Component acoustics
Component acoustics consists of several speakers, there may be two of them, in which case it is a two-component system, or there may be three, in which case it is a three-component system. As a rule, such acoustics are installed at the front of the listener.
Speakers for a component system can be selected separately or purchased as a ready-made kit. It should be noted here that all components in the kit are balanced with each other. If you want to purchase speakers separately, you will need to take into account their frequency ranges and select a crossover.
A crossover is needed in order to divide the signal between different speakers and send high frequencies to tweeters or high-frequency speakers (HF), and middle frequencies to midbass or midrange.
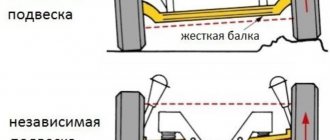
One of the advantages of component acoustics is that they can be correctly positioned in the car. This complicates installation, but significantly improves the sound quality of the system.
Due to their characteristics, high-frequency speakers have a narrow directivity, that is, undistorted sound propagates close to the direction axis. Therefore, they need to be placed facing the listener, approximately at the height of the head (ears).
HF installation example
Then you get the highest quality and detailed high-frequency sound that these tweeters can provide. They are usually installed in the corners of the side mirrors or in the windshield pillars.
Example: HF in the corner of the mirror
In three-component acoustics, the midrange speaker (MF) has a sound propagation angle that is not much greater than that of the tweeter, so its directionality is also very important. They are installed according to the same rules, usually together with tweeters
Example of setting midrange and treble
In midbass, the sound spreads much wider. Therefore, they are suitable for installation in a standard place in the door. True, to maximize the impact of good sound, they are slightly turned towards the listener, giving better directionality. This is exactly why podiums are made or door cards are remade.
Example of a podium with a twist
Do not neglect this, if you have such an opportunity, such a nuance will significantly improve the sound quality of the entire system. Thus, the location of the speakers is one of the key components of good sound, regardless of the price and level of components. After the components are installed correctly, it feels as if a film has been removed from the speakers or some kind of obstacle has been removed. The sound becomes cleaner and lighter. Therefore, direct, not reflected sounds reach the listener.
Component acoustics can be connected without crossovers - channel by channel (each speaker to a separate amplifier channel). However, be careful with the HF cutoff setting, as if the playback frequency is too low for the tweeters, they may burn out. These values are individual for each model.
Example of a channel connection diagram
In this case, if you have a sound processor, there are many possibilities for customizing the sound of the audio system. The processor can fully control the filters, their cuts and orders.
The processor also controls time delays, compensating for the difference in distances from the speakers to the listener.
External sound processor
Example: Pioneer DEX-P99RS processor radio
It is with their help that the so-called stage is set, when it seems that the instruments are positioned in space and it seems that the sound sources are some distance ahead, but this is a topic for another material.
Coaxial or wideband acoustics
Wait for the search to complete in all databases. Upon completion, a link will appear to access the found materials.
Go to search results >>>
Thanks to them, electrical impulses are converted into sounds in the acoustic range of different frequencies. For some, the pure sound of musical instruments that is as close as possible to the original is important, but for others, the voice of the vocalist, film actors, or teacher from educational video courses comes first.
How important is the sound system?
It is the basis for the entire audio system.
Moreover, different equipment options will be a priority for each. The choice is influenced by such factors as the “tailoredness” of such a system to those genres that the future owner likes and the price category.
For lovers of the most accurate sound, hi-fi speaker systems are suitable. Despite the myths, not every expensive audio equipment offers the mentioned capabilities.
When exclusivity comes first, the audio market provides fans of high-quality sound with Hi-End audio equipment.
Speaker types
There are several categories of speaker systems, each of which is capable of satisfying specific customer needs. Based on basic differences, there are 5 basic classification groups.
- The principle of equipment installation. Acoustic systems are divided into floor-standing and bookshelf depending on their size. The former are preferable for large premises such as cinemas. Using them at home for a TV or computer is unprofitable. It is best to use bookshelf speakers.
- Number of speakers. Otherwise, this is called division by the number of sound bands. The manufacturer may include from 1 to 7 speakers. The most optimal option for the budget is 3 speakers, where one band is responsible for low frequencies, another for middle frequencies and a third for high frequencies.
- The presence or absence of a sound amplifier in the speakers. In the first case they are called active, in the second - passive. Passive options are much more common. They are preferred by audiophiles due to the crossover filter and, accordingly, higher sound quality due to frequency separation.
- By design, speakers are divided into planar, dynamic, electrostatic and other types, and in some cases the equipment does not fall into any category.
- Design. Speakers can have a closed or open body; a good addition would be a bass inverter - a pipe in the speaker tuned to a certain frequency and amplifying sounds within its limits. Thanks to this hole, lower frequencies are reproduced than with conventional equipment. If the pipe is bent inside the housing, increasing its length, power and range of reproduced low frequencies, you will get speakers with an acoustic labyrinth. They are more expensive and require greater precision in manufacturing.
Areas of use of acoustic systems
The first and main area of application is home use.
