Why is the suspension called dependent?
The definition of the term contains the main feature of the mechanism - a rigid connection between the wheels of the same axle. Any change in the spatial position of one of them will necessarily affect the second. That is, the wheels are dependent, which somewhat simplifies the design, but does not always have a beneficial effect on the characteristics of the suspension.
Principle of operation
Like any other type of suspension, dependent includes:
- elastic elements in the form of coil springs, leaf springs, or more exotic devices that are quite rare on passenger cars;
- vibration dampers, usually hydraulic shock absorbers of the telescopic type;
- a guide device that maintains the wheel alignment angles more or less unchanged during the suspension's compression and rebound strokes.
When one of the wheels hits an obstacle, the second, located on the same axis, due to its connection with the first through a rigid beam, begins to change its camber angle, maintaining toe.
In this case, the contact patch shifts, its shape and area changes, which is very undesirable from the point of view of controllability at high speed. To weaken this effect, various technical tricks are used, but it is impossible to completely avoid it.
Design and diagram of dependent suspension
There are different dependent suspension schemes for driving and free axles of a car. In this case, any axle can be steered, but the steering drive does not affect the operation of the suspension and does not belong to its components.
The dependent suspension of a non-driving axle looks the simplest. Most often, this occurs on trucks, since similar designs on cars are a thing of the past, and on off-road vehicles, to which the folklore name of jeeps has been assigned, all axles are drive axles.
The free bridge is a fairly powerful forged profiled beam, at the ends of which wheel hub units with bearings and brake mechanisms are mounted.
Springs or springs can be used as an elastic element. In the first case, the sufficient strength and rigidity of the leaf spring packages in the longitudinal and transverse directions makes it possible to do without other parts of the guide vane, since the vertical spring has the necessary elasticity.
The drive axle with dependent suspension is designed in approximately the same way. Sometimes it is also called continuous. It is no longer a channel, but a hollow pipe with a housing (often called the “apple”) of the gearbox.
Rigid axle shafts go from the gearbox through the beam pipes (stockings) to the wheel hubs. If the axle is simultaneously steerable, then the axle shafts are connected to the hubs through CV joints - constant velocity joints, which allows the wheels to change the position of their plane of rotation during a turn.
A driveshaft fits to the axle hub. The suspension of the entire beam with gearbox and wheel units is similar to the non-driving axle. The same springs, springs and shock absorbers.
Car suspension classification
Essentially, suspension is classified into two types: independent suspension and dependent. Each type, depending on functionality, is already divided into different types of pendants.
Dependent suspension is a design in which both wheels of the axle are rigidly connected to each other. Moving one of them affects the other.
Independent suspension is a design in which the wheels of one axle are not connected to each other in any way, or influence only to a small extent. When operating an independent suspension, the wheel settings6 camber, wheelbase, and track may change during suspension operation.
The suspension of a car today is a rather complex structure that combines elements of hydraulics, mechanics, pneumatics and electronics at the same time. The presence of electronic suspension control systems allows you to achieve a high-quality combination of suspension parameters, comfort and vehicle controllability.
Types of dependent suspensions
Depending on the elastic elements used, the entire suspension scheme changes. Additional complication begins when designers strive to minimize the impact of the inherent shortcomings of a dependent suspension or increase its strength and load-carrying capacity.
On longitudinal springs
The most common design for trucks and other vehicles of the mid-20th century. Typically, semi-elliptical type springs are used, replacing the previously used full spring ellipses on carriages and early automobiles.
The spring is an arc-shaped set of sheets of spring steel, assembled into a package using clamps. Sometimes there are plastic anti-squeak washers between the sheets. They also reduce unwanted friction between the sheets, which reduces comfort on small uneven surfaces. The spring is attached to the bridge beam using U-shaped stepladders secured with nuts.
On off-road vehicles, in order to maximally raise the body above the road, springs can be located on top of the beam, but the design where they are located under it has become typical. This makes the car more stable due to a lower center of gravity.
