Good evening everyone! We removed the engine from the car and at the same time decided to replace the release bearing. After assembly, the clutch pedal became too soft, and the force appears at the very bottom and the clutch engages when force appears. The working stroke turned out to be too small and the operation did not allow free play of the pedal; almost immediately when the pedal is released, the car starts moving. This did not happen before; the clutch worked when approaching the middle of the pedal stroke. Who may have encountered something similar?
Clutch pedal too soft after replacement
Hi all!
It all started 2 weeks ago when I noticed that the clutch pedal was soft, but after pumping it a couple of times, it returned to normal. Well, okay. After that, every morning began to be accompanied by these manipulations. This is no longer good. After a few more days, the gears began to turn on with difficulty, and when turned off, sometimes they even shot out, as if I had turned them off without a clutch at all. In the end, each time the gear was engaged, I had to pre-pump the clutch pedal several times in order to get the gear into gear, and with the slightest release of the brake pedal and with the clutch pedal pressed to the floor, the car was already driving like an automatic machine.) You can’t drive like that anymore! I changed the clutch itself about 20k ago, and when replacing the engine in May, I inspected it, it was like new, both the basket, the disc, and the release lever. There is not much choice - either the master cylinder or the slave cylinder is dead. I decided to start by replacing the main one. I ordered Jp Group 1130601900 and it arrived the next day. Having removed the old one, I saw a torn outer elastic band and decided that the problem had been found. The replacement process is theoretically simple: remove the hose from the brake reservoir, unscrew the tube from the back of the working cylinder (under the hood, just below and to the right of the vacuum brake booster, the key seems to be 12), but the difficulty is that this nut is loose, and even in such a place that you can unscrew it only by remembering the entire rich Russian vocabulary, somehow twisting around and unscrewing a couple of mm at a time. Having unscrewed this tube, it is better to immediately develop a fitting so that you can then properly wrap it into a new cylinder. Next we go to the salon. After removing the shelf under the steering wheel, you will need to remove the retainer from the shaft securing the cylinder to the pedal and unscrew the 2 bolts securing the cylinder itself with a 6-point hexagon. Here I encountered a second difficulty: it was difficult to get there because of the abundance of wiring, and the hexagon itself was a bit short, the bolts were tightened well, and I had to tinker to get them off. Next, we transfer everything necessary from the old cylinder to the new one, not forgetting to measure and repeat the distance that was on the old cylinder between the cylinder and the mount to the pedal, and assemble everything in the reverse order. After bleeding the entire system, I realized that nothing had changed. The next day I ordered the clutch slave cylinder Jp Group 1130500900. To replace it, you need a small wrench with a 13-mm head for the bolt securing the cylinder to the box, a 12-size wrench for unscrewing the tube connecting both cylinders and a 10-size wrench for further bleeding. The replacement process itself is simple, the only difficulty is getting to this place. When installing a new cylinder, it is easier to first put the new one in place and secure it, and then install the tube; in the reverse order, it will be more difficult to insert the cylinder into the box, squeezing its rod. After pumping the clutch 10 times and expelling all the air, I finally breathed a calm breath, the pedal became hard, all gears were engaged easily and quietly, the car started moving smoothly, like new!
We also recommend reading the article on how to change gears without a clutch. From this article you will learn how to drive without a clutch, how to change gears without using the clutch pedal with minimal risk of damage to the gearbox, etc. Mechanical failure of the fork, a part connected to the release bearing, should not be ruled out.
Let us also add that a decrease in the viscosity of the brake fluid, low level, severe contamination, loss of properties, etc. Eliminated by replacing the brake fluid. If the clutch pedal becomes soft in the cold season after the car has been idle, and during warming up everything returns to normal, then you need to check the master cylinder.
Most likely his cuff will have to be replaced. The mechanical clutch drive is also characterized by a number of breakdowns.
It is more difficult to identify a problem in a mechanical clutch drive, since you will often have to disassemble the crankcase and get to the release bearing. Its deformation, as well as the breakage of the drive foot, are most often the cause of a soft clutch.