This includes the need for high-quality sound for greater immersion in video games, power and strength of sound for watching TV, clarity and proximity to the original sound for music lovers of various genres.
Moreover, for better sound, high-frequency and mid-frequency elements of the Car system are located in the front of the car. Low-frequency speakers are often assigned to the rear of the car.
Concert versions of acoustic systems are designed not only to provide sound access to any point in a large room or hall, but also to satisfy the sound quality requirements of many listeners. The most common concert audio packages include monitors for nuanced sound, front speakers for high-density direct sound, and center speakers for vocals.
Coaxial or wideband acoustics
A separate category is recording studios. They prefer studio monitors that are capable of reproducing sound with all its pros and cons, which ultimately contributes to the creation of a purer and more authentic-sounding track.
With their help, you will be able to get equipment that will bring you as close as possible to the sound of your dreams.
Most car enthusiasts cannot imagine driving without quality music in the car. Unfortunately, sometimes sound systems are not included with the car when you purchase it. You have to connect the sound yourself or turn to professionals. What is better to choose so as not to be disappointed? There are several speaker systems. Their differences are in quality, price and connection methods.
Car coaxial speakers are a simple and cheap sound option. For example, for drivers who listen exclusively to the radio while traveling and music is only background music for them, this type of acoustics is ideal.
Canton Chrono 503.2
The best component acoustics in a car
Chrono 503.2 is a real German speaker: excellent workmanship, 100% quality control of each copy, Made in Germany. Despite the stated glossy finish, the speaker is covered with film, and only the front panel is made glossy. The size of the speaker is not very large, but the speaker managed to accommodate an impressive 180 mm. Of course, it is equipped with the traditional Canton aluminum diffuser. The suspension is made in the shape of a wave for the most linear and long piston stroke of the diffuser. The 25mm tweeter dome is made from a very lightweight but durable aluminum and magnesium alloy. For reliability, it is protected by a metal grill. There are two threaded holes on the bottom for mounting on a stand or bracket.
Bookshelf speakers Canton Chrono 503.2
SoundThe musical material is presented very carefully. The frequency balance is almost perfect. The timbres of instruments are transmitted with high reliability, and small details are not lost sight of. There is no increased emotionality, but thanks to a wide and smooth dynamic range, the speakers manage to accurately convey the musical idea of the composition. The bass is collected, neat, exactly in its place. However, it is not very deep, and at low volumes it loses its position even more. At first it seems that there are too many high frequencies, but they appear exactly when you really need them, and in the right quantities. The upper register is very clean, which fans of modern electronic music will certainly appreciate.
Measurements
The frequency response is smooth, although it depends quite strongly on the listening angle - the directivity of the speakers is relatively narrow. The THD is very low and there is good headroom at low frequencies. Impedance is unstable.
Coaxial acoustics sound better, it's true
Which subwoofer for a car is better, active or passive?
Coaxial speakers differ in sound in that they have a narrow sound plane compared to component ones. But often this is precisely the plan that is necessary if the main sound supply is for the front passengers. In this case, the speakers, which have a single design, have only an auxiliary effect - sub-sounding. That is, they improve the overall sound background in the car interior. The main role in creating the sound panorama is given to component acoustics, which are located in the front part of the cabin.
Therefore, coaxial acoustics are often installed in the rear part of the cabin (doors, shelf), where frequency separation is not particularly required, or it is simply impossible to install a system of component speakers due to limited space.
sound of coaxial speakers
As for sound quality, much depends on the physical arrangement of the component elements, the orientation of the sound source in space, as well as the transient response of the crossover, which for coaxial speakers has a somewhat simplified design.
In general, it is believed that component speakers sound better, but the quality of the speakers themselves plays a more important role here, since they are the same in the design of both systems. But with the right placement and certain conditions are met, good coaxial acoustics can sound no worse than a separate system.
Polinets › Blog › How to choose acoustics for a car?
It just so happens: for a novice car audio enthusiast, when choosing a music system, the main thing is the head unit! In general, this is easy to explain: after all, it seems that the capabilities and sound of the system mainly depend on it. Unfortunately, this is not so: you definitely need to pay attention to acoustics. We'll talk about it today.
The simplest acoustics are designed for the so-called “background” sound in a car. Indeed, if you listen to news on the radio, why spend extra money? It is quite possible that even the simplest full-range speakers will suffice. Their frequency range will not provide either deep bass or truly high frequencies, but for those who are not too demanding of music, all this will not cause obvious disgust. By the way, in most cars such speakers can be installed at the factory.
If we move up the price range, then the next acoustics are coaxial acoustics. There are actually... several such speakers in the design! The playback range is divided into areas - each “subordinated” to its own dynamics. Special filters (crossovers) are used as “separators” of the electrical signal, and then each speaker has his own. More serious models may have a crossover in a separate housing, while simpler models sometimes make do with a capacitor (the simplest filter) on the speaker housing. The Full Tank community reminds us that correctly selected filter components play a significant role in the sound of the acoustics as a whole.
