- home
- Car suspension
- …
You can often hear from owners of cars of various classes that the suspension of their iron horse is stiff, some say oak. You can literally feel every small unevenness (bump or hole). The comfort in the interior of such a car is reduced, and the thought constantly floats in my head - how to make it softer? So that, as they say, the spine does not fall off onto the seat. And here a huge amount of advice appears on the Internet, which is sometimes simply amazing in its illiteracy. Today we’re going to debunk the myths and also think about real ways to make the suspension more comfortable...
What they don’t write on the Internet is to trim the springs, install other “soft shock absorbers”, ride almost on winter tires (in the summer), etc. I propose to discuss each point separately, but first think about why the suspension can be stiff
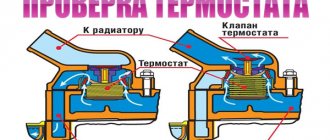
What is hard and soft suspension?
The suspension is influenced by a large number of factors:
- This is the mass of the body
- Body shape, tall or, on the contrary, squat
- Dimensions, wheelbase
- Speed and power characteristics
- Settings
A little theory, let's start with the oscillation frequency. After all, even when walking, it is present, and a person gets used to certain indicators in the life cycle.
The normal vibration frequency of a person when walking is approximately 1 Hz (Hertz). If you apply this to a car: the frequency is higher, it will be harsh, and if it is lower, it can cause motion sickness.
A car also has this parameter, only this is the vibration frequency of the body with cargo and passengers on the suspension.
The achievement of this parameter is ensured by the rigidity of the elastic element and the weight of the body with cargo and passengers bearing on it.
In simple words, the more the body weighs, the more powerful and, accordingly, stiffer the springs should be.
However, one value remains practically unchanged - the static deflection of the elastic element (spring or spring) is 25 cm. This is the difference in the values of the free spring and the compressed one on the suspension (with passengers and cargo). When applied to the wheel, because in some suspensions the springs work directly, and in others through a lever. Accordingly, the lever must be taken into account.
This is ideal!
However, now on modern cars the suspension is made a little stiffer than we would like, let’s go point by point:
- With low rigidity it is difficult to achieve high energy intensity . To prevent the soft suspension from breaking through an obstacle, you need to make a large compression stroke. BUT there are two problems here: you can’t make a big move due to restrictions on the body layout (spars or wings simply won’t allow it). And a limitation on the suspension kinematics itself. The suspension works along a radius and with a large compression stroke, unwanted movements of the levers increase, which reduces controllability and increases the load on the elements.
- Compression buffers . Probably everyone has heard the concept of “rebound” suspension operation. Some manufacturers, to please the consumer, can install soft springs and shock absorbers with “high compression,” but as a rule, such suspensions easily break through sharp bumps. Therefore, they install so-called compression buffers, rubber elements that limit the stroke. springs and leaf springs have them . BUT if the suspension reaches the “buffer” its comfort is lost significantly.
- A smaller, taller and lighter passenger car . The more difficult it is to achieve a smooth ride and, accordingly, a soft suspension. After all, soft springs are required so that they give a comfortable oscillation frequency. BUT there is another problem here, loading the car. After all, if such a machine is heavily loaded, the drawdown will be severe. It is also worth taking into account the kinematics of the suspension, because a small car will have smaller operating radii. But sometimes the car needs to be loaded just as heavily (for example, 4 people + cargo). That's why small cars are often the stiffest, especially those tuned to high speeds.
- Anti-roll bar . It is needed to increase the angular stiffness of the suspension and resist body roll when cornering. Helps in kinematics, not to go beyond the maximum permissible points of suspension radius mixing. Also helps with driving.
- Air suspension . When installed, almost any car can be made comfortable and soft (from the driver’s point of view), but the cost of the system is prohibitive. And they don’t install it on budget brands
I would like to summarize briefly. On large cars it is easier to make the suspension comfortable. Because the body weight is greater, the wheelbase is longer, there is plenty of space for the suspension to work, and the settings are for high loads and speeds. ON a large car, even huge springs will work better.
ON small, and even tall cars. Often, making a soft and comfortable suspension heavier. For example, I had a FORD FUSION, it was really made of oak (due to the short wheelbase and high body). The manufacturer has nowhere to roam in such a car. That's why they make such cars a little tougher. This is not a whim of the manufacturer, but a necessity.
Now I want to talk about myths that, although on the Internet
Advantages of softness
A soft suspension means less variation in body roll and limited ability to distribute load across the four wheels during roll. This saves energy because there is no need to move the center of the car up or down while driving. Road grip is also much improved.
However, such suspensions have significantly limited characteristics such as compression strokes. They must be consistent with the difference in axle load when there are passengers and luggage in the car, and with the load that appears when there is an uneven road surface and when turning.
