Repair manual for Lada Kalina
- Motorcycles
- Jawa Reviews/Tests
- IZH
- Minsk
- Ural/Dnepr
- Sunrise
- Scooters
- Jawa
- Jawa
- VAZ
- VAZ
- VAZ
- Motorcycles
friends of site
- Auto-Literature:
- VAZ
- UAZ
- GAS
- Audi
- Alfa Romeo
- Volkswagen
- Peugeot
- Renault
- Mercedes
- BMW
- CITROEN
- Fiat
- Ford
- Skoda
- SEAT
- Honda
- Mazda
- Nissan
- Opel
- Volvo
- Toyota
- Mitsubishi
- Daewoo
Maintenance of an injection engine (your topic is a control system)
Table, categories of operating conditions.
Category of operating conditions
A distinction is made between daily maintenance (DM), first maintenance (TO-1), second maintenance (TO-2) and seasonal maintenance (SO) for electronically controlled power systems. The frequency or mileage (in km) of TO-1 and TO-2 is established depending on the category of vehicle operating conditions. In our country, four categories (I-IV) of operating conditions have been adopted (Fig. 2.1.) (with a small letter)
The first maintenance (TO-1) includes checking the tightness of the fuel and air supply system, as well as the correct operation of the air damper drive. Fuel leaks and air leaks are not allowed. The throttle valve opening should be smooth and without jamming. During the TO-1 process, the gap between the electrodes of the spark plugs should be adjusted, and if necessary, they should be replaced. The gap between the spark plug electrodes is checked using a wrench and a feeler gauge. The gap should be 0.70-0.85 mm.
During TO-2, you should perform the same operations as during TO-1, checking the fastening of the exhaust and intake pipelines, as well as the exhaust pipes of the muffler. Loose nuts securing the fuel, air and exhaust systems should be tightened. Next, you need to check the fastening of the fuel rail, tension roller, ignition coils, engine pulleys, the condition of the exhaust gas recirculation system and clean the receiver. If necessary, replace the air filter element.
During seasonal maintenance (SO), parts of the fuel injection system must be washed without disassembling the oil deflector.
The fuel tank should be filled only with clean gasoline, and sediment and water should be drained from it periodically (in the fall). In the future, it is necessary to carefully check the tightness of the fuel line connections when the engine is idling.
Each subsequent maintenance begins with the completion of the previous operations. The operations for all brands of engines are basically the same. Some differences are caused by design features of the engines. Maintenance of the internal combustion engine consists of its external cleaning, control inspection, general diagnostics and diagnosing and regulating its systems. External cleaning of the internal combustion engine is carried out by first blowing it with compressed air, followed by wiping with cloth ends soaked in kerosene or diesel fuel.
How to check and adjust the pressure of the Priora fuel pump
Normal pressure of the Priora fuel pump is necessary for the process of supplying the combustible mixture to the carburetor and its normal spraying through the nozzles. The slightest disruption in the operation of this system leads to the fact that either an excessively saturated or lean mixture is supplied to the combustion chamber, which is why the engine operates abnormally. How to check the fuel pump pressure, and what should be done if it is abnormal?
Checking the fuel pump pressure
The first thing to do is to specifically check the operation of the pump. To do this, just turn the ignition key not to the extreme position and listen to whether the electric fuel pump turns on (and this is exactly the variation that is installed in the Lada Priora car). If you hear a noise for a few seconds, followed by a click, everything is fine.
Using a pressure gauge, the check is performed on the ramp - this is where the protective valve cap is hidden, which does not allow air to get in, but presses the fuel out with pressure. The first step is to unscrew the cap and check whether the rubber in it is broken - this may be the main reason for the inoperability of the fuel pump. If it is damaged, it is better to completely replace it; fortunately, it is cheap. Then the spool is twisted. Next, a pressure gauge is connected to the outlet of the safety valve from the pump. Normal pressure is in the range of 380-400 kPa. If it is lower, then either the pump has failed or there is a blockage in the system. If it is more, then it is quite possible that the internal pressure gauge of the fuel pump is faulty and it is simply pumping fuel excessively to the carburetor. Replacing it is easy.
Naturally, before checking the pressure, the ignition is turned on, but the engine itself is not. The pump itself will equalize the pressure to the desired parameter. If this is not done, then the pressure will be at the level of 1 atmosphere with a slight deviation, because pumping is not performed.
It should also be taken into account that all manipulations are carried out at reduced fuel pump pressure. To do this you will need:
- remove the rear seat and gain access to the pump (by removing several screws on the rubberized cover);
- release the lock and let the fuel run out completely (the engine will be in neutral gear and will stall literally after a few seconds);
- Next, you need to turn on the ignition and equalize the pressure;
- It is also recommended to turn on the starter for 2-3 seconds and immediately reset the ignition key to its original position (turn off the ignition).
What happens if the pressure deviates from the norm?
If the pressure in the fuel pump is too high, too much fuel will be supplied to the carburetor.
The air will mix with it through the filter and burn in the cylinder. But if there is a lot of fuel and not enough oxygen, the mixture will not burn completely. At the same time, black smoke comes out of the exhaust pipe, and fuel drips from its end (may even be mixed with soot).
If the pressure in the system is very low, the mixture will be lean. There is too much oxygen. At the same time, the engine power is radically reduced; at idle speed the engine simply stalls, and the choke, of course, will not help, since it only regulates the operation of the throttle valve in the carburetor.