The advantage of a coaxial speaker over a broadband speaker is its greater coverage of the reproduced frequency band. The main residence of coaxial acoustics is the same standard places, but the most expensive representatives of this “breed” can also be found in serious projects - with the manufacture of podiums and other tricks.
The next variation on the theme of acoustics is component acoustics, the most common among car enthusiasts who are not indifferent to sound. The playback range - just like that of coaxials - is divided into several parts. There are still the same crossovers, but the speakers are not made in a single design, but separately - components that no longer “interfere” with each other (for example, high-frequency drivers do not stand in the way of wave propagation by low-frequency drivers). But this solution also has a disadvantage: the “coaxial” plays “from one point,” and the component acoustics play the way they are installed.
The loudspeaker is a group emitter.
About the design and operation of the car What is better than Lada Priora or 2112. What is better than VAZ2112 or Priora. Calculations and miscalculations
A group emitter is a set of similar dynamic heads placed in the same plane at a certain distance from each other and connected to each other in phase, series or parallel, or series-parallel. To ensure good performance of a group radiator loudspeaker, it is necessary that all heads are of the same type and the same power is supplied to each head. Failure to comply with these requirements or disruption of the in-phase operation of the heads reduces the efficiency of the group emitter.
The widespread use of loudspeakers of this type abroad is due to several reasons. The first is that using several low power heads you can create a high power loudspeaker. Thus, a Swedish amateur radio magazine published descriptions of amateur loudspeakers containing up to 6-8 similar broadband heads of 20 W each. Such speakers can work with amplifiers with output power up to 100-200 W.
Another reason for the proliferation of group emitters is their inherent improvement in output at medium and especially the lowest frequencies. This improvement is due to an increase in the opening area of the diffusers, proportional to the number of heads. At the lowest frequencies, this increase is 6 dB for four heads, 8 dB for six and 9 dB for eight. Due to this, the bandwidth of effectively reproduced frequencies is expanded into the region of lower frequencies by about a third or half an octave compared to the bandwidth of a single head in the same design.
The third reason is that the depth of the cabinet box of such a loudspeaker can be 1.5-2 times less than a loudspeaker with a single head, i.e. the group emitter can be quite flat and can be placed on the floor near a wall or even hung on wall.
Let us dwell on two design options for a group radiator type loudspeaker containing four dynamic heads of 6 W each. In these loudspeakers it is most convenient to use low-frequency drivers of the 6GD-2 type. When the hole diameters are reduced, it is possible to use heads like 4GD-4 or 4GD-7, 4GD-av. 4GD-35, 4GD-36. Preference should be given to the first and last two heads.
The design of the housings of both options is shown in Fig. 3,a,b. The housings are made of chipboard 20 mm thick. The parts are assembled using screws and glue. The difference between the options lies in the shape of the front wall: in Fig. 3, and it is flat, in Fig. 3.6 – slightly folded in the middle. Both designs have approximately the same characteristics in the low-frequency region. The results of the calculations carried out by the author are shown in Fig. 4, from which it can be seen that a noticeable increase in the output of the heads with a distance between the centers of their diffusers equal to 260 mm is observed starting from a signal frequency below 600 Hz.
The main advantage of a loudspeaker with a broken front panel (Fig. 3, b) is a slightly better uniformity of radiation at mid and high frequencies in both planes. In a loudspeaker with a flat front panel (Fig. 3a), on the contrary, the radiation pattern at these frequencies narrows.
Group radiators have been widely used recently; they are often used as low-frequency radiators in systems with several signal frequency division bands. Such systems, designed for input power up to 50-100 W or more, are widely used for sound stages, dance halls and discos.
Foreign amateur radio designs. Moscow, “Radio and Communication”, 1982.
Acoustics with which we live → ← The best is the friend of the good
Low frequency driver
A woofer is often also called a woofer. For almost any class of acoustic systems, the woofer is naturally the largest radiator in area. For a low-frequency driver, a fully piston operating mode is preferred, when the diffuser moves back and forth as a single unit.
Here the problem is solved even more radically than in the case of the mid-frequency driver. The diffuser is made as rigid as possible, even by making it heavier. The fact is that at low frequencies our hearing is least sensitive to distortion. And in the case when the amplitude of vibrations is primarily important for the woofer cone, for the sake of rigidity they go for an increase in weight.
24" woofer in Pro Audio Technology subwoofer
The mass of the moving system of many large subwoofer speakers can reach 200 g or more. Diffusers in some cases receive a spatial structure similar to an aircraft wing made of a multilayer composite with the internal cavities filled with light cellular or honeycomb structures.
For audiophile systems, they still try to minimize the mass of the low-frequency driver cone, since trained ears do not like low-frequency distortion, just like everyone else.
Moreover, the oscillation amplitude of the woofers is the largest among all the listed speakers. To do this, they are equipped with a so-called long-stroke (extended) voice coil. The external suspension is made of rubber. All this allows the diffuser to have a very large excursion - this is how the diffuser’s displacement from the central point is called.