Principle of operation
The principle of operation of a dependent suspension The dependent suspension is a single rigid axle that connects the right and left wheels. The operation of such a suspension is distinguished by a certain pattern: if the left wheel falls into a hole (vertically falls down), then the right one rises up and vice versa. Typically, the beam is connected to the car body using two elastic elements (springs). This design is simple, but it provides a reliable connection. When one side of the car hits a bump, the entire car tilts. While driving, shocks and shaking are strongly felt inside the car, since such a suspension is based on a rigid beam.
Differences between dependent and independent suspension
In an independent suspension there are no connections between the wheels; each can move only within the limits set by its guide vane.
At the same time, its structure is much more complicated, since this device does not have common parts for the left and right sides, which means a lot has to be duplicated. But for passenger cars this is not so significant; they do not require a large margin of safety, which means the parts can be small in size and weight.
As for jeeps, there are constant debates about the desirability of one scheme or another. And this mainly concerns issues of ensuring clearance. With a dependent suspension, it is always constant under the beam and does not depend on the wheel travel. Only the clearance under the bottom or frame changes.
Independent allows you to provide no less than its value, but the clearance will change when the springs are compressed or unloaded. Which is better is a moot point. In addition, it is believed that continuous bridges are stronger and more durable, especially with inevitable contacts with the surface in deep ruts.
Purpose of car suspension
A car suspension is a set of devices that work closely with each other, the main functional feature of which is to provide an elastic connection between the sprung mass and the unsprung mass. In addition, the suspension lightens the load on the sprung mass, distributing dynamics evenly throughout the structure. Among the most basic components in the suspension of a modern car are:
- elastic element - provides a smoother ride, as it reduces the impact of vertical dynamics on the mass;
- damping element - vibrations obtained during loads are converted into thermal energy, thereby normalizing driving dynamics (another name for a “car shock absorber”);
- guide element - processes lateral and longitudinal kinetics on the moving wheels of the car.
Regardless of the type of suspension and structural differences of the car, the general purpose of the suspension is to dampen incoming vibrations and noise, as well as smooth out vibrations that occur when driving on an uneven surface. Depending on the functional features of the car (you will agree that they differ noticeably for a small Smart model and an all-wheel drive SUV), the type and design of the car’s suspension will differ.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of dependent suspension include:
- simplicity and low cost in production, maintenance and repair;
- high strength, especially in the version with springs; a good spring is difficult to break precisely because it is flexible;
- off-road endurance, first of all, the steel beams of the bridges will come into contact with the road, and not the body, frame and other units;
- stability of ground clearance, since it is determined by unsprung beams.
There are also plenty of negative sides:
- significant unsprung masses, which makes it impossible to ensure a smooth ride with a small body weight;
- inability to obtain acceptable stability and controllability at high speeds;
- blurred reactions to the driver’s actions, which greatly removes his sensations from the actual behavior of the wheels on the road;
- the impossibility of obtaining the effects of useful steering and programmable changes in other wheel alignment angles during suspension travel.
All this imposes restrictions on the use of these types of suspensions.
Swinging wishbone suspension
Check out Ford's Twin I-Beam suspension. On it, the lever of the right wheel is attached to the left cross member of the frame, and the lever of the left - to the right. The result is very long levers - cheap and very unusual. Moreover, it turned out so successfully that a modified version of Twin Traction Beam was used for the drive axle of the Ford Bronco and Ford Explorer, as well as on various off-road sports prototypes that needed enormous suspension travel and strength.
Application
Now dependent suspensions are used only on those cars that value the above-listed advantages of a rigid connection between the wheels.
These are off-road trucks and cars, designed for constant use on bad roads or in their absence. There, simplicity and strength are much more important than the subtleties of stability and controllability.
