First of all, you need to understand what the gear ratio is. Let's look at the example of a single-stage worm gearbox Ch-100-40. In this case, the number 40 indicates the gear ratio (ratio) of the gearbox. What does this mean: when the high-speed shaft (input) rotates, the low-speed shaft (output) must make one revolution around its axis per 40 revolutions of the input shaft.
Next, you need to understand the difference between two concepts: actual gear ratio and nominal gear ratio. The nominal gear ratio is a rounded figure of the actual gear ratio, this is necessary for convenience and standardization of the designation. Example: a Ch-100 gearbox may have an actual gear ratio of 7.75, and a nominal one will be equal to 8, and so on: 10=10; 12=12.5; 15.5=16; 20=20; 24=25; 31=31.5; 40=40; 48=50; 64=63; 84=80.
Now let's look at ways to determine the gear ratio if the tag is not readable and there is no documentation for the equipment.
- The first method is universal for almost any type of gearbox or gear part of equipment, be it a worm, cylindrical, bevel, planetary, etc. gearbox. To do this, you need to rotate the high-speed shaft and the number of its revolutions per revolution of the low-speed shaft will indicate the actual gear ratio.
- The second method is used in the case of the first option and the inability to scroll and count the revolutions of the output shaft. Here there are differences between the methods for determining the gear ratio of a worm gearbox and, for example, a cylindrical gearbox:
A. Let's look at the example of a 1Ch-160 single-stage worm gearbox.
First of all, you need to count the number of teeth of the worm wheel photo No. 1.
We got 32 teeth.
Then the number of turns on the worm shaft photo No. 2.
Number of visits 1.
Now we divide 32 by 1 and the actual gear ratio of the 1Ch-160 gearbox is equal to 32.
Now let's look at the method of calculating the gear ratio of a worm gearbox using the example of the Ch-125.
We count the number of teeth on the worm wheel photo No. 3.
We get 52 teeth.
And he counts the number of turns on the worm shaft (photos No. 4 and No. 5).
We got a number equal to 4.
Now we divide 52 by 4 and the actual gear ratio of the Ch-125 gearbox is equal to 13.
The rear axle reducer reduces engine torque and transmits it to the drive wheels.
The movement of the car is given by the power plant - the engine. The energy required for movement is taken from the rotating crankshaft of the engine, but this energy cannot be transferred directly to the wheels - they will spin too quickly and the speed of the car will be such that it will be impossible to control it. To reduce speed in a rear-wheel drive or all-wheel drive car, there are two devices - a gearbox and a rear axle gearbox.
It would seem that to reduce the shaft rotation speed, one device is enough - a gearbox. The motorcycle transmission is built in accordance with this principle - it does not have a gearbox. However, a car differs from a motorcycle in that it has two drive wheels, which is why there is a need for a second device, which is the rear axle gearbox, which distributes the rotation of one input shaft to two output shafts.
Strictly speaking, in the body of the unit, which is usually called a gearbox, two devices are hidden. The second is the differential, it distributes torque in the required proportion. The task of the gearbox is to reduce the rotation speed of the output shafts relative to the input. A gearbox that converts a high angular velocity of the input shaft into a lower one is usually called a range multiplier.
Rear axle gear ratio
Rear axle gearboxes are classified according to the so-called gear ratio. The gear ratio is the ratio of the angular velocity of the drive shaft to the angular velocity of the driven shafts. In other words, according to the rule of the theory of calculating transmission parameters, the difference in speed of the input shaft and output shafts can be calculated using a special formula. The output will remain a number called the gear ratio.
The higher the gear ratio, the greater the vehicle's load capacity
In practice, it is important to know only one thing: the higher the gear ratio, the greater the vehicle's load capacity. Accordingly, the lower the gear ratio, the faster the car will be. It is important to know this, because gearboxes with different gear ratios are often installed on the same model in different modifications. For example, the gearbox of a VAZ-2102 station wagon, intended for transporting goods, had a gear ratio of 4.4, and a gearbox with a gear ratio of 4.3 was installed on a passenger VAZ-2101. This means: for one revolution of the driven gear on the output shaft of the gearbox, each of its teeth will engage with and come out of the drive gear 4 point 3 times. The same pattern can be seen in the design of any rear-wheel drive cars, for example BMW.
And it has nothing to do with the gearbox or transfer case!
What is a gear ratio?
The most important characteristic of any gearbox is the “gear ratio”. Which is determined by the ratio of the number of teeth on the drive and driven gears.