It is interesting that the on-board computer will not report a breakdown of the fuel pump - this is truly a huge mistake by VAZ engineers. In Priora, you can only read indicators when you connect a computer to the EMU unit, but not everyone can do this. And the indicators may not be true if the on-board computer itself is damaged. That's why checking with a pressure gauge on the ramp is the best option for checking pressure.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QaJwthsYi3Q
How to change the coarse mesh
The work package for replacing the first stage filter consists of several stages:
- Buying a new part.
- Preparation of tools and repair site.
- Disassembly, removal of the gasoline pump and replacement of the mesh catcher.
To replace the old dirty mesh, you need to remove the fuel pump
How to choose a Kalina mesh filter is described in the previous section. The location for repair work does not matter, since you do not need a car overpass or inspection ditch - disassembly is carried out from the interior.
Preparatory stage
In warm weather, disassemble the car directly on the street, but in windy weather, find a quiet place, otherwise dust will blow into the interior. In winter, it is more convenient to work in an insulated garage or box.
The tools you need to prepare are:
- a Phillips and flathead screwdriver;
- pliers;
- a small chisel or metal point;
- hammer;
- clean rags.
To disassemble and dismantle the fuel pump you will need a modest set of tools
Before starting work, remove unnecessary objects from the rear row of seats, and then remove the seats themselves. They block access to the technological opening with a hatch leading to the fuel tank. The latter is attached to the bottom of the car from the outside.
Removing the fuel pump and replacing the mesh
The first step is to relieve excess pressure in the fuel line, otherwise when the pipes are removed, a stream of fuel will splash around the trim and the pungent smell of gasoline will “linger” in the cabin for a long time. There are 2 ways to relieve pressure:
- Pull out the 15 A fuse for the fuel pump electrical circuit, located under the cover in the center tunnel. Start the engine and wait until it stalls due to lack of fuel. Repeat the operation 2-3 times.
The fuel pump electrical circuit fuse is located under the cover on the center tunnel.
- Open the hood and locate the injector fuel rail valve. It is located on the right side (in the direction of travel) under the receiver and is a regular spool (the same ones are found in tires). Place a small container and press the valve, after twisting the protective cap.
The pipe with the spool is located behind the engine to the right of the ramp
After removing the rear seat, you will have access to a hatch covered by a fold-down trim flap. Place the cover aside and proceed to disassembly, performing the operations in the following order:
Take a Phillips head screwdriver and remove the 4 screws holding the hatch in place. Remove the cover.
The hatch is screwed to the bottom of the car with 4 screws
Disconnect the negative terminal from the battery, then disconnect the fuel pump power connector.
To disconnect the connector, you need to pry the plastic tab with your finger.
Squeezing the plastic retainer with your hand, pull the first pipe from the pump fitting. To remove the second tube, bend the metal bracket and plastic latch.
The pipes leading to the pump are held on by plastic latches
The pump housing is held in place by a lock washer. To unscrew it, use a small chisel and lightly use a hammer to turn the washer counterclockwise.
The lock washer is loosened by light blows of a hammer through the adapter
Remove the locking plate and carefully remove the fuel pump from the tank. At the same time, tilt the body to the side so as to pull out and not bend the float
Cover the opened hole with a clean rag to prevent debris from accidentally getting into the tank.
Pull out the pump carefully so as not to damage the float
Disconnect the internal pump connector (located under the cover) and remove it from the glass by bringing together the 4 long plastic latches.
To remove the pump from the glass, you need to press the plastic latches
The old mesh is simply pressed onto the fitting and removed by hand.
The mesh is removed and placed on the pump fitting by hand
It is advisable to remove dust with a vacuum cleaner so that it does not fall into the open tank
The new strainer is installed on the fitting until the latch clicks, after which the assembly can be assembled in the reverse order. Before doing this, look inside the glass where the gas pump is located: if you find dirt at the bottom, remove it with a rag or wash it with a brush soaked in gasoline. Before starting the engine, turn the ignition on and off several times, allowing the fuel pump to raise the pressure in the line to normal.
The above-described procedure for replacing the coarse filter element is performed in the same way on Kalinas with different body types. The same technology is used when repairing a Lada Kalina Sport car.
Replacing a faulty valve
The regulator to be replaced is located in the fuel block, which includes other elements: an electric fuel pump, a coarse filter and a Kalina fuel level sensor.
You will need to remove the entire unit from the tank and then change the regulator. To do this, relieve the pressure, as described above, and then remove the rear seat. The module is located under a hatch covered with a mat and sound insulation, which moves to the side. You need to unscrew the screws and remove the hatch, then disconnect the wires and fuel hoses.
The pressure ring holding the assembly is twisted to the left. You can move it from its place with light blows of a hammer on the protrusion through the adapter. Then the fuel module along with the float is carefully removed from the opening.
You need to remove the wire from the regulator installed in it and pull out the spring retainer with a Phillips screwdriver. After this, the valve can be easily removed and replaced with a new one. Before reinstalling, the O-rings of the new part must be lubricated with fresh engine oil.
When assembling the unit, it is important to monitor the condition of the gaskets and replace them if worn. When installing the fuel module into the opening, you need to ensure its orientation; the arrow on the cover should point towards the trunk
At the end, it doesn’t hurt to check the pressure again, and only then you can screw in the spool and start the engine.