There will be one photo, my friend will take it off his phone and I’ll post it. Based on this, a new clutch pedal was drawn and became soft for the Chevrolet Niva. To get home, I forcibly cut off 3rd gear several times.
Now, when you turn on especially the 3rd and a little 4th, a slight grinding noise is made, as happens on ZILs.
It looks like the fork has bent or the synchronizer has run out. For now it will last until spring, then I’ll open the transmission pan and take a look. Both cylinders - main and slave - should be checked separately.
The softness of the force indicates the presence of a non-rigid element in the pedal-fork-release bearing transmission chain. Statistics show that the working cylinder is prone to jamming, and the main cylinder is prone to loss of tightness and loss of injection functions.
If these manipulations do not produce results and the pedal remains soft, remove the main drive cylinder and inspect it. Usually, the loss of the ability to pump brake fluid into the circuit is associated with destruction, a crease, or the clutch pedal has become soft due to abrasion of the cuffs.
If the soft pedal effect occurs at low air temperatures, and when the engine warms up, the clutch operation is restored, we can conclude that the cause of its occurrence is the loss of elasticity of the master cylinder cuffs.
Alternatively, a defect associated with the appearance of a soft pedal effect was often eliminated by selecting brake fluid with a higher clutch pedal. For cable clutch drive systems, the appearance of a soft pedal means deformation and destruction of the drive tab or release bearing. Oh yes, I almost forgot, I also need brake fluid - about another ruble for a small flask.
The new spare parts look like this and are pleasing to the eye. The hose is a bit long, so I cut it to the length of the old one and with a little extra: Well, let’s put this whole thing in place: Don’t take cheap clamps, they don’t hold at all.
The clutch has become soft: causes and repairs
The cost of a normal strong and reliable clamp is rubles; the clutch pedal has become soft in a Chevrolet Niva. So, a new reservoir has been installed and brake fluid has been added to it. I installed the lid from the old one, since the new one did not have an internal elastic band, and this is important. All that remains is to bleed the clutch and for this my fishing partner came to help me.
How does a clutch problem manifest itself?
There can be several malfunctions in the clutch coupling, with different external manifestations:
- the clutch does not completely disengage, it “drives”, that is, it partially transmits torque through itself even when fully depressed;
- the opposite situation - the clutch is engaged, but the transmitted torque is very limited or absent, in such cases they speak of clutch slipping;
- at the moment the disks close, abrupt fluctuations in torque, jerks and vibrations occur, the clutch “crushes” and resonates;
- Extraneous noises and odors are heard from the clutch, usually a hum, crackling sound and a burning smell.
Most often, with natural wear and tear, problems begin with the appearance of slipping. Other malfunctions are a consequence or occur due to defective parts and violation of operating rules.
Moderators: mek, indy
Problem with clutch master cylinder and bleeding
#1 Post by dr.emmett » Feb 28, 2014 7:09 pm
The gears stopped turning on normally. The front ones could be plugged in with tension, but the rear ones didn’t turn on at all. The reason is that the clutch was not depressed enough. We decided to pump it up. At first they downloaded according to the rules, i.e. Add fluid to the reservoir and open/close the bleeder valve by pressing/releasing the pedal. At the first opening of the fitting, the clutch pedal became soft and the clutch was completely lost. Several hours of pumping ended in nothing. The liquid kept coming out with bubbles and somehow in very small portions. Accordingly, it also left the tank slowly. All tubes were blown out. We checked that there were no leaks anywhere. When we finally got tired of this activity, we decided to go a different route. We connected the bleeder fitting to the fitting on the brake caliper and pumped it “in the opposite direction” under pressure from the brake system. This made things more fun. The pedal became hard and the clutch started working. I drove around a bit to check - everything was fine. After that I didn’t drive for several days. And when it was needed, it turned out that the clutch again did not work (it would not be squeezed out). They concluded that the main cylinder had died. Because I couldn’t find a repair kit, so I bought a used cylinder assembly. Replaced. We started pumping. Again the same crap - it doesn’t pump. We disassembled the old cylinder and cleaned/rinsed/bleeded it. They checked it by pouring liquid into it - the liquid was squeezed out in a normal stream. They put it back on the car. We poured liquid into the reservoir and noticed that the liquid flowed by gravity all the way to the working cylinder. We were delighted and tightened the fitting. We tried the pedal - it was hard. We decided to pump it anyway in case there was air left somewhere. After the first unscrewing of the fitting, everything started all over again - the pedal is soft, pumping does not proceed.
