The operation and serviceability of the clutch can be fully assessed by carrying out a comprehensive check. See “Checking the clutch on VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099”.
If there is a knocking noise after replacing the clutch
As a rule, the cause of knocking after replacing parts is defective parts. In particular, there are dangling damper springs in the driven disk. Therefore, before installing such a spare part on a car, you need to carefully inspect it. Parts of the disk may also be poorly riveted. » alt=»»> Knocks in the clutch area can occur due to a crack in the release bearing bushing (the bushings are often made of plastic). Even at the site where the bushing fits on the flange of the gearbox input shaft, play may form, which also leads to a knocking sound.
The knocking noise occurs due to a broken clutch basket petal, but such a defect occurs infrequently. Another reason for the knocking is a broken starter housing in the Bendix area; it rattles when the car moves. A tooth on the flywheel crown may break off, and it will also knock when touching the rotating parts.
Clutch adjustment VAZ 2109
During the operation of the car, there is often a need for ongoing adjustments, settings and fine-tuning of various mechanisms and systems. This is primarily due to wear and tear of certain parts. The clutch of the VAZ 2109 car is a fairly reliable unit, and there are practically no complaints about it. In the event that it is correctly adjusted and all parts comply with factory standards.
Clutch adjustment VAZ 2109
While operating the car, you may notice that the clutch pedal changes its position over time and the stroke increases. This indicates wear on the friction linings of the clutch disc, but this does not mean that it needs to be replaced. It is enough just to make the correct adjustment, and the clutch will operate normally for some time until the linings are completely worn out.
- We will get acquainted with the design of the clutch drive mechanism later, but now we will consider the adjustment process. It is not complicated and will take a few minutes of time. To adjust, we need a set of keys, more precisely, two 17 keys and a ruler.
- We measure the working stroke of the clutch pedal. To do this, measure the distance from the center of the pedal working platform to the floor, then press the pedal with your hand all the way and measure this distance as well. As a result, we should get a clutch pedal travel of no more than 135 mm. This is the factory norm, and in this case, if the clutch operates normally, no adjustment is required. If the working stroke differs from the norm more or less, then you need to make a simple adjustment.
- Open the hood and find the bracket to which the clutch cable housing is attached. The bracket is fixed to the gearbox and has a groove in which the cable casing is secured.
- Unscrew the locknut. It is located towards the end of the cable.
- By rotating the adjusting nut located inside the bracket, we achieve the required length of the cable casing.
- We actively press the pedal several times and re-check the working stroke of the clutch pedal.
- Having achieved the desired value of the working stroke, tighten the locknut, fixing the casing in the new position.
When to adjust the clutch on a VAZ 2109
The need to adjust the clutch does not arise instantly, but gradually. But if you miss the moment, the consequences can be disappointing
A few signs that it's time to pay attention to the clutch drive:
- the clutch is driving - a clutch that is not completely disengaged results in torque from the engine being constantly transmitted to the gearbox, which can result in difficulty engaging first gear when starting off, as well as when changing gears while driving. The gearbox input shaft will rotate all the time, preventing the gears from engaging. In this case, you can hear the characteristic grinding of gearbox gears, and this is not difficult to understand by the difficulty of shifting gears. In this case, the pedal does not completely disengage the clutch, therefore, the length of the cable casing must be reduced.
- the clutch slips - when the clutch pedal is fully released, the engine cannot transmit all the torque to the gearbox. This happens because the clutch disc is not pressed tightly enough to the engine flywheel and slips. At the same time, it overheats, emitting a characteristic odor that cannot be confused with anything else. To eliminate clutch slipping, lengthen the cable housing.
Malfunctions of the VAZ 2109 clutch drive
Despite the fact that the clutch drive of front-wheel drive VAZ models is designed as simply as possible, there are some parts that can cause the clutch to not operate correctly.
First of all, this is the drive cable itself. The factory cable can last quite a long time, but it also does not last forever. Moreover, the cable always breaks at moments when we do not expect it. Therefore, experienced owners of nines must carry a spare drive cable with them.
A broken cable, as a rule, cannot be repaired, and this is not so necessary. There are many drive cables on sale, but not all of them are of decent quality.
The main thing you should pay attention to when buying a new cable is the careful workmanship in the places where the cable is attached
Maintenance of the VAZ 2109 clutch drive
Only the cable needs maintenance. When replacing it, it is worth lubricating the cable itself, then placing a certain amount of grease under the bellows cap. This lubricant will be enough to ensure that the cable in the housing moves effortlessly and smoothly.