To be sure, the Lada Kalina should be tested in motion, making sure that the dynamic properties of the car are restored.
Lada Kalina fuel pressure regulator
If on the first modifications of VAZ engines with distributed injection the fuel pressure regulator was located in the engine compartment on the ramp, now the designers of the Lada Kalina 8 valve placed it inside the tank. Now this important element of the system is located in a single fuel module along with a pump and filters for fine and coarse cleaning; this is the entire fuel system.
This solution creates certain difficulties in terms of diagnosis and replacement, since partial disassembly of the tank will be required during the operation. Despite this, even the owner of a Lada Kalina, who does not have enviable experience, is able to identify and eliminate the malfunction.
How does the regulator (RDT) work?
The fuel system has a fuel pressure regulator. This injection system component is a conventional diaphragm valve. Its task is to maintain a constant level of pressure in the line and ramp, regardless of the operating mode of the motor. The pressure generated by the pump is maintained within 3.7-3.9 bar. If the upper threshold value is exceeded for some reason, the valve immediately directs excess fuel into the tank. When the fuel pressure is insufficient, the RTD is not able to increase it. If the valve fails, it can itself cause a decrease in pressure.
The operating features of the power supply system are discussed in detail in the diagram below.
To correctly diagnose the fuel pressure regulator, you will need to familiarize yourself in detail with the algorithm of operation of the injection system.
- When the ignition is turned on, the fuel supply pump (item 6) comes into operation. It creates the required pressure in the ramp (item 2) and the line. If after a few seconds the starter is not turned on, the on-board controller gives a command to turn off the pump power circuit.
- First, the fuel passes through filters designed for coarse and fine (item 7) cleaning. Next, it is sent to the fuel pressure regulator, after which it is supplied through the line (pos. 4) to the ramp and injectors (pos. 3).
- The start and further operation of the LADA Kalina 8 valve engine is characterized by fuel combustion. It is sprayed into the manifold by means of nozzles, after which, mixing with air in a certain proportion, it is directed into the engine chambers, where combustion occurs.
At idle speed, the RTD dumps the overwhelming share of fuel into the tank (position 5), because consumption is insignificant, and the pressure generated by the pump is constantly high.
At higher speeds the situation is different. Here the valve does not operate in reset mode, since the engine requires large portions of fuel.
Experts distinguish between two types of RTD faults. This is a decrease in the pressure level in the line or, conversely, its excessive increase. In the event of a breakdown, the LADA Kalina 8 valve element cannot be repaired. It is being replaced with a new analogue.
How to diagnose a malfunction?
Among the first signs indicating that the fuel system is faulty is a sluggish engine response to pressing the gas pedal, as well as difficulty starting. If there is a decrease in pressure, then the Lada Kalina engine does not have enough fuel for normal operation. This confirms the weak speed gain during acceleration. When the pressure is excessive, the car behaves confidently while driving, but the LADA Kalina engine is not able to start stably. This is explained by fuel overflows, which is pronounced in the summer.
The first step is to measure the fuel pressure. To do this, you will need to equip yourself with a pressure gauge, which is equipped with a spool nozzle. A similar device measures the pressure inside wheel tires.
We act in accordance with the algorithm below.
- With the LADA Kalina engine cooled down, open the hood and remove the plastic cap located at the end of the fuel rail (item 1 in the diagram).
- Place a suitable container under the fitting. We press the spool to relieve pressure, and then unscrew it (see photo).
- We put the pressure gauge hose on the designated fitting.
- To start the unit, you will need a wire that connects the positive terminal of the battery to the contact present on the diagnostic connector. It is marked "11". The ignition must remain on. The time to check is about 10 seconds.
Lada Kalina engine repair, valve grinding, cylinder head repair, pistons replacement
The mileage of the Lada Kalina car is 100 thousand km. in eight years. The car has an HBO. The viburnum engine has become less dynamic, the response is not the same.
And one more thing - I didn’t like the clattering noise in the viburnum engine.
Missing the third cylinder, trimming, Brains of HBO Alpha-S.
I decided to disassemble and evaluate the condition of the crank mechanism. We removed the cylinder head and pumped the pistons. It turns out they are very worn, but the rings are in good condition. So you need to repair the Lada Kalina engine
cylinder block 8 valve engine Lada Kalina 1118
Condition of the cylinder block between the first and second, as well as between the second and third cylinders
I immediately noticed a slight burnout (carbon deposits) on the cylinder head of the viburnum fret between the second and third combustion chambers of the cylinders. Most likely the cylinder head gasket is loose
cylinder head of 8 valve engine 1118
Piston sizes are different! .On one piston the inscription G-B2
. As far as we know, this means group B
, and the “finger” marking is 2.
The connecting rods, bearings and valve guides were within normal limits. We bought a piston 2110 D=82mm E3 with rings and pins assembled. Group D was not found, so we took E. The fitting showed that everything fits perfectly.
Replacing the electric window
If the window lift cable on a Lada Kalina car has become unusable or the motor has burned out, the ESP must be changed. We carry out the replacement operation in the following order:
- dismantle the power window control unit;
- remove the door trim;
- to disconnect the window regulator from the glass, the latter must be raised all the way up;
- unscrew the four bolts that secure the glass to the ESP (two in the front and two in the back). The glass is held on by seals, but it can also be secured so that it does not fall down;
- unscrew the black metal strip (three screws);
- unscrew the eleven window regulator fasteners (10 bolts), disconnect the power plug from the electric motor;
- We begin to remove the power window from the rear, first removing one half of it;
- then we take out the front part along with the motor from the door cavity;
A burnt-out electric motor on a lift can be easily replaced. For this:
- unscrew the three studs on the mechanism body, then four more screws;
- dismantle the motor, holding the cable spool with your hand, install a new part;
- We install the window regulator in the door, connect it to the glass guides, and put the trim in place.
