Due to a malfunction of the ignition module, the following malfunctions may occur in the operation of the injection engine of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars: the engine “triples”, “doubles” (works or tries to start on two cylinders), unstable idling, “dips”, “jerks” , “twitching”, etc.
— Multimeter, autotester or other device with ohmmeter and voltmeter modes
— Socket wrenches or heads for “13” and “17”
Preparatory work
— Remove the ignition module from the engine
Disconnect the ends of the high-voltage wires. Use a key set to “13” to unscrew the two upper fastening bolts, and use a key set to “17” to loosen the tightening of the bottom bolt. Remove the module along with its bracket.
— Cleaning from pollution
Wipe with a dry cloth.
The procedure for checking the ignition module (coil) of the ignition system of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars with an injection engine
In garage conditions, you can check the secondary windings of the ignition module for an open circuit and the primary windings for a short circuit, as well as the voltage supply to the module from the ECU. This is quite enough to diagnose the problem.
— Check for short circuit
The positive probe of the multimeter in ohmmeter mode to terminal “D” of the ignition module connecting block, the negative probe to the bracket (“ground”). If there is no short circuit, the device readings tend to infinity.
— Check for “break”
Using a multimeter in ohmmeter mode, we alternately measure the resistance between terminals “1” and “4”, “2” and “3” of the ignition module.
The resistance for each measurement should be within 4 kOhm. If it is different or does not correspond to the required indicator, the module should be replaced.
— Checking the voltage supply to the ignition module
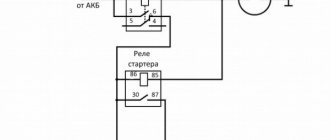
If previous checks did not reveal a malfunction, you need to check the voltage supply to the ignition module. Turn on the ignition. Using a multimeter in voltmeter mode, measure the voltage between terminals “C” and “D” of the block of the wiring harness going to the module (the terminals are marked on the block itself). The voltage must be within the vehicle's on-board voltage (12V). If it is smaller or absent, then the battery may be discharged, the wires from the computer to the ignition module are faulty, or the control unit (ECU) is faulty.
Notes and additions
— Often, one of the visual signs of failure of the ignition module can be two wet and two working spark plugs, since the module consists of two pairwise connected ignition coils that alternately produce a spark in two cylinders -1-4, 2-3. The failure of one of the coils leads to the engine running (or trying to start) on two spark plugs.
— The problems listed above in the operation of a car engine may be based not only on a malfunction of the ignition module, but also on a malfunction of the spark plugs, high-voltage wires, as well as the power and control system (ECM).
More articles on the ignition system of the injection engine of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
Comparative test repair
Ignition of gasoline in the cylinders of an internal combustion engine occurs using a spark generated by the ignition system. The ignition module is the main element of the system, creating a spark on the spark plugs using high voltage. Each car manufacturer develops and produces its own original module, but the principle of its operation is the same for all devices. During operation, deviation from the specified parameters or breakdown of the ignition module negatively affects engine operation until the power unit fails.
Purpose and principle of operation
Ignition module VAZ 2110
The ignition module of a modern car performs the function of generating high voltage to produce a spark at the spark plugs. It consists of two coils with a closed magnetic circuit and a two-channel switch. Sometimes the switch is made as a separate device, but in most cases it is combined with an electronic control unit for the engine. Externally, the modules differ in the number of wires in the connection connector: a module with a switch has 4 wires, and paired coils have 3.
The ignition module is controlled by the ECU, which supplies constant voltage in the form of low-voltage control signals to the windings of its coils at the right moment. The end of the signal is the beginning of the spark. Thanks to magnetic induction, at the moment of application, a high voltage is generated, creating a spark at the spark plug. The device is located in the engine compartment and can be easily identified by the high-voltage wires leading to the spark plugs.
Circuit parameters, its components
The ignition system circuit consists of:
- candles;
- switch;
- distributor;
- ignition relay VAZ 2109;
- coils;
- switch;
- blocking devices (does not allow starting a repeat cycle until the previous one is completed);
- anti-theft mechanism;
- Hall sensor;
- sensor-distributor mechanism (receives rotation from the camshaft);
- automatic circuit shutdown device, triggered within 8 seconds;
- current rectifier;
- systems for regulating the amount of energy in the switch.