There are also compromise options, for example, independent suspension on the front axle with a solid axle at the rear. This is how most modern jeeps are designed. Although the most uncompromising SUVs have retained rigid beams front and rear.
In budget passenger cars, a so-called semi-independent suspension is installed on the rear axle, when there is a connecting beam to the axle, but it is not rigid, but has a certain torsional elasticity. This scheme is cheaper, but its characteristics are quite acceptable.
Technical nuances
Now let’s move on to the technical side of the issue and understand the design and structure of the dependent system, as well as its varieties. Similar types of pendants include the following:
- on longitudinal springs (spring);
- with guide arms (dependent spring);
- De Dion pendant.
The first option is one of the oldest. This structure consists of a bridge beam connecting two wheels, as well as two longitudinal springs on which it is attached.
The spring in this embodiment acts as a universal elastic element - it takes on loads in the vertical and transverse planes, and also dampens body vibrations. Of course, you cannot achieve high comfort from the operation of the suspension of such a system, and at high speeds, problems with controllability begin to appear.
A design with guide arms can be called more advanced and modern. There are a lot of design options in terms of the number of levers and their configuration - this includes a suspension with a Panhard rod, and with a Watt or Scott-Russell mechanism. Compared to spring systems, these systems have much better handling and cornering behavior. The main elastic element here is the spring, and the shock absorber helps it.
As for the De Dion pendant, there is one nuance. The fact is that this system cannot be called completely dependent due to the tricky arrangement of the elements, which is due to the fact that it was developed for the rear axle of rear-wheel drive cars. In it, the differential and the beam connecting the wheels are separated.
We recommend: Motor oil for two-stroke engines
The differential is rigidly connected to the car body, and rotation from it to the wheels is transmitted through swinging drive shafts. According to experts, the De Dion suspension is superior in many respects to the best examples of independent designs, and its only significant drawback is the price, which is why you can rarely see it, and even then mainly on sports cars.
Concept of suspension
Before talking about the pros and cons, as well as the superiority of one suspension over another, if possible, I propose to understand the essence of the concept of suspension.
A suspension is a component of a car that is part of the chassis. This is an intermediate link located between the road surface and the body part of the vehicle chassis. The work of the suspension is to convert into elastic movement all the impacts that the wheels of the car have to face while driving. And these are all kinds of bumps, holes, unevenness, etc. That is, the suspension absorbs energy from impacts and increases the smoothness of the ride.
In this case, a distinction is made between the design of the front and rear suspension. They can be divided into several categories. At the same time, all structures are subject to the same requirements.
The car suspension must keep the car in a horizontal position, regardless of the acting forces, and dampen vibrations. Plus, the structures must be elastic, strong and as durable as possible. Otherwise, expensive repairs will be required.
The current classification provides for the division of pendants into 3 categories.
- Dependent. It comes with longitudinal and transverse springs, it can use guide arms or a thrust pipe. Also distinguished are the torsion-lever design and the De Dion type system;
- Independent. Such systems differ from each other in the use of oblique and double wishbones located transversely, and may have swinging axle shafts. There are options with double and single trailing arms and transverse ones. But still the most popular option is the MacPherson type suspension;
- Active or semi-dependent. Here the rigidity and position change depending on the command given through the control device. Active systems are divided into pneumohydraulic, hydraulic and pneumatic.
But this is objectively not enough to understand what the difference is between them, what differences exist and which type of suspension travel is preferable in terms of comfort. You can also read useful material about checking shock absorbers for performance.
Dependent constructs
First, let's define what it is and what the concept of car suspension dependence means. In simple terms, this is a pair of opposite wheels (left and right), which are rigidly connected to each other using a single beam. This is one of the key ways to distinguish designs from each other. Just take a look at how the left and right wheels connect to each other.
When the impact on one wheel begins, the position of the second changes. The dependence of one wheel on the other explains the name of the design. Such units are more focused on vehicles that are operated in rather difficult operating conditions. Dependent suspension is extremely rare on ordinary passenger cars designed for city driving. Therefore, finding a car is not so easy if you just need a passenger car. But the system is still in demand and is finding its place in the auto market.
