The brake mechanisms (calipers) of the front wheels of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 vehicles operate under constant exposure to an external aggressive environment (salt, dirt, water, etc.). In this regard, it is recommended to inspect and service calipers and brake pads every 15 thousand km. Jamming or “souring” of the pistons in the caliper cylinders is most often the result of a lack of periodic monitoring of the condition of the brake mechanisms, damage to their protective boots, severe wear of the brake pads in which the pistons extend too far from the cylinders, thereby coming under external influence, the presence of water or foreign substances. impurities in brake fluid.
Reference: the pistons of the brake mechanisms of the front wheels of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars have a mirror coating, the same coating is found inside the cylinders. The cylinders are equipped with rubber rings that return the pistons to their original state after extension. On the outside, the pistons are protected by anthers (protective caps with retaining rings).
Damage to the mirror coating of the pistons (“souring”) leads to a loss of their mobility in the cylinders and, as a consequence, to incomplete release of the front wheels, since the pads are constantly pressed against the brake discs. In this case, accelerated wear of the pads, overheating and warping of the brake discs occurs, fuel consumption increases, the vehicle's controllability (pulls to the side) and its dynamics are impaired, vibration and beating appear when the brake pedal is pressed.
There are at least two ways to develop a soured piston:
— without removing the brake mechanism from the car;
- with the brake mechanism removed.
In the first case, it is necessary to jack up the car, remove the wheel, clean the outside of the caliper from dirt, disconnect and lift its floating bracket.
We remove the retaining ring and the cylinder boot, remove dirt from under it using a rag soaked in gasoline and a hard brush or toothbrush. Lightly press the brake pedal so that the piston moves out a little (a centimeter at most) from the cylinder. We clean it again, being careful not to damage the piston mirror and remove only dirt and deposits. You cannot clean the piston with sandpaper, as this can damage the mirror. A popular way to clean deposits is to use a rough wooden block, which will remove deposits and not damage the cylinder. Remove the cap from the brake fluid reservoir and, using an adjustable wrench or vice, push the piston back into the cylinder. We press the brake pedal, pushing out the piston, and press it down again. We carry out this procedure for developing his mobility 20-30 times. Then we apply graphite lubricant to the protruding part of the piston, install a new boot and retaining ring.
The advantage of this method is that there is no need to drain the brake fluid from the car’s brake system circuits and pump the brakes.
In the second case, we remove the brake cylinder and disassemble and develop it. This method is suitable for a major overhaul of calipers, since it is necessary to either drain the brake fluid or plug the brake pipe, which still risks losing a certain amount of fluid and requires bleeding the brakes after the work is completed.
The piston must be squeezed out of the cylinder either before removing it (by pressing the brake pedal), or with the piston already removed, pressurized air must be supplied into the hole under the brake pipe. Before extruding, remove the retaining ring and boot from the piston. We try not to scratch the removed piston. We clean it from dirt and oxidation using the method described above, if necessary, change the rubber sealing ring, rinse and blow through the cylinder. Before assembly, lubricate the inside of the brake cylinder with brake fluid, and lubricate the piston itself with graphite lubricant. We press it inside the cylinder (for example, using a vice), put a new boot and retaining ring on top.
A little history
The first to create such a model of brakes (disc type) was Frederick Lanchester (Great Britain). It was in its design that a caliper was used that pressed the pads. However, technology at that time did not allow the creation of reliable disc brake systems.
Disc brakes were revived in aviation, and in the 50s they began to be installed on cars - first on sports models, and then on production ones. The first car with serial front disc brakes was the Chrysler Crown Imperial (in 1949).
The importance of this component is difficult to overestimate, because the brake disc and pads are passive components, while the caliper plays an active role. Due to this, the pads are pressed. Therefore, the brake caliper is the most important component.
Types of installed calipers and their prices
The same caliper is installed on a given family of cars, with the exception of the index in its marking, indicating the model of the vehicle body. Otherwise, these are identical brake devices that have a single-piston design independent of the fixed caliper. A similar modernization took place after 2001, and the last half calipers with 4 pistons were installed on the VAZ 2108.
The cost of a caliper for a VAZ 2109, 2110, 2114, 2115 can be as follows, based on its condition:
- New – 1,610-4,270 rub .
- Used – 700-1,980 rub .
- Refurbished (restoration using original components) – 1,420-2,190 rubles .