What is an ignition module called? The ignition module on a VAZ is a coil, switches, and an ECU, enclosed in one plastic housing. Where is this module located? Open the hood of the car, look for high-voltage wires - spark plugs are located at one end of the conductors, and a module at the other.
Incorrect operation of this device leads to the inability to start the engine or to its deteriorated performance. The ignition module of the VAZ 2109 injector does the job of creating a spark and its correct distribution; it has a vacuum ignition timing regulator, so it does not need to be adjusted, unlike the circuit in the “nines” with a carburetor.
Signs of a malfunctioning ignition module
A malfunction of the ignition module is determined by the following symptoms:
- Difficulty starting a cold engine due to lack of spark on one or more spark plugs.
- Floating engine speed at idle is a situation in which the speed changes without any action on the part of the driver.
- Dips in power, which manifests itself during acceleration and driving up a long climb.
- Decrease in engine power.
- Cylinders 1-4 or 2-3 do not work (engine “troits”).
- Indication of the “Check Engine” indicator.
Possible causes of ignition module malfunction
Despite the high reliability and durability of the ignition module, during operation it can fail, like any other mechanism. Among all possible causes of breakdowns, in 9 out of 10 cases the following occur and are diagnosed:
- Use of inappropriate components in the ignition system. High-voltage wires are selected based on the parameters of the module, since excessively high or low voltage creates malfunctions or burns out contacts.
- Defective or damaged parts, poor quality assembly. Defective components break down faster and damage other components or elements of the system. Practice shows that the selection of high-quality components and their periodic diagnostics allow the module to remain operational for a long time.
General information about the Nine ignition system
The ignition system in the 21099 injector or carburetor is a collection of many components and mechanisms interconnected with each other. The main purpose of the SZ is to produce an electrical discharge, which is subsequently used to ignite the fuel-air mixture in the engine cylinders. One of the main parameters of the SZ is the moment of appearance of this discharge, that is, a spark, since it is this parameter that determines the correct operation of the power unit.
What elements does the SZ electrical circuit include:
- Coil or module. This device generates a high-voltage discharge and transmits it to the spark plugs via high-voltage cables.
- Candles. These devices are used to transmit a high-voltage pulse to the cylinders of the power unit, where the fuel-air mixture is located. Spark plugs may not work correctly over time, due to wear or carbon deposits on the electrodes. Such problems can lead to incorrect operation of the engine in general, as well as difficulty starting it in particular.
- High voltage wires. They connect the distribution unit with the candles. The performance of high-voltage wires is also important, since if they break down, the driver may also experience incorrect functioning of the internal combustion engine.
- Switchgear. This unit distributes the high-voltage discharge to certain spark plugs, since the cylinders must fire in a certain order. One of the main components of the distributor is the vacuum regulator.
- Switch.
- Mounting block.
- Ignition relay.
- A switch, that is, a lock. With its help, the driver gives the command to start the engine (the author of the video is Nail Poroshin).
Checking the ignition module
Checking the ignition module for functionality is carried out in the following ways:
Replacing the ignition module with a known good one
1. The easiest way is to connect a known working module. In this case, the devices must be completely identical, the high-voltage wires are in good condition, and the reliability of the contacts has been checked.
Checking the contacts on the ignition module
2. Moving the module, which allows you to identify unreliable contacts. To do this, move the wire block and the module itself. If during exposure the engine reacts by changing its operation, then the cause of the problem lies in poor contact.
Measuring resistance at the terminals of the ignition module
3. Resistance measurement. To do this, you will need a tester switched to ohmmeter mode. Measurements are carried out on the paired terminals of the module between cylinders 1 and 4, as well as cylinders 2 and 3. The resistance value should be the same and approach 5.4 kOhm.