If you make the suspension too soft, when turning, you will feel how the wheels on the opposite side simply lift off the ground due to its too much compression.
That is why how to make the suspension softer requires knowledge of such nuances. There must be moderation in everything, which also applies to this matter. A slightly soft suspension is considered the most optimal. Very often, this range can easily smoothly migrate to hardness, and the greater the difference between the soft and hard parts of the suspension, the more difficult it is to adjust it to suit you. Any distribution of loads is the result of a decrease in the quality of traction of the wheels with the road, since additional loading of the front wheels does not mean compensation for all losses for the rear wheels when they are unloaded and vice versa.
Even when hanging such unloaded wheels, after which the grip on such an additionally loaded side improves, even fifty percent of the losses are not compensated. Among other things, this situation implies not only a drop in the level of road grip, but also a general drop in the vehicle’s handling. This can be corrected by adjusting the direct inclination of the rolling plane of the wheel according to the road. This means collapse. Thanks to appropriate operations, the car's soft suspension gives its owner pleasant and easy control. Although at high speed this figure decreases significantly.
Trim or install other springs
To cut this at all is some kind of game!
Firstly , there is no 25 cm in a loaded car, which is necessary for comfortable work. Secondly , the work of the suspension will be, on the contrary, torn, and the spring will become a little softer, it simply won’t have enough coils to hold the body normally. The center of gravity of the body will be mixed, which has an extremely negative effect on handling. If you cut off more turns, you will hit the bottom on the road, because again there is not enough spring (let’s say power) to hold the body. YES, the spring can simply fly out of its place.
Install other springs. Hypothetically, this is possible, but they are selected together with shock absorbers (more on this below). But if you make it more powerful, the car will become stiffer, but we need comfort. And if you install it softer than what you had, then the body simply won’t hold up, there will always be breakdowns.
Replacing silent blocks on Kalina
Front suspension silent block close up
The silent blocks on the Lada Kalina car are located exactly the same as in the VAZs of previous years. These elements are located generally on the wishbone or adjacent to it. You will have to change them either on the entire element at once, or by selecting the most damaged ones. Of course, if there is damage on one of them, the wishbone with rubber (stock – approx.) stabilizers must be removed and replaced with polyurethane analogues.
Removing the wishbone
- In order to begin work on replacing old silent blocks with new ones, you need to place the car on a viewing hole, a lift, or jack it up.
- Next, you need to remove the wheel and spray all the connections on the wishbone with WD-40.
- After the lubricant has penetrated into all hard-to-reach places, we begin to unscrew the bolts.
- First of all, we begin to dismantle the ball joint bolt, but before that we remove the cotter pin from the bolt.
- Then we unscrew the bolt securing the longitudinal tension hinge (where the “daisies” are attached - approx.) and remove it from the seat.
A generously lubricated bolt is a guarantee of success.
When dismantling this unit, there should be no problems.
For the best impact on the bolt, you can use a wrench extension.
Rubber-metal longitudinal tension joint
The rubber-metal longitudinal tension joint, or popularly simply “daisy”, is designed to take the brunt of the impact from uneven road surfaces; despite the fact that this element is very important, it is very easy to dismantle.
- Having previously clamped the lever in a vice, we knock out the silent blocks one by one using a chisel or a thin flat screwdriver.
Punching out “daisies” is not an easy task.
Install other shock absorbers
Despite their similarity in appearance, shock absorbers are categorically different; they can be oil, gas-oil, single-tube, double-tube, etc., you can read more here .
BUT they have different degrees of compression, in simple words - different working strokes. After all, various bypass valves can be installed inside, the performance of which directly depends on their operation. The shock absorber will be softer or harder.
If you use standard springs and install rigid “struts”, then again this will not do any good, the car will become stiffer
If you install soft shock absorbers, then the body will wobble at the slightest unevenness. It’s commonplace that the shock absorber will not support the body.
I repeat once again, you can install other shock absorbers and springs, but it is not as easy as it seems; they need to be selected according to the characteristics of your car.
And listening to experts on the Internet who say “install soft springs and shock absorbers and you will be happy” needs to be driven with a broom. With such tips, you can end up in a ditch on sharp turns.
Sequence of actions when replacing the front shock absorbers of a Lada Granta with your own hands
We prepare a set of tools, rags, WD-40 fluid, a set of new racks, and other components for related repairs.