Front brake caliper - design types
The development of these mechanisms is reflected in their division into 2 categories, depending on the layout:
- Fixed design - it consists of a body made of metal, and there are working cylinders on both sides of the brake disc. Their arrangement is symmetrical. In this case, the body itself is fixed on the steering knuckle. At rest, the pads are held in place by special springs, and during braking they are compressed, causing them to be pressed against the surface of the disc. To ensure the operation of such a design, it is required that brake fluid be supplied simultaneously to all cylinders, which is achieved through a whole system of hoses, pipes and various tubes. Such brakes are highly efficient, making them ideal for cars with powerful engines and large weight - racing and executive models. World famous brands - Brembo and others - specialize in such calipers.
- A floating caliper is the fundamental difference between such a caliper and a fixed one in that one of the pads is in a constant position. Its design involves the presence of a bracket, as well as a cylinder, which is fixed on the inside. Typically, such calipers are single- or double-piston. The braking process is as follows - the piston presses the pad and presses it against the disc, and at the end of this phase, the bracket (floating type) begins to move towards the piston, sliding along the guides. Due to this, another pad is pressed against the surface of the disc.
This design is usually found on cars in budget segments, as it is cheaper to manufacture and simpler.
What does the price depend on?
In addition to the brand, the following product parameters are involved in determining the consumer price:
- Total area of the brake wheel cylinder.
- Fixed caliper dimensions with fixed mounting holes (standard caliper fits 13″ stamped wheel rim).
- Dimensions of the movable bracket.
- Material of guide pins for movable bracket.
- Locking plate material.
The caliper for VAZ 2109, 2110, 2114, 2115 has a single-piston design , therefore it is the cheapest in its class. Among the additional pricing factors it is worth noting:
- Availability of a brake hose (reinforced, regular).
- Implementation of a casing-channel for laying hoses.
- Availability of spare bolts securing the working cylinder to the movable bracket.
Working principle of brake caliper
The brake caliper performs its main task - it provides the necessary braking force required to slow down or stop the car.
Pressing the brake pedal causes pressure to build up in the brake line. It is transmitted to the caliper pistons, which at this time strictly parallel fixes the pads relative to the disc. When braking, the calipers compress the pads on both sides of the disc, causing it to slow down. But there is another effect. It involves heating, as friction energy is transformed into heat. This significantly heats up both the disc and the pads and calipers. The temperature of the brake fluid also increases.
How to replace the brake cylinder on a VAZ 2113-VAZ 2115?
1. Remove the wheel first from the side on which you will change the cylinder (Read the article on “Replacing wheels on modern cars”, it describes how to remove the wheels correctly), when the wheel is removed, remove the brake hose from the bracket to which it is attached (the location is indicated by a red arrow) and using a wrench, tear off the nut that secures the brake hose to the brake cylinder (see small photo).
2. Now the brake caliper bracket assembly with the cylinder will need to be removed, to do this you will have to unscrew two bolts, but when unscrewing them, hold the guide pins with a second key so that the bolts in the guides do not turn (see photo 1), after which the bolts are removed from the guide pins and the bracket assembly with the brake cylinder is removed from the caliper, but the bracket cannot be completely removed, and the fault is the brake hose, which will have to be disconnected from the brake cylinder. To do this, completely unscrew the hose mounting nut (While unscrewing, hold the nut with a wrench and rotate the caliper assembly in the brake cylinder by hand, counterclockwise) and disconnect the hose, as soon as you disconnect it, immediately plug the hose with some kind of plug so that the brake fluid does not pour out through it, then firmly tighten the brake cylinder with the caliper you need a vice, but you can do without them, in general you will have to unscrew the two bolts that attach the brake cylinder to the caliper, they need to be unscrewed with a hex key or hex heads, after unscrewing, the caliper and the cylinder must be separated.
Symptoms of a problem
There are several common signs of a failing brake caliper:
- increased force - this is what needs to be applied to completely stop the machine;
- the car pulls to the side during braking;
- the pedal becomes “soft” - pressing it requires a fairly weak force;
- brake pedal pulsation;
- slight resistance in moving the pedal to the floor;
- brake sticking;
- blocking the rear brakes with great force, etc.
Caliper repair methods
Caliper malfunctions can be different. However, we can highlight the most common cases, as well as recommendations for eliminating them.
Brake pads jam in caliper
This is noticeable when, with the caliper removed, the pads do not move freely. Usually the reason is rust on the stationary caliper pads, which prevents the pads from moving.
