The serviceability of the braking system on any car is, for obvious reasons, of paramount importance, since overall driving safety directly depends on the effectiveness of the brakes. Taking into account the above, any deviations from the norm (even minor ones) in the operation of this unit are a reason to immediately identify the cause of the malfunction. In this article we will talk about what to do if the brake pedal fails while the engine is running, problems arose after replacing the brake fluid, bleeding the brakes or other elements of the brake system, etc.
We also recommend reading the article about why engine speeds fluctuate. From this article you will learn about the causes of “floating” idle speed, as well as ways to determine the malfunction.
Car brake system: types, general structure and principle of operation
To better understand why the brake pedal fails when pressed, it is necessary to consider the general operating principle and design of the brake system. This system is usually hydraulic, and problem areas are often common on many car models. Brakes operate on the principle that there is incompressible brake fluid in a closed volume.
Note that the machines previously also used a mechanical braking system with cables and other drive elements, but engineers abandoned such a device long ago. The fact is that although mechanics were not inferior in reliability, but were superior to hydraulics, the performance and smooth operation of such a solution turned out to be insufficient, taking into account the rapid development of the auto industry, the increase in the power of installed internal combustion engines, etc. Mechanical brakes simply no longer cope with increasing speed limits and effectively and safely slow down the car.
There is also a pneumatic braking system, which is used on special vehicles (trucks, large buses, various equipment). Air brakes are no worse in efficiency than hydraulics, but the system itself is too heavy and bulky to be installed on compact passenger cars. So it turns out that the hydraulic braking system has become widely installed on civilian and commercial vehicles, as well as on many other types of wheeled vehicles.
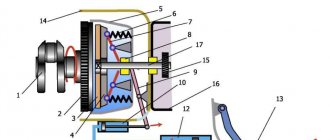
Hydraulic brakes have the following elements in their design:
- GTZ (brake master cylinder)
- RTC (brake wheel cylinders)
- Hydraulic lines
- Compensatory device
- Brake discs and brake pads
The working fluid for the brake system is brake fluid, which has certain properties. At the moment when the driver presses the brake pedal, the force is transmitted to the GTZ, which is filled with working brake fluid. The GTZ device has a piston that exerts pressure on the liquid. Through the working fluid, the force is transmitted to the RTC, which are installed in the area where each of the vehicle wheels is located. As a result, the brake pads are pressed against the brake discs or brake drums. If the force is maximum, then the pads completely block the rotation of the wheel. Let us add that depending on the type of brakes installed, the latter are divided into drum or disc. There is also a combination where the front wheels have disc brakes, while the rear wheels are equipped with drum brakes.
The main advantage of hydraulics is smooth and predictable force; the pads are pressed evenly against the brake discs. As for the force on the brake pedal itself, it is proportional to the force that compresses the pads. It turns out that the driver can clearly measure the applied force, thereby determining the degree of wheel locking and the intensity of braking. After releasing the brake pedal, the return springs, which are present at the place where the pads are installed, move them apart, that is, they allow the pads to take their original position. At the same time, the brake fluid is forced back into the master cylinder. This is the general operating principle of the entire system. At the same time, modern cars have additional elements: a vacuum brake booster, a brake force compensator, an ABS system, etc.
Now a few words about the brake circuit. This solution allows you to reduce the risk of complete failure of the braking system in the event that the brake mechanism on one of the wheels is faulty. This is very important for hydraulics, since a leak in one of the RTCs is a common malfunction. There are several schemes of multi-circuit brakes, according to which the circuits of brake systems are implemented. Let's look at some of them. The axial design allows the braking system to be divided into circuits for the front and rear axles. If the brake wheel cylinder leaks on one axle, then the other will be able to operate normally. There is also a pattern where the braking force distribution pattern is made diagonally relative to the rear and front wheels. There are also solutions that combine the wheels of the front axle and one rear wheel; RTC pistons are additionally installed (double-piston and multi-piston brakes), etc.
Why the brakes disappear and the pedal fails: symptoms, causes and what the driver should do
Having examined the general structure of the hydraulic brake system, you can understand why the brake pedal sinks to the floor or why the pedal slowly sinks when you press the brake. There may be several reasons for such a malfunction. Quite often, diagnostics must begin with checking the brake fluid level in the reservoir. Any hydraulic system has the specified compensation tank. The tank has “min” and “max” marks, which determine the normal amount of fluid in the system.
The fact is that although the brake fluid is incompressible, the volume of fluid in the system changes. This occurs due to the fact that brake pads tend to wear out during use. As a result, the RTC pistons extend further to move the pads, which requires more fluid in the system. For this reason, the minimum level of working fluid in the tank is determined. When the amount of fuel fluid drops below the minimum, then air enters the brake system circuit, that is, airing occurs.