Two outwardly absolutely identical gearboxes of the same make and model of car can differ in gear ratio and be non-interchangeable.
Therefore, before purchasing/replacing a faulty gearbox (or when replacing the main pair during its repair) on any car, especially one with a drive on both axles (both axles), it is necessary to determine the gear ratio (number of teeth) of your gearbox.
Also, if you intend to purchase a contract (used) or new gearbox and the seller cannot tell you anything about its gear ratio, then you should refuse the purchase. You don’t fill up your car with fuel without indicating its brand on the pump??? Here the consequences of the error will be more destructive.
The seller’s assurances that the gearbox he sells is from a car with the same engine as your car (and therefore will suit you) should be unconvincing for you, because:
- first of all, in most cases it is almost as if he were assuring you that the gearbox he is selling is the same color as your car. (There are manufacturers who install gearboxes with different gear ratios on a car with the same engine in different years of manufacture)
- secondly, it does not guarantee that this is true (a mistake or deception is possible in order to sell quickly...), or that the previous owner of the car (sold for parts by the seller) did not change the gearbox to another with a different gear ratio (on purpose or by accident).
Specifics of operation of the rear axle gearbox
During vehicle operation, gears cling to each other with their teeth, however, even observing high metrological standards of production and adjustment, it is impossible to avoid their wear. Gears are made from high quality hardened steel. The gear housing is filled with special oil. Since the oil, being liquid, periodically tends to leak out of the cracks of the housing, to solve this problem, special gaskets called oil seals are used in the areas where the shafts exit. Unfortunately, the service life of the oil seals is significantly lower than the gears themselves, so when they wear out, the gear housing often contains oil smudges. If the oil completely leaks out (this happens if the seals are not replaced in a timely manner), the life of the gearbox is reduced significantly. In addition, dust and dirt tend to get through worn oil seals. To prevent such phenomena, it is recommended to check the gear housing from time to time using an inspection hole.
1st method - catalogue.
Without leaving home. This method is the easiest, but not the most reliable. Often requires double-checking using the other methods outlined below. It is also not always possible to obtain complete information (the gear ratio itself) - but only the OEM number of the main pair, more on that below.
According to the VIN of the car. We write off the VIN number from the Vehicle Registration Certificate
.
.
.
And we enter it into the search form by VIN in the corresponding brand from the online catalog located on the website of the Exist store. (registration on the site may be required)
Click the Search button and get open information on your car:
We open the corresponding group of spare parts (Transmission), and in it we find the “differential” tab, if you do not use an online page translator (catalogues are displayed in English) - then focus on the combination of words (or one of these words) FRONT DIFF GEAR if want to open the front gearbox or REAR DIFF GEAR if you want to open the rear gearbox. And click on this inscription.
A map opens to us - details of the unit (in our case, the gearbox). We find the final drive gears on it and click on its spare parts list number.
We see (in the list on the left) the original part number. Attention! If the number does not open or does not open entirely (there are no numbers in the middle of the number), then you need to register on the website of this catalog (free of charge).
Note! Two numbers of this part have opened in the catalog at once (and for some brands - for example , such as Mercedes Benz, 5 - 8 parts can be opened).
Next, you need to determine the number you need. In this example, you see that opposite each number there is a column of additional information, which indicates the type of gearbox - AT (Automatic Transmission) or MT (Manual Transmission). Knowing the type of gearbox installed on your car, you can easily determine the desired number of the main pair.
Why only the number??? Where is the gear ratio???
For some car brands (Toyota, Mercedes Benz) the gear ratio is immediately written down in the catalog, for some this information is not available - in this example, for the SUZUKI brand, this is exactly the case.
But the OEM part number you receive is already half the battle.
Using this number, the seller must determine the gear ratio you need using his information (experience).
Also be careful when finalizing the part number. As you noticed, at the last stage - when several part numbers are opened at once (in this example, we were faced with the simplest choice - according to the type of gearbox, and often the choice is more complex according to different criteria / vehicle equipment) - you can easily make a mistake and buy unsuitable part.
There is also a possibility that the characteristics of the gearbox (gear ratio) currently installed on your car do not correspond to what is specified in the catalog, since it was replaced (erroneously or on purpose) by the previous owner with a gearbox with a different number of teeth, and if you have a car with both drive axles, that is, it is likely that you have them with different gear ratios (perhaps this is why your gearbox failed), by making a mistake in purchasing a gearbox (with the wrong gear ratio) - you will not eliminate the root cause of the malfunction, and it may recur .