To eliminate the problem, you should arm yourself with sandpaper, a metal brush and a file (but only a small one). Then you need to clean off the corrosion from the metal, and then lubricate the surface with a high-temperature type lubricant. However, there should be no wear on the caliper - pits from corrosion. If they are present, cleaning will not help - the pad will not be pressed tightly enough or will not move away from the surface of the brake disc quickly enough.
Sometimes such a defect can be eliminated with a file (subject to insignificant wear), but usually you have to buy a new part of the caliper (fixed).
Something else useful for you:
Video: Passat front caliper rebuild
Corrosion on the caliper piston
It can be triggered either by a defective boot or a long downtime of the machine.
To eliminate the problem, it is recommended to remove and disassemble the caliper. Remove the rust-damaged piston from it and polish it with a special paste or fine rust. After this, thoroughly wash the piston seat with WD-40 and reassemble the caliper. Installing new cuffs won't hurt either. But the best option would be to buy a new piston or caliper assembly.
The caliper guides are jammed
It is necessary to achieve free movement along the guides. To do this, you will need to dismantle the pads, then reassemble the brake caliper and try to move it along the guides. If sliding is difficult, it is recommended to take measures - inspect the guide for bends or breaks, lubricate them, clean them, etc. It is necessary to achieve free movement.
Piston jams in caliper
To check, you need to release the bleeder fitting after the pads jam. In the event of a malfunction, jamming is not observed after that. And with the caliper removed, it is extremely difficult to press the piston back.
For prevention, you can periodically move the piston all the way inside the caliper using a screw, and then push it out with the pedal. But not entirely, so that it does not fall out.
The situation when the brake caliper jams is not just unpleasant, but dangerous for the driver and passengers in the car. The caliper is the most important element of the braking system of a modern car. Its job is to press the brake pads against the brake disc when the driver presses the brake pedal. The caliper is a complex mechanism, and its serviceability must be monitored. You should not only allow the caliper to jam, but also the appearance of squeaks and knocks in it.
Where and how to buy?
You can buy a caliper at any auto store that specializes in selling components for domestically produced cars. As a rule, in such stores all goods are in stock. You can select a suitable caliper either by writing out its markings, or rather the final index of the last 5 digits, or by providing the seller with a faulty caliper (the weight of the product is only 2.17 kg ). Approximately once every 3 years, the suspension of cars of the 2109-2115 family was updated, therefore, the location of the mating threaded seats (mounting bolts) may vary slightly.
New ventilated brake discs are compatible with all mentioned calipers for VAZ 2109, 2110, 2114, 2115. The installation is fully consistent with original components.
How does a brake caliper work?
In ideal condition, the brake caliper should operate as follows:
- The driver inside the car presses the brake pedal;
- At this moment, pressure is built up inside the brake line and it is transmitted to the piston group of all calipers;
- The calipers, under the influence of pressure, bring the brake pads to the disc mounted directly on the rotating wheel;
- Due to the frictional force that arises, the rotation of the disk, and at the same time the wheel, slows down.
Rear wheel brake
Rear wheel brake on VAZ 2114
- Hub nut
- Hub flange. The brake drum is attached to it
- Lower tension spring
- Left pad
- Thrust spring
- Cylinder
- Upper tension spring
- Guide bar
- Eccentric
- Right pad
- Pad cover
Tip: when driving through deep puddles or fording a river, the brakes get wet. This dramatically reduces braking efficiency. Immediately after overcoming a water obstacle on a straight section and at low speed, brake several times. The pad linings, discs and drums will become hot and dry. The system's efficiency will be restored.
In general, the braking system of the VAZ-2114 is simple and reliable. For a person who has experience driving cars of other brands, servicing it on a “fourteen” will not be a problem. But even those drivers who got behind the wheel of a car for the first time can easily understand the operating principle and operating features of the VAZ-2114 brake system. But remember: it is better to service the brake system at warranty service stations from experienced technicians.
Brake device
The brake system of the VAZ 2114, the diagram of which is given below, is divided into hydraulic, which provides braking while driving, and parking.
The first includes such components as:
- brake structures of front and rear wheels;
- main hydraulic cylinder;
- pipelines;
- expansion tank;
- vacuum booster;
- pressure control levers;
- pedal;
- brake hose
The entire hydraulic brake system is divided into 2 connected, but working independently of each other, circuits located diagonally.
