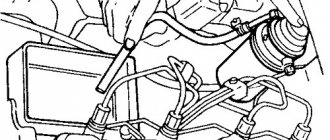
Modern injection cars form the air-fuel mixture based on the readings of the volume of air entering the engine. Several types of meters are used to calculate the amount of air. Most often this is a mass air flow sensor (MAF) or MAP (absolute pressure sensor).
If the engine sucks in oxygen bypassing these sensors, many problems arise that affect the performance of the vehicle. Therefore, at the slightest suspicion, this malfunction should be identified and eliminated.
Finding air leaks is not a simple procedure and often requires special equipment
Consequences of air leaks
An air leak will cause unwanted air to enter the engine where it is not intended. This reduces engine performance and causes some systems that rely on vacuum to malfunction.
Because air leaks cause engine inefficiency, you will notice the "Check Engine" light on your dashboard. You will also experience acceleration problems - this is because fuel is not delivered efficiently to the combustion chambers. Vacuum is used to operate actuators, sensors or brakes.
If there is a vacuum leak, some of the sensors may begin to malfunction, forcing you to make unnecessary repairs.
The essence and possible consequences of the problem
The idea is that unaccounted air entering the engine changes the mixture ratio. Because of this, the engine begins to “sausage” and its traction deteriorates. In general, one of the smallest consequences is the incorrect operation of the internal combustion engine. If you go deeper, air leaks can seriously damage pistons, valves and other heat-loaded elements. This occurs due to a severe leanness of the fuel mixture, which in turn greatly increases the temperature of the exhaust gases, and all parts suffer from this. The suction will also affect the stability of the idle speed, the warm-up speed, and the car will begin to respond to the inclusion of an additional load (electrical appliances). In general, there are many consequences and they are extremely unpleasant.
Engine Inspection
To identify air leaks, you must first understand how the engine intake system works.
Air enters through the air filter. The throttle valve controls it by creating a vacuum. Know that a car is leaking air when it makes a hissing sound after starting.
Vacuum hoses wear out during operation and become brittle. This leads to their damage. Carefully inspect the hoses on the engine and replace them if necessary. The engines are different from each other. Refer to the repair manual for hose identification.
Where exactly can air be sucked from?
There are quite a lot of places for the passage of unaccounted air. You need to understand that the culprit may be either a leaky rubber band or a crack in the intake manifold.
Most often, air is sucked from:
- Vacuum hoses on the manifold;
- Corrugations located after the flow meter;
- Loose connections (loose clamps);
- Worn gaskets, this can be at the connection between the throttle and the manifold, as well as at the junction of the intake to the cylinder head;
- Stiffened fuel injector cuffs;
- Vacuum brake booster.
Damaged gaskets often cause huge problems for car enthusiasts
If you suspect that there is unaccounted air in the intake manifold, you should immediately check all of the above areas. As a rule, the suction is quite easy to find. If difficulties arise, it is recommended to seek help from a service station or acquire a special device for searching for intake leaks.
Air leakage through the injectors is one of the most common problems, and the culprit is damaged rubber seals.
Methods for checking tightness
There are several ways to check for leaks. Some are faster than others, and some require expensive equipment. Consider the following methods to find the best solution for your case.
Inspect and check for loose hoses on the engine
The first place to check for vacuum leaks is the hoses on the engine. Check for cracks or loose fasteners. Each car has a unique vacuum tube pattern. Make sure the clamps are tight enough.
Try moving the clamps from the side. If they move easily, they need to be tightened. If you still cannot determine the location of the leak, inspect the surfaces further.
Spray soapy water around the intake area
This is probably the easiest and cheapest way to check for air leaks. Spray soapy water around the intake manifold and damaged hoses while the engine is running. You will see air bubbles in the leak areas.
Watch a video on how to look for air leaks using a soap solution:
Use a smoke generator
This is the professional way. Auto mechanics use it to check air leaks within a few minutes. But this will require expensive equipment.
Spray carburetor cleaner
There are those who use carburetor cleaner to detect air leaks. To do this, start the engine at idle speed. Spray cleaner onto areas you suspect of leaks. The engine speed will begin to increase when there is air leakage.
This is because carburetor cleaner will get into the engine and burn with the fuel.
This is a dangerous method for checking air leaks. Sprays are highly flammable. Have a fire extinguisher ready!
Signs and causes of suction
When an engine develops a leak that allows extra air to pass through, the following symptoms are observed:
- The first sign is “floating” idle speed. The engine draws in excess air, and the control unit, which analyzes the composition of the exhaust gases using a lambda probe, tries to properly prepare the fuel mixture. But the mass air flow sensor (or DBP) does not take into account part of the inflow, so the speed is unstable (signs of a sensor malfunction are written here).
- The proportion of fuel in the combustible mixture decreases, hence the difficulty of starting the power unit “cold” when enrichment is necessary.