There are almost no thoughts on what to do next. So I decided to go to the forum. True, there was also a problem with the forum - I couldn’t log into my old account and had to make a new one.
If anyone has any ideas, please help.
Re: Problem with clutch master cylinder and bleeding
#2 Post by f111uzm » 01 Mar 2014, 04:33
Re: Problem with clutch master cylinder and bleeding
#3 Post by Bel_serge » March 01, 2014, 11:28 pm
Re: Problem with clutch master cylinder and bleeding
#4 Post by DrEmmett » Mar 03, 2014 11:04 am
I wrote that they took it apart and cleaned/washed it.
Bel_serge, thank you. My cuffs are visually intact. I'll look again more carefully.
Re: Problem with clutch master cylinder and bleeding
#5 Post by f111uzm » 03 Mar 2014, 17:17
Re: Problem with clutch master cylinder and bleeding
#6 Post by DrEmmett » 03 Mar 2014, 19:52
Re: Problem with clutch master cylinder and bleeding
#7 Post by DrEmmett » 09 Mar 2014, 10:38
Tell me, could it be that the working cylinder is not leaking, but is still sucking in air? And is there any way to check this?
I'm completely exhausted with this clutch.
And he tortured others. Experienced guys from the service center first joked, saying that there’s a clutch there, we’ll do it in no time. But they poked around and poked around and also threw up their hands. They say go to the officials
Such a strange thing. With an “open” system (i.e., the bleeder fitting is open, a tube is put on it and lowered into the fluid), the clutch is pumped by simply pressing the pedal. It pumps and starts to squeeze out normally. If you tighten the bleeder fitting while the clutch pedal is depressed, then everything continues to work normally for some time. If you tighten the fitting while the pedal is pressed and release the pedal, it (the pedal) immediately becomes soft. Probably, air is being sucked in somewhere at the moment when a vacuum is created in the system when the pedal is released. But in theory, if there is some kind of “crack” (leaks) somewhere, then liquid should ooze through it under pressure when pressed. But nothing seems to be flowing anywhere.
What's the result?
If the clutch becomes soft without special adjustments, you need to look for the reasons and carry out repairs as soon as possible. Remember, driving with a faulty clutch is unsafe and also leads to increased wear of various parts, elements and assemblies.
Finally, we note that a complete replacement of the entire drive is required only in certain cases. As a rule, it is possible to limit oneself to replacing some individual parts and subsequent adjustment/adjustment of the clutch drive.
How to change gears without a clutch: driving a manual car without a clutch in case of malfunction. Tips and tricks.
Gears are difficult to engage or speeds on a manual transmission do not engage: the main causes of the malfunction and possible problems.
Correct gear shifting in a car with a manual transmission: when to engage a particular gear on a manual transmission, working with the clutch pedal, errors.
Car clutch: purpose, types, design, principle of operation. Frequent clutch malfunctions in the vehicle transmission system, signs of problems.
Reasons for difficulty shifting gears with the engine running. Transmission oil and level in the gearbox, wear of synchronizers and gearbox gears, clutch.
How is the clutch implemented in the transmission device on cars with automatic transmission compared to a manual or robotic transmission. Features and differences.
Most often, modern cars have two types of clutches:
- with a mechanical drive
- the clutch fork is connected to the pedal in the cabin using a cable; - with a hydraulic type drive
- the gas pedal is connected to the clutch slave cylinder by a pipeline filled with working fluid.
The adjustment procedure depends on the type of unit.
Adjusting the mechanical clutch
First, let’s find out whether the pedal stroke decreases or increases. We press the pedal all the way and measure how far from the floor it stops. Let's release the pedal and take measurements again. From the second indicator we subtract the first. For most models, the normal stroke amplitude is in the range of 12 - 14 cm, this can be clarified in technical documents. If the number is less, the pedal stroke needs to be increased, if it is more, it should be decreased.