Checking the ignition module using a tester
4. Check the voltage with a tester. One probe of the device is applied to contact A of the block, the second to ground. After turning on the ignition, take readings from the device. If the wire is in good condition, it will show a voltage of 12 V; if it is missing, check the fuse protecting the ignition module. Then check the continuity of the circuit with a 12 V test lamp. Apply one end of the wire to contact A and rotate the starter. If the lamp does not blink, the circuit is broken. The procedure is repeated in a similar way with other contacts.
Diagnostics of the ignition module with professional equipment
5. Diagnostics at a service station by connecting a computer with special software to the computer. Malfunctions are detected in the form of errors indicated by an alphanumeric code, after which a more in-depth diagnosis of the malfunction is carried out to make a decision - repair the ignition module or replace it. A similar check is carried out at a specialized service station using an oscilloscope.
Repair
Ignition module VAZ 2107
The design of the ignition module is quite complex: it includes one or more coils, a board, contacts and wires. Of all the above elements, only contact connections can be repaired; in some cases, replacement of parts (transistors, coils) is possible.
The module is dismantled and opened for repair purposes. For this you will need:
- Socket wrenches with heads 1, 13 and 17.
- Hexagon 5.
- Screwdriver.
- Soldering iron.
- Flux for aluminum.
- Stranded wire.
- Nail polish.
Opening the ignition module
Repair of the ignition module is carried out in the following order:
- On the removed device, open the case by prying it off with a screwdriver.
- Remove the silicone film covering the board.
- All aluminum is removed from the explosive contacts.
- On the board, new wires are soldered in place of all the dismantled old ones. To do this, the surface of the collector is cleaned of deposits, after which the board is heated to 180 o C (a characteristic smell will indicate when the desired temperature has been reached). During the soldering process, the ends of the wires are connected to the module.
- At the end of the operation, all contacts, the board and the module are covered with nail polish.
- The device is assembled in the reverse order, installed on the car and the engine is started. In case of normal operation, the ignition module is sealed tightly with sealant, while the wires are tucked inside the cavity so that they are not pinched at the edges by the plate.
If the device does not work, then a breakdown inside the module should be looked for more carefully. The transistor, electronic component may have failed, or there may be a break in the coil. Such a repair makes sense only if its price is significantly lower than the cost of a new part.
Ignition module for injection engine of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
The ignition module on the injection engine of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars is part of the ignition system.
Purpose of the ignition module
The ignition module on VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars is designed to create high-voltage voltage on the spark plugs at a certain moment.
Location by car
On the 2111 engine of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars, the ignition module is installed on a special bracket mounted on the front of the cylinder block on the gearbox side.
Ignition module design
The ignition module consists of a housing, inside of which there are two two-terminal ignition coils and a two-channel switch (two electronic units). The housing has four ignition coil terminals, which are connected to the spark plugs in a certain order. The wires for the first and fourth cylinders are connected to the two terminals of one winding, and the wires for the second and third cylinders are connected to the two terminals of the other winding. Therefore, a spark jumps in two cylinders at once (on the compression stroke - working and on the exhaust stroke - idle).
The current supply and control wires from the control unit are connected to the module through a connecting block.
Operating principle of the ignition module
The control unit of the ECM system receives a signal from the crankshaft position sensor about the position of the engine crankshaft and its rotation speed, from temperature sensors and mass air flow sensors information about the condition of the engine and the load on it. After processing the signals, it calculates the ignition timing and sends a command to the ignition module to fire the first or second pair of coils. The ignition module generates high-voltage pulses and supplies them through high-voltage wires to the spark plugs of either 1-4 or 2-3 engine cylinders.
Ignition module malfunctions
A faulty ignition module leads to difficulty starting a cold engine, jerking and failures during acceleration, especially on a cold engine (jerks may disappear after warming up the engine, and with it the ignition module), unstable engine idling (especially when warmed up), increased consumption fuel. Missing sparks lead to the release of a rich mixture into the converter, which leads to its failure.
If you suspect a malfunction of the ignition module, you should first check the high-voltage wires, spark plugs, and electrical circuit of the module.
Where is the ignition module located?