18" JBL bass woofer
The “breed” of a low-frequency speaker is especially pronounced in the drivers that are installed in subwoofers. This is a heavy, powerful device with a diameter of 8 to 15 inches (the most common size range in consumer speakers). They have very powerful magnetic systems and, therefore, a considerable total weight. At the same time, in low-frequency drivers operating from powerful semiconductor amplifiers, coils of minimal resistance are often installed - 2 or even 1 ohm.
Advantages and disadvantages
The main advantages of “coaxial” are:
- Easy to install. Their design includes elements that reproduce all frequencies, while only two terminals are used for connection. In the case of a component system, each speaker must be connected separately;
- Due to the somewhat simplified design, the cost of coaxial acoustics is somewhat lower, which is often the main factor when choosing equipment for a car;
- The market offers this type of acoustics with a wide variety of dimensional parameters, which allows you to choose the optimal model for any car;
But they also have quite a few disadvantages:
- Very often the manufacturing quality of such speakers is not up to par, especially from little-known manufacturers. As a result, they can break very quickly;
- Coaxial car speakers are very sensitive to dust and debris. Getting between the heads, dirt leads to a severe deterioration in sound quality;
- Often the number of stripes does not correspond to reality. That is, outwardly everything looks like there are several heads installed on the low-frequency speaker, but in reality there is only one head, and the rest is a fake;
- On inexpensive models, a capacitor acts as a crossover, which naturally affects the sound quality.
It is noteworthy that some manufacturers produce combined acoustic models. That is, there is a set of different-frequency speakers included in the component system. But it is possible to install high-frequency heads on a low-frequency speaker and secure them using special latches, resulting in a coaxial type.
Which is better and for what purposes?
Car acoustics: broadband, coaxial and component
So, we are faced with a difficult choice - what kind of music should we put in the car? Wideband, component or coaxial speakers? Coaxial? What kind of coaxial acoustics are these? — Such a question, alas, is not uncommon. Today we’ll dot all the i’s and learn about these categories of car acoustics in more detail. Let's start with coaxial, since it has a very interesting and promising name:
Coaxial acoustics - gets its name from the type of construction. Coaxial, or coaxial. All speakers located in the device body are located on the same axis. This allows you to significantly reduce the volume they occupy in the car interior, while dividing the reproduced frequency range between the low-mid-frequency speaker and the tweeter - the high-frequency speaker. This separation is necessary for improved sound compared to wideband acoustics (which will be discussed later). Each speaker has its own diffuser and optimal design for reproducing the frequencies assigned to it. A built-in crossover separates the frequencies between the speakers, and in very budget models its role is played by a capacitor.
The main advantage of this design, as mentioned above, is the improved sound quality compared to the sound of a single wideband speaker, with a slight increase in the cost of such acoustics compared to the same broadband speaker. The advantages are also ease of installation and significant savings in space in the cabin, compared to, for example, component speaker systems. The disadvantages include the narrow directionality of sound waves, since all the speakers are concentrated in one place and have the same direction. For this reason, it will not be possible to create a stage effect, which, in turn, allows for component acoustics, the elements of which can be distributed throughout the cabin. In some speakers, the manufacturer used a trick and made a device that allows you to separate the tweeter from the main speaker (or main ones, there are several of them) and install it, for example, in a door. But the thing is that such acoustics are still inferior in quality to component systems, since the price limits for the coaxial acoustics segment have long been determined in the car acoustics market, within which the manufacturer is limited by the quality of materials and the costs of production technology. Coaxial acoustics are an intermediate link between broadband and component and contain both the advantages and disadvantages of both of these solutions.
Wideband acoustics are as simple as two pennies - it’s a speaker that reproduces the entire breadth of frequencies on its own. All the advantages and disadvantages are obvious - price, space saving, ease of connection - simply wonderful. But one speaker, even a very wonderful one, will not cope with the entire spectrum of frequencies; it will master the low frequencies and even cope with the mids, but the high frequencies (and these are vocals) will be difficult for it, even if you conjure up reproduction technologies, then It is unlikely that you will be able to go much further than the midbass (a speaker that copes well with mid and low frequencies), but you can hit the price ceiling of the broadband acoustics niche, exceeding which it will be difficult to sell the device. Therefore, the sound quality of wideband acoustics will be inferior to both coaxial and component ones.
So, component acoustics, about which a lot has already been said above. It should be said that since these speakers are in the most expensive price segment, the technologies used in them are the most advanced. Against the backdrop of market competition, already for 12 - 15 tr. we can get an acoustic system consisting of mid- and high-frequency speakers, a subwoofer and even an external crossover for filtering frequencies. The technologies of materials and assembly of such speakers make it possible to obtain an excellent harmonic signal with low frequency response fluctuations, provide high sensitivity and allow them to withstand high power, which together gives a loud and high-quality sound. Such speakers and subwoofers (if not active ones) are already designed for use in a power amplifier system. The disadvantages of a component acoustic system include the complexity of assembly, connection and configuration, the large space occupied, the need to retrofit the car with podiums, sound insulation, and possibly a new battery or even a generator.
