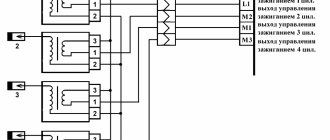
Errors p0351, p0352, p0353, p0354 are associated with faults in the ignition system. In particular, ignition coils (coils), wiring or control unit. Problems with the coil are usually caused by shorted turns on the primary or secondary winding or its breakdown. As for the wiring, this can be either a break in individual wires, damage to their insulation, or, as a consequence, a short circuit between them or to ground (housing). The most difficult case is the breakdown of the electronic control unit, in particular, the breaking off of part of the ceramic board with connectors, which is diagnosed by the electronics precisely as errors with numbers p0351, p0352, p0353 and p0354.
How does a mechanic diagnose a P0351 code?
When diagnosing this error code, a mechanic will do the following:
- Reads all stored data and error codes using OBD-II scanner
- Clear error codes from the computer's memory and test drive the vehicle to see if P0351 appears again
- If the error code appears again, check the ignition coils as well as the associated wires for wear and damage.
- Find out whether the fault concerns only one of the cylinders or all cylinders of the engine using a scanner
- If the fault concerns only one engine cylinder, check the corresponding spark plug and its wire for wear and damage.
- If a malfunction is detected in all engine cylinders, check the primary winding of the ignition coil
- If no problem is found, check the ECM
Code generation condition
Information about the formation of OBD errors p0351, p0352, p0353, p0354 is recorded in the memory of the electronic control unit when a number of the following conditions are met:
- The car engine ignition is turned on;
- the feedback signal informs the electronic control unit that the device has not worked;
- the number of failures of individual ignition coils is constantly growing;
- a corresponding error in the ECU memory will be generated when the number of failures reaches 20 in 40 test cycles.
The information provided is relevant for the popular Chevrolet Lacetti car, however, the logic for generating errors in most cars will be similar.
Conditions for clearing code from ECU memory
Errors p0351, p0352, p0353, p0354 are deleted from memory if one of the conditions is met:
- four consecutive ignition cycles have passed during which no malfunctions in the operation of the ignition coil were detected;
- the power supply to the ECM was turned off for more than 10 seconds;
- The diagnostic code must be cleared with a scan tool.
The archive of diagnostic error codes itself disappears from the ECU memory after 40 consecutive heating cycles, provided there are no faults.
Errors P0351-P0354 ZMZ PRO
Errors P0351-P0354 ZMZ PRO
Post by Angur » Sat Mar 07, 2022 18:18
ZMZ PRO
Post by Angur » Sun Mar 08, 2022 07:42
Errors P0351-P0354 ZMZ PRO
Posted by kind74 » Mon Jun 15, 2022 07:24 pm
Denial of responsibility
Opinions and comments posted in all forums are personal and do not necessarily reflect the opinion of the administration, with the exception of official messages from the administration of the Club UAZ Patriot Club.
The administration of the UAZ Patriot Club is not responsible for any actions, advice and messages from users and guests of the UAZ Patriot Club that may cause damage or loss to other users of the UAZ Patriot Club.
In addition, the Administration of the UAZ Patriot Club cannot be associated with and be responsible for the materials and content of other sites that are linked to from the UAZ Patriot Club.
Source
Error P0504
This malfunction is associated with an incorrect signal from the brake pedal switches. Most often, the cause of such a failure is a malfunction of the brake pedal position sensor, lack of proper adjustment, or a broken spring that is installed in this device. Procedure for checking and troubleshooting:
Sensor locations on video:
It should be noted that the efficiency of the neutralizer is checked with special gas analyzers.