Dependent auto suspension components have strengths and weaknesses.
Let's start with the shortcomings. There are several main points worth highlighting here:
- worse sustainability indicators;
- insufficiently clear controllability;
- reduced level of comfort;
- high requirements for road surfaces when driving at high speeds;
- low information content of management.
All this when compared with cars equipped with an independent type of suspension.
The weaknesses are quite significant, and are more pronounced on ordinary roads. But if you drive into ideal conditions for such a suspension, the car will show its maximum.
It is in the element of the dependent structure that its true advantages are revealed. Namely:
- Low cost of maintenance. Maintenance and repair (maintenance and technical work) are quite cheap, which allows you to significantly save on repairs;
- Resistant to damage. This suspension is not afraid of impacts, active driving on bad roads, etc. The design behaves well under heavy loads;
- High strength. Independent suspension is not a competitor in this regard;
- Constant ground clearance. The clearance does not change, which provides a number of advantages;
- Excellent adaptation to off-road and bad roads;
- A small number of design components, which simplifies maintenance and makes repairs more affordable. This also directly affects reliability.
As you can see, in its element, the dependent system allows you to count on a solid list of advantages. But on regular roads everything is not so perfect.
Independent suspension
Unlike the previous design, here the opposite wheels do not have a direct structural connection with each other. Each of the wheels acts and works independently relative to each other.
Such units perform well when driving on highways, in the city, and behave excellently at high speed. Therefore, independent designs are found mainly on passenger cars, crossovers and SUVs.
We recommend: Classification of passenger car bodies
This also has its strengths and weaknesses. Benefits include:
- excellent grip on the road surface;
- excellent level of comfort;
- excellent handling;
- minor deviations along the longitudinal axis.
All this affects comfort, agility and handling. Dependent suspensions are not capable of this.
But don't jump to conclusions about the superiority of the independent system. It also has disadvantages:
- repairs are much more expensive, as is maintenance;
- the lever stroke is short, which may reduce ground clearance;
- the design consists of many components;
- due to the complexity of the layout, the likelihood of breakdowns increases;
- It is almost impossible to carry out repairs in the field.
If we take an initially high-quality independent suspension as a basis, and operate the car in the conditions for which it is intended, all these shortcomings will not be so obvious.
In the beginning there was a spring
The first wheeled ones did not have any suspensions - there were simply no elastic elements. And then our ancestors, probably inspired by the design of the archery bow, began to use springs. With the development of metallurgy, they learned to impart elasticity to steel strips. Such strips, collected in a package, formed the first spring suspension. At that time, the so-called elliptical suspension was most often used, when the ends of two springs were connected, and their centers were attached to the body on one side and to the wheel axle on the other.
The first wheeled vehicles did not have any suspension.
Classic elliptic springs are used on both the front and rear axles.
Then springs began to be used on cars, both in the form of a semi-elliptical design for dependent suspensions, and by installing one or even two springs across. At the same time, an independent suspension was obtained. The domestic auto industry has used springs for a long time - on Moskvich cars before the advent of front-wheel drive models, on Volgas (with the exception of Volga Cyber), and on UAZs springs are still used.
Everyone who has at least once used the services of a GAZelle-based minibus has driven a car with a full leaf spring suspension. There are few leaves in the springs - two on the front axle and three on the rear.
Springs evolved along with the car: there were fewer leaves in the spring, up to the use of single-leaf springs on modern small delivery vans.
| Advantages of leaf spring suspension | Disadvantages of leaf spring suspension |
|
|
Similarities and differences
Both pendants serve the same purpose. They are needed to make car travel safer and more comfortable.
In terms of design, what they have in common is that in both cases elastic elements, shock absorbers and guides are used. A striking example is the use of springs. Some actively mount air bags into springs to increase comfort.
