Any battery tends to discharge, even if it is not used, that is, the car is idle for a long time. This problem is especially acute in winter, as well as when operating a car in urban conditions, when the generator simply does not have time to deliver the required charge.
Therefore, from time to time the battery needs to be charged using the standard charger. But in some cases, dismantling the battery is fraught with unpleasant consequences, so the question of whether this procedure can be performed without removing the terminals interests many.
In what cases is it necessary to charge the battery without removing the terminals?
If the car is equipped with volatile electronic devices, even a short-term power outage can cause important settings to be reset, which car owners try to avoid. Another unpleasant consequence of a power outage is the activation of the device’s security lock.
If removing the protection by entering digital codes does not take much time (provided that the driver remembers these codes), then you will have to tinker with restoring the settings.
But the worst thing that can happen when removing the battery is resetting the data in the ECU memory. For example, about daily mileage and fuel consumption, which will affect other related parameters (maintenance period, etc.). When using additional equipment, restoring settings may require contacting the manufacturer's website or service center, which means a large loss of time. Finally, careless or incorrect removal or reattachment of terminals can lead to a voltage surge with very unpleasant consequences for the electronic equipment, especially the powertrain controller. Such a failure will require flashing or, even worse, replacing an expensive unit.
Why is the battery low?
There may be several reasons for a rapid, critical discharge of a battery. Here are the most common ones:
- the battery has already reached the end of its life (due to improper or long-term use), the lead plates are badly damaged and do not produce the required amount of current;
- there is a leak in the electrical equipment of the car, and while the car is parked, it simply discharges the battery, the voltage drops;
- The alternator is not working properly, intermittently, and the car battery is not charging properly.
The first reason can only be eliminated by replacing the battery with a new one. But the other two are quite solvable, although sometimes they make you, as they say, sweat. After all, it is unlikely that you will be able to identify the cause of the voltage leak yourself; you will have to visit an auto electrician. Generator repair and diagnostics are also not within the scope of knowledge of the average car enthusiast. In any case, for me, the matter never went beyond replacing the “chocolate”. To Caesar - what is Caesar's, and to the mechanic - what is mechanic's, which means that everyone should mind their own business.
Is it possible to charge a battery without removing the terminals?
Most negative recommendations boil down to the fact that when connecting an external charger to the battery, there is a risk of a voltage surge above the permissible level for the on-board electrical network.
Most standard electronic device controllers are oriented towards a maximum permissible voltage of 15.7 V - this is indeed less than the peak values of some chargers, especially low-quality ones - they allow a short-term increase in voltage up to 18 V.
Therefore, before connecting two devices - the charger and the power source - you need to use a tester to determine the maximum voltage level in the charging circuit. If this is a calcium battery of the first generations, then charging it requires up to 17 V, which is potentially dangerous for on-board electronics. However, modern Sa-Sa batteries can be charged at a safe voltage.
Most rechargers are equipped with fuses that prevent an increase in the current parameters at the device’s output, but there are also models that do not even have such protection. Their use is strongly discouraged without removing the battery from the car.
If the carburetor
Cars equipped with a carburetor power system give a negative answer to the question of whether it is necessary to remove the terminals when charging the battery. In any case, this absolutely applies to Russian-made machines, for which connecting an external charger is absolutely safe. There are nuances with foreign cars - some carburetor models were equipped with an electronic controller, whose task was to adjust the fuel-air mixture, and the necessary data came from the catalytic converter.
Most of these cars were produced in the second half of the nineties, and this allowed domestic car owners to throw away electronics, replacing the carburetor with a mechanical domestic analogue. On those copies where the electronics have not been touched, charging is carried out according to an algorithm characteristic of a car with distributed injection.
If the injector
Today this is the prevailing type of passenger car, but whether it is necessary to disconnect the terminals when charging the battery depends on the specific design. There is a microprocessor unit on the injector itself, and control electronics on the generator. The presence of a fuse is not reliable protection, so when connecting a charger, voltage surges are possible. Therefore, most manufacturers recommend disconnecting the battery terminals.