Replacement
Replacing the RTD on a VAZ 2110 is not a complicated process when using our instructions. Even an amateur can cope with this task. Before starting work, you need to prepare the tool and vehicle.
Preparing the car
Before starting work, it is necessary to relieve the fuel pressure in the system. To do this, remove the fuel pump fuse (F15), it is located under the panel on the passenger side. We start the engine and let it run until it stalls.
Next, we remove the negative mark from the battery to avoid fire, since we will be working with flammable substances, such as gasoline.
Step-by-step instruction
Using a 24mm wrench, unscrew the nut securing the return tube to the RTD and remove it.
Installation of a new RTD is carried out in the reverse order. Before installing a new regulator, it is recommended to replace the sealing collar and lubricate it with gasoline before installation, so as not to damage it during the process of connecting the RTD to the ramp.
Checking Sensors and MI
The maintenance manual for fuel-injected vehicles equipped with electronic control systems describes the procedure for finding faults when it is impossible to start the injection engine.
The procedure for finding faults is simple and clear. If the engine does not start at temperatures above 10 degrees, this technique quickly helps to determine the malfunction of the injection engine in service conditions with diagnostic tools available.
It’s another matter when you are on the road and your engine stalls and refuses to work, or starts and immediately stalls. It’s even worse when your car is parked and the temperature outside is below -10 degrees. Under these conditions, it is not possible to carry out the described procedures completely and quickly eliminate the malfunction, especially since the engine has just been started and there were no visible problems with the control system.
Checking ventilation and stove Lada Kalina
Car owners claim that Kalina’s heater heats much better than previous VAZ models. It sometimes breaks down and requires repair. Do a full system diagnostic to ensure it's working properly.
- We start the car engine.
- Turn the left handle counterclockwise and place it in the blue zone.
- We place the fan speed switch in each of the 4 positions one by one. If the fan does not rotate in one of the positions, then check the power supply circuit of the device.
- Turn the speed controller to maximum.
- Using the right handle (damper control) we check the redirection of air flows. If we notice that there is no change, then the damper drive needs to be repaired.
- Warm up the engine to 90°C. Turn the left handle to the extreme position of the red zone.
- The air that comes out of the panels should blow warm air.
- Return the left stick to the blue zone. Cold air will come out of the nozzles again.
- If the temperature of the air flow does not change due to a change in the position of the regulator, then the control of the central damper drive is faulty.
Causes and Troubleshooting
If the above symptoms are detected, you should check the performance of the RTD using one of the suggested methods:
- measure the pressure in the fuel rail, its value should be at least 3 bar;
- find the return hose and carefully press it with pliers while the engine is running;
- disconnect the vacuum pipe leading from the manifold from the regulator.
The most reliable way is to measure with a pressure gauge. The device is connected to the fitting on the fuel rail, the test is performed with the engine running. If the pressure is below 3 Bar, additionally check the fuel pump - the unit may have lost performance. For diagnostics, you will need a tee with a pressure gauge embedded in the supply line. If the pump produces 3 Bar or more, change the RTD.
The reasons for valve failure look like this:
- the spring has lost its elasticity and allows the membrane to bypass fuel at low pressure;
- pollution with low-quality gasoline;
- rod jamming.
Due to the design features (the element body is rolled), repairing the fuel pressure regulator is impossible in most cases; the part will have to be replaced. The option of washing and blowing helps only with blockages inside the element.
Squeezing the return line is done at idle speed of the engine, preferably “cold”. If engine performance stabilizes, there is a problem with the RTD or pump. To determine the “culprit”, you will still need to measure the supply pressure. Try removing the vacuum tube from the manifold at higher speeds - if the valve has become unusable, the behavior of the power unit will not change.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=PEMmSVodwLU
In this article I will talk about what a fuel pressure regulator (FPR) is, where it is located, and also how to diagnose it yourself.
The pressure regulator is located on the fuel rail, its task is to maintain the correct pressure in the fuel system under different operating conditions.
How does the fuel pressure regulator work?
The pressure regulator is a diaphragm valve, on one side it is acted upon by fuel, on the other by the intake manifold spring. When the engine is released from the load, the valve opens, after which the unused fuel is returned back to the fuel tank. Once the fuel pump is turned on, fuel is drawn from the tank, cleaned in the fuel filter, and then passed to the regulator, which maintains the correct pressure in the fuel system during this cycle. The main task of the RTD is to maintain optimal pressure in the fuel system and ensure proper engine operation. Due to lack of pressure, engine operation changes; if you checked the pump, fuel line and found no abnormalities, most likely the problem is in the fuel pressure regulator. Signs of a faulty RTD:
1. Unstable engine operation;2. The car stalls at idle and reacts poorly to the gas pedal;3. Reduced engine power, poor dynamics;4. The engine choke while driving; 5. Increased fuel consumption.
