Reliable operation of a car engine is achieved through the correct operation of all internal combustion engine components. The VAZ 2114 is equipped with an injection engine, which is demanding on the frequency of the system and its tightness. The slightest deviations from the permissible values lead the engine to emergency operation. In order for the engine to operate correctly, it is necessary to carefully monitor the tightness of the intake system.
All air entering the engine must be taken into account by the air flow sensor, but it happens that unwanted air leaks appear in the car, which lead to unstable operation of the engine in all its operating modes.
This article talks about how air leaks affect the operation of the VAZ 2114 engine, as well as ways to find and eliminate it. It is quite difficult to find the air leak on your own, but after studying our article, you can easily find the unfortunate place where the system is depressurized.
How does air leakage affect the operation of the internal combustion engine?
For reliable operation of the internal combustion engine, a sealed air intake system is needed. This is necessary for accurate preparation of the fuel mixture. The engine control unit prepares the air-fuel mixture based on the readings of the mass air flow sensor (MAF). The air passing through the mass air flow sensor is counted and transmitted to the control unit, which sends a signal to the injectors and opens them and keeps them open until the required amount of fuel is supplied to create the correct mixture. This operation of the internal combustion engine is correct, but when unwanted air leaks appear in the engine after the mass air flow sensor, its volume increases.
It turns out that the air flow sensor transmitted readings to the ECU about the same amount of air passing through it, but in fact, due to suction, the air volume is much larger than it should be, but the ECU does not know about it. Because of this, the fuel mixture is formed incorrectly.
Revealing
Let's look at different ways to detect air leaks into the engine through the injectors.
Spraying
Signs of suction are determined by spraying water (using a syringe) onto the hoses of a running engine. Liquid getting into cracks, holes, cracked hoses or a broken gasket causes a decrease in engine speed.
Another similar method is used to irrigate the same segment of nodes with ether, which leads to an increase in speed. So, when identifying leak points, you should carefully monitor the cleanliness of the engine. To find the location of the leak, you can use the measurement of the degree of vacuum behind the throttle. In this case, the removed hose is connected to the throttle valve control element.
Video about identifying leaks using the spraying method
Smoke or steam generator
The device detects leaks in internal cavities where there is air. Closing the throttle valve with some kind of plug, connect it to the intake manifold. Streams of smoke begin to leak through leaks and cracks.
Checking air leaks using a smoke generator
The device also checks for leaks in the exhaust system by plugging the exhaust pipe of the muffler. This is achieved by setting the piston of any cylinder to TDC and ensuring that the valves overlap. In this case, the smoke, having passed the open valves, flows into the exhaust system, revealing defects in the density of this area. For this purpose, the engine is started and in idle mode the possible appearance of a hiss or a specific whistle is heard.
Video about checking air leaks using a steam generator
Possible faults
Knowing possible areas of leakage, faults are identified:
- Crack in the exhaust valve connection.
- Blown manifold gasket.
- Throttle gaskets.
- Vacuum booster, hoses.
- Problems with the IAC cover (rear).
- Sleeves from the air filter to the throttle body.
- Injector seals.
- Receiver plug.
- Canister valve.
- Fuel pressure sensor diaphragm.
If you do not hear any sounds, you can begin the process of pinching the hose going to the intake manifold.
By squeezing the sleeves of the VUT (vacuum brake booster) or mixture pressure regulator, you can hear stable engine operation. When you remove the tool (pliers), you feel a drop in speed. This defect indicates the presence of holes or cracks in the hose being tested. There may be malfunctions of the amplifier or the adsorber valve.
Signs of air leaks
Incorrect formation of the fuel mixture leads to unstable operation of the internal combustion engine and with this problem the following symptoms are observed:
- Difficulty starting the engine when cold after a long period of inactivity;
- Unstable idling, speed jumps from 500 to 2000 rpm are observed;
- Increased engine vibration at idle;
- Loss of power and former dynamics of the car; to accelerate the car you need to press harder on the gas pedal;
- Fuel consumption increases;
These signs indicate a problem with the vehicle and require a quick solution to the problem. It should be noted that these symptoms can arise for other reasons, but checking the engine for air leaks is one of the number one points in solving problems in the operation of the internal combustion engine.