By performing these few simple operations, you will get rid of problems with gear shifting, and you will also be able to adjust the position of the clutch pedal as convenient as possible for driving. Take care of your grip and have smooth roads!
VAZ 2107 - clutch adjustment
Clutch slipping after replacing all its parts
After replacing all elements, adjustment is required, but many car owners ignore this point. The cause is slipping, the car accelerates slowly, the engine speed does not correspond to the speed of the car. The engine just roars, and the car is driving quite slowly, as they say, slipping.
In cars with a mechanical clutch cable, adjustment is made by the cable itself. In hydraulically driven machines, this process is carried out using a clutch rod. In modern cars, you often come across rods that do not have adjustments. But this does not mean at all that it cannot be produced. In such cases, adjustment of the clutch pedal itself is provided, but not everyone knows about this possibility. » alt=»»>
How the clutch works, what are its typical malfunctions, and how to avoid them
An important element of a manual transmission is the clutch, which serves to briefly disconnect the engine from the transmission. In addition, the clutch is a kind of damper that protects the engine from overloads. How does it work and how to extend its life?
How does the clutch work?
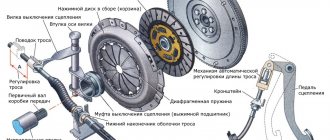
Most passenger cars with a manual transmission use a dry single-plate clutch. Its design is quite simple: it consists of two mutually adjacent disks - a drive (basket) and a driven one, a release bearing and a drive system. In the single-disc version, the transmission input shaft fits into a splined clutch in the center of the driven disk, and the surfaces of the engine flywheel, driven disk linings and basket pressure disk fit tightly together. Due to this, the transfer of power flow from the engine to the gearbox is ensured, and a working clutch calmly “digests” all the power developed by the engine.
In everyday life, the clutch drive disc, which includes a pressure plate (with a smooth shiny surface), a diaphragm spring (petals in the center) and a casing, is called a basket
When you press the clutch pedal, the release bearing acts on the plate springs of the basket, causing the surfaces of the driven and driving discs to separate. Accordingly, the input shaft is disconnected from the flywheel - that is, the engine and gearbox are physically disconnected, which allows you to change gear or engage neutral. When the clutch is engaged (the pedal is released), the release bearing stops pressing on the leaf springs, and the discs close again, and the damper springs in the central part of the driven disc dampen the torsional vibrations that occur during movement.
The four damper springs of the clutch driven disc are clearly visible, as well as the worn friction linings
When the clutch operates normally, it does not attract attention to itself. But if it malfunctions, the driver, for example, will not be able to shift gears or move away. What problems are possible?
What malfunctions can occur during clutch operation?
So, what problems in clutch operation can you encounter in practice? Firstly, this is an incomplete release of the clutch - as experienced drivers say, it “leads”. When you press the pedal, the surfaces of the flywheel and the driven and driving disks do not open completely in this case, and attempts to change gear are accompanied by the crunching and grinding of the synchronizer carriages, because complete separation of the gearbox and the motor does not occur.
The opposite problem is clutch slipping: that is, its incomplete engagement. In this case, the surfaces of the flywheel, driven disk and drive disk, on the contrary, do not fit tightly against each other and slip, which can cause a characteristic smell of burnt friction linings of the driven disk, and an attempt to suddenly pick up speed only leads to an increase in crankshaft speed. In this case, only a small part of the power is transferred from the engine to the wheels - until the wear of the surfaces becomes critical.
If the clutch “slips”, instead of the car, only the tachometer needle “accelerates”
Finally, malfunctions such as the occurrence of vibrations and extraneous sounds when the clutch is turned on and off are also possible.
What causes clutch malfunctions?
Usually, every clutch problem that arises has its own background. For example, the clutch may begin to slip due to severe wear on long vehicle runs, when the friction linings of the driven disk are worn out, and the working surfaces of the basket and flywheel are worn out.
Secondly, the clutch can simply be “burnt” - for example, due to inexperience or after prolonged overload. This, for example, happens to fans of long, “rocking” rides on the roads or in deep snow, as well as to fans of sudden starts with the gas pedal to the floor.
Vibration that occurs after replacing clutch elements
There are few reasons why vibration occurs after replacing a clutch. Vibration usually appears in two forms:
- The pressure plate (clutch basket) is not balanced;
- During assembly, the driveshaft was installed in a different position from the original installation (but this only applies to rear-wheel drive or all-wheel drive vehicles).