- Due to a lean mixture, engine power is lost - the car starts and accelerates more difficult.
- As the driver begins to press the gas pedal harder and forcefully increase the speed, fuel consumption increases.
Reference. On carburetor engines, stray airflow causes revs to jump to 2000 rpm or more, drawing gasoline through the main fuel jets, bypassing the idle system. The adjustment screws do not work.
There are several reasons why the tightness of the connections is broken and the engine sucks in air:
- deformation of adjacent planes (for example, the suction manifold to the cylinder head) as a result of overheating;
- too frequent use of car cleaning chemicals, which can soften gaskets and sealants;
- leaky hoses or clamps on the vacuum intake pipes in the engine.
Leaks in the intake manifold
If your hoses are fine, the problem may be with the intake manifold. The intake manifold gasket leaks from time to time, causing air leaks. It is located between the cylinder head and the manifold.
To check the tightness of the intake manifold, place the car on the handbrake. Start the engine and let it idle for a few minutes.
Apply the soap solution to the area between the intake manifold and the cylinder head or at the base of the carburetor. Listen to the sound coming from the engine. If it is smoothed out, then air leaks occur at the intake manifold and require repair.
If the problem is not resolved
You can try to solve the search problem using steam generators. By the way, this device perfectly helps to detect leaks and breakdowns in any devices that contain air. We close the throttle pipe with any plug and connect it to the intake manifold.
Any leakage will be easily detected by the smoke generated by the steam generator. In their work, professional auto repair shops use not a steam generator, but a smoke generator.
More often
, tightness is lost in the following components: in the intake manifold gasket, on VAZs - the idle speed sensor can cause this, throttle assembly gaskets, air filter pipes, intake manifold plug. As you understand, you can determine the symptoms of engine air leaks with your own hands. You just need a little patience and skill
As the name suggests, we are talking about searching for unaccounted air that bypasses the mass air flow sensor and enters the intake, thereby disrupting the normal operation of the engine. I will describe several methods that I tried. Obvious symptoms of air leaks: 1) unstable engine operation at idle; 2) errors such as lean mixture; 3) loss of dynamics; 4) reduction in air mass flow; 4) the injection time correction coefficient is overestimated and more than 1,000; 5) reduction of IAC steps; The values of typical parameters of January//BOSCH injection systems are available on the Internet, I based myself on them. My ECU is January 7.2. Normal values Mass air flow kg/hour at xx 8-13. Ignition timing angle deg. p.k.v. 7-17 Injection pulse duration ms 3.5-4.3 Current IAC position step 40 +/-15 Injection time correction coefficient based on DC 1 signal +/-0.2
Symptoms of air leaks
The first sign of air leaks is the Check Engine light coming on. There are many reasons to turn on this light bulb. You'll need to rule out other problems before you decide it's a leak. But be sure that it is an air leak if it is accompanied by hissing from the engine and loss of power.
Is your car not developing full power? It could be an air leak.
Leaking can cause additional engine problems such as fuel inefficiency.
A little about the signs of a malfunction
The power unit of a car is a complex engineering structure. If, after detecting even small deviations in its operation, you should deal with the problem and eliminate it. If this is left unattended, you can wait for major complications to arise, which will entail not only significant material costs, but also moral costs and prolonged downtime of the machine.
What happens when air leaks appear on a VAZ 2112, 2114 or other models? A number of signs may indicate the occurrence of such a malfunction:
- Difficulty starting the engine after a long period of parking;
- Engine idle speed “floats”;
- Engine power is lost;
- Fuel consumption increases.
Vacuum hose repair
If your vacuum hose is damaged, you don't have to buy a new one. The hose is long. You can cut off the damaged part and reattach it to the engine.
The most common damage is at the ends of the tubes. Always ensure that the clamps are tight to prevent further leaks.
After repairs, start the engine and leave it idling. Listen for any hissing sounds.
If you decide to replace the vacuum hose, use one that is similar in length and diameter. Vacuum tubes are designed for specific locations, such as the brake booster or PCV (Power Crankcase Ventilation) system.
A few words about troubleshooting
It was possible to find an air leak in the VAZ 2112, 2114 engine, now it should be eliminated. The algorithm for eliminating the problem will be different, depending on the location of the gap. If the culprits are the clamps, tighten them. If this is not possible due to the hardness of the rubber pipes, it is better to replace them with new ones. Leaky gaskets are also replaced with new ones. In some cases this can be a time-consuming process, such as when replacing the gasket between the cylinder head and block.
For this, desire alone is not enough, since you will need to use a torque wrench to tighten the cylinder head bolts, a diagram for their installation and screwing. After a short run they will have to be pressed again. It will be a little easier to replace the intake tract gasket, but you will also have to dismantle and then reinstall a number of parts.