But there are much more differences between them:
- The wheels of the dependent system have a rigid connection, making them dependent on each other. The competitor's wheels work independently;
- Independent units have more unsprung masses, which is due to the absence of a bridge;
- Independent is more sensitive to wheels that do not meet the automaker's requirements;
- The likelihood of capsizing during a sharp turn or when falling into a hole on a car with independent auto suspension is less due to the lack of a rigid connection of the wheels.
As you can see, there really is a difference, and it is significant in many ways. What exactly to choose, everyone decides for themselves.
Would you like it softer?
Which pendant do you prefer? Soft or hard? Let’s answer very simply - the one that you like, but at the same time the one that the developers equipped this car model with. When purchasing a car, choose it on a “Hard - Soft” scale, rather than trying to improve the design after purchase. Shock absorbers from different manufacturers have different reputations on the market: some are stiffer, others are softer. But the manufacturer will never directly tell you about this. The box will indicate whether this shock absorber is applicable to your car or not.
Another way in which it is permissible to slightly change the stiffness of a car’s suspension is to install tires of a higher or lower profile from the range allowed by the manufacturer.
Shock absorbers
From the course of school physics it is known that any elastic system is characterized by oscillations with a certain natural frequency. And if a disturbing force with the same frequency acts, a resonance will occur - a sharp increase in the amplitude of oscillations. In the case of a torsion bar or spring suspension, shock absorbers are designed to combat these vibrations. In a hydraulic shock absorber, the dissipation of vibration energy occurs due to the loss of energy for pumping a special fluid from one chamber to another. Nowadays, telescopic shock absorbers are ubiquitous, from small cars to heavy-duty vehicles. Shock absorbers, called gas, are actually also liquid, but the free volume, which all shock absorbers have, contains not just air, but gas under high pressure. Therefore, “gas” shock absorbers always tend to push their rod outward. But the next type of suspension can do without shock absorbers.
Torsion bars
Did you know that almost any car with a spring suspension still has torsion bars? After all, the anti-roll bar, which is now installed almost everywhere, is a torsion bar. In general, any relatively straight and long lever that exerts torsion is a torsion bar. As the main elastic suspension elements, torsion bars were used along with springs at the very beginning of the automobile era. Torsion bars were installed lengthwise and across the car and used in a variety of types of suspensions. On domestic cars, the torsion bar was used in the front suspension of Zaporozhets of several generations. Then the torsion bar suspension came in handy due to its compactness. Nowadays, torsion bars are more often used in the front suspension of frame SUVs.
An example of installing torsion bars in the Great Wall Hover front suspension.
The elastic element of the suspension is the torsion bar - a steel rod that works in torsion. One of the ends of the torsion bar is fixed to the frame or supporting body of the car with the ability to adjust the angular position. The lower arm of the front suspension is installed at the other end of the torsion bar. The force on the lever creates a torque that twists the torsion bar. Neither longitudinal nor lateral forces act on the torsion bar; it works on pure torsion. By tightening the torsion bars, you can adjust the height of the front part of the car, but at the same time, the full suspension travel remains the same, we only change the ratio of the compression and rebound strokes.
At the rear ends of the torsion bars there are levers that allow you to adjust the preload.
| Advantages of torsion bar suspension | Disadvantages of torsion bar suspension |
|
|
Independent
In this type, both wheels located on the same axis are independent of each other. When the vertical position of the right wheel changes, the left one remains stationary. One side is independent of the other, hence its name - “Independent” . The most common are three types of independent suspensions:
- McPherson;
- Double wishbone suspension;
- "Multi-lever".
Each of them has its own pros and cons, features and nuances. Let's look at each of them in detail.
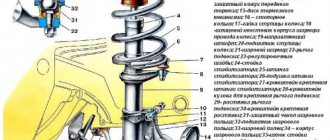
Suspension type – MacPherson
It is also called a “swinging candle” . A feature of this type is the presence of one wishbone per side and the combination of a spring and a shock absorber into one structure - a “shock absorber strut”; in some documentation you can find the term “spring strut”.