But there are models on which the opposite is true, that is, disconnecting the battery is undesirable, and charging should be performed in accordance with the instructions.
With the engine running
As soon as the engine is started, power from the on-board network is transferred to the generator, which is also responsible for charging the battery. By connecting a charger to the battery on a running power unit, you risk “ruining” the generator relay-regulator, and at the same time the controller of the charger itself.
So if there is a need to charge the battery without removing it from the car, then doing this with the engine running is strictly not recommended.
If the terminals are dirty or oxidized
The stability of the contact spot is a characteristic no less important than the stability of the current or voltage at the output of the charger. We must not forget that a dirty or oxidized terminal significantly impairs the ability to restore the nominal capacity of the battery, so before charging it is necessary to check the battery terminals and, if necessary, clean them of deposits and traces of chemical reagents.
Tips for car battery care
In conclusion, let's look at preventative measures that will help avoid problems when operating a car. Most of these measures do not take much time and can significantly extend the life of the battery. The main preventive measures are presented below:
- Periodically recharge the battery using a network charger. Ideally, you need to carry out a control-training cycle. CTC is not recommended for calcium batteries sensitive to deep discharge. In winter, the charging frequency should be higher. If possible, in winter you should avoid short trips and frequent engine starts;
- Keep electrical wiring, the car's alternator and the car's voltage regulator in good condition. Periodically check the voltage at the battery terminals while the engine is running. Normal voltage is 13─14.4 volts with headlights, music and heated windows on;
- Check the electrolyte level regularly. This can be done with a glass tube. The level should be 10-15 millimeters above the plates. If necessary, add distilled water. This does not apply to maintenance-free car batteries;
- Keep the battery case and terminals clean. It is necessary to eliminate traces of oxidation and corrosion, wipe off dirt and electrolyte leaks. This will reduce the self-discharge of the battery. The terminals can be coated with a special anti-oxidation compound;
- Periodically measure the density of the electrolyte. The normal value on a charged battery is 1.27 g/cm3. Adjust density if necessary. How to do this is described in the article entitled “What acid is in a car battery and what is the electrolyte for”;
- If you leave the car parked for a long period, then remove the battery from it, charge it and store it separately.
Features of the battery charging procedure without removing it
If you have to charge a car battery without removing the terminals, you should consider the following features of this procedure:
- The charger is connected to the network after it is connected to the battery. After completing the procedure, you first need to remove the wires and only then turn off the power to the charger. Otherwise, there is a risk of damage to the vehicle electronics.
- The positive cable is put on first, the negative cable last. This procedure reduces the likelihood of shorting the battery.
- Before connecting the charger, inspect the wires for insulation damage. Make sure that they do not touch the cooling system fan and exhaust tract components - the possibility of the engine starting even without the key in the ignition cannot be ruled out.
- Before charging the battery without removing it from the vehicle, make sure that all on-board electrical consumers are turned off.
- During charging, ensure the room is ventilated if the car is parked in a garage.
- If the battery is serviceable, make sure that the plugs are unscrewed and the electrolyte level is correct.
- In winter, it is better not to charge in an unheated room - it may take much longer than under normal conditions.
How to properly charge the battery without removing it from the car
If you still decide to charge the battery directly on the car, without removing the terminals, follow the sequential instructions.
- Preparation. Open the hood of the car. We take a tester and take readings. If it shows less than 12.7-12.8 V, then the battery needs to be recharged. For example, it is charged at 70-80%, and additional recharge is needed from an external source.
- Compound. We install the wires of the disconnected charger. The ends of the wires should have crocodile-shaped clothespins. We connect the “plus” first, then the “minus” - although, in principle, if the current circuit 220 is broken, the sequence of connecting the poles does not matter much.
- Connection to a 220 V network. Plug the charger into a socket. We activate the “on” button on the current supply device. We monitor the amperes on the charger. At the same time we look at the voltage scale.
- Standby mode. The battery will take the required amount of energy, and the charger can be turned off.
- Shutdown. Press the “off” button and remove the plug from the socket. Remove the wires from the terminals. We measure the battery voltage - it should show 12.7–12.8 V.