After the measurements, we move on to the adjustment procedure itself:
Stage 1
– open the hood, find a rod near the transmission lever that secures the cable coming from the clutch pedal.
Stage 2
– lubricate and loosen the nuts that secure the rod with liquid lubricant.
Stage 3
– using wrenches, turn the nut that was closer to the pedal. If you turn the nut towards the clutch pedal, the free play of the pedal will become greater, if in the opposite direction - less.
Stage 4
– again measure the amplitude of the pedal stroke. If it is within the normal range, tighten the second nut – the control one – until it stops. This is necessary to record the adjustments made. If the stroke is still too large or small, tighten the nut that is closer to the pedal.
Checking the clutch operation. The pedal should be pressed easily, without noise or friction. When starting, the car should not slip or move jerkily. Speeds should change smoothly and accurately.
Adjusting the hydraulic clutch
Hydraulically operated clutches are mostly self-adjusting. But you can also adjust them manually if the pusher on the working cylinder has a thread and a control nut. Here's how to do it:
Stage 1
– check the level of working fluid in the clutch. It should be at a normal level.
Stage 2
– we create conditions for working under the machine. You can place the car on a ramp or risers, use a lift or inspection pit.
Stage 3
– we look for the pusher of the working cylinder.
Stage 4
– unhook the spring from the fork with pliers. Push the fork forward as far as possible and measure the distance between it and the pusher rod. We release the fork and take the same measurements. We get the size of the clutch gap, which we check with the standard one. If it does not fit into the range specified in the technical documentation (usually about 5 mm), we make an adjustment.
Stage 5
– remove the spring installed on the bracket of the working cylinder and fork.
Stage 6
– loosen the fixing nut on the threaded connection of the pusher, turn the adjusting nut in the direction of the working cylinder to increase the size of the gap. Or in the opposite direction - to reduce them.
Stage 7
– tighten the control nut when the gap dimensions become normal.
At the end, we carry out a control check of the clutch operation.
The hydraulic clutch, like the mechanical clutch, can be adjusted manually
As you can see, problems associated with the clutch on a manual transmission in some cases can completely immobilize the car. If the problem is related to the clutch pedal, that is, the driver loses the ability to control the operation of the clutch, then repair is also necessary, however, if you have certain skills and abilities, you can drive to a service station or other place where the car is repaired under your own power.
We also recommend reading the article about
how to adjust the clutch pedal
. In this article you will learn when to adjust the clutch pedal, as well as how to adjust the clutch if necessary.
Finally, we note that at each scheduled maintenance it is optimal to check the quality of operation of all important components of the car. The clutch is also no exception. It is necessary to monitor the condition of the clutch cable and change the brake fluid in a timely manner to extend the life of the clutch master cylinder.
If necessary, it is also recommended to adjust the clutch pedal, bleed the clutch, and also take into account even the slightest malfunction of this unit during vehicle operation.
The clutch pedal has become soft: reasons
Types of clutch drive. If the clutch pedal falls, the clutch has become soft, problems have arisen with the clutch: causes and repair of major faults.
Clutch pedal adjustment: how to do it...
How to adjust the clutch pedal, what adjustment is needed for: clutch functions, clutch pedal adjustment (free play and total travel).
After replacing the clutch, the gears do not engage...
Manual transmission gears (speeds) do not engage after replacing the clutch: main reasons, settings and adjustments. Diagnosis of problems, useful tips.
For what reasons does the clutch fail prematurely?
The operating life of this unit is approximately 150-300 thousand km, which is quite a lot. Also, life activity depends on the car itself and its operation. What factors lead to its reduction? So:
- Dangerous driving style: the driver throws the pedal, presses it sharply, which leads to faster wear of the lining.
- The vehicle moves constantly under load. This often applies to commercial vehicles
- If you are towing another vehicle that weighs much more than your vehicle, the clutch may burn out. If you feel burning, you should stop moving immediately.
- Do not hold the pedal halfway down. Only if necessary.
Possible clutch malfunctions
Clutch pedal squeaking
One of the most common malfunctions that is inherent in new domestic cars or old foreign cars is the clutch pedal squeaks when pressed. It is the noise that occurs throughout the entire mechanism when the pedal is pressed and released. In the case of domestic cars, it appears after the use of low-quality lubricants. In the case of imported cars, it can appear mainly after a long period of use.