Decoding error codes Lada Granta, Kalina 2
P0030 Oxygen sensor to the converter, checking for open circuit of the heater P0031 Oxygen sensor to the neutralizer, checking the short circuit of the heater circuit to ground P0032 Oxygen sensor to the converter, checking the short circuit of the heater circuit to the on-board network P0036 Oxygen sensor after the converter, checking for open circuit of the heater P0037 Oxygen sensor after the neutralizer, checking the short circuit of the heater circuit to ground P0038 Oxygen sensor after the converter, checking the short circuit of the heater circuit to the on-board network P0101 Mass air flow sensor, signal out of acceptable range P0102 Mass Air Flow Sensor Low Output P0106 Intake manifold absolute pressure sensor circuit, signal out of range P0107 Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor Circuit Low Signal P0108 Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor Circuit High Signal P0103 Mass Air Flow Sensor High Output P0112 Intake Air Temperature Sensor Output Low P0113 Intake Air Temperature Sensor High Output P0115 Incorrect coolant temperature sensor signal P0116 Coolant temperature sensor, signal out of acceptable range P0117 Coolant Temperature Sensor Low Output P0118 Coolant Temperature Sensor High Output P0122 Throttle Position Sensor Low Output (Sensor #1) P0123 Throttle Position Sensor High Output (Sensor #1) P0130 The oxygen sensor before the converter is faulty P0131 Oxygen sensor before converter, low output signal P0132 Oxygen sensor before converter, high output signal P0133 Pre-catalyst oxygen sensor, slow response to enrichment or leanness P0134 Oxygen sensor to converter, signal circuit open P0135 Oxygen sensor to converter, heater faulty P0136 Oxygen sensor after the converter, signal circuit open P0137 Oxygen sensor after the converter, low signal level P0138 Oxygen sensor after the converter, high signal level P0140 Oxygen sensor after the converter, signal circuit open P0141 Oxygen sensor after converter, heater faulty P0171 Fuel system too lean P0172 Fuel system too rich P0200 Injector control circuit is faulty P0201 Cylinder No. 1 injector control circuit, open P0202 Cylinder No. 2 injector control circuit, open P0203 Cylinder No. 3 injector control circuit, open P0204 Cylinder No. 4 injector control circuit, open P0217 Engine overheating, engine temperature above threshold P0222 Throttle Position Sensor Low Output (Sensor #2) P0223 Throttle Position Sensor High Output (Sensor #2) P0261 Cylinder 1 Injector Control Circuit Short to Ground P0262 Cylinder No. 1 injector control circuit, short to +12V P0264 Cylinder 2 Injector Control Circuit Short to Ground P0265 Cylinder No. 2 injector control circuit, short to +12V P0267 Cylinder 3 Injector Control Circuit Short to Ground P0268 Cylinder No. 3 injector control circuit, short to +12V P0270 Cylinder 4 Injector Control Circuit Short to Ground P0271 Cylinder No. 4 injector control circuit, short to +12V P0300 Random or multiple misfires detected P0301 Misfire detected in cylinder 1 P0302 Misfire detected in cylinder 2 P0303 Misfire detected in cylinder 3 P0304 Misfire detected in cylinder 4 P0325 Broken knock sensor P0326 Knock sensor, signal is outside acceptable limits P0327 Knock sensor low signal P0328 Knock sensor, high signal level P0335 Crankshaft position sensor, no signal P0336 Crankshaft position sensor signal is out of range P0337 Crankshaft position sensor, circuit short to ground P0338 Crankshaft position sensor, open circuit P0340 Camshaft position sensor is faulty (Phase sensor error) P0342 Camshaft Position Sensor Low Signal P0343 Camshaft Position Sensor High Signal P0346 Phase sensor circuit, incorrect signal P0351 Ignition coil, open circuit check, primary current less than threshold P0352 Ignition coil, open circuit check, primary current less than threshold P0353 Ignition coil of cylinder 3, control circuit open P0354 Ignition coil of cylinder 4, control circuit open P0363 Random or multiple misfires detected to protect converter P0422 Neutralizer efficiency below threshold P0441 Incorrect air flow through the valve P0443 The canister purge valve control is faulty P0444 Canister purge valve, open circuit check P0445 Short circuit to ground in the canister purge valve circuit P0458 Canister purge valve, checking short circuit to ground P0459 Canister purge valve, checking the short-circuit circuit to the on-board network P0480 Fan 1 relay control circuit; open circuit, open circuit check P0481 Fan Relay 2 Control Circuit; open circuit, open circuit check P0485 Cooling fan, supply voltage check P0500 Vehicle speed sensor, no signal P0501 Vehicle speed sensor error P0503 Vehicle speed sensor, intermittent signal P0504 Brake pedal sensor, sensor signals change inconsistently P0505 Idle air control error P0506 Idle speed control locked, low speed P0507 Idle speed control locked, high speed P0522 Oil Pressure Sensor Circuit Low Signal P0523 Oil Pressure Sensor Circuit High Signal P0560 On-board voltage is below the system operability threshold P0562 On-board voltage is low P0563 On-board voltage is high P0601 Control unit ROM malfunction P0603 Control unit RAM malfunction P0604 Controller internal RAM checksum error P0606 Controller, ADC faulty P0607 Invalid controller knock channel signal P0615 Starter relay control circuit, open P0616 Starter relay control circuit short to ground P0617 Starter relay control circuit, short to +12V P0627 Fuel pump relay, open circuit check P0628 Fuel pump relay, checking short circuit to ground P0629 Fuel pump relay, checking the short-circuit circuit to the on-board network P0642 Sensor power bus, low signal level P0643 Sensor power bus, high signal level P0645 Air conditioning clutch relay, open circuit check P0646 Air conditioning clutch relay, checking short circuit to ground P0647 Air conditioning clutch relay, checking short-circuit circuit to the on-board network P0660 Intake system channel length control valve, open circuit P0661 Intake system channel length control valve, circuit short to ground P0662 Intake