It is also rare, but there are errors in the directories themselves.
Therefore, if the number is not clearly determined, or you are not sure that the gearbox on your car has not been changed, use (double-check it) the methods described below, the 4th method is especially reliable.
Explosion-proof versions of gearmotors
Geared motors of this group are classified according to the type of explosion-proof design:
- “E” – units with an increased degree of protection. Can be used in any operating mode, including emergency situations. Enhanced protection prevents the possibility of ignition of industrial mixtures and gases.
- “D” – explosion-proof enclosure. The housing of the units is protected from deformation in the event of an explosion of the gear motor itself. This is achieved due to its design features and increased tightness. Equipment with explosion protection class “D” can be used at extremely high temperatures and with any group of explosive mixtures.
- “I” – intrinsically safe circuit. This type of explosion protection ensures the maintenance of explosion-proof current in the electrical network, taking into account the specific conditions of industrial application.
2nd method - by nameplate
The most reliable and simplest.
Read the information on the nameplate of your gearbox.
Some manufacturers (Mitsubishi, Mercedes Benz and others) attach such a nameplate (sticker) to the gearbox, or make an engraving on the gearbox housing, which contains important information about the gearbox, including the gear ratio. It is enough to find this nameplate (sticker) on the gearbox or the engraving and read what you need on it - of course, provided that the sticker or engraving has been preserved.
There is a very small probability that the inscription on the nameplate does not correspond to the actual characteristics of the gearbox because the gearbox was rebuilt and the main pair with a different gear ratio was installed; of course, no one corrected the information on the nameplate, or the cover with the attached nameplate was changed, and the nameplate indicates characteristics of the gearbox from which the cover was removed.
Note! A nameplate (sticker or riveted plate) or engraving may contain the necessary information. But not the numbers/letters made on the body of the gearbox housing by casting. Such numbers/letters carry technological information about the body casting itself (it is in no way linked to the number of teeth on the main pair). Simply put, it is not possible that when casting a cast iron housing, they would know in advance with which power supply the pair will be installed in this housing.
Rear axle gearbox and its housing
Due to the fact that the gear housing is made from an all-metal part (casting is used), it is very durable, which is especially important for those difficult working conditions in which the gearbox has to work. Typically, cast iron blanks are used for casting, however, a body cast in this way will be heavy. To reduce weight, special alloys are used - only highly loaded areas of the body are made of cast steel elements. Lightweight gearboxes are used, for example, in sports cars.
3rd way - count.
The most reliable, but not suitable for counting numbers on a car (without disassembling the bridge).
Count the number of teeth on both gears of your gearbox, and divide the number of teeth on the large gear (driven) by the number of teeth on the small gear (drive), the resulting number will be the gear ratio. But for this, the gearbox must already be removed from the machine. Often this method is not suitable due to the cost of the process of removing and installing the gearbox.
But it is most suitable for the case when the gearbox has already been removed from the car.
Gear ratios of VAZ gearboxes
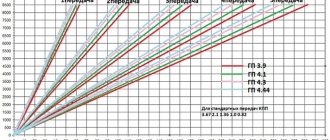
Let's take a closer look at the rear gearboxes installed on domestic VAZ cars. As mentioned earlier, there are a total of four gearboxes that were equipped with rear-wheel drive versions of AvtoVAZ. The fastest gearbox belongs to the sixth model of the Zhiguli. The rear axle gearbox of the VAZ-2106 has a gear ratio of 3.9. This figure is obtained from the ratio of the teeth of the input shaft and driven gear of 43:11.
The next fastest gearbox with a number of 4.1 belongs to the VAZ-2103. This unit has average, but also the most balanced indicators, such as acceleration, maximum speed and power. The first VAZ models had the highest torque gearboxes. Thus, the VAZ-2101 had a power transmission device according to the scheme 43: 10 = 4.3, and the VAZ-2102 - 40: 9 = 4.44. Because of this, the second model was the most convenient for driving with a trailer, although it had the lowest maximum speed - 145 km/h.
What gear ratio of the VAZ rear axle gearbox can be considered optimal? Each Zhiguli car owner will decide the answer to this simple question himself. To do this, it is enough to understand for what purposes the car will be used. If this is primarily a workhorse, the best option would be the most powerful gearbox with a 4.3 number. Ideally, of course, to install the “double” option, but the main pairs with the number 4.44 stopped being produced with the cessation of production of the VAZ-2102 a long time ago. For ordinary driving in urban conditions, the best gearbox is from a VAZ-2106 with a number of 3.9.