What is a squeak? This is a creaking noise made by dry rubbing surfaces, both metal and plastic. And, therefore, in order to eliminate noise, it is enough to carry out lubrication of all kinds of moving parts of all evil. If after all the operations the clutch pedal squeaks again, then there may be a problem with the rod and the bushing in which it moves. In addition to using high-quality lubricants, you can temporarily lubricate the almighty WD. It will not only dissolve rust in the mechanism, but also lubricate the surface, because it feels greasy to the touch. Thus, the noise will disappear for some time.
Increased pedal softness
The cylinder, both the main and the slave, is mainly responsible for this parameter. In the background is the mechanical part - the tension spring, which returns the cylinder piston to its original state after releasing the pedal. Cylinder malfunction can be in the form of:
- fluid leaks;
- increased wear of the sealing collars on the cylinder pistons;
- malfunction of the spring tension device associated with its breakage.
Clutch pedal structure
If the clutch pedal becomes soft when pressed after some period of operation, and in order for it to fail in the future, the following manipulations must be performed:
- Check the fluid level in the tank; if it is low, this indicates a leak in the system that needs to be repaired.
- If the fluid is at the same level, then it is necessary to check each cylinder individually and the tension spring.
In the first case, it is necessary to check all connections and the cylinders themselves for leaks; if any are found, remove the spare part and replace it with a new one. If a leak occurs from the cylinder when the pedal is pressed, it can be repaired by replacing the repair kit. And then if the inner surface has a perfect mirror surface. Otherwise, a new cylinder is required.
In the second case, it is necessary to carry out the same manipulations if the spring tension mechanism is working properly.
If, when pressed, the clutch pedal becomes soft or, in general, fails and does not return to its original position after replacing any of the cylinders, then most likely there is air in the system that is pumped into them, which makes the lever soft. In order to eliminate this, it is necessary to re-bleed the clutch.
The level of rigidity is normal, but there is no movement of the car
If the pedal fails and does not return on its own and the fluid level is normal, then there may be a malfunction in the release mechanism. It includes:
- fork;
- release
In this case, after pressing the pedal, if the rod is relaxed, it can jump out of the cylinder, and, consequently, liquid will flow out in a copious stream, creating a characteristic noise.
It is impossible to do without replacing the necessary components, because all spare parts of this unit cannot be repaired. After replacement, adjustment of the clutch pedal is required. There are basically two types:
- initial position of the pedal, adjustment on the mechanism itself;
- free play adjustment, regulation via a tension spring on the box itself.
The first type of adjustment is carried out if the sensor does not match the position of the pedal. In the second case, the adjustment involves changing the free play through an additional mechanism. This type of adjustment is used to compensate for the difference in fluid pressures and wear of the clutch mechanism in the box itself (basket and disc) after repair work.
Clutch pedal
Increased pedal free play
Increased free play of the clutch pedal when pressed indicates mechanical wear of the clutch basket. Structurally, it has tabs that press on the clutch disc release ring; as their elasticity decreases, the free play of the pedal increases. You can adjust it until the clutch begins to slip, and the lever thereby becomes more and more rigid. This leads to the following problem.
Increased elasticity of the clutch pedal
If the clutch pedal is already too tight, then this indicates that your clutch basket is about to wear out. And you should already think about buying a new one, because it is impossible to repair the old one, and even more so the disk must be replaced along with it. In this case, a characteristic noise appears from the box. In addition, a stiff clutch pedal may be a sign of a clogged system. To do this, you need to remove the cylinders and wash them, replacing all the cuffs, and the tube can simply be washed.
Usually, a tight clutch pedal is the cause of several breakdowns, so be careful not to get into trouble down the road.
Vibration when pressed and released
If the clutch pedal vibrates when pressed, then it’s time to check the mechanical part of the clutch, which includes: the fork, the release lever, the basket and the disc. Structurally, the fork is connected to the release bearing by means of two brackets; failure of any of them can lead to uneven lowering of the bearing onto the splines and, ultimately, to its beating against the output rod of the axle on the box. Thus, when pressed, the clutch pedal vibrates.