system channel length control valve, on-board network circuit closure P0691 Fan 1 relay control circuit; open circuit, checking short circuit to ground P0692 Fan 1 relay control circuit; open circuit, checking the short-circuit circuit to the on-board network P0693 Fan Relay 2 Control Circuit; open circuit, checking short circuit to ground P0694 Fan Relay 2 Control Circuit; open circuit, checking the short-circuit circuit to the on-board network P0830 Clutch pedal switch, circuit faulty P1102 Oxygen Sensor Heater Resistance Low P1115 Faulty oxygen sensor heating control circuit P1123 Additive component corr. by air the composition of the mixture exceeds the threshold. The composition is “rich” P1124 Additive component corr. by air the composition of the mixture exceeds the threshold. Composition “poor” P1127 Multiplicative the mixture correction component exceeds the threshold. “Rich” composition P1128 Multiplicative the mixture correction component exceeds the threshold. Composition “poor” P1135 Malfunction of the oxygen sensor heater circuit to the converter P1136 Additive component corr. fuel exceeds the threshold. “Rich” composition P1137 Additive component corr. fuel exceeds the threshold. Composition “poor” P1140 Measured load differs from calculated load P1141 Malfunction of the oxygen sensor heater circuit after the converter P1171 Low signal level from CO correction potentiometer P1172 High signal level from the CO correction potentiometer P1301 Misfire detected to protect the converter in cylinder 1 P1302 Misfire detected to protect the converter in the 2nd cylinder P1303 Misfire detected to protect the converter in the 3rd cylinder P1304 Misfire detected to protect the converter in the 4th cylinder P1335 Monitoring throttle actuator control, throttle position out of range P1336 Monitoring the control of the throttle valve drive, checking the mismatch of signals from the throttle position sensors, the sensor voltages differ by the threshold value P1384 Monitoring throttle actuator control. Engine torque out of range P1385 Monitoring throttle actuator control. Engine load signal is out of range. P1386 Knock detection channel internal test error P1387 Monitoring throttle actuator control. Injection time is out of range. P1388 Monitoring throttle actuator control, checking the accelerator pedal position, sensor voltages differ by the threshold value P1389 Throttle actuator control monitoring, engine speed out of range P1390 Monitoring throttle actuator control, no response to system malfunction P1410 Canister purge valve control circuit, short to +12V P1425 Canister purge valve control circuit, short to ground P1426 Canister purge valve control circuit, open Р1500 Open circuit in the electric fuel pump relay control circuit P1501 Fuel pump relay control circuit short to ground P1502 Fuel pump relay control circuit, short to +12V P1509 Idle air control control circuit, overload P1513 Idle air control control circuit short to ground P1514 Idle air control control circuit, open or shorted to +12V P1541 Fuel pump relay control circuit, open P1545 Throttle valve drive, deviation of the actual throttle valve position from the desired position is greater than the threshold value P1558 Throttle valve actuator, return spring faulty P1559 Throttle valve actuator, throttle position at rest is outside the permissible range P1570 Immobilizer, no positive response or open circuit P1578 Throttle valve actuator, adaptation value out of range P1558 Throttle valve actuator, throttle return time to limp home position above threshold P1559 Throttle valve actuator, throttle position out of range P1600 No connection with immobilizer P1602 Loss of on-board voltage P1603 Control unit EEPROM fault P1606 Rough road sensor, incorrect signal P1612 CPU reset error P1616 Rough road sensor low signal P1617 Rough road sensor, high signal P1620 Control unit ROM malfunction P1621 Control unit RAM malfunction P1622 Control unit EEPROM fault P1640 COURT controller, EEPROM memory read-write error P1689 Error memory malfunction P2070 Intake system channel length control valve, constantly open P2071 Intake system channel length control valve, permanently closed P2100 Throttle valve actuator, open circuit check P2101 Electric throttle actuator, control circuit faulty P2102 Throttle valve actuator, checking short circuit to ground P2103 Throttle valve drive, checking short-circuit circuit to the on-board network P2105 Controller, monitoring module faulty P2122 Pedal Position Sensor A Circuit High P2123 Pedal Position Sensor A Circuit High P2127 Pedal Position Sensor B Circuit Low P2128 Pedal Position Sensor B Circuit High P2187 Fuel system too lean (at idle) P2188 Fuel system too rich (at idle) P2135 Throttle position sensors “A”/“B”, signal mismatch P2138 Accelerator pedal position sensors “A”/“B”, signal mismatch P2176 Throttle valve control system, throttle zero position adaptation not performed P2178 Throttle valve drive, adaptation has never been carried out P2187 Fuel system too lean at idle P2188 Fuel system too rich at idle P2270 Oxygen sensor after the converter, no response to enrichment of the mixture P2271 Oxygen sensor after the converter, no response to lean mixture P2301 Ignition coil of cylinder 1, control circuit shorted to on-board network P2304 Ignition coil of cylinder 2, control circuit shorted to on-board network P2307 Ignition coil of cylinder 3, short circuit of the control circuit to the on-board network P2310 Ignition coil of cylinder 4, control circuit shorted to on-board network P2500 Generator excitation control (LT) circuit low P2501 Generator excitation control (LT) circuit highSigns of breakdown
External signs of error codes p0351, p0352, p0353, p0354 include:
- activation of the Check Engine warning light on the dashboard;
- misfires in one or more engine cylinders (depending on the number of errors), this leads to the engine “troubling”, operating unstably, and having an uneven idle;
- drop in engine power and deterioration in the dynamic characteristics of the machine;
- problems starting the engine.