By and large, on cars with front-wheel drive, you can inaccurately secure the wheel drive (CV joint), and the movement of the car will be accompanied by vibration and knocking, but this does not happen often.
If the clutch basket creates vibration, you can try moving it to a different position. As a rule, the pressure plate mounts are symmetrical. On many models, the basket is attached to the flywheel with six bolts, and the basket can be placed in three positions. In one position the vibration may disappear completely or be minimal. But it is better to exchange the warranty part immediately for another one. This will be less hassle for the car owner.
The clutch system is the main mechanism of the car, through which torque is transmitted from the power unit to the transmission. The smooth operation of the gearbox and, accordingly, the proper functioning of the gearbox depend on the correct, proper operation of the system. It consists of: a pressure plate, a clutch basket, a drive mechanism and a release bearing. When you press the clutch pedal, a mechanical (using rods) or hydraulic (using liquid) drive acts on the release bearing, which presses with the help of a damper spring, in common parlance: the clutch basket, the friction disc to the flywheel.
A bearing made of high-alloy steel is a fairly reliable part, but frequent connection of the clutch (driving a car in a big city), improper operation of the mechanism: holding the car for a long time with the clutch pedal depressed (a mistake by inexperienced drivers) leads to overheating and destruction of the bearing race. Replacing the clutch release bearing is described in the step-by-step instructions below.
How does a clutch work in a car?
The main purpose of the clutch is to smoothly connect the engine flywheel to the input shaft of the gearbox when the car starts moving, as well as when changing gears. Another important task of the unit is to protect the transmission from mechanical overloads during sudden braking, thus preventing the possibility of breakdown and costly repairs.
There are several classifications of clutches. Depending on the number of slave disks, they can be multi-disk or single-disk (this is the most common type).
Depending on the environment in which the mechanism operates, it can be “dry” or “wet”. Currently, automakers prefer the first option, which does not require a special oil bath for operation.
The classification of clutches in accordance with the drive allows us to distinguish between hydraulic, mechanical, electrical or combined mechanisms. Depending on the design features on the pressure disk, the springs can be arranged in a circle or have a central diaphragm.
The clutch consists of:
- clutch disc (called “driven”);
- pressure plate;
- release bearing and its drive fork;
- drive system and clutch switch (release pedal).
The operating principle of a single-plate automobile clutch is that the working surfaces of the flywheel, disc linings and the pressure surface of the “basket” are tightly attached to each other. Under the influence of the release springs on the pressure plate of the “basket”, the latter is pressed tightly against the clutch disc, causing it to adhere to the flywheel.
The input shaft, entering the splined coupling, receives torque from the clutch disc. When the pedal is depressed, the drive system is activated; under the pressure of the release bearing, the release springs move the working surface of the “basket” away from the disc. The freed disk stops causing the transmission input shaft to rotate, while the engine continues to run.
We recommend
Double-disc clutches consist of two discs and a “basket” that has two working surfaces. The mechanism is supplemented with limiting bushings and a system for adjusting synchronous pressing. The principle of operation itself is similar to that previously described.
Signs of a faulty mechanism
The only sign of a faulty release bearing is an unusual sound (noise, whistling, knocking) when the clutch pedal is depressed, which disappears when the pedal is returned to its place. In winter, in severe frosts, noise is often heard when the clutch is engaged, but you should not pay much attention to this, since the materials from which the mechanism parts are made react differently to temperature changes, and the sounds disappear during the warming up process. There are no external, visible malfunctions of the unit, since the bearing is located in the clutch housing. The regular appearance of noise with each press of the clutch pedal indicates an imminent replacement of the release bearing. Unusual sounds occurring when the clutch is depressed indicate a malfunction in the gearbox.
The clutch started making noise. What's happening?
The noise or hum that occurs when the clutch pedal is depressed can be barely noticeable at first. It disappears as soon as the driver releases the pedal, does not cause discomfort and does not give any particular cause for concern. Over time, the noise increases, but the car owner’s hearing gradually gets used to this sound, and meanwhile, this is a sure sign of increased wear of the release bearing. Moving along the axis of the gearbox shaft, the bearing puts pressure on the petals of the basket, briefly stopping the transmission of engine torque.
Bearing replacement
Spare parts and tools
We recommend watching this video:
Without a pit, a lift and the help of a friend, it will be very difficult to complete the task. So if you decide to replace the release bearing yourself, you should provide as much space as possible under the bottom of the car for removing and installing the gearbox. The tool set is very simple: wrenches of various sizes, a container for draining oil, molybdenum high-consistency lubricant.