A few words about the gear ratio of all-wheel drive VAZ-2121 gearboxes. Since there are two gearboxes on such cars, it is important that the number is the same and corresponds to the ratio 41: 10 = 4.1.
4th – method – calculated
Requiring an inspection hole, a jack and certain skills.
You can calculate the gear ratio by rotating the gearbox by one drive wheel and calculating the ratio of the number of revolutions made by the gearbox flange to the number of revolutions made by the wheel.
To do this you need:
- Visit the viewing hole
- Secure the vehicle with a wheel chock
- put the gearbox in neutral position
- Jack up one drive wheel (Attention! if the car has two drive axles, then it is better to calculate the gear ratio on a working axle), and put marks (with chalk) on the wheel and on the floor so that they match.
- We go down into the inspection hole and make a similar mark on the flange and gearbox housing.
Attention! Both marks (on the wheel and on the cardan) must match before starting the countdown.
- The next stage is performed with an assistant (although if you put a mark on the wheel from the inside (from the gearbox side), you can do without an assistant). One person rotates the raised wheel (in any direction), and out loud counts the number of full revolutions of the wheel made.
- And the second person at this time, also out loud, counts the number of revolutions made by the cardan. If you carry out calculations without an assistant, you will have to simultaneously count the revolutions made by the wheel and the cardan.
- It is important to keep counting until both marks match as accurately as possible (as they were originally set). At this moment, you need to stop the rotation of the wheel and remember/write down the calculated number of revolutions made by the wheel and the gearbox flange. The more accurately you achieve a match of the marks, the more accurate the calculation will be. You can be sure that on any car these marks will sooner or later match as accurately as possible. The greatest probability is that this will happen from the 16th to the 22nd revolution of the wheel.
- As a result, we got two numbers. 16 and 39 which will allow us to determine the gear ratio of this gearbox. Please note that the figures obtained are not the gear ratio or the number of teeth of the main pair of this gearbox - these are just calculated figures.
- Attention!!! When counting the number of wheel/flange revolutions made, be as accurate and attentive as possible!!! The slightest mistake (in the number of calculated revolutions) can lead to the purchase of an unsuitable gearbox!!! If in doubt, it is better to repeat the calculation once again.
The final calculation of the gear ratio using the formula
Since the mechanics of the differential operation of any gearbox is such that when one wheel rotates (as we did), the number of its revolutions doubles, we will need to make an adjustment to the obtained calculated figures (revolutions).
We adjust the number of wheel revolutions; to do this, the resulting number of wheel revolutions must be divided by 2. Example: 16/2=8. Finally we get two numbers 8 and 39.
To obtain the gear ratio, you need to divide the number of revolutions of the cardan (the larger number) by the number of revolutions made by the wheel (the smaller number)
Example: 39/8 = 4.875
The resulting number 4.875 is the gear ratio of your gearbox.
When purchasing a gearbox, please provide this number to the seller.
Design specifics of the rear axle gearbox
Wheels with meshing teeth that transmit torque to the driven shafts from the drive shaft are called gears. Due to the fact that the shafts are located at different angles, the teeth of the wheels are made of a special shape - this is the so-called. bevel gears.
The cone shape, in addition to its main purpose of transmitting torque, also provides a low noise level, which is an advantage in terms of ease of operation of a passenger car.
The drive wheel must be of a different size than the driven ones - only in this case will a reduction in gear be ensured. If this requirement is met, several full rotations of the driven shaft will correspond to one full revolution of the driving shaft - in other words, there is a decrease (reduction) in the rotation speed. There are a number of vehicles (all-terrain vehicles, for example), where a serious reduction in rotation speed is applied in the gearbox - thus ensuring a very low pace of movement so as not to get bogged down.
Thanks for subscribing!
5th - method - special for Volkswagen Touareg / Porsche Cayenne brands
For a given make/model of car, there is a table of codes from which you can determine the gear ratio.
Each gearbox (of this brand) has a code marking in which the gear ratio of the gearbox is encrypted
Location of this marking: the lower part of the gearbox - near the oil drain plug.
Photo of marking location:
Gearbox - general view from below
Marking:
Tell us your gearbox number and we will tell you the gear ratio.
Gearbox adjustment
If during engine operation there are signs of a malfunction of the REM, most often it is necessary to dismantle the gearbox and disassemble it. After this, it will be possible to determine what is needed to troubleshoot: adjustment, replacement of individual parts of the REM or installation of a new gearbox.