The device of the brake system of the VAZ 2114
The first circuit is responsible for stopping the front left and rear right wheels, and the second circuit is responsible for stopping the front right and rear left wheels. This is necessary so that if the pressure drops (for example, as a result of a leak) in one of them, the second circuit remains operational and allows braking.
In turn, stopping the car itself occurs due to the action of the front and rear brake structures on the wheels, which are somewhat different in structure.
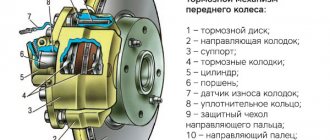
The front includes components such as:
- brake discs;
- caliper;
- pads;
- cylinder and piston;
- O-rings;
- protective casing;
- guide pins;
- finger guards.
Front brake
In turn, the rear brake structure consists of:
- hubs;
- hub fasteners;
- brake pads;
- tension springs;
- direction springs;
- wheel cylinder;
- parking brake lever finger;
- expansion bar;
- hand brake lever;
- protective casing of the brake mechanism.
Rear brake mechanism
As you can see, the rear brake structure is somewhat more complex than the front one. This is due to the fact that it is responsible for the operation of not only the main brake system, but also for the operation of the handbrake.
The latter consists of such elements as:
- lever equipped with a locking button;
- cable;
- equalizer;
- adjusting nut;
- locknuts;
- protective cover.
Parking brake VAZ 2114
The handbrake cable is its weakest link and requires regular inspection. If creases, delaminations and other damage are found on its surface, it should be replaced immediately.
As for hydraulic brakes, the brake pads are subject to the greatest wear, the degree of wear of which should also be periodically checked.
Why does the brake caliper squeak and jam?
A signal that there are problems with a car caliper is a squeaking sound. It may indicate that the caliper is worn out and needs to be replaced, or that a part needs diagnostic maintenance. The squeaking sound when calipers operate most often occurs for one of the following reasons:
The pads are not installed correctly. If the pads are not parallel to the brake discs (or are not in the right place, for example, due to an error during repair), this can lead to squeaking;
- Worn brake discs, which are also directly involved in the braking process;
- There is no lubricant or the lubricant selected is incorrect. Often, drivers (and private services) save on grease for calipers, which is absolutely not allowed. The fact is that it is necessary to select for the caliper not only a lubricant with the ability to cool and prevent friction. Also, the caliper lubricant must be resistant to external influences, especially in winter, when there is a lot of dirt and salt on the road.
The situation is critical when the brake caliper not only creaks, but jams during operation. In other words, the driver presses the brake pedal, and when it is released, the caliper does not remove the pads from the brake discs, which leads to uncontrolled braking of the car, excessive wear and overheating of parts in the brake mechanism.
Simple step-by-step instructions for installing rear disc brakes
Step 1
We loosen the tension of the cables and bring the rear pads together, then use a 12mm wrench to unscrew the guide pins. Use a metal brush to clean the seat and carefully knock down the brake drum. I recommend using a rubber mallet to avoid damaging anything. Truly super tuning of a VAZ 2114 car requires patience and strength. Using a screwdriver, pry up the spring that tightens the pads and remove it. We pull out the spacer bar and take out the upper tension spring. After this, remove the brake pad, first lowering the handbrake lever.
Step 2
When all the old parts have been removed, you can begin installing the HCD. Decide how you want the caliper to be placed - behind or in front of the axle. The effectiveness of the brakes will not change in any way from this operation. I put the axles behind. This is more symmetrical and the weight of the brake mechanism will help with braking. Now you need to join the hub and faceplate into one piece. This operation should be taken seriously. It will be useful to watch a video on this issue, where domestic masters show their tuning of Russian cars in order to share their experience and show some of the intricacies of performing this work. The centering process must be carried out very carefully.
Step 3
Now you can straighten the corners of the beam before placing the hub combined with the faceplate on the beam. This must be done so that the corners do not interfere with the caliper. Personally, I flattened them with a hammer. This work can also be done using a grinder. You should not install a grinder under the left hub bolt, otherwise you will have to work with the grinder again and file the head of the bolt. The brake caliper bracket may rest against it.