The lower end of the rack is connected to the steering knuckle, and the upper end is connected to the power element of the body. The last mount is not rigid; it uses a bearing. It ensures rotation of the stand around its axis, and accordingly the mobility of the wheel.
That is, when the steering wheel rotates, the wheel turns thanks to this bearing. Therefore, the car’s controllability depends on its serviceability.
This type of suspension is used for front-wheel drive and all-wheel drive vehicles. It can be used in the front and rear chassis.
Advantages:
- Relatively low production costs, which reduces the price of a new car.
- Compact and light weight design. Due to its small dimensions, there is more space under the hood to accommodate the engine; it is located below the axis of the car, reducing the center of gravity. This in due course has a positive effect on the stability of the machine. More luggage space, not limited by a beam or axle.
- Easy diagnostics of the suspension due to the small number of parts in it.
Flaws:
- It is less reliable than the “double lever”. The wishbone design is more durable than MacPherson struts because there are only two mounting points that bear the entire load.
- High cost of repairs. Replacing a part in this type of suspension requires a lot of time and effort.
- Cannot be used for cargo transportation or off-road driving.
Double lever circuit
This is one of the first types of independent suspension in a car. It was installed more than 100 years ago. Owners of “classic” VAZ models remember it well.
The name of this type speaks for itself. This type uses two wishbones on one side. There is no shock absorber strut; shock absorbers and springs are separately attached to the power elements of the body.
The upper and lower arms reliably fix the hub in the longitudinal direction. Due to several wheel mounting points, the load during movement is evenly distributed over the body, reducing wear on moving parts. The fender liner is not subject to damage from the operation of the shock absorber strut, as in the MacPherson strut suspension. This saves the body from corrosion.
Pros:
- The most reliable type. The entire load is evenly distributed across all its elements; there are no nodes that are most susceptible to wear.
- It is considered more comfortable than MacPherson.
- Improved vehicle handling.
- Cheap maintenance and repairs. Although it has additional parts, you do not need to disassemble the entire structure to replace them. For example, to replace shock absorbers, you don’t need to remove the entire strut and then hold the spring with pullers - everything is easier to change.
The last point is not relevant for all brands of cars. The fact is that in modern cars the levers are made non-separable. That is, silent blocks and ball joints are pressed into their design. Due to the wear and tear of these “penny” parts, the entire lever has to be replaced.
Flaws:
- The extra upper control arm steals space under the hood. Therefore, the engine has to be placed higher than with MacPherson strut. Modern cars use a system with different lever lengths to minimize this suspension drawback.
- Increased weight of the entire structure.
- It is only used on the front of rear wheel drive vehicles. It cannot be used in the rear suspension either - it eats up the useful volume of the trunk.
Multi-lever
In addition to two levers, it uses additional levers. That's why it's called multi-link independent suspension. In some designs there can be up to 8 pieces on one side.
This type improves the vehicle's directional stability, as it ensures constant contact with the road. It is more comfortable and handles any unevenness in the road surface better. Therefore, it is installed in sports and premium cars.
Flaws
The main disadvantage of a multi-link suspension is the cost of production, which increases the final price of the car. Expensive maintenance and repairs due to its design complexity.
It can be called “delicate” because it wears out quickly on bad roads. And repairs will be expensive.
High cost of repairs. The presence of a large number of levers increases the cost of its complete “overhaul”. In most cases, all parts are non-separable. Therefore, it is not possible to replace the ball joints separately from the lever; it can only be replaced as an assembly. This also applies to silent blocks and other small details of the chassis. In another type of suspension, each element could be replaced separately, but here such a trick will not work.
Advantages
- High level of comfort and controllability.
- Smooth ride and excellent “steering” of the car.
Top of page