Which is better and for what purposes?
As a result, we get three price niches with different types of acoustics in each. The first is broadband acoustics, the most inexpensive and undemanding, suitable for the same undemanding listener who will use it to listen to the radio or music at low volume. Standard, broadband acoustics in inexpensive cars can cope with such tasks.
Coaxial acoustics are suitable for lovers of fairly high-quality music, but on a limited budget. It will give its user both bass and treble and some volume and sound quality. It is also used in fairly expensive audio systems as rear speakers, saving space and providing fairly high-quality sound support for rear seat passengers.
The main differences between an acoustic component and a coaxial one
Surely you know that acoustics can be coaxial and component. And if you are not sure which one to choose, if you want to learn about the difference between these types or how to carry out the installation correctly, then this material will be useful to you.
The main difference between coaxial speakers and component speakers is their form factor or design. In principle, this is where the pros and cons come from. The name of coaxial speakers comes from the Latin words CO - joint and AXIAL - axis. The name speaks for itself, because here there are two or three speakers together on one axis - high-frequency and mid-bass and/or mid-frequency. In component acoustics, they are separated and are separate elements - components. We've sorted out the names.
The answer to the questions - which is better, which type is preferable to improve the sound of music in the car and what to buy - is simple. These are component acoustics, but not in all cases. Read on if you want to find out why.
Thinking out loud, comparison
Unfortunately, at the moment there is no manufacturing company that would produce ideal component speaker systems; each has its own advantages and disadvantages. And if we assume that the car radio spends most of its working time broadcasting, then a reasonable question arises about the advisability of such high material costs. The ordinary wideband speakers already installed by the automaker will be sufficient, since no acoustic system will be able to qualitatively reveal the deep bass and high frequencies of your favorite radio station. The main difference between coaxial acoustics and component ones is that the coaxial one plays from one point, while the component one plays from the same point as its speakers. As for the playback range, in both cases it is divided into several parts, but in both cases the “high-frequency speakers” do not interfere with the propagation of low-frequency waves. In principle, the speakers in both cases should be as close to each other as possible, this condition is especially true for “high-frequency speakers” connected in a three-way system. Speaker systems differ in the number of connected speakers and sound reproduction formats (implemented by combining several acoustic systems):
- Two-way includes LF/MF (midbass) and MF (tweeter) speakers;
- Three-way - adds another midrange speaker.
Wharfedale Jade 3
The British company Wharfedale traditionally spares neither effort nor materials even on budget lines. And the Jade 3 model once again confirms this. In our test, this is the largest and heaviest shelf speaker, and the only 3-way one. A body with curved walls is a feature of the top lines of many other manufacturers, but not Wharfedale. Both the body shape and the additional bulkheads make the body as acoustically inert as possible, preventing unwanted sound coloration. High frequencies are handled by an aluminum dome tweeter. At the border of 3 kHz it is replaced by a midrange speaker with a diffuser made of aluminum-cellulose composite. And already in the region of 350 Hz, the initiative is seized by the woofer, equipped with a woven diffuser made of a mixture of carbon and fiberglass. The combination of such materials with a braided structure brings the diffuser closer to an ideal piston, eliminating the problematic resonance phenomena inherent in metal diffusers.
Bookshelf speakers Wharfedale Jade 3
The speakers operate in a closed volume. The crossover for the speaker was optimized on a computer for maximum linearity of signal phase transmission.
Sound Wharfedale speakers sound traditionally beautiful. All instruments are clearly arranged spatially. The music stage is clean and spacious.
The speakers deliver bass carefully, not forcefully, as if they are afraid of damaging the balance of the overall sound picture. The same can be said about upper case.
The softness of the presentation of musical material is interestingly and harmoniously combined with excellent sound detail. In addition, the speakers play very well at low volumes.
Measurements
The frequency response of the model is flat, but at high frequencies it behaves in a peculiar way - a decline and a sharp rise. The bass is deep. The SOI is almost perfectly flat and extremely low. Very solid headroom for low frequencies. The impedance is quite stable.
Nuances when choosing
Now about which coaxial speakers are better
When choosing acoustics, you should first pay attention to the manufacturer. Little-known brands do not always produce high-quality products
You should also look at the materials used to make the speaker cones. Low- and mid-frequency speakers sound best when their cones are made of special paper rather than any other materials. As for high-frequency elements, the best option here is a silk diffuser.
Another nuance is the sensitivity of the speaker. The higher this indicator, the better the sound volume.
In high-quality Hi-End coaxial acoustic systems, the crossover is made remote to obtain high sound quality.
Finally, let’s look at what to choose – coaxial or component speakers. It is worth noting here that each of these systems has its own purpose, and they complement each other. If the car does not have any acoustics at all, then after installing only coaxial speakers it is impossible to get good sound. But installing only a component system will not provide surround sound. Therefore, it is recommended to install both of these systems on the car, and subsequently the acoustic system can be improved by installing additional component speakers and better coaxial speakers.