Vacuum hose repair
If your vacuum hose is damaged, you don't have to buy a new one. The hose is long. You can cut off the damaged part and reattach it to the engine.
The most common damage is at the ends of the tubes. Always ensure that the clamps are tight to prevent further leaks.
After repairs, start the engine and leave it idling. Listen for any hissing sounds.
If you decide to replace the vacuum hose, use one that is similar in length and diameter. Vacuum tubes are designed for specific locations, such as the brake booster or PCV (Power Crankcase Ventilation) system.
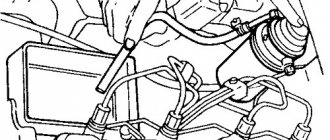
Places where there may be suction
Air leakage can be anywhere where it passes to the combustion chamber, be it the intake corrugation or the receiver. There are several places where system depressurization occurs quite often.
Places of possible suction:
- Joints of the corrugation with the sensor and throttle assembly;
- Idle air control;
- Small breather;
- Vacuum brake booster;
- Absorber tubes;
- Injector rings;
- Intake receiver gaskets;
All of the above places are prone to air leaks in the VAZ 2114 system and if leaks are suspected, it is necessary to inspect these particular suspicious places.
Briefly about each place
Corrugated joints
The corrugation is connected to the throttle assembly and the mass air flow sensor through a clamp; sometimes this clamp may not provide reliable tightening, which leads to suction.
RXX
The idle air control is installed in the remote control through an o-ring, which ensures the tightness of the system. Often this ring loses its properties and begins to let air through.
It should be noted that the IAC is installed only on cars with a mechanical throttle.
Breather
The small breather communicates with the intake corrugation through a clamp; relaxation of this clamp leads to possible air leakage in front of the throttle assembly.
VUT
The vacuum brake booster is connected to the intake receiver through a special hose, which can become damaged and begin to let in unwanted air; also in the VUT, the membrane and intake fitting are often damaged, which leads to air leaks through the brake booster.
Injector rings
To seal the junction of the injectors with the cylinder head, special rubber rings are used, which ensure reliable tightness of the system and prevent its depressurization. Due to high temperatures, rubber rings tend to lose their elasticity and become rigid, which leads to air leakage through them.
Receiver seals
The plastic receiver is connected to the cylinder head through rubber sealing rings that adhere to the surface of the head. Due to high temperatures, they lose their properties and begin to let in excess air.
Reasons for airing
Where can air get into the carburetor? As a rule, this is due to loose tightening of the electromagnetic valve or holder (on some cars, instead of an electromagnetic valve, a nozzle holder is screwed in), drying out and damage to the rubber cuff of the adjustment screws, damage to the vacuum tubes and other reasons.
Let's take a closer look.
- Often, due to various reasons, EM valves are turned out and even lost. In addition, the valve makes it possible to regulate stable engine speeds in idle mode. If there is a holder, it must be screwed in to the proper depth. Finally, the EM valve has its own rubber seal, which can dry out over time. You should definitely check it out.
- Both adjusting screws are equipped with O-rings. Over time, the latter may no longer hold, and then air is sucked in from here.
- Vacuum tubes are laid from the distributor to the carburetor device, and also from the brake control unit to the intake manifold. On such a long line, yes, there are gaps, and in some places the hoses break or holes form. Thus, airing of the system occurs.
Carburetor gasket
In addition, you need to pinch the hoses one by one near the carb fittings and try to start the engine. Let's say the engine does not start due to severe air intake. By pinching the hoses, you can block the suction, which a priori will help the power plant start.
Gaskets occupy a special place in the carburetor system. They also need to be checked for leaks. If the gaps are not noticeable externally, and the sounds of suction are not audible when the starter device is turned, you need to tighten the bolts of the intake mechanism and fuel mixer, hoping that the gaskets are loose. Then check engine starting again.