Causes of fuel pressure regulator malfunction
1. The valve cannot hold the required pressure. The reason may be that the valve spring has sagged, causing it to return fuel back to the tank, causing the engine to start poorly;2. Fuel flow is obstructed or a complete blockage has occurred; 3. The valve is stuck. The pressure changes unevenly, as a result of which the car begins to jerk, especially during acceleration.
How to check the fuel pressure regulator, that is, do-it-yourself diagnostics of the RTD
There are several ways to check RTD at home. One of the most “ancient” testing options is to clamp or disconnect the “bypass valve”, while monitoring the force of the jet. This method of checking the fuel pressure regulator was practiced by our grandfathers on the first VAZ models. After carburetors were replaced by injectors, the method became irrelevant.
The most accurate and effective way to check the pressure in the fuel system is to use a pressure gauge.
In order to measure the RTD pressure in the engine at idle speed, it is necessary to connect a pressure gauge between the fitting and the fuel hose, and disconnect the vacuum hose. During measurements, the pressure in the system should increase from 0.3 to 0.7 Bar.
The process of checking the pressure in the fuel system
You will need: an air (or preferably a water) pressure gauge, onto which you need to put a hose with a diameter of 12 mm and tighten it with a clamp. The engine should be cold and the generator covered with a rag.
- Unscrew the cap of the control fitting on the fuel rail (fitting). Near the timing belt (on the right in the direction of travel), or on the left near the oil filler neck (for the VAZ 21129 engine);
- Unscrew the spool from the fitting using the wheel valve cap. At this moment, due to the residual pressure in the rail, gasoline will splash out (you can first relieve the rail pressure by removing the fuse from the fuel pump with the engine running and wait until it stalls).
- We put the pressure gauge hose on the ramp fitting and secure it with a clamp;
- Turn on the ignition. The fuel pump will turn on;
- We check the readings on the pressure gauge.
What pressure should be in the fuel rail? On VAZ 2110, 14-15, 99 models it should be in the range of 2.8 - 3.2 bar. On modern engines (Priora, Granta, Kalina, Vesta, XRAY, etc.) the pressure should be 3.6–4.0 bar. The process is also shown in the video:
How to check the fuel pressure regulator?
There are several simple ways to determine the causes of problems and defective components:
- Visual method. A simple inspection without the use of any fancy tools is fine for carburetor engines. Pinch or disconnect the valve and observe the flow of fuel. The intensity of the fuel flow will help identify the malfunction. This method of verification is effective in its own way, but one cannot count on absolute accuracy.
- Method using a pressure gauge. Place a pressure gauge between the fuel hose and the fitting. To do this, temporarily disconnect the vacuum hose. The pressure level should change from 0.3 to 0.7 Bar. If the pressure indicator has not changed, repeat the operation with another hose.
- Hose clamping method. The pressure regulator is checked by pinching the return hose. A pressure gauge connected to the fuel system should give an immediate response. If the motor does not develop normal speed, you can determine the inoperability of the RTD without the device. Start the engine and clamp the return hose. Then track the RPM and listen to the engine. If the engine starts to run smoothly, then the problem lies in a faulty control valve that needs to be replaced.
Features of checking the fuel regulator
To solve the problem, it is important to know how to check the fuel regulator. This can be done using a regular pressure gauge. Everything is simple here. The device is mounted in the space between the fitting and the fuel pipe. To take measurements, the vacuum hose must be disconnected.
In this case, measurements should be made in four different modes:
- When the ignition is turned on. The nominal parameter is “three” atmospheres;
- when measured at idle – 2.5 atmospheres;
- in case of squeezing of the return flow hose - 7 atmospheres;
- with the hose removed from the pressure regulator - 3.3 atmospheres.
If the measured parameter does not correspond to the specified data or does not increase at all, then the device is faulty. In such a situation, it is enough to figure out how to change the fuel pressure regulator and perform the replacement.
Be attentive to your car, promptly respond to problems that arise, carry out diagnostics and make repairs. This is the only way to extend the life of your VAZ car and protect yourself from high costs in the future. Good luck on the roads and of course no breakdowns.
Basic malfunctions of the injection engine power system
All modern cars with gasoline engines use a fuel injection system, since it is more advanced than a carburetor, despite the fact that it is structurally more complex.
The injection engine is not new, but it became widespread only after the development of electronic technologies. This is because it was very difficult to mechanically organize control of a system with high operating accuracy. But with the advent of microprocessors this became quite possible.
The injection system differs in that gasoline is supplied in strictly specified portions forcibly into the manifold (cylinder).
The main advantage of the injection power system is compliance with the optimal proportions of the constituent elements of the combustible mixture at different operating modes of the power plant. Thanks to this, better power output and economical gasoline consumption are achieved.
LADA KALINA. Injector malfunction, which takes out the brain.
Hello. Today I want to continue the series of articles about the symptoms of faulty injection wiring. Using the Lada Kalina car as an example.
In my practice, there were cases of malfunctions in the engine control system, which sometimes baffled me. One of these reasons was on Kalina.
The owner of the car complained about floating speed, increased fuel consumption, loss of dynamics, and an illuminated engine malfunction lamp.
When connecting diagnostic equipment, we see an error on the oxygen sensor: “lean mixture”. At the same time, at idle, the oxygen sensor works: it draws a sine wave. But as soon as the engine cooling fan turns on, its signal shows 0.1-0.2 Volts, which corresponds to a lean mixture. The engine begins to idle unsteadily.
After the fan works, the oxygen sensor also hangs in a lean mixture until you change the gas several times.
