As you know, the safe operation of any vehicle directly depends on the proper operation of the braking system. At the same time, the driver may notice that at some point the car brakes worse, extraneous noise appears during braking, the brake pedal sinks, the brake pedal becomes hard or soft, etc.
In any case, if the brake pedal is hard to press or the brake pedal is soft and does not brake the car well, you must immediately stop using the car, determine the cause and eliminate the problem. Next, we will look at why the brake pedal is hard to press, the brakes are too soft, or the brake pedal is either soft or hard.
The brake pedal has become hard: the reason
So, during operation, you can discover that the brake pedal has become hard, medium or too soft. The reasons for a tight pedal, that is, when the brake pedal on a car is too hard, can be either a design feature of a particular car or a malfunction. In other words, a hard brake pedal may be normal for certain car models. If the brakes become hard for another reason, repairs are necessary.
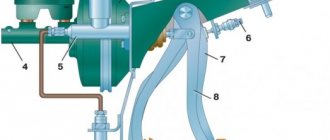
In a nutshell, the design of the brake system involves the presence of a brake pedal, from which the levers go to the vacuum brake booster. The Vacuum Assist (VUT) uses rarefied air to increase pedal efficiency. Next, the brake master cylinder distributes the force it received from the vacuum booster to the wheels.
To transfer pressure, brake fluid is poured into the system. The fluid is supplied through steel pipes and rubber hoses from the master cylinder to the brake wheel cylinders. The working cylinders use their piston to transmit pressure to the brake calipers, pressing the brake pads against the brake disc or drum.
The list of main reasons why the brake pedal is hard to press or the brake pedal is not pressed includes problems with the vacuum booster. The following problems should be noted:
- Malfunction of the vacuum brake booster limit switch. Replacing the end switch solves the problem;
- The vacuum booster also has a special check valve. If the valve sticks or does not work, the specified element must be replaced;
- The VUT may also have a dirty air filter, which prevents dirt from entering the system. If the filter is clogged, in a similar situation the brake pedal is also pressed hard;
- The amplifier also has a special check valve. If the VUT valve is stuck, this element must be replaced;
- Often the reason why the brake pedal becomes hard after several presses or the brake pedal is hard after parking is the brake booster diaphragm. The VUT diaphragm breaks or cracks, and the entire amplifier must be replaced;
- At the same time, we note that fuel may enter the booster chamber (often due to a broken check valve), which will also immediately affect the operation of the brake pedal;
- One common cause of a hard brake pedal that won't press down is the hose connecting the intake manifold to the booster. The specified hose wears out and becomes deformed, that is, over time it may require replacement. It also happens that it loosens on the fitting. In this case, a tight fit can solve the problem;
- The list ends with the use of dirty brake fluid that has lost its properties, the ingress of third-party fluids into the brake cylinders, as well as swelling of the sealing rings. To fix the problem, the cuffs and seals need to be replaced (repair of brake cylinders), and the brake fluid must also be replaced. In some cases, entire brake cylinders need to be replaced.
Let's sum it up
Therefore, it is obvious that any abnormality in the braking system (for example, a soft brake pedal, a hard brake pedal, or a combination of problems) requires immediate diagnosis. After the fault has been identified, it is necessary to properly fix the problem.
It is also necessary to promptly replace the fluid, pump up the brakes, check the brake lines for defects and leaks, promptly install new brake pads, discs or drums, lubricate the brake caliper guides, etc. This approach will allow you to safely operate your vehicle and obtain high-quality performance of the braking system in any conditions.
If the brake pedal is pressed hard: diagnostics
As you can see, a tight brake pedal is often due to problems with the vacuum booster. At the same time, its operation can be quickly checked on the spot.
To diagnose VUT, you can use two methods. In the first case, you need to start the engine for the vacuum booster to start working. Normally, the pedal is soft; after two or three strong presses on the brake, the engine speed will briefly increase.
If, after starting the engine, the brake pedal is hard, then you need to check the hose or the booster itself. Also, a lack of pedal softness may be associated with the brake booster valve. Problems are indicated by hissing and extraneous sounds when you press the brake.
Another test involves pressing the brake several times with the engine off. Normally, the pedal should be soft for 2-3 presses, then it becomes hard. After this, you should press the brake and start the engine without releasing the pedal. The pedal should go down after the engine starts. If this does not happen, then you also need to look for a problem with the VUT.
Personal experience of car owners.
Alexei:
“I am a driver with little experience, so it was very difficult for me to independently determine the cause of the pedal hardness. I couldn’t even figure out how to remove this or that part in order to diagnose specific problems. In the end, I took my Audi A6 to a service station. The craftsmen working there determined the nature of the damage without even removing the units. Correct diagnostics helped me significantly save on repairs.”
Ivan:
“When the amplifier of my VAZ 2114 broke down, I verified that it was faulty in a simple way. To do this, the hose is removed and the amplifier is turned off. The presence of a vacuum when starting the engine indicates that the “vacuum valve” is faulty.”
Novel:
“The vacuum booster and cylinders are very difficult to diagnose. The best vehicle diagnostics can be provided only by those car services that have pressure gauges.”
Soft brake pedal: reasons
Having figured out why the brake pedal can be hard, you should pay attention to an equally common problem when the brake pedal has become soft. In such a situation, the brakes may be weak and perform poorly, which is no less dangerous than a hard pedal.
