Each cylinder must receive a spark at a strictly defined time. On old engines, a switch was used for this - a distributor. It supplied a high-voltage pulse from a single ignition coil to the desired spark plug. Since the operating principle of the unit is mechanical (an ordinary slider with contacts), the reliability left much to be desired.
Modern engines use an electronic ignition module. The injector synchronizes the timing of fuel injection with the supply of a spark. The engine runs more smoothly, fuel consumption decreases, and efficiency increases. There is also the other side of the coin. If any owner of a Zhiguli or Moskvich could repair the mechanical ignition system with his own hands, the ignition module of the new model requires knowledge of the circuit and certain skills.
Of course, you can contact the specialized service for any reason. But then the cost of owning an iron horse will increase. A basic check of the ignition module takes a few minutes of your time; all you need is a tester. Most often, to repair an electronic module, you just need to ring the wires and understand the principle of operation of the device.
We disassemble the design of the ignition module of a modern injector
As an example, consider a similar device used on injection VAZ cars. The module operates according to the good old principle: 12 volt power is supplied to the input, and a high voltage is generated at the output contacts for sparking.
The control is electronic, but the operating principles differ from a simple distributorless ignition system:
- All components are located in one housing. On the one hand, this is convenient - fewer wires and contacts - lower probability of breakdown. On the other hand, if the ignition module burns out, it must be repaired; simply replacing the failed element will not work.
- The device is compact and can be conveniently placed in the engine compartment.
- The ignition module is powered at low voltage, which increases the reliability of the device.
- The cost of the finished device is low.
- This ignition module has two coils. This contributes to the survivability of the device - each transformer is loaded twice as much.
The secret of the module’s operation is as follows: it uses not four, but two coils for 4 cylinders. Masters of the old school call this device a two-spark bobbin. Alternating connection of each coil produces two sparks: working and idle. Due to proper distribution among the spark plugs, the idle spark is ignited at the moment when there is no air-fuel mixture in the corresponding cylinder.
As a result, we get savings on coils (as a result - a reduction in cost), and stable performance of the motor.
The signal for sparking is given by the switch (acting as an electronic distributor). Before checking the ignition module, you need to make sure that control pulses are coming to the contact blocks from the switch.
This block is responsible for the so-called ignition advance, that is, it generates a signal at the right moment. The control pulse about the position of the crankshaft is issued by the Hall sensor, which also synchronizes the operation of the entire system.
Types of ignition systems VAZ 2107
The evolution of the VAZ 2107 has transformed the ignition system of this car from an unreliable mechanical design into a modern computer-controlled electronic system. Changes occurred in three main stages.
Contact ignition of carburetor engines
The first modifications of the VAZ 2107 were equipped with a contact-type ignition system. This system worked as follows. The voltage from the battery was supplied through the ignition switch to a transformer (coil), where it increased several thousand times, and then to a distributor, which distributed it among the spark plugs. Since voltage was pulsed to the spark plugs, a mechanical breaker located in the distributor housing was used to close and open the circuit. The breaker was subjected to constant mechanical and electrical stress, and it often had to be adjusted by setting the gaps between the contacts. The contact group of the device had a short resource, so it had to be changed every 20–30 thousand kilometers. However, despite the unreliability of the design, cars with this type of ignition can still be found today.
The contact ignition system requires adjustment of the gap between the breaker contacts
Contactless ignition of carburetor engines
Since the beginning of the 90s, a contactless ignition system was installed on carburetor VAZ 2107, where the breaker was replaced with a Hall sensor and an electronic switch. The sensor is located inside the ignition distributor housing. It reacts to the rotation of the crankshaft and sends a corresponding signal to the switching unit. The latter, based on the data received, supplies (interrupts the supply) voltage from the battery to the coil. Then the voltage returns to the distributor, is distributed and goes to the spark plugs.
In the contactless ignition system, the mechanical breaker is replaced by an electronic switch
Contactless ignition of injection engines
The latest VAZ 2107 models are equipped with electronically controlled injection engines. The ignition system in this case does not provide any mechanical devices at all, not even a distributor. In addition, there is no coil or commutator as such. The functions of all these components are performed by one device - the ignition module.
The operation of the module, as well as the operation of the entire engine, is controlled by the controller. The principle of operation of such an ignition system is as follows: the controller supplies voltage to the module. The latter converts the voltage and distributes it among the cylinders.