Checking the battery with a multimeter
One of the alternative solutions that makes it possible to reduce the risk of shorting the on-board network when supplying current from an external source is to connect the charger to the cigarette lighter. In this case, the load will be taken over by the spare power supply, which will prevent the risk of a short circuit.
Safety precautions
Even the usual procedure for restoring the capacity of a car battery cannot be called simple, and when trying to charge the battery without removing the terminals, additional difficulties arise.
That is why the procedure must be performed in compliance with the following safety rules:
- you need to work using personal protective equipment (goggles, rubber gloves and an apron), especially if the battery is serviceable;
- when connecting the charger to the battery, the required polarity and order should be observed (described in the paragraph above);
- to prevent accidental turning on of the ignition, remove the key from the lock, having first turned off all electrical appliances;
- do not allow wires to come into contact with any metal surfaces other than the battery terminals;
- Provide fresh ventilation if charging occurs indoors.
Remember that charging the battery without removing it from the car is possible and safe only if the electrical characteristics of the charger correspond to the parameters of the vehicle's on-board network.
Precautionary measures
When working with electric current, safety comes first. For this reason, it is prohibited to perform this operation in a damp room. Failure to comply with this requirement may result in electric shock or damage to the charger.
Modern battery charging devices are well protected from polarity reversal. If the terminals are connected incorrectly, the fuse will blow, but the main circuit should remain unaffected.
It is not recommended to check the functionality of the safety elements, so you should be careful when connecting the wires coming from the charger to the battery.
All electrical contacts must be in perfect working order. The presence of sparks in the immediate vicinity of flammable substances can result in a fire.
Still have questions or have something to add? Then write to us about it in the comments, this will make the material more useful, complete and accurate.
Consequences of battery disconnection
There is no strictly defined range of consequences of disconnecting the battery when it is necessary to charge it. Actually, even in car models that are very similar in functionality, when removing the terminals, you can find completely different results. The most common occurrences are:
- resetting the on-board climate control settings in the cabin;
- blocking the standard radio.
Of course, such problems do not pose great threats. To unlock the media, you just need to enter the code, and the electrical adaptation settings themselves will be restored after a couple of tens of kilometers. However, less common, but no less unpleasant consequences of briefly disconnecting the battery from the car circuit also occur:
- climate system settings failure;
- deleting RAM memory;
- failures in the system of modern speaker systems, which may lead to the need to reinstall the software.
Obviously, after a car owner encounters at least one of the described (or undescribed) problems, he has a desire to eliminate them in the future. Therefore, the question of whether a battery connected in a circuit can be charged becomes relevant and quite logical.
Self-chrome plating of parts: instructions, tips
Carburetor type
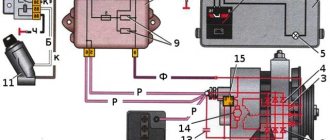
There can be no problems here at all - ZERO. There is simply nothing to burn here, because there is no computer here! Except for the relay-regulator , but even if it fails, most likely it will simply recharge your battery. BUT the charger has no effect on this relay! How does the charging system of this variant work? The diagram is a little exaggerated, but it is just needed to understand the process.
After starting the engine, the generator begins to produce energy; it is closely connected to the engine crankshaft through a belt drive. The energy is intermittent and is removed by special “brushes” from the rotor. Next, the energy is “rectified” through a special “relay-regulator rectifier”. It provides a constant voltage of, say, 13.8 - 14.2 V, sufficient to charge the battery.
It is clear that when the power unit is operating, the generator powers all other equipment necessary for igniting fuel, lighting, etc., the battery is simply charged in this mode.
The generator cannot recharge the battery, everything is controlled by special “relays”; this is the mechanical principle of charging.
In a carburetor car, there are no specialized control units at all; here many operations are performed mechanically.
Actually, if you do not remove the battery from the car, connect the ends of the charger to the terminals, and the engine will not work at this time. Nothing bad can simply happen, the battery will be charged the same way as from a generator, and the “relay” will essentially be de-energized. Personally, I myself have done this many times, on my VAZ 2101 - 2105.