It turns out that if the brake pedal fails, the causes of such a malfunction can often be a critical decrease in the fluid level or air ingress. When pressed, the brake pedal goes to the floor all the way, the brakes do not work completely or barely work. To prevent possible consequences, the level of brake fluid in the expansion tank must be checked visually, without waiting for the moment when the emergency lamp lights up on the instrument panel in the cabin.
It should also be added that airing of the brake system is possible for other reasons. If the ABS brake pedal suddenly fails or the pedal falls to the floor on cars without an anti-lock braking system, and checking the fluid level in the reservoir does not give anything (the level is normal), then overheating of the brakes may be the culprit. Brakes overheat in cases where there is intense and frequent braking at high speeds, constant and prolonged driving at low speed with the brake pedal pressed (for example, descents on mountain serpentines). More often, deterioration of the system in such modes occurs in conjunction with high outside ambient temperatures.
In other words, the brake fluid boils under such conditions and the brakes are overheated. As a result, the brake pedal fails, since the intense release of air during boiling of the fuel fluid disrupts the operation of the hydraulic system, regardless of the circuit implementation scheme. Taking into account the above, it is necessary to avoid sudden, constant and intense braking in the heat on cars that are not prepared in advance for such operating conditions. For the same reason, it is recommended to modernize and modify the brake system on cars whose engine has been seriously boosted for driving in aggressive mode. To avoid overheating of the brakes, you need to install ventilated brake discs and use special brake fluid, which requires operation in high-heat conditions.
We also recommend reading the article about what a boosted engine is. From this article you will learn about various methods of modifying and tuning the engine.
As for topping up, it is necessary to use the type of brake fluid recommended by the vehicle manufacturer. Mixing different types of liquids, as well as products from different manufacturers, is highly not recommended. For example, if the use of DOT4 is allowed, then you need to pour such a liquid, and use a product from the same brand. Ignoring this rule may lead to seals in the brake system becoming unusable, lines may become clogged, etc.
In parallel with this, at each maintenance the wear of the brake pads and brake discs/drums on each axle should be checked. Try not to drive on heavily worn pads, as wear and heat on the discs/drums will also increase. If the brake discs themselves are worn out, then they should be replaced or sharpened to remove wear. Elements should be changed and sharpened in pairs, that is, on each axis.
After replacing the brake pads, the brake pedal fails
A fairly common occurrence after certain work related to the brake system is that after replacing the brake fluid, the brake pedal fails. The malfunction may also appear after replacing pads, discs, and drums. Drivers quite often encounter the problem of pumping the brakes, but the pedal falls through. Let's figure it out.
Let's start with the fact that after replacing the pads/discs, replacing the fluid and bleeding the brakes, the system may malfunction for some time. You need to be prepared for this in advance, that is, you cannot immediately operate the car in the usual way. The point is that new brake discs and brake pads need to get used to it. While the grinding is not completed, the car may jerk after pressing the brake, the brake pedal begins to vibrate, and when braking, light vibrations can be transmitted to the steering wheel. Let us add that the general grinding in of new pads and discs takes from 250 to 400 km. mileage If the symptoms do not stop, then you should check the quality of the parts and the correct installation of the elements.
A common cause of brake problems, where the brake pedal slowly sinks, is a damaged or misaligned brake caliper that is present in the design of the brake system. The displacement of the vertical axis of the caliper relative to the axis of the brake disc does not allow the system to work normally. Also, the caliper may be in good working order, but poorly secured. In such cases, the brake pads are simply not able to properly rub into the disc.
The fact is that in case of problems with the caliper, the new pad is not pressed against the disc over the entire area of the antifriction lining. As a result, parts of the lining wear out quickly and severely, and the brake system is ineffective. The brake pedal slowly goes lower and lower when pressed. For this reason, when replacing pads, you need to check the condition of the caliper, its axial relationship to the disc. This is necessary in the case when only the pads, pads and discs are changed, as well as the pads, discs and calipers at once.
When the engine is running, the brake pedal falls down
The most common reasons for the brake pedal to fail when the car is running are air in the system, problems with the turbocharger, low fuel fluid level, critical wear of the pads/discs, overheating of the brakes, etc. We also note that if symptoms appear, when the brake pedal does not fall, but remains very tight after starting and the effectiveness of the brakes is greatly reduced, then you should check the vacuum brake booster. Additionally, its malfunction is indicated by the fact that the engine speed fluctuates when you press the brake, although the fluid does not leave the brake system reservoir, and also when the engine is turned off, the brake pedal always remains elastic, and not after several presses.
Let's return to the so-called “vacuum tank”. This device helps the driver by reducing the force applied to the brake pedal during braking. A common cause of problems is damage to the brake booster vacuum diaphragm. The specified pneumatic brake booster operates only when the engine is running. Damage or wear of the diaphragm does not allow vacuum to be achieved in the amplifier chamber, as a result of which the brake pedal is difficult to press after starting the internal combustion engine. This is easy to believe by pressing the brake when the engine is not running. After 2-3 pumps the pedal should become elastic. Afterwards the engine starts. If the pedal does not become a little softer, then diagnostics of the vacuum booster is needed.