- We place the car within the perimeter of the repair area, jack it up, and secure the rear row of wheels with wheel chocks;
- We remove the wheel, disconnect the tie rod end, the ball joint;
- We loosen the rod (key to “9”), while holding the main nut to “22”;
- With a key set to “13”, unscrew the three nuts securing the upper support;
- In order to minimize the violation of the camber angle - wheel toe, we use a chisel to mark the relative placement of the steering knuckle and the bracket;
- Unscrew the bolts at the bottom of the fastening (key set to “17”);
- We remove the Grant shock absorber assembly;
- Use a puller to compress the spring several turns.
We replace the Granta racks and assemble the elements in the reverse order. At the same time, we carry out troubleshooting and replace worn-out consumables with new ones (anthers, bumpers). Don’t forget to visit a service station and have your wheel alignment adjusted. Otherwise, the tires will wear out faster. Motorists at a number of service stations prefer replacing the shock absorber assembly, as opposed to partial repairs. The cost of the service is a third less than the price of a new rack, but no one guarantees the serviceability of the accompanying elements. Ultimately, the cost of purchasing consumables will increase.
High tread tires
This is a surer way to make the suspension a little softer. For example, if you have a low tread, 35 – 40 – 45. THEN the car will be a little stiffer.
You can take a disc with a smaller diameter, but with a larger tread of 55 - 60.
Due to the fact that the rubber cord has become larger, the energy intensity will increase slightly, but as practice shows, not by much. If we exaggerate greatly, then only 5 - 7% can be added to smoothness if we measure the noise level in DB.
You can also install less noisy tires , I wrote about this here.
Summarize
Now you know which racks are best to install. Replacing the shock absorber strut, as well as disassembling it in order to change specific parts, did not turn out to be a complicated procedure. This work can be done by an ordinary Lada Granta owner who has the desire and the tools. Upon completion of the repair work, do not forget to check and adjust the alignment.
Before you begin actual assembly, make sure that all marks are completely aligned with each other. Also be sure to check the angles at which the front wheels of the Lada Grant are installed. If you are convinced of problems, perform a wheel alignment to ensure more reliable operation of the car.
It is worth paying attention to the fact that the front struts on the shock absorbers are made telescopic, and if the need arises to replace them, the procedure can be performed either completely or partially, simply by disassembling it into parts. , you can consider an example of working with one of the racks, because the second one is removed in a completely similar way
Do not forget that it is best to lift the car using a lift, but if you don’t have one, carry out the task on a flat surface.
Light wheels
There is also some truth here. You can work with wheels, just like with tires. Again, reduce the diameter of the rim (if you install tires with a larger profile).
And you can also reduce the weight of the disk, and accordingly you can reduce the sprung mass, how well this has a beneficial effect on comfort, not critical, but still.
For example, instead of a heavy stamped wheel, you can put a lightweight forged disk. Sometimes casting is lighter, but you need to look for it; some alloy wheels, on the contrary, are heavier.
With this approach, softness will increase a little, but again you shouldn’t expect miracles.
Air suspension
In essence, this is a completely redesigned car suspension, sometimes even working on different principles. Here pneumatic elastic cylinders can be added, which can work perfectly as an additional damper. In general, there are a huge number of buildings, but that’s not about that now.
BUT there are two problems here:
- Not all cars have them. Especially for small cars
- Cost is usually expensive. A complete set, if you take a domestic car, not China, starts from 100,000 rubles
BUT with this solution, you can achieve softness and comfort.
Air suspension installation
Completely replacing the factory suspension with an air suspension is a radical decision that costs a lot of money.
Installation of air suspension should be carried out in specialized service centers, since for each car model it requires personal installation parameters. Its undeniable advantage is that the driver, by adjusting the air pressure in the airbags, can change the level of rigidity of the car's chassis and its ground clearance.
People's decision
How to decide the comfort of the suspension in garage conditions. Everything is simple, just put one or two bags of sand in the trunk. And lo and behold, the goat that was jumping over uneven surfaces becomes much softer. But why?
Yes, it’s simple, initially the suspension was designed for loaded weight, it’s trivial that it should support this weight (especially on cars with a short wheelbase). As I wrote above, without loading it will be a bit harsh, but as soon as you load it, the mass changes and the suspension begins to work differently, as a rule, it becomes softer.
Now we are watching the video version
I'll end here. In conclusion, I would like to say that manufacturers are far from fools; they do not have the task of making “gear-crushing” cars. If your car has a stiff suspension, then most likely this was done for some reason, or because your car is small, tall, or has a short wheelbase. Either it is dynamic, has a powerful engine (takes turns at 100 km/h and has a maximum speed of 250 - 300 km/h), etc. And thoughtlessly changing characteristics is simply dangerous, think about it.
Similar news
- Beam or multi-link. What's better? Comparing the rear suspension
- What kind of fluid is poured into the power steering? Composition, color and light…
- The shock absorbers (struts) are leaking. What to do and is it possible to drive? How…