Advice! If this is the first time such an operation is performed, write down the order in which components and parts are removed. This will make them easier to install during assembly.
Mechanics have noted cases where VAZ 2112, 2114 power units had air leaks in the fuel rail. For some reason, VAZ manufacturers install a rubber hose, compressed with two clamps in the fuel supply system. After compressing them again, the problem usually goes away. Most often, replacing “outdated” rubber products in the intake tract solves all problems that have arisen.
It is much more difficult to eliminate malfunctions of intake tract sensors such as MVR, idle speed, and idle air control. We are not talking about replacing gaskets, but about sensor malfunctions, which can cause air leaks in the engines. Experts do not undertake to eliminate air leaks in these devices; they simply replace them with new ones. It is possible to repair conductive paths, eliminate contamination or oxidation. The appearance of air leaks in VAZ cars in the fuel system is accompanied by the presence of leaks.
Important! If the driver ignores the resulting fuel leak, there is a risk of a fire.
This may be the connection between the electric fuel pump and the fuel line, the fuel pressure regulator, and other places. Before starting work immediately after stopping the engine, you should relieve the pressure in the fuel system. Otherwise, fuel may escape and ignite.
This article is not a direct guide to action, it is for informational purposes only. It is difficult to describe all the possible causes of the problem and how to eliminate them. If readers have questions, watch the video: https://vk.com/video240089429_170844002
How does the Lada Kalina gasoline vapor recovery system work?
The EVAP system in question was created to prevent the release of harmful gasoline vapors into the surrounding atmosphere resulting from fuel evaporation; it includes:
- fuel shut-off valve;
- adsorber;
- solenoid valve for purging the absorbent element;
- connecting pipelines.
The most important component in the system is the adsorber (also called a carbon filter), the basis of which is activated non-edible carbon, enclosed in a plastic housing. The resulting gasoline vapors are absorbed by the carbon of the absorbent element, gradually accumulating in it. When the engine starts, the canister purge valve (KPA) is turned on, and due to the vacuum, all accumulated vapors enter the intake manifold and then burn out.
On the Lada Kalina, the adsorber is located in the gas tank area, and getting to it is very difficult. To dismantle this EVAP element, it is necessary to remove the fuel tank, but the control unit is located in an accessible place - the valve is located in the engine compartment, in close proximity to the battery, on the rear wall of the air filter housing. It should be noted that for turbocharged engines, a vacuum is not created in the intake manifold, and in order to force the vapors in the desired direction, an additional two-way valve is included in the circuit.
Reasons for airing
Where can air get into the carburetor? As a rule, this is due to loose tightening of the electromagnetic valve or holder (on some cars, instead of an electromagnetic valve, a nozzle holder is screwed in), drying out and damage to the rubber cuff of the adjustment screws, damage to the vacuum tubes and other reasons.
Let's take a closer look.
- Often, due to various reasons, EM valves are turned out and even lost. In addition, the valve makes it possible to regulate stable engine speeds in idle mode. If there is a holder, it must be screwed in to the proper depth. Finally, the EM valve has its own rubber seal, which can dry out over time. You should definitely check it out.
- Both adjusting screws are equipped with O-rings. Over time, the latter may no longer hold, and then air is sucked in from here.
- Vacuum tubes are laid from the distributor to the carburetor device, and also from the brake control unit to the intake manifold. On such a long line, yes, there are gaps, and in some places the hoses break or holes form. Thus, airing of the system occurs.
Carburetor gasket
In addition, you need to pinch the hoses one by one near the carb fittings and try to start the engine. Let's say the engine does not start due to severe air intake. By pinching the hoses, you can block the suction, which a priori will help the power plant start.
Gaskets occupy a special place in the carburetor system. They also need to be checked for leaks. If the gaps are not noticeable externally, and the sounds of suction are not audible when the starter device is turned, you need to tighten the bolts of the intake mechanism and fuel mixer, hoping that the gaskets are loose. Then check engine starting again.
By tightening torque. It is recommended to fasten the carburetor clamps with a force of 13-16 N.m, and the manifold nuts with a torque of 21-26 N.m. This means that you should not pull too much, otherwise you can easily damage the threads. It is extremely dangerous to overdo it on a hot engine.
Some experts do this. Cover the connections with VD-40 liquid or soap foam. Then they observe. If a window forms in the foam, this is where the leak occurs.
In general, you should not overtighten the nuts! Due to excessive tightening, the seating plane of the carb can easily become deformed, and then air leaks will occur for this reason.
The defect of an uneven surface is detected as follows. Place the carburetor, removed from the car, on a flat table. The plane should be completely free of grooves and bumps. It is better if it is a sheet of thick glass placed on a table. Then you need to look carefully to see if there is a gap between the surface of the carb and the glass. If yes, then this indicates deformation.