It is placed on a bracket and is attached to it with three nuts, so immediately decide how you will remove the module from the car, either together with the bracket or separately from the bracket (It is easier to remove the module together with the bracket), so let’s get back closer to the topic, the module is located deep in the engine and its location is not very convenient, for clarity, in the photo below it is indicated by a red arrow, and in the photo below one of the spark plugs is indicated by a blue arrow, so first find the spark plugs in the car and then look for yourself a little lower module.
Recent comments
- Mechanik on Carburetor starting device 2108, 21081, 21083 Solex Check the fuel level in the carburetor float chamber. Plus check if the fuel pump is pumping.
- Boris on Carburetor starter 2108, 21081, 21083 Solex After gas does not work on gasoline. The engine starts for 2-3 seconds and stalls. Half a minute later the same thing.
- Boris on Carburetor starter 2108, 21081, 21083 Solex engine starts but stalls after 2-3 seconds. after 0.5 minutes the same thing
- Andrey on Replacing thresholds on a VAZ 2108 Thank you, useful article. I also have to change the threshold on the eighth road.
How to check the ignition module?
We have already learned what the ignition module is and what are the signs of its malfunction (unstable idling, failures during acceleration, engine twinkling).
In this article we will talk about how to check the ignition module with your own hands.
From personal experience: on the Internet, while reading various forums on this topic, I came across a post that broken high-voltage wires do not affect the ignition module in any way. In fact, faulty high-voltage wires can lead to the fact that a spark, in search of the shortest direction, can be sent to a nearby relay, which contributes to module burnout.
Let's move on directly to checking the ignition module. To correctly and accurately check the ignition module, you need a device such as an oscilloscope. But, as a rule, the average driver does not have anything like this, except for the usual warning light and tester, so our task is to use only these devices that are available to everyone.
Checking the ignition module
Before checking the module itself, we need to check the block of wires coming to it. To do this, first of all, disconnect the wiring block, take the tester and connect one tester probe to the block at pin A, connect the other probe to engine ground. Turn on the ignition and look at the tester readings: the voltage should be around 12V. If there is no voltage, then you need to check the fuse. going to the ignition module. The next step is to take a 12V control lamp and connect it to contacts A and B. Turn on the starter and look: the lamp should blink, if it does not blink, then there is an open circuit on contact A. We perform this operation similarly with contact B.
There are several ways to check the ignition module, and we will look at some of them.
1. The first and easiest way to check a module is to replace the module with a known working one. Everything is simple here: we take the module from the donor’s car and change it. But there are certain disadvantages:
- The donor car may not be available, buying a new module does not suit our task;
- Not every car will have an ignition module: “of course!” - you say, - “from SAMAR this will do.” But not everything is so simple: as a rule, the first Samaras with a 1.5 liter engine are equipped with an ignition module. New Samaras with 1.5 and 1.6 liter engines are often equipped with ignition coils. Let me remind you that the ignition module consists of a switch and an ignition coil. In new Samaras the switch is located in the ECU. Therefore, the module is eliminated as unnecessary, leaving only the coil. Take this fact into account and look for a new donor;
- It is imperative to make sure that the high-voltage wires are in good condition: how to check the high-voltage wires?
Otherwise, there is a high probability that the ignition module will burn out.
2. The next method is the method of moving the module. To do this, we move the block of wires, knock and move the module itself. If, at the moment of our influence on the module, the operation of the engine changes noticeably, then the matter is most likely in poor contact. This malfunction is not catastrophic, so you can try to repair the module yourself: Repairing the ignition module. If the module cannot be repaired, then it must be replaced (Replacing the ignition module).
3. To check we need a tester. Using a tester in ohmmeter mode, we measure the resistance at the paired high-voltage terminals of the ignition module 1 and 4 of the cylinder; and between cylinders 2 and 3. The resistance should be the same but vary around 5.4 kOhm.
How to check and ring the ignition module of a VAZ-2114
In a car, each part is assigned certain functions. The ignition module also performs a number of important tasks, for example, when it breaks down, the engine is not able to work properly and it becomes difficult to start the car.
Functions of the VAZ-2114 ignition module
The ignition module in the VAZ-2114 solves important problems in the functioning of the car:
- first creates pulses passing through high voltage;
- then transfers them to the spark plugs.