Primary introductory
To begin with, it would be nice to understand that no matter what kind of speaker system you like, it will still be a layout diagram, which is not only a car radio and a pair of speakers, but also an amplifier, a changer, a subwoofer, a lot of wires and mounting devices (example in the next photo).
The difference between component and coaxial acoustics
Coaxial acoustics
The difference between coaxial and component acoustics
Judging by the increasing price factor, the first on this list is an ordinary wideband speaker.
Next on the list is a coaxial speaker for a car radio, whose advantage over a broadband speaker is its greater coverage of the audio frequency range. The design feature of the coaxial speaker system itself is as follows:
- There are several speakers in one housing;
- Reproduction of sound vibrations of various frequencies is divided into areas;
- To separate the electrical signal going from the “head” to the speaker, a special filter is used - a crossover* (in more “serious” models it is carried out in a separate housing, in more “simple” ones an ordinary capacitor is used as a filter).
A crossover is a “capacitor-inductor” circuit, the purpose of which is to separate certain values of the entire frequency spectrum along audio tracks. It is used in both component and coaxial speaker systems.
Advice! Choosing the right filter components plays a huge role in the sound of the entire speaker system.
The main advantage of a coaxial acoustic system is that, without having a large sum of money on hand, it is quite possible to assemble a decent version of the acoustic layout circuit for yourself. And what’s more, installing this system will not cause any difficulties for the car owner; all installation and connection work can be done with your own hands in several stages:
- We install new equipment in its standard place (more expensive modifications, as a rule, are installed non-standardly, on a pedestal, etc.);
- We connect the speaker output directly to the radio itself or to a signal amplifier.
The disadvantages of the system described above include, despite the praise described above, the sound quality, which is somewhat away from the ideal parameters. The thing is that one speaker simply physically cannot clearly reproduce the entire spectrum of sound; frequency mixing is inevitable, which affects the sound quality.
Component acoustics
What is the difference between coaxial acoustics and component acoustics?
A component speaker system looks more favorable in terms of sound quality and undistorted frequencies, in which each speaker reproduces exactly its own frequency range and is connected to its own individual channel of the car radio/amplifier, due to which the entire acoustic circuit works harmoniously and its components do not interfere or interrupt each other.
- The price for this type of acoustics is much higher;
- High demands on the car radio itself (see Compare car radios and choose the best), the prices for which are also “biting” (having connected all the professional “stuffing” to an ordinary “head” you are unlikely to become a connoisseur of good sound);
- Difficulties of installation (it will be somewhat problematic to correctly distribute the frequencies and install the speakers in the car with your own hands, although who knows, it’s not gods who burn the pots, and there are plenty of video instructions on the Internet...);
- In most cases, it will not be possible to avoid the use of additional soundproofing materials in the car interior.
Triangle Color Bookshelf
Very nice-looking speakers from the French manufacturer Triangle are available in three lacquer colors - white, black and red. The Color line stands out with its bright, cheerful style among all Triangle products and takes its place as the entry-level line.
The bookshelf model uses a tweeter with a titanium membrane and a midrange/woofer with a paper cone. In general, the speaker is quite interesting; its suspension is wide, corrugated and basically made of fabric. The paper diffuser is coated with a special compound. The dust cap is designed in the shape of a bullet. The design of the crossover uses developments from the top Magellan line. The bass reflex port is located on the rear wall of the speaker.
Bookshelf acoustics Triangle Color Bookshelf
Coaxial acoustics
So. The advantages of coaxial acoustics are ease of installation. Take the speaker, mount it in its standard place, connect it, and your speaker system is ready. Also, coaxial cables tend to be cheaper. And the main disadvantage, oddly enough, stems from the ease of installation and location of the speakers in one basket. Then you will understand why.
Most often, “coaxials” are used to add audio to the rear zone of a car, as well as in situations where physical separation of high-, mid- and low-frequency speakers is not necessary, or is simply impossible.
Common installation locations are rear doors or rear parcel shelf.
Results
Coaxial acoustics : ease of installation, relatively low price, but the sound quality is lower compared to component acoustics. It is better to use it for sound in the rear area of the car, if needed. Common installation locations are rear doors or rear parcel shelf.
Component : costs more, requires an installation approach. But the sound quality is much higher. Has ample customization options. Installed from the front of the listener.
Description of coaxial acoustics
Here, one design combines more than two speakers. Typically, one speaker with a low frequency is installed, and from one to three high-frequency devices are placed on it. There are models with the addition of mid-frequency speakers. But they are more expensive.
The system can be divided into strips. Then the speakers will reproduce the frequencies each separately. To do this, a special filter is built into the design - a crossover. For simple models, a capacitor is connected. It performs a filtering function.
Coaxial speakers are a veteran of car sound. But it does not lose popularity among car enthusiasts. Since the system is easy to install and affordable. In addition, this option is more suitable than others for small cars. After all, in small salons it is difficult to achieve high-quality sound. Then why invest large amounts of money on sound design?