By tightening torque. It is recommended to fasten the carburetor clamps with a force of 13-16 N.m, and the manifold nuts with a torque of 21-26 N.m. This means that you should not pull too much, otherwise you can easily damage the threads. It is extremely dangerous to overdo it on a hot engine.
Some experts do this. Cover the connections with VD-40 liquid or soap foam. Then they observe. If a window forms in the foam, this is where the leak occurs.
In general, you should not overtighten the nuts! Due to excessive tightening, the seating plane of the carb can easily become deformed, and then air leaks will occur for this reason.
The defect of an uneven surface is detected as follows. Place the carburetor, removed from the car, on a flat table. The plane should be completely free of grooves and bumps. It is better if it is a sheet of thick glass placed on a table. Then you need to look carefully to see if there is a gap between the surface of the carb and the glass. If yes, then this indicates deformation.
Checking the internal combustion engine for air leaks
To make sure there is an air leak in the engine, there is no need to go to a service station and pay a tidy sum. You can check the presence of air leaks yourself.
- To do this, unscrew the mass air flow sensor from the air filter box and remove it.
- Next, start the car and close the inlet with your hand or some other object.
- With a sealed system, the engine should stall and the intake corrugation should compress and remain in a compressed position for several seconds.
If the car does not stall or stalls, but the corrugation does not compress, then most likely there is an air leak in the car and you need to start looking for it.
Engine Inspection
To identify air leaks, you must first understand how the engine intake system works.
Air enters through the air filter. The throttle valve controls it by creating a vacuum. Know that a car is leaking air when it makes a hissing sound after starting.
Vacuum hoses wear out during operation and become brittle. This leads to their damage. Carefully inspect the hoses on the engine and replace them if necessary. The engines are different from each other. Refer to the repair manual for hose identification.
How to find the leak location
Air leaks can be found in several ways. The most popular method is a smoke generator, but if this is not available, then you can use a regular soap solution.
Using a smoke generator
A smoke generator is a device that produces a large amount of smoke. It is connected to the intake system, smoke spreads throughout the system and begins to seep out in places where there is no tightness.
Video
With pump and soap
Finding the place where air leaks occur without a smoke generator can be done using a soap solution.
To do this, prepare soapy water.
- Next, we close the mass air flow sensor with a plastic bag, namely, we put the bag on the sensor, then we put a clamp with corrugation on top.
- We connect a compressor or pump through the absorber fitting and pump pressure into the system.
- Then we water all suspicious areas with soapy water.
- In those places where there is air leakage, soap bubbles will begin to inflate.
Possible places for leaks in the intake tract
Refrigerator air temperature sensor
All tubes and hoses of the vacuum system. Most often, hoses dry out at the connection points with fittings and crack at bends.
Also, the leakage of unaccounted for air can occur due to carelessness, when after repairs they forget to connect or confuse the hoses, or inadvertently pull them off the fittings.
Vacuum brake booster system. Air leaks can occur not only through a check valve or hose, but also through a torn membrane, depressurization of the vacuum chamber housing
We have already looked at how to check the VUT. Intake manifold gasket.
Sealing rubber bands for injectors.
- IAC seal at the point where it is screwed to the DZ housing.
- Mechanical throttle valve rotation axis. The depletion that occurs at high mileage leads to the appearance of backlash. Throttle valves with an electric wire do not suffer from the problem of suction of unaccounted air in such places.
- Crack in the intake manifold. A fairly typical problem for cars with plastic manifolds.
- Crankcase ventilation system. The cause of suction is leakage of hoses, tubes, and valves.
- Leakage of the gas tank ventilation system.
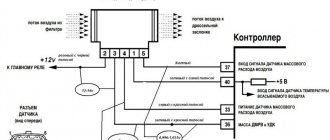
Application of the diagnostic tool
The scanner allows you to identify additional symptoms indicating that the cause of unstable idle speed is air leaks. The device will allow you to observe in real time:
- lambda probe readings;
- throttle valve opening degree;
- idle speed control position;
- desired and actual idle speed;
- long-term and short-term fuel trims.