Step 4
Well, now the most important thing. We install the bracket on the faceplate and put the brake disc on the hub. Place spacers at the connection points. This must be done at connection points. It happens that the size of the washers may differ, then you need to buy them for a specific car, in our case it is tuning a 14 model car. We tighten the faceplates and the connection of the brackets (I recommend doing this with a force of 3-4 N.M). We screw the hose to the caliper, install the pads, and you can close the tube sealing line. Now we seal the brake line. We check the line for leaks by pumping up the pressure with the pedal. If everything works as it should, then you can begin installing the HCD on the other side.
What to do if the caliper creaks or jams
If the brake caliper creaks or jams, and the part is in good condition, you can try to fix the problems yourself. To do this, it is recommended to perform the following set of actions:
- The first step is to unscrew the brake caliper; to do this, you need to put the car on a jack and remove the wheel. It is worth noting that in some car models the caliper can be unscrewed counterclockwise;
- Having removed the caliper, unscrew the piston using a wrench, then it must be pulled out of the cylinder;
- The removed parts must be carefully inspected for chips, rust, corrosion and various damages. If rust is found, it needs to be cleaned well. When the calipers are heavily worn, problems may arise with cleaning the rust with improvised means; in such a situation, the part will need to be sanded;
Important: When reassembling the caliper, pay special attention to the boot so as not to accidentally damage it. If there are cracks on the boot, be sure to replace it.
Removing the caliper VAZ 2114
Removal and installation
Withdrawal. Raise the front of the car and place it on stands and remove the wheel. Unscrew the pipeline fitting and disconnect the flexible hose from the line; Plug the holes in the hose and tube to prevent brake fluid from leaking. Remove the hose from the guide bracket.
After unscrewing the two bolts that secure the shoe guide to the steering knuckle, remove the guide assembly with the caliper and working cylinder.
Installation of the brake mechanism is carried out in the reverse order of removal. After installation, restore the brake fluid level in the reservoir and bleed the hydraulic drive system to remove air.
Disassembly and assembly
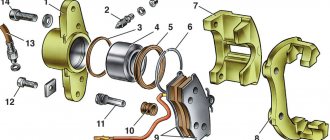
Rice. 6-20. Unscrewing the cylinder mounting bolt: 1 – cylinder mounting bolts; 2 – cylinder; 3 – bolts connecting the cylinder with the caliper
Rice. 6-21. Parts of the front wheel brake mechanism: 1 – wheel cylinder; 2 – fitting for bleeding the brake drive; 3 – sealing ring; 4 – piston; 5 – protective cap; 6 – retaining ring; 7 – caliper; 8 – pad guide; 9 – brake pads; 10 – protective cover; 11 – guide pin; 12 – guide pin fastening bolt; 13 – brake hose; 14 – bolt securing the cylinder to the caliper
Disassembly. Disconnect the hose from wheel cylinder 2 (Fig. 6-20). Unlock and unscrew bolts 1 securing the wheel cylinder to the guide pins, holding the guide pin by the edge with a wrench. Remove guide 8 (Fig. 6-21) of the pads and pins. Remove the brake pads 9.
WARNING. Do not unscrew bolts 3 (see Fig. 6-20) connecting the caliper and cylinder, except when replacing the caliper or cylinder.
Remove the retaining ring 6 (see Fig. 6-21) and the protective cap 5 from the cylinder and piston. Carefully push a stream of compressed air through the fluid inlet to push the piston out of the cylinder. To avoid damaging the piston on the surface of the caliper when pushing it out, install a wooden pad under the piston (Fig. 6-22).
Unscrew the bleeder fitting from the cylinder body and carefully inspect the working surface of the cylinder. There should be no scoring, damage or corrosion.
Rice. 6-22. Pushing the piston out of the cylinder
Assemble the brake mechanism in the reverse order of disassembly. In this case, it is recommended to replace sealing ring 3 (see Fig. 6-21) and cap 5 with new ones. Lubricate the cylinder mirror, piston 4 and the sealing ring with brake fluid, and apply graphite grease or Ditor grease to the surface of the piston, install the piston in the cylinder and, without removing any remaining grease, put on the protective cap 5 so that its edges fit into the groove of the piston and cylinder, then install retaining ring 6. Lubricate the guide fingers with UNIOL-1 grease (1.5 g for each finger). Tighten the bolts securing the caliper and cylinder to the pins to the torques specified in Appendix 1, then lock them. Before tightening the bolts, apply sealant to them to prevent corrosion of the threaded part of the connection. After assembling and installing the brake mechanism, restore the fluid level in the reservoir and bleed the hydraulic drive system.