The power supply of the unit involves operation starting from the on-board system of the vehicle, the minus wire is controlled by the body of the car. The subtlety of the module’s operation is that it simultaneously produces 2 sparks, one of which occurs at the moment of maximum compression of the air-fuel mass, and the other depends on the release, which is why it is called idle.
As for the connection method, the spark plugs are connected to the 1st and 4th cylinder, and the idle sparks fit to the 2nd and 3rd cylinder structure.
What does the ignition module consist of?
The ignition module built into the VAZ-2114 consists of 2 high-power transformers and the same 2 electronic-based control units. One side of the product has 4 outputs at once; they are responsible for connecting the candles. To keep the structural components in their original form and protect them, the manufacturer provides a plastic coating. The weight of the entire structure slightly exceeds 1 kg.
The spark plugs suitable for the engine are fixed together with the ignition module by running high-voltage wiring. A device called a “controller” controls the process. First, he takes the performance indicators of the structure, then analyzes them and, finally, decides what should be changed to achieve optimal performance - the crankshaft rotation speed, the temperature reached by the coolant in the VAZ-2114, or the engine load.
Frequent malfunctions of the VAZ-2114 ignition module
The following malfunctions occur in the VAZ-2114 ignition module:
- intermittency is formed at idle;
- power indicators leave much to be desired;
- the engine is not working correctly;
- in the paired operating mechanism, the cylinders are acting up (that is, the functioning of only one pair of cylinders can be heard);
- if the Check Engine light comes on.
If you suspect a faulty factory module in your car, then it's time to check the ignition module. It doesn’t hurt to make sure with your own hands that the wires are connected correctly and firmly; check that the spark plugs remain intact and are not damaged. Before you begin diagnostics and repair work, you need to stock up on protective equipment that will protect you from dangerous situations - the tool must be treated with insulating material, and gloves are required.
How to determine malfunctions in the ignition module at a service station
At a service station, diagnosing a VAZ-2114 factory module looks very simple - professional diagnostic equipment eliminates errors. Service station workers use an error code scanner and an application suitable for a computer diagnostic adapter. What errors are displayed on the display if the VAZ-2114 ignition module requires adjustment and repair?
- P3000-3004 – the car will not start;
- P0351 - indicates damage to the integrity of the windings of a pair of cylinders from 1 to 4;
- P0352 - determines the break in the section in the winding of 2-3 cylinders.
Design of the ignition module VAZ 2109 injector
The design of the ignition module on the VAZ 2109
One of the most complex electrical devices in a VAZ 2109 car on the injector system is undoubtedly the ignition module. This element is found in injection cars; for carburetor cars, an ordinary coil is installed. In fact, the ignition module performs only one, but very important function - it generates a high voltage current, up to 30 thousand watts. Next, the current is directed through high-voltage wires to the spark plugs, and they produce sparks that ignite the fuel in the cylinder block.
Features of the operation of different ignition systems
Ignition on the VAZ 2109 is necessary to ignite the air-fuel mixture when starting the engine. If the ignition does not work correctly, the engine will start and run intermittently, and its power during start-up and acceleration will noticeably decrease. In addition, fuel consumption will be noticeably increased. The conclusion from this is that the correct operation of the ignition system should be constantly monitored.
It’s worth mentioning right away the differences in the ignition design of “nines” with different types of fuel supply. Their SZ is similar, but they differ in the elements of electric charge distribution.
- In “nines” equipped with a carburetor, there is a coil and a distributor.
- For systems with an injector, an ignition distribution module consisting of several coils and an electronic controller is installed.
The second difference is how the system works. In cars with an injector it is not required, but in VAZs with a carburetor you have to do it manually.
In nines, two types of ignition systems are used:
- contact;
- contactless with transistors.
The first is installed in carburetor “nines”, and the second in injection ones. Thanks to the use of contactless ignition, the system has the following advantages:
- Working with a Hall sensor, which makes the system more stable and increases its overall efficiency.
- The absence of contact with the working parts and elements of the system increases the service life of the elements and makes maintenance of the circuit components easier.