After all the checks (measuring fuel pressure, checking for air leaks, timing marks), all that remained was to check the injection wiring. And indeed, when the wiring moves, next to the electronic engine control unit, the oxygen sensor readings return to normal.
We unravel the injection wiring in the car interior and find massive twists. Over time, the copper in them oxidizes and the ADCs of the sensors begin to float.
We also unscrew and clean the ground wire that goes from the engine to the body.
I wrote about this in previous articles, but the symptoms of the malfunction were simply different.
We solder the twists. After this, we are happy that the engine is working properly.
This wiring problem occurs on Lada Kalina cars produced before 2011, with a mechanical throttle cable.
I hope the article will be useful to car enthusiasts.
Malfunctions in the fuel vapor recovery system Lada Kalina
Since the solenoid valve itself is not a complex device, it has few malfunctions as such - it may not open or close when necessary, or may freeze in a certain position. But the culprit of the breakdown may not only be Evap-Solenoid; the gasoline vapor recovery system does not work correctly for other reasons:
- connecting pipes are pinched or clogged;
- normal vacuum is not created in the system;
- due to an open circuit, there is no voltage on the valve;
- the carbon filter is completely clogged (which is rare);
- The control unit malfunctions.
If the CPA is stuck in the open position and does not block the channel, the following defects may occur:
- the fuel mixture becomes richer, causing “blackness” to appear on the electrodes of the spark plugs;
- the engine begins to operate unstably, this is especially noticeable at idle;
- gasoline consumption increases;
- The throttle response of the internal combustion engine decreases.
When the EVAP channel is constantly blocked by the purge valve, excess vapor pressure is created in the gas tank, due to this:
- there is a risk of fuel pump failure;
- The fuel level sensor may fail.
It should be noted that purge occurs in a certain mode after starting the engine, the program is executed depending on the crankshaft speed, and the system does not work at idle. An impulse arrives at the CPA if:
- the coolant has heated to a temperature of at least 75 degrees Celsius;
- the throttle valve is open at least 4%;
- the car is moving at a speed of more than 10 km/h (but this is not a necessary condition).
Problems in the electrical part of the EVAP are detected by the control unit, and the Check Engine warning lamp lights up on the instrument panel. The fault code can be determined using a special diagnostic scanner or a computer with a program installed; the most common errors in the vapor recovery system detected by the diagnostic device are P0441 and P0455.
Payment via PayPal
After selecting payment via PayPal, the PayPal payment system will launch, where you need to select the payment method: bank card or PayPal account.
If you already have a PayPal account, then you need to log into it and make a payment.
If you do not have a PayPal account and you want to pay using a bank card via PayPal, you need to click on the “Create an Account” button - shown with an arrow in the picture.
PayPal will then prompt you to select your country and provide your credit card information.
After specifying the information required to make the payment, you must click on the “Pay Now” button.
Signs of malfunction of the fuel pressure regulator viburnum
Hello everyone, I continue to run in the new engine, I started turning it up to 5000 rpm. And sometimes problems with traction appeared, namely, a cut-off effect was created at 4000 rpm. Those. The revolutions stupidly dropped to zero and the car did not want to go until the revolutions dropped below 3000. This happened on the old engine, but then I blamed it on a burnt gasket, but then I realized that this was connected with one of the engine systems. It also happened that with about 13 liters left in the tank, the car swallowed air and stalled like a diesel engine, at first it sputtered terribly and then fell silent, although the pump should clear the air lock. All symptoms pointed to problems in the fuel system.
the injectors were washed during assembly, the fuel pressure regulator (fuel pressure regulator) and the pump itself remained.
Checking the pressure in the system is very simple. You need a pressure gauge, a hose and 2 clamps. Do not forget that the pressure gauge accurately shows in the second third of the scale, i.e. if you need to measure pressure in the region of 2-4 kgf/cm2, you need to take a pressure gauge from 1 to 8-10 kgf/cm2. As a last resort, you can remove the pressure gauge from the pump, the main thing is that the limit is around 7 kgf/cm2. I took a certified pressure gauge for 10 kgf/cm2.
It is connected to the old and new model ramps in the same way. Remove the plastic cap from the end of the ramp
Under the cap there is a fitting in which a regular wheel spool is wrapped, unscrew it with the cap from the wheel (IMPORTANT! The system is under pressure, be careful when unscrewing the spool
), or better yet, remove the pump fuse or connector from it and start the car to relieve pressure in the system. And then we put on our hose with a pressure gauge.
Now we check the pressure regulator; to do this, at idle, remove the vacuum hose from the receiver; the pressure should jump sharply by 0.7-0.9 kgf. If this does not happen or happens slowly, the regulator is faulty.
Worked great for me, I changed it a year ago.
Next, we check the fuel pump itself; to do this, open the throttle at idle and look at the readings. The pressure should not fall below 2.2 kgf. If the pressure does not drop, read how to check the filter, if it drops like mine, then just read why it could be
, I dropped to 1kg. The drop may occur due to clogged filters or a half-dead pump. Now, in order to find the culprit of all the troubles, at idle we use pliers to pinch the fuel return, which comes from the pressure regulator. In this case, the pressure should reach 5-7 kgf/cm2. Those. the pump should pump more than 5 kgf at point-blank range. Now we watch how this happens, if the pressure reaches above 6 kgf but for a very long time, about a minute or more, clogged filters are to blame (coarse cleaning in the tank, or fine cleaning near the tank). If it does not reach at least 4 kgf, then the pump is dead, i.e. it works but not as it should. My pump cannot pump up even 3 kgf at point-blank range. The verdict is pump replacement.