Pioneer wideband speakers
Car enthusiasts leave good reviews about this installation - Pioneer 16 cm. Coaxial speakers 16 cm have a rated power of 50 Volts and a maximum power of 300 W. This three or two-way design offers clear sound from 28 to 41,000 hertz. This is an excellent indicator for such speakers. The sound is clear even at high volumes.
The system is also easy to install and connect. The sound is not distorted at any power. With all its qualities, the price of the equipment is low and the design of the speakers is stylish.
For many, it is not only the quality of sounds that matters, but also the volume limits. For example, if people like to listen to songs in nature. Such users prefer to choose powerful equipment. And it is Pioneer that is best suited for them.
Pioneer wideband speakers
Since 16 cm speakers have many advantages:
- They tolerate powerful overloads well;
- small sizes;
- the sound is deeper than that of 13 or 20 centimeter analogues;
- the best system in terms of quality indicators.
Pioneer coaxial speakers are a high-tech development of manufacturers. The use of a reverse magnetic system allows you to bring the quality of music to a high level without inflating the price.
- Wideband speakers - how do they work?
- The path of development of speaker systems: from broadband to multi-band
- Additional components of any speaker system
- Wideband acoustics and its design
- Several recommendations for choosing and installing car speakers
Perhaps many of you, dear readers, have repeatedly wondered about improving the acoustic situation inside your car. Agree, on a long trip, sitting in complete silence is not so much fun, so the minimum that can be done in such a situation is to install a regular inexpensive radio in advance. With its help, you can listen to your favorite music, find out about events in the country, or get a weather forecast for the next few days (provided that it supports radio communication). However, in order to ensure high-quality sound from the car radio, you will have to use additional devices called an acoustic system. Today we will discuss one of its options, which is presented in the form of a broadband (or as it is also called “single-way”) speaker system.
Types, design features
Let’s immediately figure out what types of speakers the market offers for these products and what their differences are. There are two types:
- Coaxial acoustics;
- Component acoustics;
First, what does coaxial acoustics mean? To put it simply, these are speakers that combine elements with different sound frequencies in one device. In component speakers, each speaker with its own frequency is installed separately.
Infinity coaxial speakers
The design of a coaxial speaker is as follows: there is a low-frequency speaker (quite large), in which smaller heads (aka strips) are installed on one axis, and they sound in the mid and high frequencies. Additionally, the design includes a crossover - a block of filters that divide the frequency range among themselves. It is the design features that distinguish coaxial acoustics from other types.
The number of installed heads can be very different, but the most common is 2- and 3-way coaxial acoustics, in which the speakers included in the design reproduce sound at low, medium and high frequencies. You can even find 5-way speakers, but in reality, so many heads are of no particular use.
This is where the next question arises: coaxial or component acoustics - which is better? It is impossible to answer unequivocally here, since each of them serves a specific purpose. Essentially, these two types of speakers have the same components, but in the case of a component, they are separated.
What are full range speakers
The human ear is capable of perceiving a frequency range from 20 Hz to 20 kHz. For this purpose, wideband speakers have been created - these are devices that are capable of reproducing this range without separation. But at the border of the high- and low-frequency range, these speakers transmit sound worse than the middle of the spectrum. This is due to the design of the device.
In standard speakers, the size of the diffuser is increased for low-frequency reproduction. For example, a diameter of 30 cm provides a frequency transmission of 40 Hz. But then another problem arises. With such a speaker diameter, transmission in the high-frequency range deteriorates, because the diffuser does not have enough time to transmit vibrations to the surface.
This led to the development of modifications. The design of the models may additionally include a high-frequency diffuser that operates faster than a universal one. All models of full-range speakers on the market can be divided into two groups:
- Devices with a central cap . This is a standard speaker consisting of a single cone-dome.
- Devices with a cone-visor , which is called a bullhorn or pipe. This design is easy to understand. The horn has a small diameter and is built inside a wider cone. Such a sighting cone quickly picks up vibrations.
When choosing this speaker, it is important to buy a device that will clearly reproduce sound in the audible range, which is from 60 Hz to 16 kHz. The technical brevity of the design does not harm the device. On the contrary, it increases the reliability and sensitivity of the device to 90-92 dB. The resistance of the voice coils is higher than that of similar devices using other technologies.
In acoustics, there is the concept of a point source of sound - this is an object with such localization, the direction of which the listener can accurately detect. Wideband speakers have characteristics close to those of a point sound source. This is the secret of popularity.
Most often, such acoustics are used in cars. Through these speakers you can listen to the radio and music recordings, and these devices are inexpensive. But this technology is used not only in cars. These speakers are installed in portable speakers, televisions, etc.