Since such signs may indicate other problems with the engine, reading diagnostic codes with an error scanner is mandatory, this will allow you to move on to further specific checks.
Causes of malfunction
There are five main malfunctions that cause OBD errors p0351, p0352, p0353, p0354 to be generated in the memory of the electronic control unit. Among them:
- Faulty spark plugs or their wires. Spark plugs can fail either partially (for example, due to contamination of the electrodes) or completely, as a result of which a spark will not appear on the electrodes at all. In rare cases, a P0363 code may also be displayed.
- Ignition coil malfunction. Typically this failure is caused by the primary and/or secondary windings being shorted. Moreover, this can be either an interturn short circuit or a short circuit between the primary and secondary windings. In the first case, usually the voltage generated is not enough to ignite the air-fuel mixture, and in the second, there will be no voltage at all. Often, when a short circuit occurs, the corresponding fuses blow. Another option is a partial failure of the rubber tip of the coil, which causes a spark to simply break through to the body.
- Wiring problems. In this case, there may be breaks: between the control unit and the coil, between the coil and the spark plug, or the supply wiring. In this case, this can be either a complete break in the wires or damage to the insulation section/sections. For example, when rubbing in places of bending, exposure to extreme temperatures, and so on. In any case, diagnostics must be performed using an electronic multimeter, which allows you to find the corresponding damage.
- Control unit malfunction. This is the worst case. As mentioned above, inside the block there is a ceramic plate on which power and signal electrical contacts are installed (the design of the control unit may differ for individual car models). Due to constant overheating, the plate becomes fragile, and sometimes a situation arises when a piece of the plate with contacts simply falls off from its main part.
Another, but rather rare reason why the indicated errors with code p0351, p0352, p0353, p0354 are formed in the ECU memory are the so-called “glitches” of the control unit. In particular, its bugs in its software. This can happen, for example, after reflashing the unit, or after mechanical damage (for example, as a result of an accident).
System diagnostic methods
There are two ways to identify errors in Grant and its analogues. Both methods have clear advantages and disadvantages.
Self-diagnosis of Lada Granta
The principle of the method is to use standard systems installed on the machine. The procedure does not require connecting additional equipment or studying complex instructions. To perform the check, just follow a simple sequence of actions:
- simultaneously hold down the daily mileage reset button located on the dashboard and turn the key in the lock cylinder to position 2;
- if everything is done correctly, the machine will go into self-diagnosis mode, all the arrows will make a full revolution and the indicators will light up;
- Use the button on the steering column wiper position switch to select the required option;
- Information about the firmware version appears first in the list. By clicking on the positions further, you can see the required error combination.
Note!
If, when switching to self-diagnosis, any indicators do not light up, their circuits must be checked first.
The disadvantage of this method is the low accuracy of the indicators. The display displays compressed information about the breakdown, which can only indicate the direction from which to start looking for the problem.
In the most popular versions of ECU firmware, network errors are noted as:
- The specified Lada Granta error code indicates the presence of a critical power surge in the on-board network. In 90% of cases it indicates a short circuit or damage to electrical appliances.
- You need to check the float sensor in the gas tank and its circuit. There may be a short circuit or damage to the sensor.
- The motor has overheated or the antifreeze temperature sensor has broken.