Removing the gearbox
To dismantle REM, you will need:
- hex wrench 12;
- set of open-end wrenches;
- jack;
- supports for the rear axle;
- wheel shoes;
- container for draining oil.
Types of main gear by type of gear connection
If we divide the types of main gears, then we can distinguish:
- cylindrical;
- conical;
- worm;
- hypoid;
Cylindrical final drives are used in front-wheel drive passenger cars with a transverse engine and gearbox. Its gear ratio is in the range of 3.5-4.2.
Spur gears can be spur, helical or chevron. The cylindrical gear has a high efficiency (at least 0.98) but it reduces ground clearance and is quite noisy.
The bevel final drive is used on rear-wheel drive light and medium-duty vehicles with a longitudinal arrangement of the internal combustion engine, where overall dimensions do not matter.
The axes of the gears and the wheels of such a transmission intersect. These gears use straight, oblique or curved (spiral) teeth. Noise reduction is achieved by using an oblique or spiral tooth. The efficiency of the final drive with a spiral tooth reaches 0.97-0.98.
The worm main gear can be either with a lower or an upper worm arrangement. The gear ratio of such a main gear is in the range from 4 to 5.
Compared to other types of gears, the worm gear is more compact and less noisy, but has a low efficiency of 0.9 - 0.92. Currently, it is rarely used due to the complexity of production and the high cost of materials.
Hypoid final drive is one of the popular types of gear connection. This transmission is a kind of compromise between a bevel and a worm final drive.
The transmission is used on rear-wheel drive cars and trucks. The axes of the gears and the wheels of the hypoid gear do not intersect, but are crossed. The transmission itself can be either with a lower or an upper offset.
A bottom offset final drive allows the driveline to be positioned lower. Consequently, the center of gravity of the car also shifts, increasing its stability when driving.
Compared to bevel gears, hypoid gears are smoother, quieter, and smaller in size. It is used on passenger cars with a gear ratio of 3.5-4.5, and on trucks instead of a double main gear with a gear ratio of 5-7. In this case, the efficiency of the hypoid transmission is 0.96-0.97.
With all its advantages, the hypoid transmission has one drawback - the jamming threshold when the car reverses (exceeding the rated speed)
For this reason, the driver must take special care when selecting the speed of reversing.
Operational coefficient (service factor)
Service factor (Sf) is calculated experimentally. The type of load, daily operating duration, and the number of starts/stops per hour of operation of the gearmotor are taken into account. The operating coefficient can be determined using the data in Table 3.
Table 3. Parameters for calculating the service factor
| Load type | Number of starts/stops, hour | Average duration of operation, days | |||
| <2 | 2-8 | 9-16h | 17-24 | ||
| Soft start, static operation, medium mass acceleration | <10 | 0,75 | 1 | 1,25 | 1,5 |
| 10-50 | 1 | 1,25 | 1,5 | 1,75 | |
| 80-100 | 1,25 | 1,5 | 1,75 | 2 | |
| 100-200 | 1,5 | 1,75 | 2 | 2,2 | |
| Moderate starting load, variable mode, medium mass acceleration | <10 | 1 | 1,25 | 1,5 | 1,75 |
| 10-50 | 1,25 | 1,5 | 1,75 | 2 | |
| 80-100 | 1,5 | 1,75 | 2 | 2,2 | |
| 100-200 | 1,75 | 2 | 2,2 | 2,5 | |
| Operation under heavy loads, alternating mode, large mass acceleration | <10 | 1,25 | 1,5 | 1,75 | 2 |
| 10-50 | 1,5 | 1,75 | 2 | 2,2 | |
| 80-100 | 1,75 | 2 | 2,2 | 2,5 | |
| 100-200 | 2 | 2,2 | 2,5 | 3 | |
Features of using gearboxes on rear-wheel drive vehicles
Cars with rear-wheel drive, as already noted, are equipped with gearboxes with different gear ratios. The transmission configuration of modern cars is difficult to predict.
So, for example, during the years of production of the VAZ 2102* car, one could say with confidence that it had a gearbox with a gear ratio of 4.44. The modern generation of “twos” - VAZ 2104 * - is usually equipped with a gearbox with diametrically opposite parameters - VAZ 2106, 3.9. This is very unusual for a utility vehicle, but the manufacturer is guided by its own considerations. The situation is also the same with the equipment of other models of the classic Zhiguli. In this matter, judging by experience, there are certain patterns, but there are no hard and fast rules. Therefore, in general terms, we can assume that the “classic” can have any kind of gearbox.