Before this, about 3 years ago I already changed the pump, I had no experience then and a couple of times I got up with a dry tank. And now this happened due to a faulty device. All the readings on it are lying, so a replacement is being prepared for it with a 2110 tidy. In general, do not leave gasoline at the bottom of the tank, always keep at least 15 liters in it, the pump does not operate dry, there is no cooling by the flowing medium, i.e. gasoline, in the best cases, wear of the pump and a drop in pressure, and then complete failure. At worst, overheating and ignition inside the pump. There will be no explosion, but it will definitely scare you with smoke.
There was nothing to do, I had to take money and look for a new pump, by the way, 3 years ago I bought the original BOSCH for 750 rubles. He stood the same. Now, having asked for the original, I was shocked by the price of 1600 rubles. It's all about Kalinas and Priors, the prices of spare parts for them are higher than for the same Samara, but the pump, unfortunately, is the same everywhere, and thanks to the new markings because... Samaras are out of production, considered like a pump for a Priora, which is why the price is the same. But I went a different route and found in Magnitogorsk a functional analogue of the BOSCH from SOATE. But the price is 780 rubles. I also took a new coarse filter (crow's foot) and fine filter from SCT.
For those blog readers who follow my YouTube channel, the information will not be new, but for the rest I will describe everything here. So over the past few days my Kalina has started having problems. And they were as follows:
- After a long period of inactivity, the engine began to start poorly, often even on the second try.
- the car became very “dull”, and it felt like the loss of power was about 20%
- fuel consumption increased by 10% when the engine was idling, and when driving too
In general, based on all the signs described above, it looked like a dying gas pump. Of course, I checked the mass air flow sensor first, since its operating voltage is also already close to critical. But when it was turned off, nothing changed for the better.
As a result, I began to deal with the fuel system. I’ll say right away so that there are no unnecessary questions:
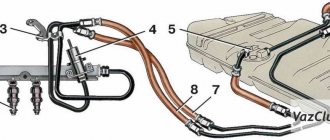
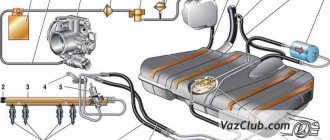
Fuel system Lada Kalina
Engine power system diagram:
1 - separator;
2 — filling pipe; 3 — hose for supplying fuel vapors from the tank to the separator; 4 — pipe for removing fuel vapors from the separator to the adsorber; 5 — ventilation tube; 6 — ventilation tube hose; 7 — filling pipe hose; 8 — fuel tank; 9 — tee; 10 — adsorber; 11 — fuel supply tube to the fuel rail; 12 — fuel vapor supply tube to the canister purge solenoid valve; 13 — adsorber purge solenoid valve; 14 — fuel rail with injectors; 15 — throttle assembly; 16 — hose fuel supply to the tee; 17 — fuel filter; 18 — fuel supply hose to the fuel filter;
19 - fuel module.
Fuel is supplied from a tank installed under the bottom in the rear seat area. The fuel tank consists of two stamped steel parts welded together. The filling pipe is connected to the tank with a gas-resistant rubber hose. A ventilation tube is welded into the upper part of the filling pipe, connected to the tank with a plastic hose. The ventilation tube is used to remove air displaced from the tank when it is filled with fuel. The fuel tank ventilation inlet and outlet valves are built into the filler plug.
Fuel module
A fuel module, including a fuel pump, a fuel pressure regulator and a fuel level sensor, is installed in the fuel tank. For rough fuel cleaning, there is a strainer at the module inlet.
Fuel gauge sensor
The fuel level indicator sensor controls the operation of the dial gauge and signaling device located in the instrument cluster
Fuel pump
Fuel pump - electric, submersible, rotary. The fuel pump is turned on by a command from the electronic control unit (controller) when the ignition is turned on, through a relay. The pump creates a pressure in the system that exceeds the operating pressure in the fuel rail
Fuel filter
From the pump, fuel is supplied under pressure to the fuel filter. The fine fuel filter is non-separable, with a paper filter element. The filter is mounted on the fuel tank bracket, on the right. There is an arrow on the filter housing that must coincide with the direction of fuel movement.
Fuel pressure regulator with o-rings
After the filter, a tee is built into the fuel delivery line, through which fuel is supplied to the fuel rail and the fuel pressure regulator located in the fuel module. The fuel pressure regulator is a valve that opens when the fuel pressure in the line exceeds, releasing part of the fuel into the tank.
The pressure regulator is not dismountable and must be replaced if it fails.
Fuel rail
The fuel pressure in the fuel rail with the ignition on and the engine not running should be between 3.6 and 4.0 bar. The fuel rail is a tube with injectors installed on it. The ramp is attached to the inlet pipe with two screws.
Fuel under pressure is supplied to the internal cavity of the ramp, and from there through nozzles into the intake pipe.
O-ring nozzle
The injector is an electromagnetic valve that allows fuel to pass through when voltage is applied to it and closes under the action of a return spring when there is no power. At the injector outlet there is a sprayer through which fuel is injected into the intake tract. The controller controls the operation of the injectors. The injectors are sealed in the ramp and inlet pipe with rubber rings and fixed to the ramp with metal clips. If the winding is broken or shorted, the injector should be replaced. If the injectors are clogged, they can be washed without dismantling at a special service station.