In addition, it can also occur due to a malfunction of the basket itself, because it is not a simple device and, in addition to the paws, has a brake disc, which is attached to it by means of elastic steel levers.
If any of them fails, it can lead not only to vibration, but also to breakage and damage to the surface of both disks. The characteristic noise from the box will let you know about this. Therefore, if the clutch pedal vibrates, do not close your eyes to it, take action before it is too late.
How the clutch works, what are its typical malfunctions, and how to avoid them
An important element of a manual transmission is the clutch, which serves to briefly disconnect the engine from the transmission. In addition, the clutch is a kind of damper that protects the engine from overloads. How does it work and how to extend its life?
How does the clutch work?
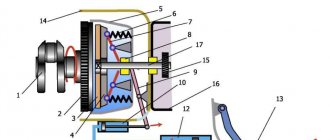
Most passenger cars with a manual transmission use a dry single-plate clutch. Its design is quite simple: it consists of two mutually adjacent disks - a drive (basket) and a driven one, a release bearing and a drive system. In the single-disc version, the transmission input shaft fits into a splined clutch in the center of the driven disk, and the surfaces of the engine flywheel, driven disk linings and basket pressure disk fit tightly together. Due to this, the transfer of power flow from the engine to the gearbox is ensured, and a working clutch calmly “digests” all the power developed by the engine.
In everyday life, the clutch drive disc, which includes a pressure plate (with a smooth shiny surface), a diaphragm spring (petals in the center) and a casing, is called a basket
When you press the clutch pedal, the release bearing acts on the plate springs of the basket, causing the surfaces of the driven and driving discs to separate. Accordingly, the input shaft is disconnected from the flywheel - that is, the engine and gearbox are physically disconnected, which allows you to change gear or engage neutral. When the clutch is engaged (the pedal is released), the release bearing stops pressing on the leaf springs, and the discs close again, and the damper springs in the central part of the driven disc dampen the torsional vibrations that occur during movement.
The four damper springs of the clutch driven disc are clearly visible, as well as the worn friction linings
When the clutch operates normally, it does not attract attention to itself. But if it malfunctions, the driver, for example, will not be able to shift gears or move away. What problems are possible?
The main reasons for a soft clutch pedal
To depress the clutch pedal when the drive is fully operational, you need to apply a certain force. This setting can be adjusted. Some drivers deliberately use a soft clutch. However, most often this is a sign of breakdowns and malfunctions, especially if the driver notices a difference compared to the norm. For mechanical and hydraulic drives, the problems will be different, not counting cases of mechanical failure of some parts.
- Let's start with the hydraulic clutch drive. First of all, air in the system is a common problem. During any repair of the hydraulic drive, air enters the tubes. This makes the pedal stroke soft. In this case, you should check the quality of tightening of the pipeline fittings, and also bleed the entire system (bleed the hydraulic drive).
You can also highlight a malfunction of the clutch slave and master cylinders. The working cylinder most often jams, and when the main cylinder fails, it loses its tightness and, as a result, its pumping capacity.
If the clutch pedal becomes soft in the cold season after the car has been idle, and during warming up everything returns to normal, then you need to check the master cylinder. Most likely his cuff will have to be replaced.
- The mechanical clutch drive is also characterized by a number of breakdowns. It is more difficult to identify a problem in a mechanical clutch drive, since you will often have to disassemble the crankcase and get to the release bearing.
Its deformation, as well as the breakage of the drive foot, are most often the cause of a soft clutch. The problem may also be associated with the destruction of one or more damper springs of the driven disk. Often this can also be found out only after disassembly.
Clutch functions on a car
The clutch serves to transmit torque from the engine to the gearbox, after which the torque is transmitted to the wheels. In simple terms, the clutch disc is pressed against the flywheel on the crankshaft.
It is possible to press and release the disk from the flywheel using the clutch pedal, with which the driver actually acts on the clutch drive. When the pedal is in the up position (the pedal is not pressed), the disc is pressed. If the pedal is depressed, the disc and flywheel are disconnected. It turns out that by pressing the pedal the driver disengages the clutch.