- Excellent spark distribution between spark plugs.
- Generating a powerful spark, which prevents system failures.
- Fuel economy.
- Works even with low battery charge.
Over time, the contact type SZ has practically ceased to be used, so from now on we will focus on the contactless analogue.
Design features
It is possible to understand how the ignition module works only using the example of the entire system. So, it includes the following components:
- Ignition coil in a VAZ 2109 car injector. There are always two coils and this is the very mechanism that generates the current.
- High-voltage key switches, there are also two of them, through them the current goes to the spark plugs, in addition, the controller regulates how long the current will be turned on, it calculates the required time based on the data received from the crankshaft sensor.
- Electronic control unit.
- The body of the device itself is made of durable plastic.
In addition, the following elements can be distinguished in the electronic ignition system:
- Crankshaft position sensor.
- High voltage wires.
- Pulley with ring gear.
- Controller.
- Spark plugs that produce sparks.
We will not dwell on these components in more detail and will discuss the principle of operation of the ignition module itself.
Module location
Those who are not very familiar with the structure of the car should know that the device is located in the engine compartment of the car. It's very easy to find. First of all, find the high-voltage wires. One end of them approaches the spark plugs, and the other comes directly from the desired device. The device itself is not very large and is enclosed in a plastic case.
Ignition module for VAZ 2109
Lada 2109 › Logbook › Dual-circuit ignition on the VAZ 2109
I suffered several times in the winter with starting the engine. Even when it’s not cold, but at 0 degrees, you come to start it and the car is silent. You unscrew the damp spark plugs and the battery eventually dies! With a good battery, it starts normally. As it turned out in the end, I had a contact ignition coil B- 117 from the classics. I immediately changed it to a coil from BSZ. And the car started to start and drive much better, but I didn’t stop there and decided to make a dual-circuit ignition with 2 hall sensors, 2 switches and 2 coils from the Volga ZMZ- 406
To begin with, I began to assemble the distributor because it is the most basic and subtle part of the system. I took the distributor from OKI as a basis, or an ordinary nine-wheel one. I just had it from the window and was lying in the garage. I completely disassembled it and started installing the 2nd hall sensor directly on the standard platform at an angle of 90 degrees. I marked out the approximate position of the 2nd sensor There are risks at the site regarding the approximate position of the middle of the sensor:
Drilled and tapped the threads for the bolts:
Then I carefully cut the hall sensors themselves with a metal cloth so that they do not interfere with each other. It looks something like this:
Then I modified the shaft, replaced the ignition angle advance weights with nine-shaft ones. They are smaller and lighter than those of the Oka, the photo shows Okushinsky weights! And accordingly, I also replaced the springs. The curtain remained the standard Okushenskaya one, I didn’t touch it. If you make it from a nine-shaft shaft, then you need a curtain too modify it by sawing off two opposite ones so that it looks like in the photo:
That's all for the shaft! Next, I cut out a small piece from the distributor body itself to attach the fork of the 2nd hall sensor, drilled a hole and cut a thread for the bolt
Then I put the whole thing together. Here’s what happened:
Note: during assembly it turned out that the platform on which the hall sensors from the Oka are attached is larger than from the 2109 and it turned out to be easier to mount the sensor, so another one +, It is advisable to buy the same sensors themselves in the same store from the same batch as they are slightly different! That's all for now with the distributor!
Then I bought the rest of the necessary parts: 2 coils from the Volga ZMZ-406, a wiring harness for the BSZ 2108, an “Astro” switch, as I already had the same one
I connected the wiring according to the diagram:
Note: when connecting according to scheme 1, the tachometer will show half the revolutions. If you want to make a normal tachometer, then there is also scheme 2, there you will need to solder 2 KD213A diodes. But I did not do this and did it according to scheme 1. And don’t try to connect wires without diodes according to scheme 2, as you parallel both coils and it turns out that all 4 spark plugs spark simultaneously when both hall sensors are triggered! Tested personally)
I made a metal mount for the coils, but it didn’t turn out very well:
And now about the most important thing: for the system to work well, you need to adjust the synchronization of the hall sensors so that the spark on all cylinders is the same advance. To do this, you need to make the opposite mark on the flywheel, this will be the TDC of the 2nd cylinder. You need to count 64 teeth along the crown from the standard mark .And using a strobe light, combine both marks from the 1st and 2nd cylinders, moving the 2nd hall sensor up and down or both sensors in the direction of the white arrows. To do this, I drilled holes with a thin drill in the sensors to move them.