The brake pedal fails: the brake fluid does not drain
In practice, quite often car owners are faced with the fact that the brake pedal fails the first time they press it. In this case, a superficial inspection of hoses and cylinders does not reveal leaks, there is no noticeable change in the level of brake fluid in the reservoir, etc. Please note that it only takes a few drops of brake fluid to leak for the brake pedal to start to sink when pressed.
If there is a leak, the brake system inevitably becomes airy. It turns out that if the brake pedal sinks, but the fluid does not leave, this does not mean that the system is sealed. Two or three drops of fuel oil will not affect the level in the reservoir, the leak itself may be difficult to detect, but the brakes will not work properly.
We also note that brake fluid can leak through the main brake cylinder, and the leak can only be detected by disconnecting this cylinder from the brake booster. It often happens that the cylinder is not completely filled.
What's the result?
As you can see, there can be many reasons for a failing brake pedal. If you are not confident in your abilities and skills, then you should refrain from trying to fix the problem yourself and immediately contact experienced specialists. It must be remembered that it is recommended to change the brake fluid in a timely manner, since the maximum service life is no more than 24 months. Also a sign of the need for replacement is cloudiness and blackening, and the appearance of a characteristic odor. Note that brake fluid tends to accumulate water, which significantly deteriorates its properties over time and serves as an additional reason for replacement.
In such a situation, it is better to brake by gradually lowering the gear from high to low with shifting in a car that is equipped with a “mechanics” (manual gearbox). In some cases, you can use the contact emergency braking method, when the car deliberately collides with an obstacle and slows down after such contact or several contacts. This technique allows you to stop with minimal risks for the driver of a faulty vehicle and other road users.
After changing the brake fluid, the brake pedal fails
Another common problem is when the pedal fails after bleeding the brakes. In other words, the owner has just changed the brake fluid and bled the car's brakes, and the pedal is falling out. First of all, this may mean that air remains in the system.
Often, two people bleed the system (one person works with the pedal, and the other opens and closes the bleeder fittings). So, problems with the brakes appear if the one who pressed the pedal released it early, while the assistant did not have time to close the bleeder fitting.
Let us also add that if, in addition to replacing the brake fluid, the calipers were also repaired/replaced, the brake pads were changed at the same time, and the brake pedal fails (usually on the first press), this happens as a result of the “breaking in” of the parts.
The pistons of the working cylinders are positioned in such a way that the gaps between the pads and the brake discs/brake drums are minimal. In this case, the reverse stroke of the piston is blocked in one way or another (depending on the design features).
When all the parts are in working position, the brake pedal will stop falling. If the brake pedal fails after repair, then there is a high probability that errors were made during assembly, the system is not pumped well enough, there are brake fluid leaks, etc.
Air
This is another problem that causes interruptions in the operation of mechanisms. Airing the brake system is dangerous because the fluid may boil. As a result, it will be completely impossible to reduce the speed of the car, except perhaps with the handbrake. What is the reason? Air can enter the system if the tightness of the lines is broken. Typically, metal pipes (copper or aluminum) are used in the braking system. However, on the front calipers they need to provide mobility. In view of this, rubber tubes are also used in the design. They have a double layer. If the tube is frayed, you have time to notice the problem. However, if you ignore the problem, the base layer will also begin to fray. As a result, the liquid will flow out, and air will be sucked in from the atmosphere instead. Always pay attention to puddles under the car after parking. Perhaps at this moment one of the tubes was damaged. If the brake pedal fails when the engine is running due to air in the system, how to solve the problem?
Brakes lost after heavy braking
It happens that the brake pedal falls when pressed hard. Typically, this can happen because there is a brake fluid leak. The reason may be a break in the brake hoses, tubes, or breakdown of the brake cylinders (main or working). The brake pedal also drops sharply when there is severe wear on the discs or brake drums or brake pads. In this case, the piston of the working cylinder is pushed out.
Another reason may be overheating of the brake fluid during very active braking (brake overheating). This occurs due to heavy loads on the braking system (active braking) at the same time that the fluid in the system has lost its properties, “pulled” moisture, etc. It is precisely taking into account the fact that the TZ has a limited service life, it must be changed at least once every two years (preferably once a year).
It is also necessary to inspect the brake hoses and pipes every 6 months. If cracks are noticed, the hoses need to be replaced. In this case, for replacement, you should purchase “fresh” hoses according to the date of manufacture. Usually, if the product is more than 24 months old from the date of release, then it is better to refuse to purchase such a spare part. The fact is that rubber dries out and cracks on its own over time.
Emergency situation
Brake failure while driving can be very dangerous. In this case, the main thing is not to panic. You need to smoothly tighten the handbrake, then, if the car has a manual transmission, gradually shift to lower gears.
During switching, be sure to re-throttle to equalize the rotation speed of the primary and secondary shafts. If possible, it is better to drive into a roadside obstacle than into an oncoming car.