- Failure in the power supply circuit of the ambient temperature meter.
- Additionally, it indicates overheating of the power plant or incorrect operation of the thermostat. Indirectly affects more complex faults such as cylinder head gasket breakdown.
- The pressure in the fuel rail has dropped critically. You will need to check the pumps and the condition of the injectors. A popular error in the first generation Grant engine.
- If the brakes have failed or the pads have worn out badly, diagnostics of the modules is necessary.
- Severe voltage drop in the on-board network. There may be problems with the battery.
If “E” is displayed on the device, this indicates that the firmware is not working correctly.
Computer diagnostics
The next method involves connecting special equipment to the machine. The bottom line is this:
- there is a special connector under the dashboard;
- a laptop with the program is connected to the terminal via a special connector;
- device pairing begins;
- After establishing a stable connection and reading information from the BC, Lada Granta error codes will be displayed in the software window.
If everything is done correctly, special codes are displayed on the monitor. Moreover, each part of the code speaks of its own circuit.
Beginning (letter)
- P – the integrity of the electrical wiring is compromised or the sensors are damaged;
- C – probably the breakdown is in the suspension units, chassis;
- B – problems with the internal equipment of the car;
- U – resynchronization of several interconnected circuits is observed.
The following are standard notations:
- 0 – failure in the OBD 2 module;
- 1/2 – enterprise code (what this is is known only to the car manufacturer);
- 3 – malfunction of spare wiring parts.
The next part indicates the serial number of the on-board circuit section where the breakdown is located:
- 0 – exhaust cleaning device;
- 1 – motor air supply system;
- 2 – fuel lines, pumps and injectors;
- 4 – control devices;
- 5 – malfunctions or disruption in the operation of additional systems;
- 7/8 – transmission, chassis.
Next comes another two-digit number - the last part of the index points directly to the system where there is a problem.
Diagnosis and problem solving
Try wiggling and testing the wiring at coil #1 and along the harness to the PCM. If manipulation of the wiring causes misfire, correct the wiring problem. Check the reliability of the contact in the coil connector. Make sure the bundle of wires is not rubbing against anything. Repair if necessary.
If the engine is currently experiencing rough operation, stop the engine and disconnect the #1 coil wire connector. Then start the engine and check the driver signal on coil #1.
Use a voltmeter on the AC current scale in hertz. See if there is a reading between 5 and 20 Hz or so, which indicates the driver is working. If the readings vary, replace the No. 1 ignition coil.
If there is no frequency signal from the PCM in the ignition coil driver circuit, leave the coil disconnected. Check the DC voltage in the driver circuit at the ignition coil connector. If there is significant voltage on this wire, then there is a short somewhere. Find the short circuit and repair it.
If there is no voltage in the driver circuit, turn off the ignition. Disconnect the PCM connector and check the continuity between the PCM and the coil. If there is no continuity, repair the open circuit or short circuit.
If there is a break, check the resistance between ground and the ignition coil connector. There must be endless resistance. Other indicators indicate a short, repair the short to ground in the coil driver circuit.
If you find that the engine is misfiring, the coil fires correctly, but the P0351 code keeps popping up. There is a possibility that the PCM coil monitoring system may be faulty.
On which cars is this problem most common?
The problem with code P0352 can occur on different machines, but there are always statistics on which brands this error occurs more often. Here is a list of some of them:
- Audi
- Chery
- Chevrolet (Chevrolet Aveo, Cruz, Lanos, Lacetti)
- Chrysler
- Citroen (Citroen C4, C5)
- Daewoo (Daewoo Matiz, Nexia)
- Dodge (Dodge Intrepid)
- Fiat (Fiat Punto, Stilo)
- Ford (Ford Mondeo, Ranger, Focus, Explorer, F-150)
- Honda (Honda Passport)
- Hyundai
- Jeep (Jeep Grand Cherokee)
- Lexus (Lexus rx350)
- Mazda (Mazda Demio, Surname)
- Mercedes
- Opel (Opel Astra, Vectra, Zafira)
- Peugeot (Peugeot 206, 307, 407)
- Porsche (Porsche Cayenne)
- Renault (Renault Duster, Logan)
- Toyota (Toyota Avensis, Auris, Camry, Corolla, Prado, Rav4)
- Volkswagen (Volkswagen Polo Sedan)
- Volvo
- VAZ 2114
- Gazelle Business, Cummins
- Lada Granta, Kalina, Priora
- UAZ
With fault code P0352, you can sometimes encounter other errors. The most common ones are: P0102, P0174, P0183, P0194, P0351, P0353, P0354, P1000, P1336, P1338, P1339, P2106, P2195.