Main malfunctions of the ignition module
Perhaps the main indicator of a malfunction is when there is no spark at the spark plugs. However, there are other signs of unstable module operation:
- No dynamics when accelerating. You can feel obvious dips at the moment of a sharp increase in speed.
- The car does not have the usual power; it even happens that the car simply does not pull uphill.
- Floating idle.
- One of the pairs of cylinders is not working. In this case, most likely there is no current from the ignition coils.
If you encounter similar problems, you should check the spark plugs that do not have a spark, the crankshaft position sensor and the ignition module itself.
Checking the system for functionality
So, it’s best to start with candles that have no spark. This is done in an elementary way and even a person very far from car repair can cope with such a task. For greater clarity, let's divide the whole process into stages:
- The first thing you need to do is unscrew the spark plugs. This is done quite simply. Remove the high-voltage wires and then simply unscrew the spark plugs with a special wrench.
- Now that the spark plugs from which there is no spark have been removed, carefully inspect them. Spare parts should not have carbon deposits or mechanical damage.
- Throw away damaged candles and put new ones in their place; most likely, this will solve the problem. If everything is in order, then there is no spark for another reason.
Next, before proceeding directly to diagnosing the ignition module itself, you should check the block of high-voltage wires that fit to it. Perhaps there is no spark due to their fault. This is done using a special tester. The voltage on the wires during testing should be around 12 volts.
If everything is in order with the wires, most likely there is no spark precisely because the ignition module is faulty. There are many options for checking the functionality of this device. Let us examine in detail the most important of them:
- The most basic one is that you can simply replace the module with one that is known to be functional. Is it true. The problem is that often there is simply nowhere to get an additional module, and buying a new device just to test it is not very smart.
- Another not very difficult way to check is by moving the module. This is done as follows: while the engine is running, move and knock on the device. If the engine's performance changes in any way at this point, most likely the problem is that the necessary contact is missing. In fact, the malfunction is not catastrophic and in this case everything is fixable. At least there is no need to spend money on a new module.
- This option is the most accurate and requires a tester. We put the tester in ohmmeter mode, after which we measure the resistance on the wires, the same high-voltage ones that conduct current. It is necessary to concentrate specifically on the terminals of the ignition module between cylinders 2 and 3 and between the first and second. If the module is working properly, the value should be identical, around 5.4 kOhm.
Preventing ignition module malfunctions
Despite the fact that the ignition module is a very reliable device, cases when it fails still occur.
However, if you use a few simple tips, the device will work much longer:
- Always ensure that high-voltage wires are in the correct order. If they have a resistance higher or lower than required, the ignition coils may fail.
- Timely replacement of spark plugs is also very important. A large gap on these spare parts has a very negative effect on the operation of the module.
High voltage wires
Often, the main difficulty when repairing a carburetor VAZ 2109 is the reconnection of high-voltage wires that were previously disconnected from the distributor cover. It's also an ignition distributor.
The difficulty is that many people forget the connection procedure or simply do not know. But in practice, returning high-voltage wires is much easier than understanding the ignition module used on the injection VAZ 2109.
By following a few simple rules, you can easily return the wires to their rightful places.
- The ignition distributor cover is installed in its place, that is, on the distributor, only in a single position. Therefore, even if you wanted to, you won’t be able to confuse anything here. Otherwise the lid simply won't fit.
- There is an installation mark on the cover, which indicates the location of the wire socket from the first cylinder.
- The wires must be connected in the following sequence - 1, 3, 4, 2. Move counterclockwise when looking at the distributor cover from the side of the expansion tank.
If for some reason there are no installation marks on the VAZ 2109 carburetor distributor cover, just follow the connection principle shown in the image.