In the video, a diagnostic specialist explains exactly how to use these values to diagnose air leaks in the engine.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=8abNP9WN_EU
https://youtube.com/watch?v=v4t4rqSmXG0
Let's localize the cause
Let's look at the main methods for determining the cause of air leaks without using a smoke generator.
- Splashing of carburetor cleaner near the intake tract elements. Cleaners contain easily volatile and flammable components. Getting into the cylinders through the air intake point, the cleaner enriches the fuel mixture. In particularly critical cases, at such moments a short-term increase in engine speed is observed. But it is much more reliable to observe short-term fuel correction using a diagnostic tool during the test. The values will rise when the cleaner is sucked in, as the lambda probe will register an enrichment of the mixture.
- Splashing water. The purpose of the test is to hear the characteristic sound of water being sucked in, which will definitely happen at the point of air leakage. For convenience, fill the bottle with water after making a small hole in the lid. Generously water the connection points of the vacuum system hoses, if possible the junction of the cylinder block and the intake manifold. Check the area after the throttle valve with special care, as this is where the vacuum and the risk of suction are highest. But you shouldn’t completely fill the engine with cold water, especially the exhaust manifold. A sudden change in temperature can lead to cracking.
Smoke generator test
The point of the test is to supply smoke into the intake tract. In places where air is leaking, smoke will come out, which will localize the leak. You can buy a smoke generator or build the device yourself. There are plenty of different design options on the Internet, one of which is shown in the video below.
How can I use a smoke generator to find the place where air is leaking?
- Block the inlet pipe in front of the air filter. If this is not done, the smoke pressure in the intake tract will increase slowly.
- Disconnect one of the available vacuum system hoses and connect the smoke generator hose instead.
Use a compressor to supply smoke. When the system is completely filled, you just have to watch for smoke leaks, which can cause unaccounted air to leak into the intake manifold.
Diagnostic methods
The engine's refusal to idle is a consequence of a lean mixture, caused by excess air in the fuel line.
This is accompanied by:
- Rusty fuel supply pipes.
- Fuel hoses that have dried out as a result of long use and are no longer held in place by clamps.
- Fuel filter with seal defects.
- Exhaust pipes that have lost their seal.
- Injection pump seals.
- Air entering through the manual lever of the fuel pump.
- Fuel pump seals.
- Obsolescence of seals.
First way
Diagnosis of the defect involves turning off the fuel pump and powering it from another vessel (for example, a plastic canister) . Independent work will require a 3÷4 liter container, two transparent hoses, one meter long, and a pair of clamps. Observing cleanliness measures, the forward and return fuel lines from the injection pump are replaced with transparent tubes, and the air is removed from it.
One of the ways to remove suction is to clean the place of work and the location of the tank above the fuel pump . It is necessary to unscrew the “return” bolt, through which, according to the principle of a siphon, air escapes before fuel appears. The fitting bolt returns to its place. Running the engine for a few minutes removes any remaining air.
Video about diagnosing the fuel pump for air leaks
Second way
It consists of testing the fuel filter (standard), placing it below the injection pump . The method is focused on determining suction through a filter. If there is no result, all tubes, tank, and hoses are checked. This method of powering gives precise indications of difficulty starting the engine.
The origin of leaks in the fuel system of cars with a diesel engine is based on atmospheric pressure. It is higher than the pressure that is created when pumping fuel from a car tank. This is due to the replacement of brass fuel lines with rubber and plastic tubes and connecting them with clamps. Meanwhile, hoses made of such materials have a shorter service life. Reference is made to the fact that synthetic pipes in the engine compartment heat up, sag, rub, and, as they wear out, contribute to air leakage .
Thus, mechanical stress, overheating, and the use of cleaning agents capable of softening non-metallic materials and hermetic compounds can be attributed to the root causes of suction.