In extreme cases, the brake pedal may not rise after being pressed or may sink to the floor when braking. Naturally, in the case of a “cotton” pedal, owners are interested in what is the cause of the malfunction, why the pedal is soft after bleeding the brakes, and also how to make the brake pedal harder.
So, if during the operation of the car or carrying out service or repair work (for example, after replacing the turbocharger) the pedal becomes soft, this often indicates that air is getting into the brake system. In other words, a soft brake pedal indicates air in the brake system. In this case, the brake fluid should be changed at the initial stage, and the brakes themselves need to be pumped.
We also recommend reading the article about why the brake pedal fails when the engine is running. From this article you will learn about the main reasons why the brake pedal fails after starting the power unit.
If bleeding has already been carried out, there is a high probability that mistakes were made, undetected breakdowns, brake fluid leaks, etc. occurred. For example, drivers often encounter a problem when, after replacing the brake pads, the pedal is soft, the brake pedal falls off after replacing the brake fluid, after bleeding the brake pedal fails, but the fluid does not drain, etc.
- One way or another, the main reason is depressurization of the brake system. Pipes fray and crack, problems with brake cylinders are possible, dirty brake fluid damages the cylinder mirror. Jamming of the TC pistons should not be ruled out.
At the same time, it is necessary to inspect the locations of all connections, fittings and other elements, since even a few drops of brake fluid leakage have no effect on the level in the reservoir, but air still enters the system, which is the cause of the soft pedal.
It should also be taken into account that if certain elements of the brake system have been changed (discs, pads, drums, working cylinders, etc.), in this case the braking efficiency will be slightly reduced until the parts are broken in. In this case, over several tens of km. The pedal may also feel softer than usual, or the brake pedal may alternate between being soft and stiff.
Let us also add that a change in pedal hardness can also occur if the brakes overheat and “boil”. High loads on the braking system (for example, long descents with the brake pedal not fully depressed) lead to a significant increase in temperatures from pad friction. Also, unnoticed jamming of the pads when the brake release mechanism does not work properly can also overheat the brakes.
If the brake fluid is dirty, old and has lost its properties, it may boil due to heat. This leads to the brake pedal sinking or becoming too soft (“cotton”). This situation is dangerous because the problem may have a so-called “floating” nature. If such symptoms appear, you need to start with a complete replacement of the brake fluid.
Swelling of rings in cylinders.
The condition of the brakes largely depends on what kind of brake fluid is used during operation. If it is a product of a well-established company, the vehicle is rarely damaged or disabled. But if the fluid is of poor quality, one or more cylinders may not function well due to their O-rings swelling. The same thing happens when fuel and lubricant gets on the ring.
Previously, especially in the era of the Soviet automobile industry, the car owner sooner or later had to sort out the working cylinders. Such an activity was long and burdensome even for professionals. But now hardly anyone will do this if the vehicle is faulty. From the point of view of saving time, it is much easier to change them, and at the same time the brake fluid. However, you can avoid unnecessary financial costs if you use high-quality, albeit expensive, liquid from the very beginning, since repair costs are always higher.
Why is the brake pedal higher than the gas pedal?
Drivers often wonder why on many models all the pedals in the car are not on the same plane. As a rule, on a car with an automatic transmission, the brake pedal is noticeably higher than the gas pedal. On cars with manual transmission, the clutch and gas are also often lower than the brake.
Let us note that there is a lot of debate on this matter and there are a number of conjectures and assumptions. Some car enthusiasts claim that this is inconvenient, others complain that if the pedals were in the same plane, it would be easier to control the car, etc.
One way or another, in fact, this arrangement of the brake pedal is made for maximum safety. The simplest explanation is that if the driver accidentally or due to inexperience mixes up the pedals, he will first press the brake and not the gas. In an emergency situation, it is also easier to “grope” the brake pedal located above or simply “hit” the entire pedal assembly, hitting the brake pedal with your foot first, and not the accelerator pedal located below.
Let’s also add that some owners believe that the brake pedal is placed higher in order to increase its travel, and also taking into account the need for more force (lever).
Reviews
Hard pedal - failure of the vacuum pump or vacuum booster or leaking vacuum hose. Or the master cylinder wedge.
https://www.bmwclub.ru/threads/propadajut-tormoza-tverdaja-pedal.896947/
I had the same problem, if I let someone drive my car, they complained that the brake pedal was hard. They were sent with the statement that normal, well, there is strength - the mind... As a result, during the next maintenance, it turned out that the CH was a little high (gasoline). When I started looking into it, it turned out that air was being sucked into the vacuum brake booster through a worn-out gasket. At high speeds there is sufficient vacuum, but at low speeds the pressure gradually drops. Replacing the gasket solved the problem...
https://audi-belarus.by/forum/viewtopic.php?t=44405
I also struggled with this pedal for a long time. I'll pump it up for a couple of days. Then again. The vacuum operator with the main brake also made a mistake. Then I replaced the pads at the rear and the problem disappeared.
https://www.drive2.ru/c/2425257/
In order for the brake pedal to work well, you need to regularly change the fluid, lubricate the caliper guides, and inspect the VUT elements for damage.
Source