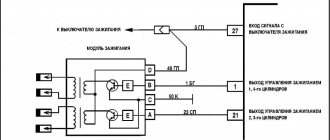
Ignition module: connection diagram
To diagnose and repair breakdowns, you need to understand which wires come from where and what they are responsible for. If the engine fails, is it the spark plugs or the switch? Again, let's look at the circuit using the example of the VAZ 2114, 2115 ignition modules.
On the body of the device there is a block with 4 contacts A,B,C,D (of course, modules from other cars have different markings, but the principle remains the same). Ground contact is the default; the design of the car allows all electronic modules to be connected by a negative bus. Power is supplied from a 12 volt bus, “RUN ON”, that is, it works after turning the ignition key (don’t forget about this when testing with a tester). The system is powered through a fuse, often shared with some other devices. Diagnosis of the ignition module begins with checking the fusible element.
Two main contacts: output to 1-4 candles, and 2-3 candles. It is to them that the control signal comes from the switch. The connections are straight, dialed through the contacts of the pads. The pad itself is quite flimsy and must be handled with care. The same cannot be said about power outputs for high-voltage wires.
Important! For safety reasons, it is recommended to disconnect the battery terminals before removing high-voltage wires. At least at this moment the ignition key should be in the "off" mode.
These contacts are directly connected to the working terminals of the spark plugs. Often the problem lies in high-voltage wires. It is enough to replace them, and repair of the ignition module will not be required.
By running your hand along these wires away from the spark plugs, you can easily determine where the ignition module is located. Of course, in the engine compartment, at a short distance from the cylinder block (extra length of the high-voltage cable reduces the reliability of the system). As a rule, removing the ignition module for diagnostics, repair or replacement does not require dismantling other components.
Replacement
Replacement is quite simple and effortless. To replace, you will need a ratchet with an extension and a 10mm socket.
Replacement process
- We remove the negative mark from the battery, since the work is carried out on the electrical equipment of the car. This will avoid an unintentional short circuit in the vehicle's network.
- We remove the high-voltage wires from the MZ and the power connector.
- We unscrew the nuts securing the MZ and dismantle it.
Pay attention to the order in which the wires are connected. Do not confuse them, otherwise the car engine will not start. Cylinder numbering starts from the timing mechanism from left to right. Connect the wires as it is written on the Ministry of Health.
Source
Signs of a malfunctioning ignition module
The list is relevant only if the other systems (spark plugs, injectors, crankshaft position sensor, cylinder compression, fuel system) are in good working order and operate according to the established parameters. The symptom of a faulty spark plug may not differ from a banal loss of contact between the ignition module and the high-voltage cable.
- Troubles the engine. In fact, there are many reasons, but the main culprit is our module. Moreover, this could be a contact phenomenon, or a breakdown of the radio element. A clear sign of coil failure is that failures occur in two cylinders simultaneously. That is, candles either Nos. 1 and 4 or Nos. 2 and 3 “do not burn.”
- The engine thrust has noticeably decreased. The car does not hesitate, it runs smoothly, but acceleration uphill or under load occurs lazily.
- During sharp acceleration, a kind of failure of thrust occurs in the engine. It's as if the fuel pump is not performing enough. If the gas tank is in order, look for the cause in the ignition module.
- At idle the speed fluctuates (of course, with the IAC running).
And of course, the “check engine” alarm. If the fault is detected by the ECU module, this is good for diagnosis. You can read OBD errors in any available way:
- using electronic odometer codes (if such an option is available);
- using the on-board computer, if it has a decoding function;
- any diagnostic scanner, for example, ELM327 paired with a smartphone.
If you recognize error codes associated with misfires specifically in a pair of spark plugs, the most likely cause is a faulty ignition module.
Mechanism Operation Manual
What do you need to know about the operation of the device to prevent its premature breakdown?
First of all, you need to follow a few simple rules:
- If you do not plan to start the engine soon, do not leave the ignition on. This will negatively affect the operation of the ignition coil and may subsequently cause failure of these system components.
- From time to time, carry out simple diagnostics of the condition of the main components. If necessary, system elements should be cleaned of dust and dirt, and worn and failed parts should be quickly replaced.
- Monitor the condition of high-voltage wires. We are also talking about their body, which should under no circumstances be exposed to moisture. If the wire shows cracks or other signs of damage, it will need to be replaced.