The clutch drive on modern cars is mechanical and hydraulic (or electro-hydraulic). The first option is relatively simple and cheap. Installed mainly on budget passenger cars. If we omit the technical details, the point is that the clutch pedal is connected to the drive via a sheathed steel cable. The mechanism for adjusting the free play of the pedal is located on the same cable.
In the hydraulic version, the cable is replaced by cylinders (as in a brake system) and the principle of incompressible fluid (in this case, brake fluid) is used. Most often, a hydraulic drive is installed in modern cars, since it is more advanced and reliable. In any case, when the car has a too soft clutch pedal, gears do not engage and other difficulties arise with shifting, normal operation without repair is simply impossible.
How to get to the service station yourself?
It is much better when the breakdown of parts in a car occurs at your home, or, directly, near your home. Then you can consider yourself lucky. There is no problem in bringing your car into the yard and getting it repaired. What should those drivers do if such a problem as a soft clutch pedal occurs on the road? What to do and how to get to the nearest service station? To be honest, I wouldn’t even wish my enemy to break down on the road.
But not everything is as critical as it seems. With a broken part, you can drive or still push the car to the nearest service station. So, let's look at how and what needs to be done.
If on the road you feel that your clutch pedal is soft instead of an elastic pedal, as it should be, do not worry. This grief, as they say, cannot be helped. All you need to do is follow clear sequences with which you can try to fix the breakdown yourself or make sure that the car can get to the service station.
Option one. To try to restore the operation of the pedal, you need to do the following: set the gearbox lever to neutral and at the same time release the gas. When the lever starts to stick, you need to apply the gas a little, this will free it.
Method two. Refers to a situation where car repair is impossible on the highway, but requires the intervention of specialists. In this case, to get out of this situation you need to turn off the engine and set the gearbox to the minimum speed (first). Next, you need to turn the starter in order to start the engine again. When the car starts up, things that you do not understand may happen to it: it will move jerkily. This is because the gear engaged does not match the speed mode. To upshift you need to press the gas, then set the lever to neutral and then engage second gear. But, it is not advisable to perform such maneuvers; it is better to slowly but surely drive to a repair shop and have the problem repaired.
To summarize, we can emphasize that there may be several reasons why the clutch pedal fails. They can be solved either directly at the breakdown site or at a service station. But, so that you never have breakdowns on the road, take care of your car. And he will become a reliable friend for you.
How to fix the problem
Knowing that the system is faulty, you need to take measures to repair it. First you need to determine the breakdown, because it is likely that only one part has broken.
Without wanting to spend money, you can solve minor problems yourself:
- lubricating or replacing the release clutch bearing;
- replacing fluid in the hydraulic drive with subsequent pumping;
- changing the driven disc pads or springs if the elements are worn out, weakened or deformed;
- replacing the basket and all parts with a new assembly recommended by the vehicle manufacturer.
Even if these steps are taken, the tightness may still remain. Then you need to try to replace the cable, clean its jacket from dirt and corrosion, and also lubricate it with machine oil. Hydraulic systems can also have cylinder failures, which is also quite serious.
Broken clutch cable
In any case, the most accurate diagnostics can be carried out in services where the nodes are disassembled and their suitability for use is determined. There, the car will be put in order and the stiffness of the lever, which interferes with comfortable driving, will be corrected.
Signs of slippage?
A clutch only engages by friction, so if there is no material there to provide that friction, then your clutch will not work properly. If the clutch is slipping, you will feel that when you release the pedal and accelerate, the car will move slowly and the engine speed will increase. You may also notice that the clutch releases sooner than expected without applying much pressure.
Potential causes of clutch slippage:
- The clutch linkage or cable needs adjustment because the cable is being compressed or the cable housing is filled with rust;
- Clutch linkage is bent, misaligned or damaged;
- The pressure plate is loose or deformed;
- The clutch assembly is contaminated with oil due to your engine or transmission oil leaking;
- Broken engine mounts.
Keep in mind that if your clutch does not disengage properly, it will continue to rotate the input shaft. This can cause grinding and prevent your vehicle from starting.