Algorithm for performing repair work on a unified unit
The work of dismantling the unit is labor-intensive, but does not require special mechanical skills; the main thing is to follow the sequence of actions:
- disconnect the battery;
- disconnect the cable or hydraulic clutch. On some cars, for example: Nissan, this requires removing the air filter and the battery mounting plate;
- disconnect the gear selector;
- dismantle the engine compartment protection;
- on cars with front-wheel drive or all-wheel drive, it is necessary to drain the oil from the gearbox, after which we disconnect and remove the front drives;
- on cars with rear-wheel drive and all-wheel drive, remove the driveshaft;
- disconnect all sensors and wires leading to the gearbox;
- Having installed the stops under the gearbox, unscrew the bolts connecting the gearbox to the power unit and mounting it to the car body, and carefully, without damaging the input shaft, remove the assembled mechanism;
- release the spring fastenings of the clutch release clutch and disconnect it from the drive;
- remove the clutch from the gear selection shaft;
- remove the bearing from the coupling;
- apply a thin layer of high-consistency lubricant to the surface of the gearbox input shaft (excess lubricant in the clutch mechanism leads to slipping of the clutches);
- install a new release bearing;
- install the transmission in the reverse order;
- connect all sensors, actuators and connectors;
- fill in the transmission fluid recommended by the manufacturer;
- pump the hydraulic clutch drive;
- adjust the mechanical drive of the system;
- install and connect the battery.
For proper use of fasteners, it is worth putting them, when dismantling, into labeled containers.
Features of the clutch system of some cars
Car manufacturers have taken different approaches to the design of the clutch mechanism; in cars of the French concern PEUGEOT, the release bearing, when you press the pedal, does not press, but pushes out the damper.
On some cars, for example: Volkswagen, equipped with a 020 gearbox, the release bearing is replaced without removing the gearbox. This part is located in the rear part of the gearbox. To replace it, you need to remove the left front wheel, disconnect the clutch drive, remove the box housing plug, move the pusher aside and replace the bearing.
What happens if you don't change the input shaft bearing?
When operating a box with a faulty input shaft bearing
Clutch disc failure and many other malfunctions may occur, the elimination of which will require spending a lot of money.
Interesting materials:
How is an examination by a narcologist for your license carried out? How is an appointment with a narcologist? What is the procedure for replacing rights? How to puncture a wheel with a self-tapping screw? How to pave the way? How to clean the air flow sensor? How to flush the throttle valve? How to flush the internal combustion engine when changing the oil? How to wash the catalyst on a diesel engine? How to flush out old oil from a gearbox?
Main problems after replacing the clutch
What does the concept of replacing a clutch include? Clutch replacement means complete replacement of the clutch disc. Quite often, after such manipulations, previously non-existent side effects appear.
If you think about this problem, then there are not very many special prerequisites for the emergence of such negative aspects. As practice shows this:
- illiterate work of non-professional craftsmen;
- factory defect of a new spare part;
- incorrect diagnosis of the problem, due to which the wrong elements or not all components requiring repair were replaced. As a rule, after this, hidden defects reveal themselves fully.
In general, the problem of the emergence of new problems and defects in the operation of a car is very complex and individual in each specific case. But there are still common characteristics.
Adjusting the clutch system and release bearing
Good performance properties of a car depend on the quality of operation of three motion systems: gas, brake and clutch mechanisms. To adjust the clutch, sometimes it is enough to adjust the drive; in other cases, repair and replacement will be required. Adjustments must be made on time to avoid breakdowns that require large financial costs. The main signs of a malfunctioning clutch mechanism: the car moves jerkily, jumpily, the lever sinks, various sounds are emitted from the gearbox. Ideally, after depressing the pedal, the car should move slowly and smoothly. Sometimes a lot depends on the little things, and it would seem that such a small part of a large machine, like a release bearing, is a drop in the bucket. But in practice, everything is not so; even the smallest particle that has become unusable requires attention. An experienced driver will be able to repair or replace the release bearing; a beginner will most likely go to the nearest service station or try to solve the problem on his own by reading this article. Good luck on the roads!
Which release bearing to choose
Release bearing with fork from Valeo
It is better not to purchase only a release bearing. If clutch elements are from different manufacturers, an imbalance may occur during operation. It’s not difficult to select the entire clutch system kit: focus on popularity among customers, reviews, the name of the manufacturer and the established reputation of the store. A one-piece set of excellent quality is produced by Valeo.