- When the ignition is activated, the high-voltage cables must not be disconnected.
Loading …
How to check the ignition module yourself?
Let's say you have clearly determined that the engine is malfunctioning (maybe another malfunction) due to the ignition module. You know where it is located, the pinout of the input block is known. To decide whether to repair the module or replace it with a new one (this is your cost), we will test it at least with a multimeter.
- The easiest way is to replace the unit with a known good one. This is only possible if you have a good friend with a similar car. With such a check, the so-called “support group” - cables, electronic switch.
- Performance of the contact group. While the motor is running, press on the plugs of the high-voltage wires (Caution!) and the control block. If the nature of the motor’s operation has changed (it does not oscillate, the speed has become stable), check the condition of the contacts.
- We measure the resistance at the coil contacts. Secondary windings are guaranteed to be tested. Between the output contacts of 1.4 and 2.3 candles, the resistance should be the same and within 5 Ohms.
- We examine the disassembled module. Of course, you need to have basic skills in electrical engineering (the level is somewhat higher than “screwing in a light bulb in a hallway”). Broken wires or burnt contacts are immediately visible, and the serviceability of transistors can be checked with a multimeter. The primary winding of the coils becomes accessible.
If the parts are replaceable, we carry out repairs. Wiring and contacts are restored simply.
Version of the module on the 8-valve VAZ-2110
The top ten was equipped with two 8-valve engines of different sizes - 1.5 (2111) and 1.6 liters (21114). The ignition modules for these engines are different.
- The one and a half liter engine has a module with article number 2112-3705010,
- and the 1600 cc is equipped with module 2111-3705010.
Video on repairing KZ VAZ
Often, when the ignition module breaks down, the car owner immediately runs to the store and buys a new one. But, for the VAZ-2112 there is an alternative method - repair. Of course, without proper knowledge in auto electrics, it will be difficult to understand all the circuits and communications. This article will tell you in the most accessible way how to repair the ignition module with your own hands.
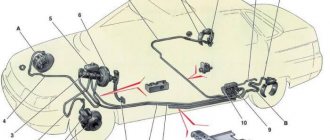
Connecting and replacing VAZ short circuit
The procedure for removing and installing the ignition coil on old VAZ models:
- First, disconnect the central high-voltage wire leading to the distributor (ignition distributor).
- Disconnect all power wires from the coil contacts. Since they are fastened with nuts, you will need an 8 wrench for this.
- If you don’t know which wires to connect to which connector later, it’s better to immediately remember or mark them somehow, so that later during installation you can connect them correctly.
- Unscrew the coil housing. It is attached to a clamp (clamp), which is pressed to the car body with two nuts.
- After the work has been done, you can remove the ignition coil and replace it if necessary.
For new type VAZ cars:
- We remove the “minus terminal” from the battery.
- Remove the top protective cover of the engine. If the engine volume is 1.5 liters, then this part is missing and this step is skipped.
- We remove the high-voltage wires from the coil.
- Now, using a 13mm wrench, unscrew the two fasteners.
- Using a 17mm wrench, loosen one bolt securing the coil.
- We take out the module.
- Use a hexagon to unscrew the coil from the holder.
- Assembly is carried out in reverse order.
Particular attention should be paid to the connection, since high-voltage wires must be located in the strict order provided for by the design. If this is not done, the car will stall or the engine may not start at all.
Replacing the ignition coil on a VAZ is quite simple. Even a novice motorist can do this in his garage, and if everything seems too complicated, contact a car service center. Particular attention should be paid to the choice of product, since this will determine how well the engine and ignition system will work.
Repair
So, for the VAZ 2110 the most common problem is the disappearance of voltage on cylinders 2 and 3. After some time, the engine starts working normally again if you press the rear plate of the module.
You should not put up with such a situation; it is better to immediately check the functionality of the unit, restore or replace it completely.
Removing the module
The procedure is quite simple.
- Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
- Remove the plastic cover that covers the motor.
- Remove the wires from the spark plugs.
- Disconnect the wires from the ignition module. Their numbering is indicated on special white rings. And the cylinder number is indicated on the ignition module housing.
- Disconnect the connector from the ignition module.
- Using a 10mm socket, unscrew the three nuts that hold the block we are looking for.
- Carefully remove it, after which you can begin further work.