Magnat Quantum 753
The speaker from Magnat's mid-priced Quantum 750 line looks solid. The front wall is made thick (40 mm) to radically combat body resonances. A solid 30 mm thick podium also emphasizes the solidity of the structure. It is curious that the front panel and podium are polished to a shine, while the rest of the surface of the case is matte. The F-max tweeter is equipped with a dome made of a double textile compound and has an extended operating frequency range. The midrange/bass speaker diffuser is made of ceramic/aluminum. The voice coil is well ventilated. The aluminum speaker basket design is optimized for optimal airflow and reduced resonances.
Bookshelf speakers Magnat Quantum 753
The bass reflex port with a large horn is located on the rear wall. The crossover is optimized for signal phase and amplitude and is assembled from selected high-quality elements.
Sound The speakers play emotionally, dynamically, quickly. At the same time, the timbres of instruments are perfectly conveyed, and the musical scene is not obscured by extraneous sounds - they are pure and deep. Sound source localization is excellent. The detailing is also at a high level.
The HF level is enough for an open sound with the presence of airiness, and at the same time the upper register is very neat and unobtrusive.
Bass of medium depth, collected and fast. There is a little lack of physicality and density of presentation. At low volumes, the enthusiasm of the speakers is lost, the emotionality fades.
Measurements
The unevenness of the frequency response is minimal, but the frequency imbalance towards the HF is obvious. The SOI varies within 1% and noticeably depends on the volume, but no obvious resonances are noted. Good SOI margin at low frequencies. Impedance is unstable.
How to install a sound system
Coaxial devices are located in the rear parts of the cabin. On rear shelves or doors. Simpler options are installed in panels at the front. But you need to understand that it is not recommended to overload the front panels. If you want to connect sound to the front of the car, the elements are mounted in the front doors.
Sound system installation
The best coaxial acoustics should please not only the driver, but also the passengers
Therefore, the quality of the system is very important. Setting up effective sound is easy
And many do the work themselves. There is no need to carry out complex calculations or make special podiums. This does not affect the sound quality.
By following the following recommendations, you can complete the installation without difficulty.
- Select speakers with the appropriate diameter. If the colonies are not commensurate with the holes, use adapter rings.
- When connecting sound to a car, you need to know the power characteristics of the radio and speakers. Also, choose your amplifier wisely.
- The energy source for the car's electronics is its battery. Therefore, keep in mind that with a large number of equipment, there will not be enough power. The likelihood of stalling at the wrong time increases. To solve this problem, capacitors are installed. Devices reduce electricity consumption.
- To secure the speakers, a wooden spacer ring is made.
- The rear shelf of the car is designed for speakers. To secure them, you need to remove the shelf. Only proper fastening will prevent the elements from creaking and rattling.
- Wires are selected separately. It is better to buy them with sections up to 4 mm. Wires are included with the system, but it happens that they are not suitable for power and can only be connected to low-power heads (up to 20 W). If you connect wires with a small cross-section, you will not get high-quality sound and normal operation of the speakers.
- Before you start connecting elements and wires, check all items for proper power.
Speakers for cars
The loudspeaker is an organ pipe.
High requirements for the quality of operation of an acoustic installation, on the one hand, and the limited area of living space where loudspeakers can be placed, on the other, force designers to look for solutions that meet these requirements, or to find an acceptable compromise. In this regard, the design of a single-way loudspeaker with two broadband dynamic heads connected in phase, in series, is of particular interest. The loudspeaker is described in American amateur radio literature. Sketches of its front panel and cross section are shown in Fig. 2.
The described acoustic design has a body in the form of a column with a cross section of 200x200 mm, a height of 800 mm with two slots at the base formed between the floor and the side walls shortened by 26 mm, as shown in Fig. 2. At the top of the case there are two holes for installing dynamic heads on the front and rear walls of the case. The dimensions of the cutout and the characteristics of the heads allow the use of domestic dynamic heads of the ZGD-38 type in this design. The walls of the housing are made of plywood or chipboard with a thickness of about 15 mm.
The elongated shape of the loudspeaker housing and the small floor area occupied by it allow the use of such loudspeakers in stereo and quad-raphonic installations. In addition, the loudspeaker of the described design is characterized by improved low-frequency response and an expanded radiation pattern in the horizontal plane.
The first advantage is due to the phenomenon of standing waves observed inside the loudspeaker cabinet, which behaves like an organ pipe tuned to a frequency of about 100 Hz. It is at this frequency that one quarter of the wave is laid along the speaker body, which contributes to the rise of the lower frequencies. At a frequency twice as high, equal to 200 Hz, on the contrary, exactly half the wavelength fits along the length of the body. At the same time, suppression of radiation from the lower part of the body is observed, which eliminates the unpleasant booming sound characteristic of acoustic installations with large linear dimensions.
The second advantage is associated with the use of two heads emitting in opposite directions. By changing the direction of the speakers' emissions by rotating them relative to their longitudinal axis, you can achieve the best sound reproduction in a particular room. At the same time, one should not regret that half of the emitted power is directed in the opposite direction relative to the listener. Low and mid frequencies, reflected from walls and furniture, produce multiple re-emissions of sound, as if blurring the small size of the sound sources themselves and creating the impression of spatial sound.