Air supply elements to the throttle assembly:
1 - air intake;
2 — air filter; 3 — mass air flow sensor housing; 4 — air supply hose to the throttle assembly;
5 — hose of the main crankcase ventilation circuit
Air is supplied to the engine throttle body through an air intake, an air filter and a corrugated rubber hose. The air filter is installed in the front left part of the engine compartment on three rubber holders (supports). The filter element is paper. After the filter, the air passes through the mass air flow sensor.
Throttle assembly
The throttle assembly is a throttle body (with channels made in it), on which the idle speed regulator and throttle position sensor are installed. The throttle assembly is fixed to the intake pipe. To avoid freezing of the throttle assembly at low temperatures and high humidity of the ambient air, a heating unit is built into the assembly, through which the cooling system fluid circulates. When you press the gas pedal, the throttle valve opens, changing the amount of air entering the engine (the fuel supply is calculated by the controller depending on the air flow).
Idle air control (IAC)
When the engine is idling (throttle valve closed), the controller controls the air supply using the idle air control (IAC). The idle air control is a stepper motor that moves the valve. The valve shut-off element (needle) changes the flow area of the channel and provides regulation of air flow bypassing the throttle valve. To increase the crankshaft rotation speed at idle, the controller sends a control signal to open the valve, increasing the air supply bypassing the throttle valve, and, conversely, to reduce the rotation speed, a command is sent to close the valve. In addition to controlling the crankshaft rotation speed at idle, the controller controls the IAC, reducing the toxicity of exhaust gases: when braking the engine, the throttle valve closes sharply. In this case, the IAC increases the air supply bypassing the throttle valve, resulting in a leaner fuel mixture. This helps reduce hydrocarbon and carbon monoxide emissions. The idle air control is non-separable and must be replaced if it fails.
Separator
The separator is installed in the right rear wheel arch. Fuel vapor from the tank is partially condensed in a separator, from which the condensate is drained back into the tank through a hose and filling pipe. The separator is equipped with a gravity valve that prevents fuel from leaking out of the tank when the vehicle rolls over. From the separator, fuel vapors enter the adsorber (installed on the top of the fuel tank, on the left side) through a fitting labeled “TANK”, where they are absorbed by activated carbon. The second canister fitting with the inscription “PURGE” is connected through the solenoid valve for purge of the canister with the throttle assembly, and the third with the inscription “AIR” is connected to the atmosphere.
Adsorber
The canister purge solenoid valve is installed on a bracket attached to the air filter housing.
Canister purge solenoid valve
When the engine is stopped, the purge solenoid valve is closed, and in this case the canister does not communicate with the throttle assembly. The controller, by controlling the solenoid valve, purges the canister after the engine has operated for a specified period of time from the moment it switches to the closed-loop fuel supply control mode (control sensor oxygen must be heated to the required temperature). The valve connects the adsorber cavity with the throttle assembly - and the sorbent is purged: fuel vapors are mixed with air and discharged through the throttle assembly into the intake tract and further into the engine cylinders. The greater the engine's air consumption, the longer the duration of the controller's control pulses and the more intense the purge.
Selecting new filter elements
To purchase fuel purification system parts for VAZ 1117-19 models, you need to know what they look like:
- The coarse filter is a flat mesh bag made of chemically resistant plastic that captures large particles of 80-100 microns. In the center of the element there is a plastic fitting that fits onto the counterpart of the gasoline pump.
- The fine filter is made in the form of a cylinder with two fittings at the ends. The body is made of metal or special plastic - polyamide, and there is filter paper inside it. It traps particles measuring 15-50 microns. The pipes are equipped with clamps for fastening fuel hoses.
There are no tricks in choosing a coarse mesh - the parts are made according to a single sample and cost from 30 to 45 rubles. The only caution: in order not to purchase a low-quality product or a fake, contact well-established stores. Although the fuel pump mesh costs a penny, it plays an important role in the fuel system: it catches large debris that can quickly clog the filter paper of the next cleaning element.
In operation, the plastic case is not inferior to the metal one in terms of reliability.
The material from which secondary filters are made does not play a big role
What is important is the contents of the “barrel”, which cannot be seen or touched. Therefore, there are only 3 selection criteria:
- correspondence between the body dimensions and the diameter of the fittings;
- the presence of plastic clamps;
- brand (manufacturer).
The mounting clamp on the Kalina is designed for a case diameter of 56 mm
There are many different fuel filters sold in stores, and not all of them are equipped with clamps (in other cars, the hoses can be secured with clamps). The part for “Kalina” must have latches, otherwise the tubes cannot be secured.
A plastic latch secures the hose to the filter fitting
In the countries of the former USSR, the following manufacturers of gasoline filters have proven themselves best:
- BOSCH;
- FRAM;
- FILTRON;
- SCT Germany;
- UFI.
At the moment, second-generation Kalina machines are equipped with fine filters made of polyamide. But users are not very complimentary about the factory spare parts: after disassembly, it was discovered that the paper “accordion” was poorly glued to the body. As a result, half of the fuel passed through the gas pipeline without filtering. At the same time, based on the practice of isolated cases, it cannot be unequivocally stated that metal filters are better than plastic ones.
Inside the filter element there is porous paper that traps small particles